Deck 10: Complex Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Complex Design
1
Which of the following represents a main effect without an interaction?
A)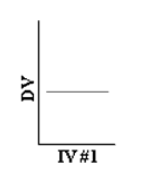
B)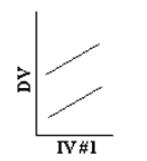
C)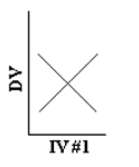
D)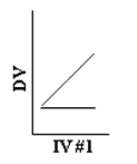
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
If an interaction were found in a factorial experiment,then:
A) one independent variable produced a bigger effect than another independent variable
B) the scores made at one level of one independent variable were bigger than the scores made at another level of the same variable
C) the scores made at one level of one independent variable were bigger than the scores made at a level of another independent variable
D) the effect of one independent variable was bigger at one level than another level of a second independent variable
A) one independent variable produced a bigger effect than another independent variable
B) the scores made at one level of one independent variable were bigger than the scores made at another level of the same variable
C) the scores made at one level of one independent variable were bigger than the scores made at a level of another independent variable
D) the effect of one independent variable was bigger at one level than another level of a second independent variable
the effect of one independent variable was bigger at one level than another level of a second independent variable
3
What is the minimum number of conditions required in a multi-factor factorial experiment (hint: multiply the minimum number of factors in a multi-factor experiment by the minimum number of levels for any given variable)?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) > 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) > 4
4
4
In a graph of results,an interaction is shown by:
A) some points being higher than others
B) one line that is higher than another
C) two lines that are not parallel to the x axis
D) two lines that are not parallel to each other
A) some points being higher than others
B) one line that is higher than another
C) two lines that are not parallel to the x axis
D) two lines that are not parallel to each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a 2 3 factorial experiment using a between-subjects design,each subject serves in ____ condition(s)out of ____ conditions in the experiment.
A) 1; 5
B) 1; 6
C) 2; 5
D) 3; 6
A) 1; 5
B) 1; 6
C) 2; 5
D) 3; 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Each of the following is a reason for doing multi-factor experiments instead of single factor ones except:
A) increased control over subject variables
B) enhanced similarity to the complexity of behavior
C) increased ecological validity and generalizability
D) increased internal validity
A) increased control over subject variables
B) enhanced similarity to the complexity of behavior
C) increased ecological validity and generalizability
D) increased internal validity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The word factorial in experimental designs refers to:
A) using more than one independent variable
B) using more than one dependent variable
C) testing all combinations of treatment levels
D) testing all combinations of the dependent variables
A) using more than one independent variable
B) using more than one dependent variable
C) testing all combinations of treatment levels
D) testing all combinations of the dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the table below,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the table below,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important A main effect
B) an important B main effect
C) important A and B main effects
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A
A) an important A main effect
B) an important B main effect
C) important A and B main effects
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One experiment tried to determine whether men prefer women who are blond or women who are brunette.The hair color of the men also was varied.The experimenter found that both blond and brunette men prefer blond women to brunettes,but the effect was much greater for dark-haired men than for blond men.These results show:
A) the main effect
B) two main effects
C) an interaction
D) neither a main effect nor interaction
E) both a main effect and an interaction
A) the main effect
B) two main effects
C) an interaction
D) neither a main effect nor interaction
E) both a main effect and an interaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When one independent variable has the same effect at all levels of a second,we say that the two variables:
A) interact
B) are additive
C) are multiplicative
D) do not have an impact on the dependent variable
A) interact
B) are additive
C) are multiplicative
D) do not have an impact on the dependent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the table below,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) both main effects and the interaction are important
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) both main effects and the interaction are important

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a main effect is found in a factorial experiment,then:
A) one independent variable produced a bigger effect than another independent variable
B) one independent variable influenced another independent variable
C) the scores made under one independent variable were different than the scores made under another independent variable
D) the scores made under one level of an independent variable were different from the scores made under another level of the same independent variable
A) one independent variable produced a bigger effect than another independent variable
B) one independent variable influenced another independent variable
C) the scores made under one independent variable were different than the scores made under another independent variable
D) the scores made under one level of an independent variable were different from the scores made under another level of the same independent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In an experiment dealing with recall of high and low imagery words following elaborative or rote rehearsal,the factors are:
A) high imagery and low imagery
B) rote rehearsal and elaborative rehearsal
C) word imagery and rehearsal type
D) the number of words recalled
A) high imagery and low imagery
B) rote rehearsal and elaborative rehearsal
C) word imagery and rehearsal type
D) the number of words recalled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the table below,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the table below,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for B
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement is true regarding interactions in a 2-factor experiment?
A) If you obtain main effects on both variables,there must be an interaction.
B) Interactions are independent of main effects.
C) Crossover interactions are the weakest form of interaction.
D) An interaction represents the effects of a single variable.
A) If you obtain main effects on both variables,there must be an interaction.
B) Interactions are independent of main effects.
C) Crossover interactions are the weakest form of interaction.
D) An interaction represents the effects of a single variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a factorial experiment,the number of factors is the number of ____ variables,and the number of levels is the number of instances of each ____ variable included in the experiment.
A) independent; dependent
B) independent; independent
C) dependent; independent
D) dependent; dependent
A) independent; dependent
B) independent; independent
C) dependent; independent
D) dependent; dependent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a 5 2 3 factorial experiment (between subjects),there are ____ independent groups.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 20
E) 30
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 20
E) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An experiment that employs two different factors,one with six levels and one with two levels,and uses all possible combinations,is called a ____ factorial design.
A) 2 2
B) 2 6
C) 2 2 2
D) 2 3
A) 2 2
B) 2 6
C) 2 2 2
D) 2 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The impact of one independent variable on the effect of another defines a main effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which statement is true regarding complex within-subjects designs?
A) Their use generally reduces the likelihood of extraneous variables being responsible for obtained effects.
B) They are not generally used in cognitive psychology research.
C) They eliminate the possibility of carryover effects.
D) They should always be replicated with between-subjects designs.
A) Their use generally reduces the likelihood of extraneous variables being responsible for obtained effects.
B) They are not generally used in cognitive psychology research.
C) They eliminate the possibility of carryover effects.
D) They should always be replicated with between-subjects designs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In matched-groups designs,participants are assigned to conditions in an unbiased fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Knowing about main effects tells us much about interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If you wanted to demonstrate differences between experienced and inexperienced drivers,which design would you surely not use to examine experience?
A) between-subjects
B) within-subjects
C) mixed design
D) random groups
E) matched groups
A) between-subjects
B) within-subjects
C) mixed design
D) random groups
E) matched groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a random-groups design,an attempt is made to equate groups in terms of some important characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Crossover interactions cannot be explained by problems in measuring and scaling the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the below table,the pattern of results indicates:
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A
A) an important main effect for A
B) an important main effect for B
C) important main effects for A and B
D) an important interaction
E) interaction and a main effect for A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A colleague conducting a 2 2 between-subjects factorial experiment decides to assign each incoming participant to the next available condition until an equal number of participants has been obtained in each condition.The order of assignment to conditions remains the same regardless of the number of incoming participants.This most closely resembles an example of a(n)____ design.
A) completely counterbalanced
B) random-groups
C) incompletely counterbalanced
D) matched-groups
A) completely counterbalanced
B) random-groups
C) incompletely counterbalanced
D) matched-groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Certain visual illusions get weaker and weaker as we continue to stare at them.If you wanted to see whether this "illusion decrement" followed the same course for both men and women,which design and which independent variables would you use?
A) treatment ( treatment; subjects; sex and illusion type)
B) matched groups; time and illusion form
C) mixed design; sex and viewing time
D) random groups; sex and illusion type
A) treatment ( treatment; subjects; sex and illusion type)
B) matched groups; time and illusion form
C) mixed design; sex and viewing time
D) random groups; sex and illusion type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Factorial designs reflect an equal number of levels for each independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In studies of the Advanced Traveler Information Systems (ATIS),different participants were provided traffic information with different degrees of reliability.Each participant was instructed to drive to familiar locations on some trials,and unfamiliar locations on other trials.This represents an example of a ____ design.
A) within-subjects
B) between-subjects
C) mixed
D) single factor
A) within-subjects
B) between-subjects
C) mixed
D) single factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
With a cross-over interaction,sometimes there may be no main effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In comparison to a random-groups factorial design,the use of a complex within-subjects design:
A) requires more measures per subject
B) requires a greater number of subjects
C) is more likely to confound individual differences and treatment conditions
D) is much less efficient
A) requires more measures per subject
B) requires a greater number of subjects
C) is more likely to confound individual differences and treatment conditions
D) is much less efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In graphical depictions of the results of a 2 2 factorial,parallel lines of data indicate the absence of an interaction between variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a mixed design,there is (are):
A) one or more independent variables and one or more dependent variables
B) at least one within-subjects independent variable and at least one between-subjects independent variable
C) two independent variables and an interaction between the two
D) both repeated measures and within-subjects comparisons
A) one or more independent variables and one or more dependent variables
B) at least one within-subjects independent variable and at least one between-subjects independent variable
C) two independent variables and an interaction between the two
D) both repeated measures and within-subjects comparisons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a 4 4 factorial design,there are eight treatment combinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Factorial designs have been used to study the sleeper effect,where positive memories for a message (that was originally presented along with a discounting cue)improve with time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a random-groups factorial experiment,the most important thing to control is:
A) the ordering of treatment combinations for a given subject
B) the additivity of the effects of the two independent variables
C) the additivity of the independent and dependent variables
D) the equivalence of the groups receiving the various treatment combinations
A) the ordering of treatment combinations for a given subject
B) the additivity of the effects of the two independent variables
C) the additivity of the independent and dependent variables
D) the equivalence of the groups receiving the various treatment combinations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The major danger in the use of complex within-subjects designs is:
A) carryover effects
B) nonequivalent groups
C) confounding subject variables with levels of the independent variable
D) an unrepresentative sample resulting from matching restrictions
A) carryover effects
B) nonequivalent groups
C) confounding subject variables with levels of the independent variable
D) an unrepresentative sample resulting from matching restrictions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Altman (2004)revealed an interaction between task-switching and cue-stimulus interval on task performance that depended on the use of a within-subjects design,rather than a between-subjects design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In studies of foreign language learning,subjects are given a key word to which they image a relation to the translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Learning the vocabulary of a foreign language tends to occur more rapidly when using the keyword method than when not using it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Complex within-subjects experiments are often preferred over corresponding between-subjects experiments because the former designs are more efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Mixed designs are often used to get repeated measures on different subject groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



