Deck 13: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/121
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
1
Blood flowing out of a capillary bed first enters structures called
A)arterial anastomoses.
B)venous valves.
C)arteriovenous anastomoses.
D)precapillary sphincters.
E)venules.
A)arterial anastomoses.
B)venous valves.
C)arteriovenous anastomoses.
D)precapillary sphincters.
E)venules.
E
2
Why do veins have relatively thin walls?
A)It allows a typical vein to change the diameter of its lumen.
B)It allows a typical vein to be stretched as its diameter increases during ventricular systole.
C)A typical vein's wall allows exchange to occur quickly by diffusion across endothelial cells or through gaps between adjacent endothelial cells.
D)A typical vein does not need to withstand much pressure.
E)There are sphincters associated with the walls of veins, which allow vasomotion to occur.
A)It allows a typical vein to change the diameter of its lumen.
B)It allows a typical vein to be stretched as its diameter increases during ventricular systole.
C)A typical vein's wall allows exchange to occur quickly by diffusion across endothelial cells or through gaps between adjacent endothelial cells.
D)A typical vein does not need to withstand much pressure.
E)There are sphincters associated with the walls of veins, which allow vasomotion to occur.
D
3
The muscular layer of blood vessels is the
A)tunica intima.
B)tunica externa.
C)tunica media.
D)tunica interna.
E)tunica adventitia.
A)tunica intima.
B)tunica externa.
C)tunica media.
D)tunica interna.
E)tunica adventitia.
C
4
The vessels that permit exchange of materials between the blood and the surrounding interstitial fluid are called
A)capillaries.
B)arterioles.
C)arteries.
D)venules.
E)veins.
A)capillaries.
B)arterioles.
C)arteries.
D)venules.
E)veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When necessary, blood bypasses a capillary bed through
A)an arterial anastomosis.
B)venous valves.
C)arteriovenous anastomoses.
D)precapillary sphincters.
E)venules.
A)an arterial anastomosis.
B)venous valves.
C)arteriovenous anastomoses.
D)precapillary sphincters.
E)venules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Thick-walled vessels, which are large and extremely resilient, are called ________ arteries.
A)coronary
B)pulmonary
C)elastic
D)muscular
E)arteriolar
A)coronary
B)pulmonary
C)elastic
D)muscular
E)arteriolar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In general, for a vessel of a given size, a typical artery ________ compared to a typical vein.
A)is more elastic
B)has less smooth muscle in its tunica media
C)has no endothelium
D)has thinner walls
E)has a larger lumen
A)is more elastic
B)has less smooth muscle in its tunica media
C)has no endothelium
D)has thinner walls
E)has a larger lumen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which vessel type typically has an internal diameter of about 30 μm and has a tunica media comprised of 1-2 layers of smooth muscle cells?
A)capillaries
B)muscular arteries
C)arterioles
D)venules
E)elastic arteries
A)capillaries
B)muscular arteries
C)arterioles
D)venules
E)elastic arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Water and solutes that are not reabsorbed by capillaries ultimately return to the bloodstream by way of
A)venules.
B)lymphatic vessels.
C)distributing arteries.
D)arterial anastomoses.
E)arteriovenous anastomoses.
A)venules.
B)lymphatic vessels.
C)distributing arteries.
D)arterial anastomoses.
E)arteriovenous anastomoses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The outermost layer of the arterial wall is the
A)endothelium.
B)tunica intima.
C)tunica externa.
D)tunica media.
E)serosa.
A)endothelium.
B)tunica intima.
C)tunica externa.
D)tunica media.
E)serosa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Regarding the typical structure of blood vessel walls, those that have only a tunica intima are the
A)arteries.
B)arterioles.
C)veins.
D)venules.
E)capillaries.
A)arteries.
B)arterioles.
C)veins.
D)venules.
E)capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which condition is described as the formation of lipid deposits in the tunica media associated with damage to the endothelial lining?
A)atherosclerosis
B)phlebitis
C)thrombus
D)aneurysm
E)pulmonary embolism
A)atherosclerosis
B)phlebitis
C)thrombus
D)aneurysm
E)pulmonary embolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The difference in pressure from one end of a vessel to the other is called ________, which greatly determines the rate of flow.
A)osmotic pressure
B)pulse pressure
C)pressure gradient
D)pressure point
E)pulse point
A)osmotic pressure
B)pulse pressure
C)pressure gradient
D)pressure point
E)pulse point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the correct match between the blood vessel and its corresponding characteristic.
A)artery/largest lumen
B)arteriole/controls blood pressure
C)capillary/has valves
D)venule/most permeable
E)vein/may be elastic or muscular
A)artery/largest lumen
B)arteriole/controls blood pressure
C)capillary/has valves
D)venule/most permeable
E)vein/may be elastic or muscular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The force that tends to reabsorb or pull water back into a capillary is called ________ pressure.
A)capillary hydrostatic
B)blood osmotic
C)arterial
D)venous
E)pulse
A)capillary hydrostatic
B)blood osmotic
C)arterial
D)venous
E)pulse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Choose the correct description of a typical medium-sized vein.
A)In these vessels, the thin tunica media is surrounded by a thick tunica externa composed of mostly collagen fibers.
B)Ranging from 2 mm to 9 mm in diameter, its thin tunica media consists of one to two layers of smooth muscle cells.
C)It has a diameter of approximately 0.4 cm and has more smooth muscle cells and fewer elastic fibers.
D)It ranges from 2 mm to 9 mm in diameter, and the relatively thick tunica externa has longitudinal bundles of elastic and collagen fibers.
E)It has a diameter up to 2.5 cm, and its tunica media is dominated by elastic fibers rather than smooth muscle cells.
A)In these vessels, the thin tunica media is surrounded by a thick tunica externa composed of mostly collagen fibers.
B)Ranging from 2 mm to 9 mm in diameter, its thin tunica media consists of one to two layers of smooth muscle cells.
C)It has a diameter of approximately 0.4 cm and has more smooth muscle cells and fewer elastic fibers.
D)It ranges from 2 mm to 9 mm in diameter, and the relatively thick tunica externa has longitudinal bundles of elastic and collagen fibers.
E)It has a diameter up to 2.5 cm, and its tunica media is dominated by elastic fibers rather than smooth muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is the
A)capillary pressure.
B)pulse pressure.
C)arterial pressure.
D)venous pressure.
E)hydrostatic pressure.
A)capillary pressure.
B)pulse pressure.
C)arterial pressure.
D)venous pressure.
E)hydrostatic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Arteries with a thick tunica media are ________ arteries.
A)anastomotic
B)elastic
C)conducting
D)large
E)muscular
A)anastomotic
B)elastic
C)conducting
D)large
E)muscular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the advantage of the small diameter of capillaries?
A)It dampens the rise in pressure during ventricular systole.
B)It slows blood flow, allowing sufficient time for capillary exchange to occur.
C)It absorbs the pressure changes that occur during the cardiac cycle.
D)It allows the vessels to overcome the force of gravity without a need for valves.
E)It prevents the backflow of blood, improving venous return.
A)It dampens the rise in pressure during ventricular systole.
B)It slows blood flow, allowing sufficient time for capillary exchange to occur.
C)It absorbs the pressure changes that occur during the cardiac cycle.
D)It allows the vessels to overcome the force of gravity without a need for valves.
E)It prevents the backflow of blood, improving venous return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which blood vessels are able to absorb the pressure changes that occur during the cardiac cycle?
A)elastic arteries
B)arterioles
C)muscular arteries
D)arterial anastomoses
E)capillaries
A)elastic arteries
B)arterioles
C)muscular arteries
D)arterial anastomoses
E)capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a process called autoregulation, ________ in response to a decline in dissolved oxygen levels within a tissue.
A)blood flow to the area decreases
B)the precapillary sphincters relax
C)vasomotion is not a factor
D)the diameter of the supplying capillaries' entrance narrows
E)the volume of blood arriving at the venules decreases
A)blood flow to the area decreases
B)the precapillary sphincters relax
C)vasomotion is not a factor
D)the diameter of the supplying capillaries' entrance narrows
E)the volume of blood arriving at the venules decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following has the greatest effect on blood flow to the tissues?
A)diffusion distance across vessel walls
B)venous valves
C)peripheral resistance
D)blood pH levels
E)collagen fiber content of tunica externa
A)diffusion distance across vessel walls
B)venous valves
C)peripheral resistance
D)blood pH levels
E)collagen fiber content of tunica externa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In which of the following would vascular resistance be the least?
A)a vessel < 30 μm in diameter
B)a vessel 10 microns in diameter
C)a vessel 8 μm in diameter
D)a vessel 1 mm in diameter
E)a vessel 1 cm in diameter
A)a vessel < 30 μm in diameter
B)a vessel 10 microns in diameter
C)a vessel 8 μm in diameter
D)a vessel 1 mm in diameter
E)a vessel 1 cm in diameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If blood has low viscosity, which result would be likely under normal conditions?
A)Blood flows at higher pressures.
B)Blood flows against high resistance.
C)Blood flow cannot occur.
D)Blood flows at lower pressures.
E)Blood contains increased numbers of plasma proteins and suspended blood cells.
A)Blood flows at higher pressures.
B)Blood flows against high resistance.
C)Blood flow cannot occur.
D)Blood flows at lower pressures.
E)Blood contains increased numbers of plasma proteins and suspended blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The instrument used to measure blood pressure is the
A)stethoscope.
B)thermometer.
C)endoscope.
D)sphygmomanometer.
E)hydrostatic pressure cuff.
A)stethoscope.
B)thermometer.
C)endoscope.
D)sphygmomanometer.
E)hydrostatic pressure cuff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The force that pushes fluid out of the capillaries is called
A)capillary hydrostatic pressure.
B)osmotic pressure.
C)systolic pressure.
D)diastolic pressure.
E)pressure gradient.
A)capillary hydrostatic pressure.
B)osmotic pressure.
C)systolic pressure.
D)diastolic pressure.
E)pressure gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As blood travels from the aorta toward the capillaries,
A)cardiovascular pressure decreases.
B)vascular resistance decreases.
C)vascular flow increases.
D)viscosity decreases.
E)both cardiovascular pressure and vascular flow increase.
A)cardiovascular pressure decreases.
B)vascular resistance decreases.
C)vascular flow increases.
D)viscosity decreases.
E)both cardiovascular pressure and vascular flow increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider a blood pressure reading of 120/80. 120 corresponds to the
A)diastolic pressure.
B)systolic pressure.
C)pulse pressure.
D)mean arterial pressure.
E)blood osmotic pressure.
A)diastolic pressure.
B)systolic pressure.
C)pulse pressure.
D)mean arterial pressure.
E)blood osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The pressure at which the pulse can first be heard corresponds to the ________ pressure.
A)peak systolic
B)peak diastolic
C)mean arterial
D)average pulse
E)capillary hydrostatic
A)peak systolic
B)peak diastolic
C)mean arterial
D)average pulse
E)capillary hydrostatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The tendency for water and small solutes to move out of the blood is greatest at the
A)venous end of capillaries.
B)transition between muscular arteries and arterioles.
C)transition between elastic and muscular arteries.
D)arteriole end of capillaries.
E)transition between venules and medium-sized veins.
A)venous end of capillaries.
B)transition between muscular arteries and arterioles.
C)transition between elastic and muscular arteries.
D)arteriole end of capillaries.
E)transition between venules and medium-sized veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
________ tend to diffuse across the capillary lining, driven by their individual concentration gradients.
A)Plasma proteins
B)Red blood cells
C)White blood cells
D)Platelets
E)Solute molecules
A)Plasma proteins
B)Red blood cells
C)White blood cells
D)Platelets
E)Solute molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As blood travels through the venous system toward the heart, why do the veins become larger in diameter?
A)The transition causes the resistance to increase further so that the flow rate of blood increases.
B)The transition causes the resistance to decrease further so that the flow rate of blood increases.
C)The transition causes the resistance to decrease further so that the flow rate of blood decreases.
D)The transition causes the resistance to increase further so that the flow rate of blood decreases.
E)The transition reflects no change in the resistance, but causes the flow rate of blood to increase.
A)The transition causes the resistance to increase further so that the flow rate of blood increases.
B)The transition causes the resistance to decrease further so that the flow rate of blood increases.
C)The transition causes the resistance to decrease further so that the flow rate of blood decreases.
D)The transition causes the resistance to increase further so that the flow rate of blood decreases.
E)The transition reflects no change in the resistance, but causes the flow rate of blood to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
________ refers to the factors that oppose blood flow in the entire cardiovascular system.
A)Turbulence
B)Vascular resistance
C)Total peripheral resistance
D)Viscosity
E)Elastic rebound
A)Turbulence
B)Vascular resistance
C)Total peripheral resistance
D)Viscosity
E)Elastic rebound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The third and fourth heart sounds are generated by
A)vascular resistance.
B)opening valves.
C)closing valves.
D)viscosity.
E)turbulence.
A)vascular resistance.
B)opening valves.
C)closing valves.
D)viscosity.
E)turbulence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The term blood pressure refers to the pressure in ________ of the cardiovascular system.
A)the venous component
B)the capillary vessels
C)all the vessels
D)the arterial vessels
E)the arteriovenous component
A)the venous component
B)the capillary vessels
C)all the vessels
D)the arterial vessels
E)the arteriovenous component

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is(are)the only factor(s)that can be adjusted by the nervous or endocrine system to regulate blood flow?
A)vascular resistance
B)turbulence
C)viscosity
D)vascular resistance and viscosity
E)turbulence and viscosity
A)vascular resistance
B)turbulence
C)viscosity
D)vascular resistance and viscosity
E)turbulence and viscosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the connection between breathing and venous return?
A)Inhalation decreases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
B)Inhalation increases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
C)Exhalation decreases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
D)Both inhalation and exhalation increase pressure in the pleural cavity, thus less blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
E)Both inhalation and exhalation decrease pressure in the pleural cavity, thus less blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
A)Inhalation decreases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
B)Inhalation increases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
C)Exhalation decreases pressure in the pleural cavity, thus more blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
D)Both inhalation and exhalation increase pressure in the pleural cavity, thus less blood flows into the inferior vena cava.
E)Both inhalation and exhalation decrease pressure in the pleural cavity, thus less blood flows into the inferior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Considering the factors affecting blood flow, choose the correct relationship.
A)Under normal circumstances, blood flow equals cardiac output.
B)When pressure rises, blood flow decreases.
C)When resistance increases, blood flow increases.
D)Resistance and blood flow are directly related.
E)Vessel length and blood flow are directly related.
A)Under normal circumstances, blood flow equals cardiac output.
B)When pressure rises, blood flow decreases.
C)When resistance increases, blood flow increases.
D)Resistance and blood flow are directly related.
E)Vessel length and blood flow are directly related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why is the osmotic pressure higher in the blood compared to that in the surrounding interstitial fluid?
A)Interstitial fluid contains more dissolved proteins than blood.
B)Blood has lower solute concentrations.
C)Interstitial fluid has higher solute concentrations.
D)There are equal concentrations of dissolved proteins in blood and interstitial fluid.
E)Blood contains more dissolved proteins than does interstitial fluid.
A)Interstitial fluid contains more dissolved proteins than blood.
B)Blood has lower solute concentrations.
C)Interstitial fluid has higher solute concentrations.
D)There are equal concentrations of dissolved proteins in blood and interstitial fluid.
E)Blood contains more dissolved proteins than does interstitial fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If venous pressures in the venules range from 17-21 mm Hg and pressures in the venae cavae range from 2-4 mm Hg, what is the pressure range of the driving force pushing blood through the venous system?
A)2-4 mm Hg
B)13-19 mm Hg
C)15-17 mm Hg
D)19-25 mm Hg
E)21-23 mm Hg
A)2-4 mm Hg
B)13-19 mm Hg
C)15-17 mm Hg
D)19-25 mm Hg
E)21-23 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A decrease in peripheral vein diameter is called
A)vasoconstriction.
B)venoconstriction.
C)vasodilation.
D)viscosity.
E)peripheral resistance.
A)vasoconstriction.
B)venoconstriction.
C)vasodilation.
D)viscosity.
E)peripheral resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When blood flow in a capillary bed decreases in response to locally high oxygen levels, it is caused by
A)intercellular chemicals.
B)angiotensin.
C)autoregulation.
D)neural processes.
E)endocrine processes.
A)intercellular chemicals.
B)angiotensin.
C)autoregulation.
D)neural processes.
E)endocrine processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Release of histamines and nitric oxide (NO)
A)triggers baroreceptor reflexes.
B)stimulates the cardioacceleratory centers.
C)promotes increased peripheral resistance.
D)triggers the release of EPO.
E)causes localized vasodilation.
A)triggers baroreceptor reflexes.
B)stimulates the cardioacceleratory centers.
C)promotes increased peripheral resistance.
D)triggers the release of EPO.
E)causes localized vasodilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following changes will result in increased blood flow at an injury site during inflammation?
A)increased blood volume
B)increased vessel diameter
C)increased blood pressure
D)decreased peripheral resistance
E)relaxation of precapillary sphincters
A)increased blood volume
B)increased vessel diameter
C)increased blood pressure
D)decreased peripheral resistance
E)relaxation of precapillary sphincters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
________ is released in response to a decrease in blood volume.
A)Renin
B)Erythropoietin
C)ADH
D)ACTH
E)Angiotensin
A)Renin
B)Erythropoietin
C)ADH
D)ACTH
E)Angiotensin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which hormone is released by the kidneys when blood pressure falls or the oxygen content of the blood becomes abnormally low?
A)ADH
B)ANP
C)angiotensin II
D)erythropoietin
E)renin
A)ADH
B)ANP
C)angiotensin II
D)erythropoietin
E)renin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Shock is an acute circulatory crisis marked by
A)low blood pressure and increased blood volume.
B)hypotension and increased tissue perfusion.
C)high blood pressure and inadequate peripheral blood flow.
D)high blood pressure and decreased tissue perfusion.
E)hypotension and inadequate peripheral blood flow.
A)low blood pressure and increased blood volume.
B)hypotension and increased tissue perfusion.
C)high blood pressure and inadequate peripheral blood flow.
D)high blood pressure and decreased tissue perfusion.
E)hypotension and inadequate peripheral blood flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
As exercise begins, ________ occur(s)as the rate of oxygen consumption in skeletal muscles increases.
A)extensive changes in the pattern of blood distribution
B)vasomotor activation
C)decreased cardiac output
D)decreased venous return
E)extensive vasodilation
A)extensive changes in the pattern of blood distribution
B)vasomotor activation
C)decreased cardiac output
D)decreased venous return
E)extensive vasodilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the short-term response to hemorrhage, ________ occurs.
A)decreased vasomotor activity
B)increased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
C)increased venous return through venoconstriction
D)immediate erythropoietin activation
E)a recall of fluids from the interstitial spaces
A)decreased vasomotor activity
B)increased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
C)increased venous return through venoconstriction
D)immediate erythropoietin activation
E)a recall of fluids from the interstitial spaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When one exercises at maximum levels, only the blood supply to the ________ is unaffected.
A)lungs
B)liver
C)brain
D)skin
E)skeletal muscles
A)lungs
B)liver
C)brain
D)skin
E)skeletal muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When blood pressure rises, increased output from the baroreceptors stimulates which center?
A)cardioacceleratory
B)vasomotor
C)respiratory
D)cardioinhibitory
E)pulmonary
A)cardioacceleratory
B)vasomotor
C)respiratory
D)cardioinhibitory
E)pulmonary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
During the long-term response to hemorrhage, which hormone(s)prominently promote(s)fluid retention and reabsorption at the kidneys?
A)ADH and aldosterone
B)angiotensinogen II
C)EPO
D)epinephrine and norepinephrine
E)renin
A)ADH and aldosterone
B)angiotensinogen II
C)EPO
D)epinephrine and norepinephrine
E)renin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following monitors blood pressure at the end of the systemic circuit?
A)aortic baroreceptors
B)carotid sinus baroreceptors
C)aortic body chemoreceptors
D)carotid body chemoreceptors
E)atrial baroreceptors
A)aortic baroreceptors
B)carotid sinus baroreceptors
C)aortic body chemoreceptors
D)carotid body chemoreceptors
E)atrial baroreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Regarding endocrine processes in cardiovascular regulation, long-term adjustments
A)involve sympathetic responses that adjust cardiac output and peripheral resistance to stabilize blood pressure and blood flow to tissues.
B)involve alterations in blood volume that affect cardiac output and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from active tissues.
C)cause immediate, localized homeostatic adjustments.
D)drastically alter blood pressure and blood flow to vital organs.
E)involve the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medullae, which stimulate cardiac output and peripheral vasoconstriction.
A)involve sympathetic responses that adjust cardiac output and peripheral resistance to stabilize blood pressure and blood flow to tissues.
B)involve alterations in blood volume that affect cardiac output and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from active tissues.
C)cause immediate, localized homeostatic adjustments.
D)drastically alter blood pressure and blood flow to vital organs.
E)involve the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medullae, which stimulate cardiac output and peripheral vasoconstriction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
________ involves the alteration of peripheral resistance by acting directly on precapillary sphincters.
A)ANP release
B)Autoregulation
C)Chemoreceptor reflex
D)Renin release
E)Baroreceptor reflex
A)ANP release
B)Autoregulation
C)Chemoreceptor reflex
D)Renin release
E)Baroreceptor reflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following monitors the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid?
A)sensory neurons on the surface of the medulla oblongata
B)sensory neurons found in the carotid bodies
C)sensory neurons found in the aortic bodies
D)sensory neurons in the walls of the right atrium
E)sensory neurons in the walls of the carotid sinus
A)sensory neurons on the surface of the medulla oblongata
B)sensory neurons found in the carotid bodies
C)sensory neurons found in the aortic bodies
D)sensory neurons in the walls of the right atrium
E)sensory neurons in the walls of the carotid sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the primary function of the vasomotor center of the medulla oblongata?
A)increases cardiac output through sympathetic innervation
B)reduces cardiac output through parasympathetic innervation
C)monitors the chemical composition of blood
D)monitors the degree of stretch in the walls of expandable organs
E)controls the diameters of arterioles through sympathetic innervation
A)increases cardiac output through sympathetic innervation
B)reduces cardiac output through parasympathetic innervation
C)monitors the chemical composition of blood
D)monitors the degree of stretch in the walls of expandable organs
E)controls the diameters of arterioles through sympathetic innervation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Baroreceptors that function in maintaining adequate blood flow to the brain are located in the
A)carotid sinus.
B)brain stem.
C)left ventricle.
D)common iliac artery.
E)aortic bodies.
A)carotid sinus.
B)brain stem.
C)left ventricle.
D)common iliac artery.
E)aortic bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Angiotensin II elevates systemic blood pressure by
A)triggering arteriole constriction.
B)promoting the release of ANP.
C)inhibiting aldosterone.
D)promoting the excretion of sodium.
E)inhibiting ADH.
A)triggering arteriole constriction.
B)promoting the release of ANP.
C)inhibiting aldosterone.
D)promoting the excretion of sodium.
E)inhibiting ADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following will cause a decrease in blood pressure?
A)increased levels of aldosterone
B)increased levels of angiotensin II
C)increased blood volume
D)increased levels of ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
E)increased levels of ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
A)increased levels of aldosterone
B)increased levels of angiotensin II
C)increased blood volume
D)increased levels of ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
E)increased levels of ADH (antidiuretic hormone)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
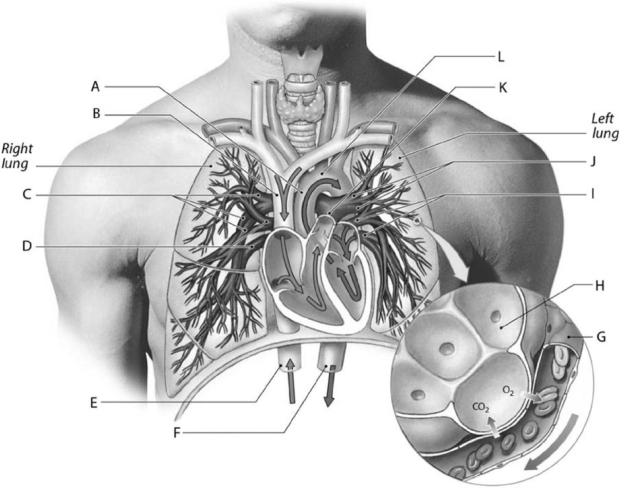 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label F represents the
A)common iliac vein.
B)inferior vena cava.
C)azygous vein.
D)descending aorta.
E)celiac trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
What does label H represent?
A)alveolus
B)alveolar capillary
C)alveolar vein
D)alveolar artery
E)alveolar venule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label C represents the
A)pulmonary trunk.
B)ascending aorta.
C)right pulmonary arteries.
D)right pulmonary veins.
E)superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In females, gonadal arteries are called
A)testicular arteries.
B)uterine arteries.
C)placental arteries.
D)ovarian arteries.
E)umbilical arteries.
A)testicular arteries.
B)uterine arteries.
C)placental arteries.
D)ovarian arteries.
E)umbilical arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label L represents the
A)brachiocephalic trunk.
B)aortic arch.
C)left pulmonary arteries.
D)left pulmonary veins.
E)pulmonary trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
After crossing the axilla, the axillary artery becomes the
A)radial artery.
B)ulnar artery.
C)brachial artery.
D)subclavian artery.
E)digital artery.
A)radial artery.
B)ulnar artery.
C)brachial artery.
D)subclavian artery.
E)digital artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label D represents the
A)pulmonary trunk.
B)ascending aorta.
C)right pulmonary arteries.
D)right pulmonary veins.
E)superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label E represents the
A)common iliac vein.
B)inferior vena cava.
C)azygous vein.
D)descending aorta.
E)celiac trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is(are)an anastomosis(es)?
A)palmar arch
B)digital arteries
C)aortic arch
D)intercostal arteries
E)dural sinus
A)palmar arch
B)digital arteries
C)aortic arch
D)intercostal arteries
E)dural sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The ________ divides the aorta into a superior thoracic aorta and an inferior abdominal aorta.
A)pericardium
B)mediastinum
C)diaphragm
D)peritoneum
E)pleura
A)pericardium
B)mediastinum
C)diaphragm
D)peritoneum
E)pleura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Near the level of vertebra L4, the abdominal aorta branches to form the
A)common carotid arteries.
B)common iliac arteries.
C)femoral arteries.
D)popliteal arteries.
E)tibial arteries.
A)common carotid arteries.
B)common iliac arteries.
C)femoral arteries.
D)popliteal arteries.
E)tibial arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label K represents the
A)brachiocephalic trunk.
B)aortic arch.
C)left pulmonary arteries.
D)left pulmonary veins.
E)pulmonary trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
What does label G represent?
A)alveolus
B)alveolar capillary
C)alveolar vein
D)alveolar artery
E)alveolar venule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label A represents the
A)pulmonary trunk.
B)ascending aorta.
C)right pulmonary arteries.
D)right pulmonary veins.
E)superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label I represents the
A)brachiocephalic trunk.
B)aortic arch.
C)left pulmonary arteries.
D)left pulmonary veins.
E)pulmonary trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label B represents the
A)pulmonary trunk.
B)ascending aorta.
C)right pulmonary arteries.
D)right pulmonary veins.
E)superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Blood from the superficial structures of the head and neck is collected by the
A)vertebral vein.
B)axillary vein.
C)brachiocephalic vein.
D)internal jugular vein.
E)external jugular vein.
A)vertebral vein.
B)axillary vein.
C)brachiocephalic vein.
D)internal jugular vein.
E)external jugular vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The celiac trunk provides blood to the
A)brain.
B)diaphragm.
C)liver and spleen.
D)large intestine.
E)suprarenal glands.
A)brain.
B)diaphragm.
C)liver and spleen.
D)large intestine.
E)suprarenal glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How can the impact of a temporary or even permanent occlusion (blockage)of a single blood vessel be reduced?
A)by increasing blood flow
B)through the presence of anastomoses
C)by increasing vessel length
D)by increasing blood viscosity
E)through decreasing body temperature
A)by increasing blood flow
B)through the presence of anastomoses
C)by increasing vessel length
D)by increasing blood viscosity
E)through decreasing body temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
 Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary Circuit
Figure 13-1 Cardiovascular Components of the Pulmonary CircuitUse Figure 13-1 to identify the labeled part.
Label J represents the
A)brachiocephalic trunk.
B)aortic arch.
C)left pulmonary arteries.
D)left pulmonary veins.
E)pulmonary trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



