Deck 5: Describing Data With Z-Scores and the Normal Curve
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Describing Data With Z-Scores and the Normal Curve
1
When two normal z-distributions are plotted on the same graph, what can we say about the relative frequency of each z-score?
A)It will always be the same.
B)It will always be different.
C)It depends on the raw score mean.
D)It depends on the raw score standard deviation.
A)It will always be the same.
B)It will always be different.
C)It depends on the raw score mean.
D)It depends on the raw score standard deviation.
A
2
Which of the following statements accurately describes the sampling distribution of means?
A)The distribution of several sample means when an infinite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
B)The distribution of all possible sample means when a given finite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
C)The distribution of all possible sample means when an infinite number of samples of variously sized Ns are selected from several raw score populations.
D)The distribution of all possible sample means when an infinite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
A)The distribution of several sample means when an infinite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
B)The distribution of all possible sample means when a given finite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
C)The distribution of all possible sample means when an infinite number of samples of variously sized Ns are selected from several raw score populations.
D)The distribution of all possible sample means when an infinite number of samples of the same size N are selected from one raw score population.
D
3
Given a normal distribution, as zscores' absolute values increase, those z-scores and the raw scores that correspond to them occur
A)more frequently.
B)less frequently.
C)more frequently at first and then less frequently.
D)less frequently at first and then more frequently.
A)more frequently.
B)less frequently.
C)more frequently at first and then less frequently.
D)less frequently at first and then more frequently.
B
4
For any approximately normal distribution, how can we find the relative frequency of the scores?
A)Convert the raw scores to z-scores and then use the standard normal curve.
B)Draw a graph of the raw scores and approximate the area under the curve.
C)Convert the raw scores to z-scores and then use the standard error of the mean.
D)Draw a graph of the raw scores and then use the standard error of the mean.
A)Convert the raw scores to z-scores and then use the standard normal curve.
B)Draw a graph of the raw scores and approximate the area under the curve.
C)Convert the raw scores to z-scores and then use the standard error of the mean.
D)Draw a graph of the raw scores and then use the standard error of the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sally's z-score on a given measure is -2.5, where the population mean is 5 and the standard deviation is 1.5.What is Sally's raw score?
A)1.25
B)14
C)3.5
D)8.75
A)1.25
B)14
C)3.5
D)8.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a z-distribution, the standard deviation will always be
A)greater than 1.
B)less than 1.
C)equal to 1.
D)equal to 0.
A)greater than 1.
B)less than 1.
C)equal to 1.
D)equal to 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A z-score of zero always means
A)the raw score does not exist.
B)the raw score exists, but is negligible.
C)the raw score almost never occurs.
D)the raw score is equal to the mean.
A)the raw score does not exist.
B)the raw score exists, but is negligible.
C)the raw score almost never occurs.
D)the raw score is equal to the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
We can use the standard normal curve as our model for
A)perfectly normal distributions only.
B)perfectly normal distributions only, when transformed to z-scores.
C)any approximately normal distribution, when transformed to z-scores.
D)any approximately normal distribution, when transformed to percentiles.
A)perfectly normal distributions only.
B)perfectly normal distributions only, when transformed to z-scores.
C)any approximately normal distribution, when transformed to z-scores.
D)any approximately normal distribution, when transformed to percentiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not one of the things the relative frequency of z-scores allows us to calculate for corresponding raw scores?
A)Relative frequency
B)Percentile
C)Comparison against other variables
D)Values in terms of goodness or badness
A)Relative frequency
B)Percentile
C)Comparison against other variables
D)Values in terms of goodness or badness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Your relative standing informs you
A)of how your scores compares with the sample or population from which it is derived.
B)of the significance of your score.
C)whether your score is from a sample or a population.
D)of surprisingly very little.
A)of how your scores compares with the sample or population from which it is derived.
B)of the significance of your score.
C)whether your score is from a sample or a population.
D)of surprisingly very little.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The mean of the sampling distribution of means is always
A)greater than the population mean.
B)less than the population mean.
C)equal to the population mean.
D)the population mean divided by the square root of N.
A)greater than the population mean.
B)less than the population mean.
C)equal to the population mean.
D)the population mean divided by the square root of N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
To evaluate a person for possible brain damage, a neuropsychologist gives the person a visual memory test and a reading test.To compare the person's performance across these two tests, what should the neuropsychologist do?
A)Graph the raw score distribution for each test on the same graph.
B)Calculate a z-score for each test.
C)Calculate z-scores for the sample means.
D)Find the simple frequency of the person's raw score for each test.
A)Graph the raw score distribution for each test on the same graph.
B)Calculate a z-score for each test.
C)Calculate z-scores for the sample means.
D)Find the simple frequency of the person's raw score for each test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A zscore communicates a raw score's
A)absolute magnitude.
B)distance from the mean in standard deviations.
C)direction from the standard deviation.
D)variability.
A)absolute magnitude.
B)distance from the mean in standard deviations.
C)direction from the standard deviation.
D)variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Pat's last statistics test score was 72.If the instructor tells Pat the grade distribution was approximately normal, the class mean was 67, and the standard deviation was 3, which of the following is correct?
A)A score of 72 is never good.
B)Pat should be worried about this score, because many other students did better.
C)Pat should be fairly happy about this score, because many students did not do as well.
D)Pat should be ecstatic, because this is obviously one of the highest grades in the class.
A)A score of 72 is never good.
B)Pat should be worried about this score, because many other students did better.
C)Pat should be fairly happy about this score, because many students did not do as well.
D)Pat should be ecstatic, because this is obviously one of the highest grades in the class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The distribution of z-scores is always
A)positively skewed.
B)negatively skewed.
C)the same shape as the distribution of raw scores.
D)more spread out than the distribution of raw scores.
A)positively skewed.
B)negatively skewed.
C)the same shape as the distribution of raw scores.
D)more spread out than the distribution of raw scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In sampling distributions, all the samples contain sets of raw scores
A)with the same variance.
B)from the same population.
C)with the same mean.
D)that are representative of the population mean.
A)with the same variance.
B)from the same population.
C)with the same mean.
D)that are representative of the population mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
You should first transform X to z in all of the following cases except if you seek
A)X that marks a given relative frequency beyond X in tail.
B)percentile of an X above the mean.
C)percentile of an X below the mean.
D)relative frequency of scores beyond X in tail.
A)X that marks a given relative frequency beyond X in tail.
B)percentile of an X above the mean.
C)percentile of an X below the mean.
D)relative frequency of scores beyond X in tail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
z-scores can be calculated from
A)any data.
B)interval or ratio scores.
C)nominal or ordinal scores.
D)the range.
A)any data.
B)interval or ratio scores.
C)nominal or ordinal scores.
D)the range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Sampling distributions of means are always
A)approximately normally distributed.
B)positively skewed.
C)negatively skewed.
D)more variable than the population from which the samples were drawn.
A)approximately normally distributed.
B)positively skewed.
C)negatively skewed.
D)more variable than the population from which the samples were drawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Chris wants to calculate a zscore for his own height.The average height in the class is 66 inches, and Chris's height is 62 inches.Chris calculated his zscore to be +1.5.What's wrong with his calculation?
A)The z-score is an inappropriate calculation here.
B)The z-score should be a higher number.
C)He didn't have the standard deviation.
D)The z-score should be a negative number.
A)The z-score is an inappropriate calculation here.
B)The z-score should be a higher number.
C)He didn't have the standard deviation.
D)The z-score should be a negative number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For the following set of scores, what is the z-score for a raw score of 23? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For a z-score of 0.63, what is the area beyond the z-score in the tail?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Jason's z-score for his time in the 10-K race was −3.If the raw score standard deviation was 5 and the mean running time for the competitors was 55 minutes, what was his raw score?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The sample mean for a recent introductory psychology test was 78, and the sample variance was 9.If a student's z- score = -2.0, what was this student's raw test score?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If raw scores ranging from 1 to 50 represented all the corresponding negative z-scores on the distribution, and raw scores ranging from 50 to 100 represented all the corresponding positive z-scores, what would be the total relative frequency of 50 to 100?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a distribution with 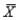 = 50 and
= 50 and 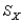 = 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 65.
= 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 65.
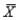 = 50 and
= 50 and 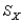 = 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 65.
= 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 65.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose the population mean of some measure is 6 and the population standard deviation is 12.For a sample of 36, what is the standard error of the mean?
A)2
B)1
C)1/6
D)1/2
A)2
B)1
C)1/6
D)1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a distribution with 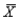 = 50 and
= 50 and 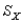 = 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 50.
= 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 50.
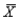 = 50 and
= 50 and 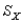 = 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 50.
= 5, find the z-score for a raw score of 50.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For a distribution with 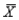 = 50 and
= 50 and 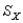 = 5, find the raw score for z-score of +2.6.
= 5, find the raw score for z-score of +2.6.
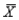 = 50 and
= 50 and 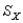 = 5, find the raw score for z-score of +2.6.
= 5, find the raw score for z-score of +2.6.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What raw score is at the 34th percentile 34.13 to be exact) when the mean of the distribution is 50 and the standard deviation is 4?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For a z-score of 2.53, what is the area between the mean and the z-score?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the area above a zscore of -0.48?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The central limit theorem is particularly helpful in terms of understanding the basic nature of
A)normal distributions.
B)statistical significance.
C)measurement error.
D)statistical association.
A)normal distributions.
B)statistical significance.
C)measurement error.
D)statistical association.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For a distribution with 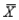 = 50 and
= 50 and 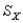 = 5, find the raw score for zscore of -1.2.
= 5, find the raw score for zscore of -1.2.
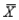 = 50 and
= 50 and 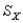 = 5, find the raw score for zscore of -1.2.
= 5, find the raw score for zscore of -1.2.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If there were 500 students in Jamal's class, approximately how many actual students scored higher than Jamal on
the quiz if Jamal had a z-score of −1?
the quiz if Jamal had a z-score of −1?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the area below a z-score of 1.40?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a z-score of 2.80, what is the area beyond the z-score in the tail?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Another term for the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of means is known as
A)the standard error of the mean.
B)the central limit theorem.
C)relative frequency.
D)the sampling distribution of means.
A)the standard error of the mean.
B)the central limit theorem.
C)relative frequency.
D)the sampling distribution of means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the appropriate values from the z-table, find the area for scores greater than z = +0.89.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The sample mean for a recent introductory psychology test was 78, and the sample variance was 9.If a student
received a score of 82, what was this student's z-score?
received a score of 82, what was this student's z-score?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A sampling distribution of means for samples of students taking the SAT exam has a population mean of 500 and a standard error of 200.What proportion of sample means would fall between the population mean and a sample mean of 800?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose you know that a population standard deviation for a given measure is 18.For a sample of 169 subjects who have taken this measure, would would the standard error of the mean be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Briefly note the three basic procedures used to describe a sample mean from any underlying raw score population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose you have a z-score value of 3.You also know the values of the mean of the sampling distribution and the standard error of the mean, both of which are 5.Would would be the sample mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the area above a z-score of 1.96?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If only the upper 30% of a normally distributed class passed a quiz for which the mean was 70 and the standard deviation was 10, what was the lowest score a student could have received and still have passed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose a standardized test given to ninth-graders in Texas has a mean score of 125.Suppose at a given school in Texas, the ninth-graders have a mean score of 105.Why is this discrepancy present, and is it problematic?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Barbara's z-score is -1.5.What does this score tell us relative to the mean of the population from which these scores originated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If your sense of direction, relative to a sample of college students, gave you a z-score of +1.5, what is your percentile?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the standard deviation of any z-distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider the z-scores in parentheses) for the following individuals: Frank 0.5), Zoe -1.2), Jimmy 2.9), and Lilly - 3.3).Which of these individuals would have a) the lowest score, b) highest score, c) and most common score in the distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What percentage of scores in a normal distribution fall outside of the range of +3 SDs from the mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For the following set of scores, what is the percentile for a score of 24? 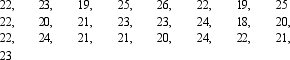
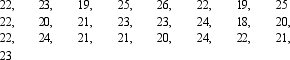

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



