Deck 26: The Keynesian Short-Run Policy Model: Demand-Side Policies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/220
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: The Keynesian Short-Run Policy Model: Demand-Side Policies
1
Most economists agree that it is possible for fiscal policy to fine-tune the economy.
False
2
As a response to the 2008 recession, the U.S. government employed expansionary policy, and the economy returned to its level of potential output.
False
3
If the economy is not in a long-run equilibrium and other things are equal, then prices will eventually adjust to bring the economy to a long-run equilibrium.
True
4
According to Keynes, market economies:
A)never experience significant declines in aggregate demand.
B)quickly recover after they experience a significant decline in aggregate demand.
C)may recover slowly after they experience a significant decline in aggregate demand.
D)are constantly experiencing a significant declines in aggregate demand.
A)never experience significant declines in aggregate demand.
B)quickly recover after they experience a significant decline in aggregate demand.
C)may recover slowly after they experience a significant decline in aggregate demand.
D)are constantly experiencing a significant declines in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
After the 2008 expansionary policy, unemployment remained higher than desired and output was much lower than desired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to Keynes, why might deflation create problems for an economy?
A)Consumers might expect prices to fall further and cut back consumption now.
B)In expectation of increased spending, too many entrepreneurs would begin businesses and most would fail.
C)Producers might increase production to take advantage of falling input prices.
D)People would drop out of unions because unions would become ineffective at keeping wages of members high.
A)Consumers might expect prices to fall further and cut back consumption now.
B)In expectation of increased spending, too many entrepreneurs would begin businesses and most would fail.
C)Producers might increase production to take advantage of falling input prices.
D)People would drop out of unions because unions would become ineffective at keeping wages of members high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the AS/AD model, as the price level falls, the holders of money become richer and buy more. This is one reason why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Some economists believe that the good times of the early 2000s were not sustainable because they were creating a dangerous financial bubble and trade deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If productivity and wages both rise by 3 percent, then the aggregate supply curve shifts up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping in part because increases in aggregate demand cause some firms to increase their price markups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Potential income is that level of income that:
A)the economy always produces.
B)toward which the economy gravitates in the short-run.
C)an economy is capable of producing without generating higher inflation.
D)an economy is capable of producing without generating unemployment.
A)the economy always produces.
B)toward which the economy gravitates in the short-run.
C)an economy is capable of producing without generating higher inflation.
D)an economy is capable of producing without generating unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Equilibrium income is that level of income:
A)which the economy always produces.
B)toward which the economy gravitates in the short-run.
C)which an economy is capable of producing without generating accelerating inflation.
D)which an economy is capable of producing without generating unemployment.
A)which the economy always produces.
B)toward which the economy gravitates in the short-run.
C)which an economy is capable of producing without generating accelerating inflation.
D)which an economy is capable of producing without generating unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Keynes believed the economy was:
A)fluctuating around potential income.
B)always at potential income.
C)always moving away from potential income.
D)always moving toward potential income.
A)fluctuating around potential income.
B)always at potential income.
C)always moving away from potential income.
D)always moving toward potential income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Keynes believed equilibrium income was:
A)not fixed at the economy's potential income.
B)fixed at the economy's potential income.
C)always below the economy's potential income.
D)always above the economy's potential income.
A)not fixed at the economy's potential income.
B)fixed at the economy's potential income.
C)always below the economy's potential income.
D)always above the economy's potential income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Starting from a long-run equilibrium, an increase in government expenditures increases output in the short run but not in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the Keynesian model,
A)wages are flexible because workers wouldn't otherwise be able to keep their jobs.
B)the price level is somewhat fixed due to social forces, which keeps an economy from remaining at an equilibrium level of unemployment.
C)prices are subject to significant fluctuations as demand and supply change.
D)the government puts price controls on the economy, keeping the price level fixed.
A)wages are flexible because workers wouldn't otherwise be able to keep their jobs.
B)the price level is somewhat fixed due to social forces, which keeps an economy from remaining at an equilibrium level of unemployment.
C)prices are subject to significant fluctuations as demand and supply change.
D)the government puts price controls on the economy, keeping the price level fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The repercussions that the money wealth and international effects have on aggregate production and aggregate expenditure cause the aggregate demand curve to become steeper than it would be without such repercussions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In principle, we would expect the aggregate demand curve to be vertical because the price level is a reference point, the actual value of which should not matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Keynes believed that:
A)the government could not aid market forces to push the economy to its potential income.
B)market forces pushing the economy into cumulative spirals were weak.
C)market forces pushing the economy to potential income were weak.
D)market forces pushing the economy to potential income were strong.
A)the government could not aid market forces to push the economy to its potential income.
B)market forces pushing the economy into cumulative spirals were weak.
C)market forces pushing the economy to potential income were weak.
D)market forces pushing the economy to potential income were strong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to Keynes, the economy could become stuck at a low income level if:
A)declines in aggregate demand and aggregate supply reinforce one another.
B)declines in aggregate demand are not accompanied by declines in aggregate supply.
C)declines in aggregate supply are not accompanied by declines in aggregate demand.
D)aggregate demand and aggregate supply are independent of one another.
A)declines in aggregate demand and aggregate supply reinforce one another.
B)declines in aggregate demand are not accompanied by declines in aggregate supply.
C)declines in aggregate supply are not accompanied by declines in aggregate demand.
D)aggregate demand and aggregate supply are independent of one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Keynes believed that an increase in savings would:
A)raise aggregate demand by reducing investment.
B)raise aggregate demand by increasing consumption.
C)reduce aggregate demand by reducing investment.
D)reduce aggregate demand by reducing consumption.
A)raise aggregate demand by reducing investment.
B)raise aggregate demand by increasing consumption.
C)reduce aggregate demand by reducing investment.
D)reduce aggregate demand by reducing consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in real money balances resulting from a lower price level will:
A)reduce both interest rates and investment.
B)reduce interest rates and increase investment.
C)increase interest rates and reduce investment.
D)increase both interest rates and investment.
A)reduce both interest rates and investment.
B)reduce interest rates and increase investment.
C)increase interest rates and reduce investment.
D)increase both interest rates and investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An increase in the price level:
A)increases the purchasing power of money, leading to lower interest rates, which increases investment.
B)increases the purchasing power of money, leading to higher interest rates, which decreases investment.
C)decreases the purchasing power of money, leading to lower interest rates, which increases investment.
D)decreases the purchasing power of money, leading to higher interest rates, which decreases investment.
A)increases the purchasing power of money, leading to lower interest rates, which increases investment.
B)increases the purchasing power of money, leading to higher interest rates, which decreases investment.
C)decreases the purchasing power of money, leading to lower interest rates, which increases investment.
D)decreases the purchasing power of money, leading to higher interest rates, which decreases investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The shapes of the curves in the AS/AD model are based upon the:
A)principle of substitution.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)relationship between a single good and its price.
D)relationship between the price level and total output.
A)principle of substitution.
B)principle of opportunity cost.
C)relationship between a single good and its price.
D)relationship between the price level and total output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As prices fall, the value of people's existing assets rises and people increase expenditures. This occurs as a result of the:
A)international effect.
B)multiplier effect.
C)interest rate effect.
D)money wealth effect.
A)international effect.
B)multiplier effect.
C)interest rate effect.
D)money wealth effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the price level falls but people don't feel richer because of that fall, then the AD curve would likely:
A)shift in.
B)shift out.
C)be flatter than it otherwise would be.
D)be steeper than it otherwise would be.
A)shift in.
B)shift out.
C)be flatter than it otherwise would be.
D)be steeper than it otherwise would be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The paradox of thrift will not arise if:
A)increases in saving are translated into identical increases in investment.
B)increases in saving are translated into identical decreases in consumption.
C)decreases in saving are translated into identical increases in investment.
D)decreases in saving are translated into identical decreases in consumption.
A)increases in saving are translated into identical increases in investment.
B)increases in saving are translated into identical decreases in consumption.
C)decreases in saving are translated into identical increases in investment.
D)decreases in saving are translated into identical decreases in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Keynes argued that, for the period that he was writing about:
A)the long run is a more important policy concern than the short run.
B)the short run is a more important policy concern than the long run.
C)both the short run and the long run are equally important.
D)the distinction between the short run and the long run is irrelevant.
A)the long run is a more important policy concern than the short run.
B)the short run is a more important policy concern than the long run.
C)both the short run and the long run are equally important.
D)the distinction between the short run and the long run is irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The AS/AD model looks similar to the microeconomic supply and demand model
A)but is not based on it.
B)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because the AS/AD is a macro representation of the micro model.
C)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because both are based on the principle of substitution.
D)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because both are based on opportunity costs.
A)but is not based on it.
B)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because the AS/AD is a macro representation of the micro model.
C)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because both are based on the principle of substitution.
D)and is based on the microeconomic supply and demand model because both are based on opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the price level rises, the interest rate effect will cause investment:
A)and the quantity of aggregate demand to increase.
B)and the quantity of aggregate demand to decrease.
C)to increase and the quantity of aggregate demand to decrease.
D)to decrease and the quantity of aggregate demand to increase.
A)and the quantity of aggregate demand to increase.
B)and the quantity of aggregate demand to decrease.
C)to increase and the quantity of aggregate demand to decrease.
D)to decrease and the quantity of aggregate demand to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
From 2007 to 2012, the U.S. personal savings rate rose. If the additional savings were not translated into investment, Keynes would predict that aggregate income would:
A)decline and remain there.
B)rise indefinitely.
C)accelerate.
D)rise and remain there.
A)decline and remain there.
B)rise indefinitely.
C)accelerate.
D)rise and remain there.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why would one expect the AD curve to be vertical?
A)If the price level rises, relative prices haven't changed so people would not change their choices.
B)If the price level rises, changes in choices by suppliers are offset by changes in demanders.
C)People do not make choices based on relative prices, but instead based on absolute prices.
D)Substitution is not one of the reasons why the AD curve has its slope.
A)If the price level rises, relative prices haven't changed so people would not change their choices.
B)If the price level rises, changes in choices by suppliers are offset by changes in demanders.
C)People do not make choices based on relative prices, but instead based on absolute prices.
D)Substitution is not one of the reasons why the AD curve has its slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The interest rate effect helps to explain why:
A)an increase in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
B)an increase in the price level raises investment.
C)a decrease in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in the price level reduces investment.
A)an increase in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
B)an increase in the price level raises investment.
C)a decrease in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in the price level reduces investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The theoretical proposition that the price level is just a numeraire and should not affect aggregate expenditures suggests the AD curve is:
A)downward sloping.
B)horizontal.
C)vertical.
D)upward sloping.
A)downward sloping.
B)horizontal.
C)vertical.
D)upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
By the 1950s, the views of the Classical economists among American economists:
A)had been largely eclipsed by Keynesian views.
B)had largely replaced Keynesian views.
C)were about as widely held as Keynesian views.
D)were just starting to be developed in response to the Great Depression.
A)had been largely eclipsed by Keynesian views.
B)had largely replaced Keynesian views.
C)were about as widely held as Keynesian views.
D)were just starting to be developed in response to the Great Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The paradox of thrift occurs when:
A)an increase in saving raises output.
B)an increase in saving reduces output.
C)saving is unrelated to output.
D)a decrease in saving reduces output.
A)an increase in saving raises output.
B)an increase in saving reduces output.
C)saving is unrelated to output.
D)a decrease in saving reduces output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A fall in the price level:
A)reduces the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy less goods.
B)reduces the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy more goods.
C)increases the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy less goods.
D)increases the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy more goods.
A)reduces the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy less goods.
B)reduces the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy more goods.
C)increases the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy less goods.
D)increases the value of money in peoples' pockets, so people buy more goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The reason why the AS/AD model does not depend upon the concepts of substitution and opportunity cost is that:
A)in groups, people do not make the same choices as when they are alone.
B)the AS/AD model considers total output. There are no goods to substitute.
C)the AS/AD model considers the effects of other countries' decisions.
D)other things remain constant in the AS/AD model.
A)in groups, people do not make the same choices as when they are alone.
B)the AS/AD model considers total output. There are no goods to substitute.
C)the AS/AD model considers the effects of other countries' decisions.
D)other things remain constant in the AS/AD model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the following graphs. 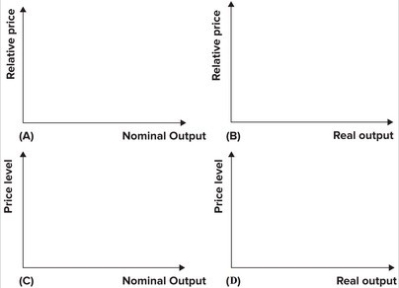 Which of the graphs correctly labels the axes of the AS/AD model?
Which of the graphs correctly labels the axes of the AS/AD model?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 Which of the graphs correctly labels the axes of the AS/AD model?
Which of the graphs correctly labels the axes of the AS/AD model?A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A fall in the price level will:
A)increase the value of money in people's pockets.
B)decrease the value of money in people's pockets.
C)not affect the value of money in people's pockets.
D)reduce real wealth.
A)increase the value of money in people's pockets.
B)decrease the value of money in people's pockets.
C)not affect the value of money in people's pockets.
D)reduce real wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A decrease in the expected future income of the United States would likely:
A)shift its AD curve to the left.
B)shift its AD curve to the right.
C)make its AD curve flatter.
D)make its AD curve steeper.
A)shift its AD curve to the left.
B)shift its AD curve to the right.
C)make its AD curve flatter.
D)make its AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the multiplier effect did not exist, the aggregate demand curve would:
A)be steeper.
B)be flatter.
C)be horizontal.
D)not exist.
A)be steeper.
B)be flatter.
C)be horizontal.
D)not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Most economists agree that the aggregate demand curve is:
A)vertical.
B)relatively steep.
C)relatively flat.
D)horizontal.
A)vertical.
B)relatively steep.
C)relatively flat.
D)horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the 1990s, the price level in Japan fell relative to the price level in the United States. If the exchange rate did not change, one would expect that:
A)U.S. exports to Japan would rise and U.S. imports from Japan would decline.
B)U.S. exports to Japan would decline and U.S. imports from Japan would rise.
C)both U.S. exports to Japan and U.S. imports from Japan would rise.
D)both U.S. exports to Japan and U.S. imports from Japan would fall.
A)U.S. exports to Japan would rise and U.S. imports from Japan would decline.
B)U.S. exports to Japan would decline and U.S. imports from Japan would rise.
C)both U.S. exports to Japan and U.S. imports from Japan would rise.
D)both U.S. exports to Japan and U.S. imports from Japan would fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the money wealth, interest rate, and international effects increase the quantity of aggregate demand by 2 percent when the price falls by 2 percent and the multiplier is 4, then the slope of the aggregate demand curve is:
A)−1/4.
B)−1/2.
C)−1.
D)−4.
A)−1/4.
B)−1/2.
C)−1.
D)−4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If businesses expect future demand to increase, this will cause a:
A)movement down the aggregate demand curve.
B)movement up the aggregate demand curve.
C)rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
D)leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
A)movement down the aggregate demand curve.
B)movement up the aggregate demand curve.
C)rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
D)leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A fall in a foreign country's income will most likely cause:
A)a reduction in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts left.
B)a reduction in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts right.
C)an increase in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts left.
D)an increase in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts right.
A)a reduction in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts left.
B)a reduction in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts right.
C)an increase in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts left.
D)an increase in U.S. exports, so the U.S. aggregate demand curve shifts right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a country is experiencing high inflation, other things equal, the expectations of worsening inflation in the future would probably:
A)shift the AD curve to the left.
B)shift the AD curve to the right.
C)make the AD curve flatter.
D)make the AD curve steeper.
A)shift the AD curve to the left.
B)shift the AD curve to the right.
C)make the AD curve flatter.
D)make the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A fall in the U.S. price level will cause foreigners to:
A)substitute U.S. goods for their own domestically-produced goods.
B)substitute their own domestically-produced goods for U.S. goods.
C)buy more of their own domestically-produced goods.
D)buy fewer U.S. goods.
A)substitute U.S. goods for their own domestically-produced goods.
B)substitute their own domestically-produced goods for U.S. goods.
C)buy more of their own domestically-produced goods.
D)buy fewer U.S. goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the money wealth, interest rate, and international effects reduce the quantity of aggregate demand by 3 percent when the price rises by 6 percent and the multiplier is 2, then the slope of the aggregate demand curve is:
A)−1/2.
B)−1.
C)−2.
D)−3.
A)−1/2.
B)−1.
C)−2.
D)−3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A)An increase in foreign income
B)A depreciation in the value of the country's currency
C)A higher future expected price level
D)A decrease in exports
A)An increase in foreign income
B)A depreciation in the value of the country's currency
C)A higher future expected price level
D)A decrease in exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not a reason why the AD curve slopes downward?
A)International effect
B)Interest rate effect
C)Substitution effect
D)Money wealth effect
A)International effect
B)Interest rate effect
C)Substitution effect
D)Money wealth effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose prices in the United States are expected to decline in the future. The effect today is likely to:
A)shift the AD curve to the left.
B)shift the AD curve to the right.
C)make the AD curve flatter.
D)make the AD curve steeper.
A)shift the AD curve to the left.
B)shift the AD curve to the right.
C)make the AD curve flatter.
D)make the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An increase in the price level might cause:
A)a decrease in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the substitution effect.
B)an increase in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the money wealth effect.
C)a decrease in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the interest rate effect.
D)an increase in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the multiplier effect.
A)a decrease in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the substitution effect.
B)an increase in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the money wealth effect.
C)a decrease in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the interest rate effect.
D)an increase in the quantity of aggregate demand because of the multiplier effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The multiplier effect makes the aggregate demand curve:
A)steeper.
B)flatter.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
A)steeper.
B)flatter.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the AS/AD model, the repercussion that a change in aggregate quantity demanded has on production and subsequently on income and expenditures is called the:
A)accelerator effect.
B)expenditure effect.
C)multiplier effect.
D)money wealth effect.
A)accelerator effect.
B)expenditure effect.
C)multiplier effect.
D)money wealth effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A rise in the U.S. price level will cause:
A)both exports and imports to increase.
B)both exports and imports to decrease.
C)exports to increase and imports to decrease.
D)exports to decrease and imports to increase.
A)both exports and imports to increase.
B)both exports and imports to decrease.
C)exports to increase and imports to decrease.
D)exports to decrease and imports to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A)An increase in foreign income
B)An appreciation of the value of a country's currency
C)A lower future expected price level
D)An increase in imports
A)An increase in foreign income
B)An appreciation of the value of a country's currency
C)A lower future expected price level
D)An increase in imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The multiplier effect exists because:
A)production and expenditures are interdependent.
B)when one person increases expenditures, everyone decreases expenditures.
C)production and expenditures are independent.
D)production lowers expenditures.
A)production and expenditures are interdependent.
B)when one person increases expenditures, everyone decreases expenditures.
C)production and expenditures are independent.
D)production lowers expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the money wealth, interest rate, and international effects reduce the quantity of aggregate demand by 5 percent when the price rises by 10 percent and the multiplier is 3, then the slope of the aggregate demand curve is:
A)−1/2.
B)−2/3.
C)−2.
D)−3.
A)−1/2.
B)−2/3.
C)−2.
D)−3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the graph shown. From 1980 to 1985, the U.S. dollar appreciated over 60 percent. The effect of this appreciation on the AD curve can be shown by a movement from: 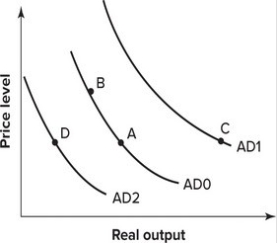
A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the early 1930s, U.S. government expenditures increased as part of the New Deal without any change in taxes. This:
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the U.S. government increases its expenditures (without any changes in taxes)while the Federal Reserve Bank decreases the money supply:
A)the AD curve would likely shift to the left.
B)the AD curve would likely shift to the right.
C)the AD curve would likely remain unchanged.
D)what happens to the AD curve is unclear.
A)the AD curve would likely shift to the left.
B)the AD curve would likely shift to the right.
C)the AD curve would likely remain unchanged.
D)what happens to the AD curve is unclear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the graph shown. From 1938 to 1943 the Federal deficit rose from $1.0 billion to $53.8 billion due to increased defense spending. The effect of this on the AD curve can be shown by a movement from: 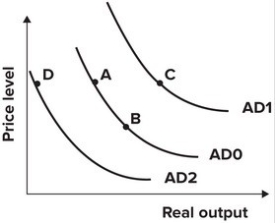
A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A fall in the value of the dollar relative to other currencies will:
A)increase foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the right.
B)increase foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)decrease foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the right.
D)decrease foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left.
A)increase foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the right.
B)increase foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)decrease foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the right.
D)decrease foreign demand for U.S. goods, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the dollar were to depreciate against major foreign currency, the dollar's depreciation should result in:
A)an increase in U.S. exports and an outward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
B)an increase in U.S. exports and an inward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
C)a decrease in U.S. exports and an outward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
D)a decrease in U.S. exports and an inward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
A)an increase in U.S. exports and an outward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
B)an increase in U.S. exports and an inward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
C)a decrease in U.S. exports and an outward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.
D)a decrease in U.S. exports and an inward shift of the U.S. aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The new government of Pakistan transfers money from the rich to the poor. This will likely:
A)shift the Pakistani AD curve to the left.
B)shift the Pakistani AD curve to the right.
C)make the Pakistani AD curve flatter.
D)make the Pakistani AD curve steeper.
A)shift the Pakistani AD curve to the left.
B)shift the Pakistani AD curve to the right.
C)make the Pakistani AD curve flatter.
D)make the Pakistani AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
To combat inflation in 1955 and 1956, the Fed reduced the money supply. In terms of the AS/AD model, this change should have:
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If total income in Sweden remains the same but the wage share of income rises, the Swedish AD curve will most likely:
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the summer of 1953, the Korean War ended and government expenditures decreased. In terms of the AS/AD model, this change should have:
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In 1968, the government instituted a 26 percent income tax surcharge. In terms of the AS/AD model, this change should have:
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.
A)shifted the AD curve to the left.
B)shifted the AD curve to the right.
C)made the AD curve flatter.
D)made the AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the graph shown. During the Reagan Administration (1981 to 1989), tax rates were reduced significantly, while federal defense spending rose by 80 percent. The effect of these policies on the AD curve is best shown as a movement from: 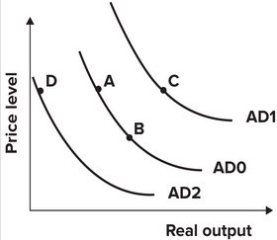
A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If total income remains the same but profits fall and real wages rise, the aggregate demand curve will most likely:
A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.
A)shift to the right.
B)shift to the left.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the graph shown. In 1930, the United States passed the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which raised tariffs on imported goods at an average of 60 percent. Other countries retaliated with similar tariffs and world output declined. The effect of the decline in foreign output on the U.S. AD curve can be shown by a movement from: 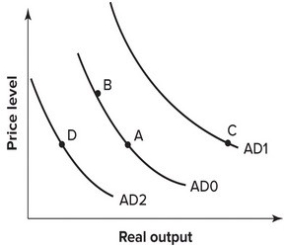
A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the graph shown. From 1929 to 1933 the money supply fell in the United States by 40 percent. The effect of this on the AD curve is best shown by a movement from: 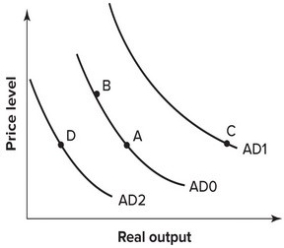
A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)A to C.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the U.S. government increases its expenditures (without any change in taxes)and at the same time the Federal Reserve Bank increases the money supply, the AD curve would:
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the U.S. government increased taxes without changing spending, the U.S. AD curve would:
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.
A)shift to the left.
B)shift to the right.
C)become flatter.
D)become steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the graph shown. In 1975 U.S. President Gerald Ford instituted a large tax cut. At the same time, the Fed expanded the money supply. The effect of these policies on the AD curve is best shown as a movement from: 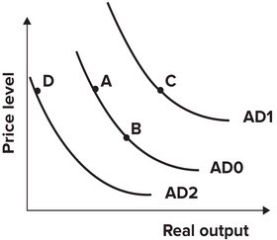
A)A to B.
B)D to A.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

A)A to B.
B)D to A.
C)A to D.
D)B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose the Brazilian currency, the real, depreciates significantly. The AS/AD model predicts that this would cause a trade:
A)deficit for Brazil and shifted its AD curve left.
B)surplus for Brazil and shifted its AD curve left.
C)deficit for Brazil and shifted its AD curve right.
D)surplus for Brazil and shifted its AD curve right.
A)deficit for Brazil and shifted its AD curve left.
B)surplus for Brazil and shifted its AD curve left.
C)deficit for Brazil and shifted its AD curve right.
D)surplus for Brazil and shifted its AD curve right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
From 1975 to 1995, the value of the dollar in terms of yen fell from over 300 yen per dollar to about 100 yen per dollar. Considering the impact of this alone, this would likely:
A)shift the U.S. AD curve to the left.
B)shift the U.S. AD curve to the right.
C)make the U.S. AD curve flatter.
D)make the U.S. AD curve steeper.
A)shift the U.S. AD curve to the left.
B)shift the U.S. AD curve to the right.
C)make the U.S. AD curve flatter.
D)make the U.S. AD curve steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 220 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



