Deck 19: International Financial Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: International Financial Policy
1
What is an exchange rate, and what are the factors that influence it?
The exchange rate is the rate at which one country's currency can be traded for another country's currency.The demand and supply of both currencies influence the exchange rate (they may not change it in the case of a fixed exchange rate).
2
How is a country's exchange rate related to its balance of payments?
Exchange rates are determined by the demand and supply of currencies.When private quantity demanded of the currency equals the private quantity supplied, the balance of payments is in equilibrium.If the exchange rate is too high (demand greater than supply), there will be a deficit in the balance of payments.If the exchange rate is too low (supply greater than demand), there will be a surplus in the balance of payments.
3
What are four economic advantages and three disadvantages of adopting a common currency, such as the euro?
The advantages are:
(1) It eliminates the cost of exchanging currencies when trading among member countries.
(2) It promotes price transparency, which means that people will be able to compare prices in member countries using one currency.
(3) Targeting a larger market allows firms to take advantage of economies of scale.
(4) It encourages individuals throughout the world to hold their assets in the new common currency.
The disadvantages are:
(1) Member countries will no longer be able to conduct independent monetary policy.
(2) Nations lose an important national symbol.
(3) Increased economic interconnections among member countries can create domestic political problems.
Short Answer Questions
(1) It eliminates the cost of exchanging currencies when trading among member countries.
(2) It promotes price transparency, which means that people will be able to compare prices in member countries using one currency.
(3) Targeting a larger market allows firms to take advantage of economies of scale.
(4) It encourages individuals throughout the world to hold their assets in the new common currency.
The disadvantages are:
(1) Member countries will no longer be able to conduct independent monetary policy.
(2) Nations lose an important national symbol.
(3) Increased economic interconnections among member countries can create domestic political problems.
Short Answer Questions
4
How can a country influence its exchange rate through expansionary fiscal policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How is currency support different from currency stabilization? Why is it difficult for countries to achieve either currency support or currency stabilization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the difference between currency support and currency stabilization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How can a country influence its exchange rate through expansionary monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the difference between a fixed, flexible, and partially flexible exchange rate regime? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these exchange rate regimes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explain the effect of an expansionary monetary policy on the exchange rate value of the U.S.dollar via the income and price routes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a country wants to fix its exchange rate at a rate that is lower than the market rate, what monetary or fiscal policy must it use? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A country that wants to fix its exchange rate cannot achieve an interest rate target and an exchange rate target simultaneously.Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is purchasing power parity and how is it related to changes in the real exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is a fixed exchange rate policy? What must the government do to fix its exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How does the balance of payments differ from the balance on goods and services? How do these balances relate to the international supply and demand for a nation's currency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What kind of pressure will a surplus in the U.S.balance of payments account place on the value of the dollar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a government wants to fix its currency at its long run equilibrium value and decides to use the purchasing power parity method to estimate the long-run equilibrium value of its currency.Many economists would say that the purchasing power parity method is not a good method to use.Explain their reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is purchasing power parity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a country wants to use stabilization policy to fix its exchange rate, why is it important for the country to know what the long-run equilibrium exchange rate of its currency is?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is an exchange rate and how is it related to its balance of payments? What are the four fundamental determinants of a country's exchange rate and what is likely to happen to the exchange rate in the following cases?
(1) A fall in the U.S.interest rate relative to interest rates abroad (dollar).
(2) A higher inflation rate in Japan compared to other countries (yen).
(3) A severe recession in Europe (euro).
(4) The U.S.imposes a 15% tariff on Japanese imported cars (dollar).
(1) A fall in the U.S.interest rate relative to interest rates abroad (dollar).
(2) A higher inflation rate in Japan compared to other countries (yen).
(3) A severe recession in Europe (euro).
(4) The U.S.imposes a 15% tariff on Japanese imported cars (dollar).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Define the balance of payments, and briefly describe its two components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the net effect of contractionary fiscal policy on the exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Demonstrate graphically and explain in words the effect of a decrease in demand for Japanese yen on the exchange rate for yens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the three pathways through which monetary policy can influence exchange rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
List the advantages and disadvantages of a fixed exchange rate system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Answer the questions below based upon the following Balance of Payments table for Tundraland (figures are in millions of cugats):
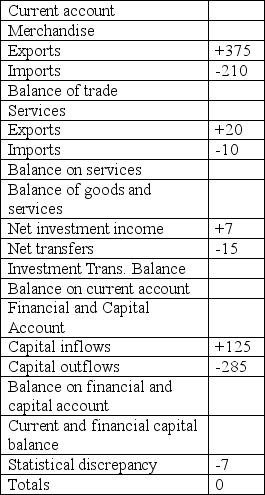 (a) What is the balance on the current account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?
(a) What is the balance on the current account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?
(b) What is the balance on the financial and capital account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?
(c) Suppose Tundraland had purchased cugats.How would you know? Would it be trying to lower or raise the value of its currency? Show graphically.
 (a) What is the balance on the current account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?
(a) What is the balance on the current account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?(b) What is the balance on the financial and capital account? Did more cugats flow in or out of that account?
(c) Suppose Tundraland had purchased cugats.How would you know? Would it be trying to lower or raise the value of its currency? Show graphically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
List the advantages and disadvantages of a flexible exchange rate system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What are the dangers associated with maintaining a high fixed exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain the effect of an expansionary fiscal policy on the exchange rate of the U.S.dollar through the price path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain the effect that a rise in a country's interest rate has on exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Explain the effect of an expansionary fiscal policy on the exchange rate of the U.S.dollar through the interest rate path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Demonstrate graphically and explain in words the effect of a decrease in the demand for dollars by Europeans on the exchange rate for euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
(a) Why is the supply of dollars upward sloping? Why is the demand for dollars downward sloping?
(b) Given the private supply and demand for the dollar shown below, if the government wants to keep the exchange rate value of the dollar at P0 by intervening in the exchange market, what must it do?
(c) How does this action show up on the balance of payments account?
(d) At an exchange rate of P0, does the country have a private balance of payments surplus or deficit? Or is it in balance?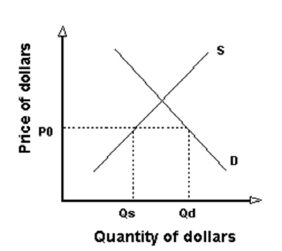
(b) Given the private supply and demand for the dollar shown below, if the government wants to keep the exchange rate value of the dollar at P0 by intervening in the exchange market, what must it do?
(c) How does this action show up on the balance of payments account?
(d) At an exchange rate of P0, does the country have a private balance of payments surplus or deficit? Or is it in balance?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using a supply and demand diagram for British Pounds, demonstrate graphically and explain in words how Great Britain can increase the exchange rate value of the Pound by influencing private demand for its currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Where would each of the following appear in the balance of payments account?
(a) You order some tulip bulbs from a supplier in Holland.
(b) While on vacation in London, you pay to have your shoes repaired.
(c) A U.S.firm buys shares in a German company.
(d) You receive dividends from the ownership of a German company's stock.
(e) A Japanese citizen buys a U.S.bond.
(f) A U.S.company builds a manufacturing plant in Mexico.
(a) You order some tulip bulbs from a supplier in Holland.
(b) While on vacation in London, you pay to have your shoes repaired.
(c) A U.S.firm buys shares in a German company.
(d) You receive dividends from the ownership of a German company's stock.
(e) A Japanese citizen buys a U.S.bond.
(f) A U.S.company builds a manufacturing plant in Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the difference between a fixed, flexible, and partially flexible exchange rate regime?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For each of the following, state whether it creates a demand for or a supply of U.S.dollars:
(a) A Japanese automobile firm builds an assembly plant in Ohio.
(b) A U.S.importer purchases a shipload of Saudi Arabia oil.
(c) A U.S.student spends a summer in England studying in Oxford.
(d) A French exporter ships products to Argentina using an American freighter.
(e) Currency traders feel that the value of the U.S.dollar will fall in the near future and act on that feeling.
(a) A Japanese automobile firm builds an assembly plant in Ohio.
(b) A U.S.importer purchases a shipload of Saudi Arabia oil.
(c) A U.S.student spends a summer in England studying in Oxford.
(d) A French exporter ships products to Argentina using an American freighter.
(e) Currency traders feel that the value of the U.S.dollar will fall in the near future and act on that feeling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Explain the effect of a contractionary fiscal policy on the exchange rate of the U.S.dollar through the income path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What overall effect does contractionary monetary policy have on a country's exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What are the three pathways through which fiscal policy can influence exchange rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following diagram showing supply and demand for euros in Germany: 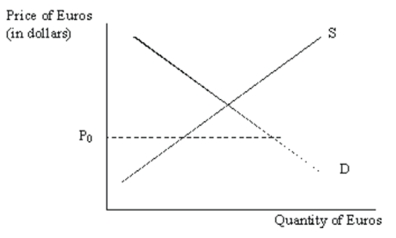 If the price of euro is currently $P0, what does this tell us about the private balance of payments?
If the price of euro is currently $P0, what does this tell us about the private balance of payments?
 If the price of euro is currently $P0, what does this tell us about the private balance of payments?
If the price of euro is currently $P0, what does this tell us about the private balance of payments?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe what has happened to the real exchange rate value of the dollar in each of the following examples:
(a) The U.S.price level rises by 10 percent, the European price level remains constant, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate falls by 10 percent.
(b) The U.S.price level rises by 9 percent, the European price level rises by 6 percent, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate falls by 2 percent.
(c) The U.S.price level falls by 2 percent, the European price level remains constant, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate rises by 4 percent.
(d) The U.S.price level remains constant, the European price level rises by 3 percent, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate rises by 2 percent.
The %Δ real exchange rate = %Δ nominal exchange rate + U.S.inflation - European inflation.
(a).0 = -10 + 10
(b).-1 percent = -2 + 9 - 6
(c).2 percent = 4 + -2 - 0
(d).-1 percent = 2 + 0 - 3
(a) The U.S.price level rises by 10 percent, the European price level remains constant, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate falls by 10 percent.
(b) The U.S.price level rises by 9 percent, the European price level rises by 6 percent, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate falls by 2 percent.
(c) The U.S.price level falls by 2 percent, the European price level remains constant, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate rises by 4 percent.
(d) The U.S.price level remains constant, the European price level rises by 3 percent, and the nominal U.S.exchange rate rises by 2 percent.
The %Δ real exchange rate = %Δ nominal exchange rate + U.S.inflation - European inflation.
(a).0 = -10 + 10
(b).-1 percent = -2 + 9 - 6
(c).2 percent = 4 + -2 - 0
(d).-1 percent = 2 + 0 - 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following supply and demand for Mexican pesos: 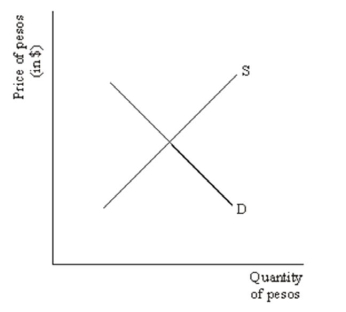 Suppose income in Mexico increases.Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally the impact this will have on the market for pesos illustrated above.
Suppose income in Mexico increases.Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally the impact this will have on the market for pesos illustrated above.
 Suppose income in Mexico increases.Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally the impact this will have on the market for pesos illustrated above.
Suppose income in Mexico increases.Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally the impact this will have on the market for pesos illustrated above.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the actual euro/dollar exchange rate is greater than the purchasing power parity (PPP) exchange rate, is the dollar or euro overvalued? What if the actual exchange rate is lower than the PPP exchange rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following supply and demand diagram for dollars in exchange for euros: 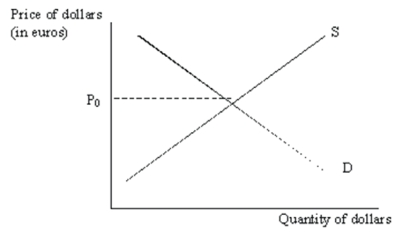 Describe and illustrate the impact each of the following will have on the supply and demand diagram shown above.
Describe and illustrate the impact each of the following will have on the supply and demand diagram shown above.
(a) Unemployment increases in Europe.
(b) Inflation in the U.S.drops to an all-time low relative to all other industrialized countries
(c) The European Central Bank raises interest rates.
 Describe and illustrate the impact each of the following will have on the supply and demand diagram shown above.
Describe and illustrate the impact each of the following will have on the supply and demand diagram shown above.(a) Unemployment increases in Europe.
(b) Inflation in the U.S.drops to an all-time low relative to all other industrialized countries
(c) The European Central Bank raises interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose the market for Japanese yen is as illustrated in the following supply and demand diagram: 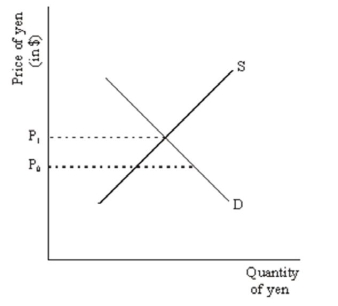 If the private market price is P1 but the government wants to facilitate exports by having a price of P0, what can it do?
If the private market price is P1 but the government wants to facilitate exports by having a price of P0, what can it do?
 If the private market price is P1 but the government wants to facilitate exports by having a price of P0, what can it do?
If the private market price is P1 but the government wants to facilitate exports by having a price of P0, what can it do?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You have recently been net surfing with your friends in Russia; the main topic of your recent e-mail exchange is the newest Drake album.You inform your friends in Russia that you can purchase the album at a U.S.seller for $11.99.You are told that in Russia the album costs 70,000 rubles.Suppose that the current dollar/ruble exchange rate is 1 ruble = $.000175 (or equivalently $1 = 5,714 rubles).According to the purchasing power parity view of exchange rate calculations, does the current exchange rate represent a long-run equilibrium exchange rate? Is the dollar overvalued or undervalued? The ruble? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



