Deck 11: Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/37
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Monetary Policy
1
What is a central bank? What are its distinguishing characteristics and primary functions?
A central bank is a banker's bank.A central bank is where a bank would go to borrow money.For example, if there is a run on a bank, the bank may get low on reserves, and need to borrow some from the central bank to meet its reserve requirement.When the central bank makes the loan, the proceeds (IOUs from the central bank) are able to serve as bank reserves (e.g currency and deposits at the Federal Reserve).
2
Define the discount rate, and explain how it can be used as a tool for the conduct of monetary policy.
The discount rate is the rate the Fed charges banks when they borrow money from the Fed.Banks try to hold as little as possible in excess reserves (reserves in excess of the reserve requirement) because they lose the opportunity to make profitable loans and the Fed pays very little interest on reserves.Due to variations in daily operations, they may find their thin excess reserve "cushion" has proven inadequate, and that they must borrow from the Fed (or some other source) to meet their reserve requirement.The higher the discount rate, the more they are encouraged to keep a larger cushion of excess reserves, to avoid having to borrow from the Federal Reserve.If banks increase their excess reserve cushion, they can make fewer loans (and this reduction in loans is magnified by the multiplier effect).In the past, the discount rate was lower than the market rate, so on the basis of price alone, banks would want to borrow as much as possible from the Fed.However, now the discount rate is kept higher than the banks' other sources of funds.When the discount rate goes up banks tend to hold more reserves and the money supply contracts.
3
Explain how the Fed uses the discount rate to influence the money supply.
Since 2003, the Federal Reserve sets the discount rate slightly higher than the banks' other costs of funds.An increase in the discount rate discourages banks from borrowing and thus contracts the money supply: a decrease in the discount rate encourages banks to borrow from the Federal Reserve and thus increases the money supply.
4
What is the Taylor rule and why is it important for monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Would you expect the Fed to increase the rate it pays on excess reserves when it is decreasing the Fed Funds rate target?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An expansionary monetary policy raises nominal income but never raises real income.True or False? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How has the payment of interest on reserves changed the conduct of monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Describe the various documents that are prepared for, and presented at, a typical FOMC meeting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How does monetary policy work in the context of the AS/AD model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe how the Federal Reserve uses Open Market Operations to change the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Define open market operations, and explain how executing them can be used as a tool for the conduct of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Give examples of central banks in two other countries and briefly explain how their conduct of monetary policy differs from the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Briefly explain what goes on in a typical FOMC meeting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the monetary base? What role does it play in macroeconomic policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the yield curve? What happens when one moves out along the yield curve? How does its shape reflect the fact that the Federal Reserve's ability to control the economy through controlling short-term interest rates is limited?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Define reserve requirement, and explain how it can be used as a tool for the conduct of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In recent years the Fed has begun paying interest on reserves.How has this changed the conduct of monetary policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Define the term "liquidity trap" and describe the problem it creates for the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the Federal funds rate and how does the Fed use it as an operating target? How does the Fed influence the Federal Funds rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that the Fed has currently set the reserve requirement at 10%.Further suppose that banks do not hold any excess reserves.
(a) How much money can the banking system support if it currently has $1,000,000 in reserves?
(b) If the Fed wanted to cause the money supply to expand, how could it use the reserve requirement to achieve its goal? Give an example.
(a) How much money can the banking system support if it currently has $1,000,000 in reserves?
(b) If the Fed wanted to cause the money supply to expand, how could it use the reserve requirement to achieve its goal? Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain how distinction between the real and nominal interest rate poses problems for the conduct of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain the difference between real and nominal interest rates.How are they related?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose banks hold no excess reserves, the reserve requirement is 20%.
(a) If banks have $10 million in reserves what will the money supply be?
(b) How will your answer to (a) change if the Fed increases the reserve requirement to 30%?
(a) If banks have $10 million in reserves what will the money supply be?
(b) How will your answer to (a) change if the Fed increases the reserve requirement to 30%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain how the Fed influences the Federal Funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imagine you are a Federal Reserve board governor and you are examining the economy.You discover that the money supply is currently $2,000,000, that banks have $1,000,000 in reserves.You want to increase the money supply by $500,000 using an open market operation.What would you do?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Using the following AS/AD diagram, answer the question below. 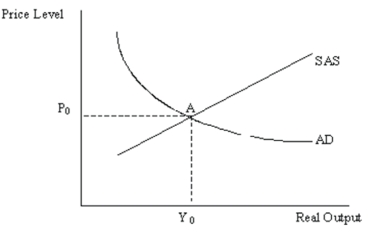 If the economy is currently at point A, does the Fed have enough information to decide whether it should conduct expansionary or contractionary monetary policy? Explain your answer.
If the economy is currently at point A, does the Fed have enough information to decide whether it should conduct expansionary or contractionary monetary policy? Explain your answer.
 If the economy is currently at point A, does the Fed have enough information to decide whether it should conduct expansionary or contractionary monetary policy? Explain your answer.
If the economy is currently at point A, does the Fed have enough information to decide whether it should conduct expansionary or contractionary monetary policy? Explain your answer.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What ultimately limits the amount of expansionary pressure the Fed can create? Has the Fed ever found itself up against this limit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain the difference between the Fed's offensive and defensive actions as parts of its control over monetary policy.Give an example of each type of action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If inflation exceeds target inflation by 3%, target inflation is at 2%, and total output is 1% above its potential, what is the Federal Funds rate that the Fed will set according to the Taylor rule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are the Fed's ultimate targets? Explain how the Fed achieves ultimate economic targets using its available tools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What are Federal funds? What is the Federal funds rate? Explain how the Fed uses the Federal funds rate as a target.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(a) Show the effects of expansionary and contractionary open market operations on the interest rate using demand and supply curves and the market for government bonds.
(b) What should the Fed do if the interest rate is below its target rate? What should the Fed do if the interest rate is above its target rate?
(b) What should the Fed do if the interest rate is below its target rate? What should the Fed do if the interest rate is above its target rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose banks have $25 million in reserves, the reserve requirement is 5%, and people do not hold any cash outside of banks.If the Fed makes an open market sale of $1 million of government securities, by how much will the money supply change? (Assume that the public does not hold any of its money in the form of currency.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally that the impact of expansionary monetary policy on the economy depends upon the position of equilibrium output in relation to potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally (using the AS/AD model) the effect of the Fed's sale of government bonds when the economy is below potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Explain the difference between expansionary and contractionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



