Deck 23: Metabolism and Energy Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Metabolism and Energy Production
1
Which is the first stage of catabolism?
A)Digestion
B)Citric acid cycle
C)Fatty acid oxidation
D)Glycolysis
E)Formation of acetyl CoA
A)Digestion
B)Citric acid cycle
C)Fatty acid oxidation
D)Glycolysis
E)Formation of acetyl CoA
Digestion
2
How many molecules of CO2 are produced for each turn of the citric acid cycle?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
2
3
How many reactions make up the citric acid cycle?
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)8
8
4
Which coupled reaction properly indicates the role of the coenzyme as an oxidizing agent?
A)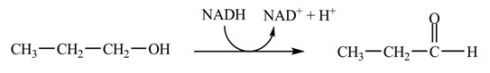
B)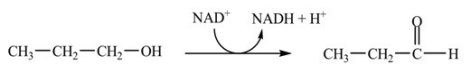
C)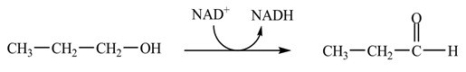
D)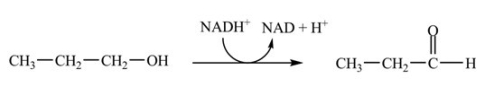
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Considering the energy changes associated with the two individual reactions below,what is the energy change associated with the energetically favorable coupled reaction? 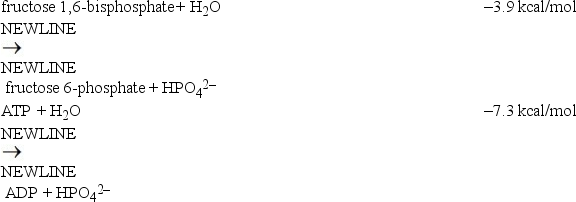
A)- 11.2 kcal/mol
B)- 3.4 kcal/mol
C)- 7.3 kcal/mol
D)+ 3.4 kcal/mol
E)+ 11.2 kcal/mol
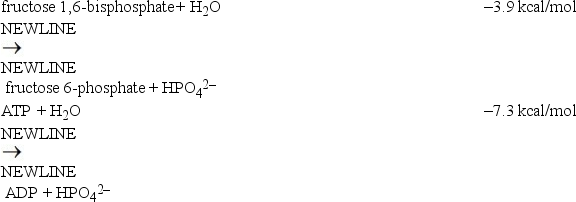
A)- 11.2 kcal/mol
B)- 3.4 kcal/mol
C)- 7.3 kcal/mol
D)+ 3.4 kcal/mol
E)+ 11.2 kcal/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The addition of a phosphate group to ADP,forming ATP,is an example of what type of reaction?
A)Hydration
B)Hydrolysis
C)Phosphorylation
D)Reduction
E)Decarboxylation
A)Hydration
B)Hydrolysis
C)Phosphorylation
D)Reduction
E)Decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How many molecules of GTP are produced for each turn of the citric acid cycle?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which molecule contains the largest amount of stored energy?
A)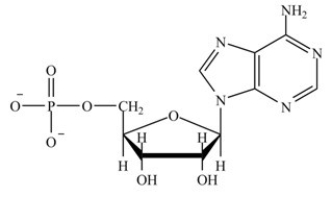
B)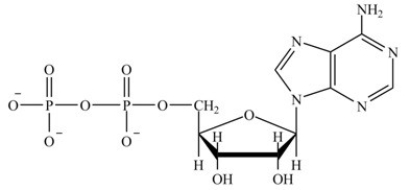
C)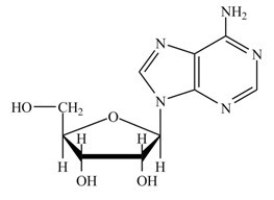
D)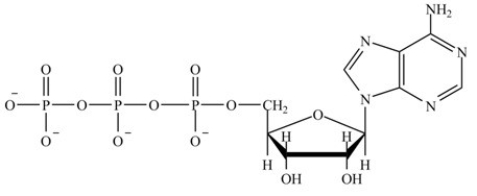
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Considering the energy changes associated with the individual reactions below,which reaction can be coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP to generate a coupled reaction that is energetically favorable? 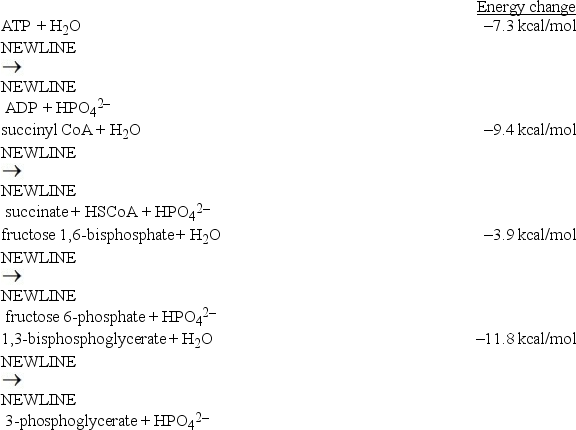
A)Fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O
B)Succinate + HSCoA + HPO42- succinyl CoA + H2O
succinyl CoA + H2O
C)3-phosphoglycerate + HPO42- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + H2O
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + H2O
D)All of the reactions can be coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP to generate a coupled reaction that is energetically favorable.
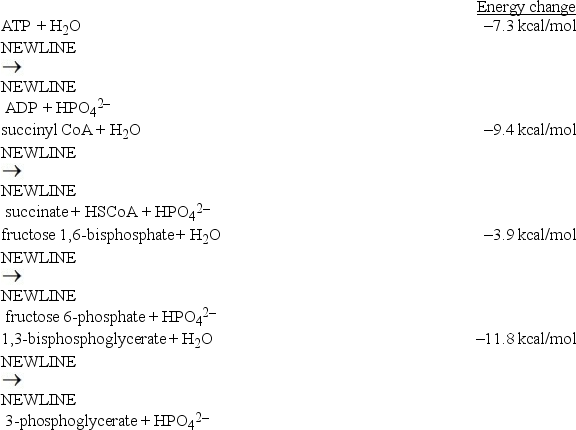
A)Fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42-
 fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2OB)Succinate + HSCoA + HPO42-
 succinyl CoA + H2O
succinyl CoA + H2OC)3-phosphoglycerate + HPO42-
 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + H2O
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + H2OD)All of the reactions can be coupled with the hydrolysis of ATP to generate a coupled reaction that is energetically favorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Where does energy production occur in animal cells?
A)Cell membrane
B)Cytoplasm
C)Mitochondria
D)Nucleus
A)Cell membrane
B)Cytoplasm
C)Mitochondria
D)Nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is the sum of all of the chemical reactions that take place in an organism?
A)Anabolism
B)Metabolism
C)Catabolism
D)Citric acid cycle
A)Anabolism
B)Metabolism
C)Catabolism
D)Citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Considering the energy changes associated with the two individual reactions below,what coupled reaction is an energetically favorable one? 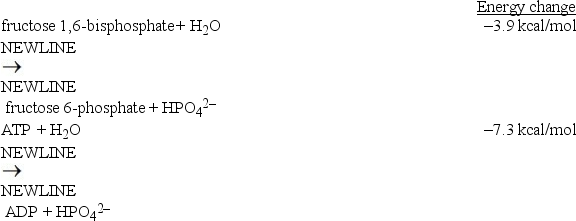
A)Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42-
fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42-
B)ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate ATP + fructose 6-phosphate
ATP + fructose 6-phosphate
C)ATP + H2O ADP + HPO42-
ADP + HPO42-
D)ADP + fructose 6-phosphate ATP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
ATP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
E)ATP + fructose 6-phosphate ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
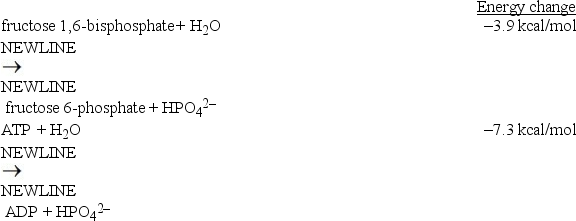
A)Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O
 fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42-
fructose 6-phosphate + HPO42-B)ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
 ATP + fructose 6-phosphate
ATP + fructose 6-phosphateC)ATP + H2O
 ADP + HPO42-
ADP + HPO42-D)ADP + fructose 6-phosphate
 ATP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
ATP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphateE)ATP + fructose 6-phosphate
 ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
ADP + fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which functional group is not contained in coenzyme A,whose structure is shown below? 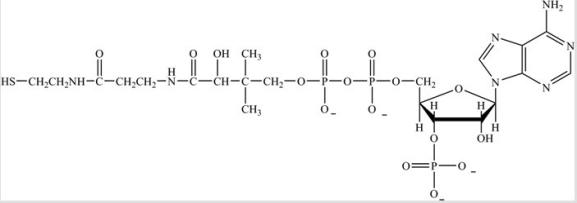
A)Alcohol
B)Sulfhydryl
C)Phosphoester
D)Amide
E)Aldehyde

A)Alcohol
B)Sulfhydryl
C)Phosphoester
D)Amide
E)Aldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which is not true about coenzymes?
A)Many reactions in metabolic pathways involve coenzymes.
B)When a coenzyme gains hydrogen atoms the coenzyme is an oxidizing agent.
C)Many coenzymes are involved in oxidation and reduction reactions.
D)The coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide,NAD+,is a common biological reducing agent.
A)Many reactions in metabolic pathways involve coenzymes.
B)When a coenzyme gains hydrogen atoms the coenzyme is an oxidizing agent.
C)Many coenzymes are involved in oxidation and reduction reactions.
D)The coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide,NAD+,is a common biological reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How many molecules of reduced coenzymes are produced for each turn of the citric acid cycle?
A)2
B)4
C)16
D)32
A)2
B)4
C)16
D)32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which is the abbreviated structure of acetyl CoA?
A)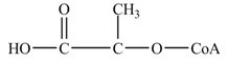
B)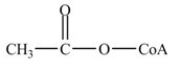
C)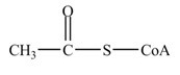
D)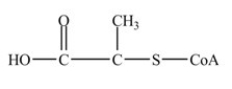
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the classification of the reaction shown? 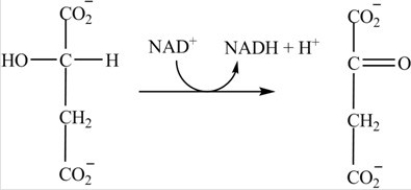
A)Redox
B)Isomerization
C)Decarboxylation
D)Hydrolysis

A)Redox
B)Isomerization
C)Decarboxylation
D)Hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many molecules of ATP are produced for each unit of GTP formed in the citric acid cycle?
A)4
B)3
C)2
D)D1
A)4
B)3
C)2
D)D1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the phosphorylation of GMP to form GDP requires 7.3 kcal/mol of energy,what is the energy change associated with the hydrolysis of GDP to form GMP?
A)7.3 kcal/mol
B)-7.3 kcal/mol
C)14.6 kcal/mol
D)Not enough information is given to determine the change in energy.
A)7.3 kcal/mol
B)-7.3 kcal/mol
C)14.6 kcal/mol
D)Not enough information is given to determine the change in energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Where does the hydrolysis of carbohydrates to monosaccharides begin?
A)In the stomach
B)In the saliva
C)In the liver
D)In the small intestines
A)In the stomach
B)In the saliva
C)In the liver
D)In the small intestines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In which region of a mitochondrion would the pH be lower?
A)The matrix
B)The intermembrane space
C)The inner mitochondrial membrane
D)All regions of a mitochondrion have the same pH
A)The matrix
B)The intermembrane space
C)The inner mitochondrial membrane
D)All regions of a mitochondrion have the same pH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Where does the electron transport chain process take place?
A)In the inner membrane of mitochondria
B)In the outer membrane of mitochondria
C)In the intermembrane space of mitochondria
D)In the matrix of mitochondria
A)In the inner membrane of mitochondria
B)In the outer membrane of mitochondria
C)In the intermembrane space of mitochondria
D)In the matrix of mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How much ATP is generated for each acetyl CoA during stages [3] and [4] of catabolism?
A)4 molecules of ATP
B)5 molecules of ATP
C)8 molecules of ATP
D)10 molecules of ATP
E)16 molecules of ATP
A)4 molecules of ATP
B)5 molecules of ATP
C)8 molecules of ATP
D)10 molecules of ATP
E)16 molecules of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which intermediate in the citric acid cycle contains two chirality centers?
A)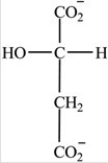
B)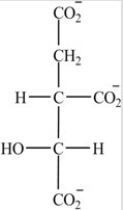
C)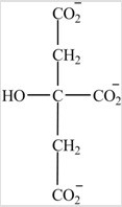
D)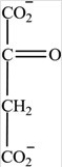
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which product(s)of the citric acid cycle are funneled into the electron transport chain?
A)ATP
B)NAD+ and FAD
C)NADH,FADH2,and H+
D)NADH,FADH2,H+,and ATP
A)ATP
B)NAD+ and FAD
C)NADH,FADH2,and H+
D)NADH,FADH2,H+,and ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which steps of the citric acid cycle generate CO2?
A)Steps 2 and 3
B)Steps 3 and 4
C)Steps 4 and 5
D)Steps 5 and 6
A)Steps 2 and 3
B)Steps 3 and 4
C)Steps 4 and 5
D)Steps 5 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How many reactions in the citric acid cycle generate NAD+?
A)0
B)1
C)3
D)8
A)0
B)1
C)3
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In which stage of catabolism is starch hydrolyzed to glucose with the aid of the enzyme amylase?
A)Stage [1]
B)Stage [2]
C)Stage [3]
D)Stage [4]
A)Stage [1]
B)Stage [2]
C)Stage [3]
D)Stage [4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which steps of the citric acid cycle generate reduced coenzymes necessary in the production of ATP?
A)Steps 2,3,4,and 7
B)Steps 1,4,7,and 8
C)Steps 3,4,5,and 7
D)Steps 3,4,6,and 8
A)Steps 2,3,4,and 7
B)Steps 1,4,7,and 8
C)Steps 3,4,5,and 7
D)Steps 3,4,6,and 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the classification of the reaction shown? 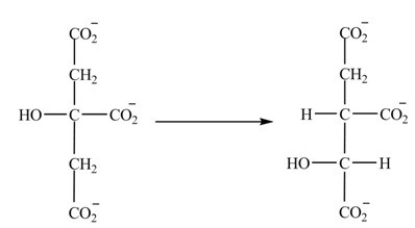
A)Oxidation
B)Reduction
C)Decarboxylation
D)Hydrolysis
E)Isomerization

A)Oxidation
B)Reduction
C)Decarboxylation
D)Hydrolysis
E)Isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is the primary energy-carrying molecule in metabolic pathways?
A)AMP
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)Acetyl CoA
E)FADH2
A)AMP
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)Acetyl CoA
E)FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which is the major product of stage [2] of catabolism?
A)NADH
B)Acetyl CoA
C)GTP
D)CO2
A)NADH
B)Acetyl CoA
C)GTP
D)CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which is an oxidizing agent?
A)Fe2+
B)NAD+
C)FADH2
D)ATP
A)Fe2+
B)NAD+
C)FADH2
D)ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many reactions in the citric acid cycle generate FADH2?
A)0
B)1
C)3
D)8
A)0
B)1
C)3
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which intermediate in the citric acid cycle is a secondary alcohol?
A)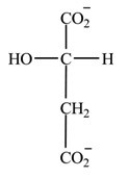
B)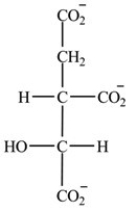
C)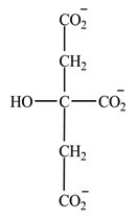
D)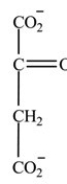
E)Two of the intermediates are secondary alcohols.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)Two of the intermediates are secondary alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In which stage of metabolism are biomolecules degraded into two-carbon acetyl units?
A)Stage [1]
B)Stage [2]
C)Stage [3]
D)Stage [4]
A)Stage [1]
B)Stage [2]
C)Stage [3]
D)Stage [4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which is not a reaction found in stage [2] of catabolism?
A)Fatty acid oxidation
B)Glycolysis
C)Oxidative phosphorylation
D)Amino acid catabolism
A)Fatty acid oxidation
B)Glycolysis
C)Oxidative phosphorylation
D)Amino acid catabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why is hydrogen cyanide,HCN,poisonous?
A)HCN is a strong acid,dramatically altering the pH in cells.
B)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to the Fe3+ ion of cytochrome oxidase.
C)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to acetyl CoA.
D)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to NAD+.
A)HCN is a strong acid,dramatically altering the pH in cells.
B)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to the Fe3+ ion of cytochrome oxidase.
C)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to acetyl CoA.
D)Cyanide ions (-CN)irreversibly bind to NAD+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement best describes what occurs with a substrate is oxidized using FAD to product FADH2?
A)FAD is a reducing agent,and FADH2 is its oxidized form.
B)FAD is a reducing agent,and FADH2 is its reduced form.
C)FAD is an oxidizing agent,and FADH2 is its oxidized form.
D)FAD is an oxidizing agent,and FADH2 is its reduced form.
A)FAD is a reducing agent,and FADH2 is its oxidized form.
B)FAD is a reducing agent,and FADH2 is its reduced form.
C)FAD is an oxidizing agent,and FADH2 is its oxidized form.
D)FAD is an oxidizing agent,and FADH2 is its reduced form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How many carbons enter into the citric acid cycle with each new Acetyl CoA?
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)6
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Since more energy is released from the hydrolysis of creatine phosphate than is needed for the phosphorylation of ADP,the coupling of these two reactions results in the formation of ATP from ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The citric acid cycle is activated with the amount of available ADP is low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The citric acid cycle is also called the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
NAD+ and FAD are oxidized in the electron transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which is the enzyme that hydrolyzes triacylglycerols?
A)Acetyl CoA
B)Protease pepsin
C)Amylase
D)Lipase
A)Acetyl CoA
B)Protease pepsin
C)Amylase
D)Lipase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Each NADH that enters the electron transport chain will result in the formation of ________ units of ATP.
A)10
B)2.5
C)1.5
D)32
E)7.3
A)10
B)2.5
C)1.5
D)32
E)7.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Oxaloacetate is the starting material in the first step of the citric acid cycle and the product of the last step. The last step of the citric acid cycle,the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate,is shown. What is the structure of oxaloacetate? 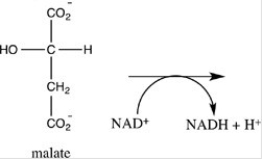
A)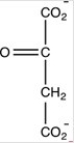
B)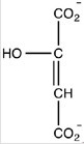
C)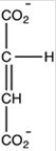
D)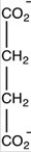

A)

B)

C)

D)
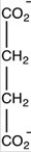

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Coenzyme A is synthesized in cells from pantothenic acid,vitamin B5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
All steps of the citric acid cycle are enzyme catalyzed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which best describes the function of the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD in catabolic pathways?
A)Competitive inhibitors of the enzymes present in each pathway
B)Noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzymes present in each pathway
C)Oxidizing agents that accept electrons and hydrogen ions from molecules undergoing oxidation
D)Transport molecules that carry acetyl units to or from the different stages of metabolism
A)Competitive inhibitors of the enzymes present in each pathway
B)Noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzymes present in each pathway
C)Oxidizing agents that accept electrons and hydrogen ions from molecules undergoing oxidation
D)Transport molecules that carry acetyl units to or from the different stages of metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle in metabolism?
A)To break down food molecules into smaller components so they can be absorbed by the blood
B)To synthesize ATP from the energy produced in the hydrolysis of citric acid
C)To provide the enzymes necessary to aid in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates,proteins,and lipids
D)To convert acetyl groups to CO2 molecules and provide reduced coenzymes for the electron transport chain
A)To break down food molecules into smaller components so they can be absorbed by the blood
B)To synthesize ATP from the energy produced in the hydrolysis of citric acid
C)To provide the enzymes necessary to aid in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates,proteins,and lipids
D)To convert acetyl groups to CO2 molecules and provide reduced coenzymes for the electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
At which stage of metabolism is the most energy in the form of ATP produced?
A)Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
B)Digestion
C)Citric acid cycle
D)Transcription
A)Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
B)Digestion
C)Citric acid cycle
D)Transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement concerning the digestion of food groups is incorrect?
A)Carbohydrates are ultimately broken down to glucose and other monosaccharides.
B)Triacylglycerols are ultimately broken down by lipases into glycerol and fatty acids.
C)Proteins are ultimately broken down by proteases into amino acids.
D)Polysaccharides are ultimately broken down to nucleotides.
A)Carbohydrates are ultimately broken down to glucose and other monosaccharides.
B)Triacylglycerols are ultimately broken down by lipases into glycerol and fatty acids.
C)Proteins are ultimately broken down by proteases into amino acids.
D)Polysaccharides are ultimately broken down to nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Coenzyme A is a biological oxidizing agent used to convert alcohols to carbonyl-containing compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which statement best describes how the interconversion of ATP and ADP is responsible for storing and providing energy for cellular reactions? 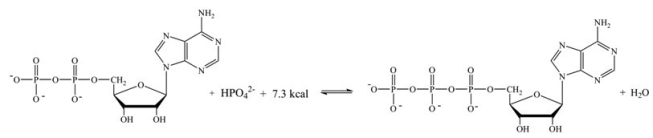
A)The energy stored in ADP is released when ATP is synthesized.
B)The energy required to phosphorylate ADP is stored in ATP,and released when ATP undergoes hydrolysis.
C)The energy released in the phosphorylation of ADP can be coupled with unfavorable reactions within the cell.
D)The energy required to hydrolyze ATP comes from the energy producing reactions in the cell; the energy lost is then stored in ATP.

A)The energy stored in ADP is released when ATP is synthesized.
B)The energy required to phosphorylate ADP is stored in ATP,and released when ATP undergoes hydrolysis.
C)The energy released in the phosphorylation of ADP can be coupled with unfavorable reactions within the cell.
D)The energy required to hydrolyze ATP comes from the energy producing reactions in the cell; the energy lost is then stored in ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The primary function of the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation is which of the following?
A)To provide electrons and energy for the phosphorylation of ATP
B)To synthesize the reduced coenzymes necessary for digestion
C)To oxidize the reduced coenzymes NADH and FADH2,and provide energy for the synthesis of ATP
D)To transport electrons from ATP to ADP,and synthesize acetyl CoA molecules
A)To provide electrons and energy for the phosphorylation of ATP
B)To synthesize the reduced coenzymes necessary for digestion
C)To oxidize the reduced coenzymes NADH and FADH2,and provide energy for the synthesis of ATP
D)To transport electrons from ATP to ADP,and synthesize acetyl CoA molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The second step of the citric acid cycle,the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate,is shown. What is the structure of isocitrate? 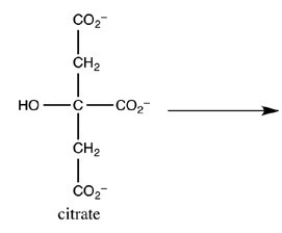
A)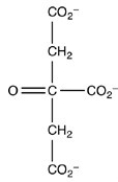
B)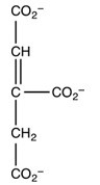
C)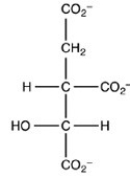
D)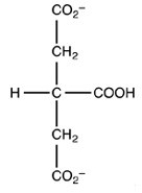

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Each FADH2 that enters the electron transport chain will result in the formation of ________ units of ATP.
A)7.3
B)10
C)1.5
D)2.5
E)32
A)7.3
B)10
C)1.5
D)2.5
E)32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Step 6 of the citric acid cycle is shown. Which statement best describes the role of FAD in this reaction? 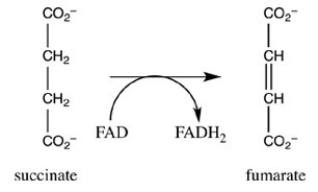
A)FAD causes the reduction of succinate to form fumarate.
B)FAD causes succinate to undergo hydration to form fumarate.
C)FAD causes the oxidation of succinate to form fumarate.
D)FAD causes the isomerication of succinate to form fumarate.

A)FAD causes the reduction of succinate to form fumarate.
B)FAD causes succinate to undergo hydration to form fumarate.
C)FAD causes the oxidation of succinate to form fumarate.
D)FAD causes the isomerication of succinate to form fumarate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Step 7 of the citric acid cycle is shown. Which statement best describes what occurs in this step? 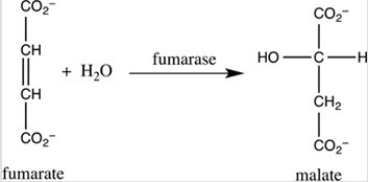
A)Fumarate undergoes hydrolysis with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.
B)Fumarate undergoes reduction with the aid of the cofactor fumarase.
C)Fumarate undergoes hydrogenation with hydrogens and electrons provided by the enzyme fumarase.
D)Fumarate undergoes hydration with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.

A)Fumarate undergoes hydrolysis with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.
B)Fumarate undergoes reduction with the aid of the cofactor fumarase.
C)Fumarate undergoes hydrogenation with hydrogens and electrons provided by the enzyme fumarase.
D)Fumarate undergoes hydration with the aid of the enzyme fumarase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The citric acid cycle comprises stage [4] of metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Acetyl CoA contains an acetyl group bonded to coenzyme A by a thioester bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Two electrons are donated by each NADH in the electron transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Part [2] of the citric acid cycle includes two separate decarboxylation reactions and a hydrolysis reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Energy released from H+ movement in the electron transport chain fuels the phosphorylation of ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The conversion of Fe3+ to Fe2+ in the electron transport chain is an example of Fe3+ acting as an oxidizing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Stage [3] of catabolism is sometimes called aerobic respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The final stage of the electron transport chain forms water in an anaerobic process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The reaction shown below requires the overall input of energy. 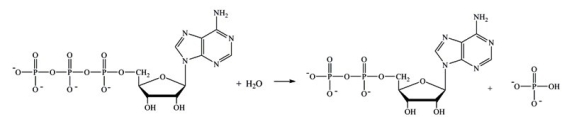


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The rate of the citric acid cycle depends on the body's need for energy. When energy demands are low and NADH concentration is high,the cycle is inhibited.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The electron transport chain is a multistep process that relies on five enzyme systems as well as mobile electron carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
GTP is a high energy compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The cleavage of a protein with chymotrypsin occurs in stage [1] of catabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The structure of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)is shown here. 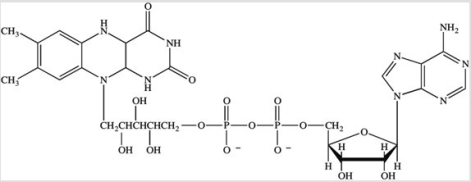


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
H+ ions generated by reactions in the electron transport chain,as well as H+ ions present in the matrix of the mitochondria,are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space at three different sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The terms phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation may be used interchangeably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Each NADH enters the electron transport chain at complex I in the inner mitochondrial membrane and the resulting cascade of reactions produces enough energy to synthesize 4 ATPs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
NAD+ is the abbreviation for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The cells in heart tissue have more mitochondria than the cells in bone tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the electron transport chain,H+ ions are pumped across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion,forming a high concentration of H+ ions in the intermembrane space,thus creating a potential energy gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



