Deck 16: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Carbohydrates
1
Which of the following can be classified as a ketohexose? 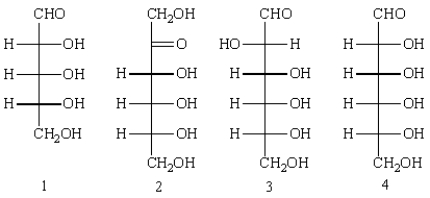 _
_
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 1, 3, and 4
 _
_A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 1, 3, and 4
2
2
Which of the following can be classified as an aldopentose? 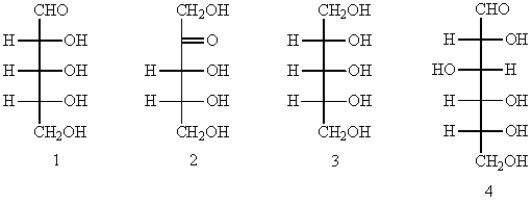
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 3 and 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 3 and 4
1
3
Which of the following can be considered a polysaccharide?
A) sucrose
B) cellobiose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) cellulose
A) sucrose
B) cellobiose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) cellulose
cellulose
4
Glucose can be classified as a:
A) monosaccharide
B) disaccharide
C) trisaccharide
D) polysaccharide
E) table sugar
A) monosaccharide
B) disaccharide
C) trisaccharide
D) polysaccharide
E) table sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The linkage between the sugar units in starch are:
A) ( )
B) ( )
C) ( )
D)( )
E) none of these
A) ( )
B) ( )
C) ( )
D)( )
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The acyclic structure of D-glucose is: 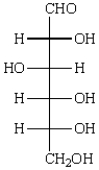 The formula for ethyl -D-glucopyranoside is:
The formula for ethyl -D-glucopyranoside is:
A)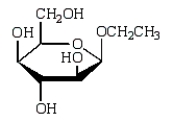
B)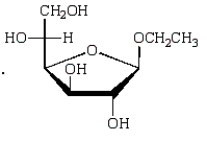
C)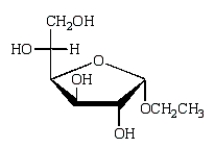
D)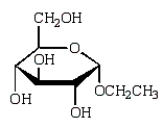
E)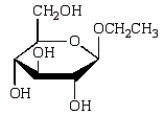
 The formula for ethyl -D-glucopyranoside is:
The formula for ethyl -D-glucopyranoside is:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Reduction of an optically active aldopentose with NaBH4 gives an optically inactive alditol.The aldopentose could be:
A)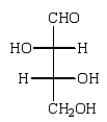
B)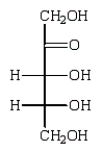
C)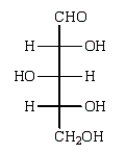
D)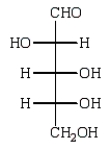
E)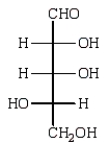
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Another name for the disaccharide, 4-O-( -D-galactopyranosyl)- -glucopyranose, is:
A) sucrose
B) cellobiose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) amylose
A) sucrose
B) cellobiose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 1,4- -linkage between two glucose units produces a disaccharide called:
A) dextrose
B) cellobiose
C) ribose
D) maltose
E) amylose
A) dextrose
B) cellobiose
C) ribose
D) maltose
E) amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 1,4- -linkage between two glucose units produces a disaccharide called:
A) dextrose
B) cellobiose
C) ribose
D) maltose
E) amylose
A) dextrose
B) cellobiose
C) ribose
D) maltose
E) amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following structures represent glycosides? 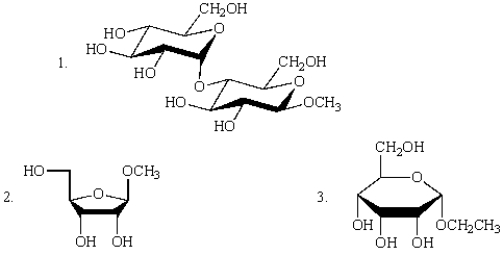
A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 1, 2, and 3

A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Hydrolysis of the disaccharide maltose produces: 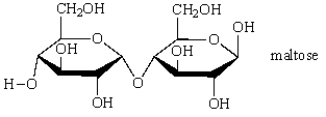
A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) mannose
D) glucose and fructose
E) glucose and galactose

A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) mannose
D) glucose and fructose
E) glucose and galactose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The difference between the pyranose and furanose forms of a given aldohexose is:
A) the ring size
B) the number of the anomeric C
C) the type of functional groups
D) the number of functional groups
E) there is no difference
A) the ring size
B) the number of the anomeric C
C) the type of functional groups
D) the number of functional groups
E) there is no difference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The formula for maltose is: 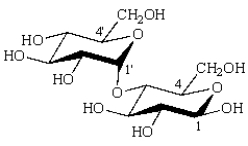 The acetal carbon(s) is(are):
The acetal carbon(s) is(are):
A) C1
B) C1 and C1'
C) C1 and C4
D) C1'
E) C1' and C4'
 The acetal carbon(s) is(are):
The acetal carbon(s) is(are):A) C1
B) C1 and C1'
C) C1 and C4
D) C1'
E) C1' and C4'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How many hydroxyl groups are present in the pyranose form of glucose?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following can be classified as epimers? 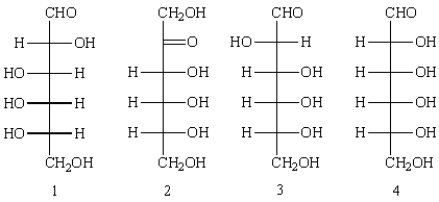
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 3 and 4
E) none are epimers

A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 3 and 4
E) none are epimers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The anomeric carbon of 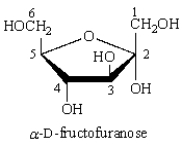 is:
is:
A) C1
B) C2
C) C3
D) C5
E) C6
 is:
is:A) C1
B) C2
C) C3
D) C5
E) C6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Haworth projection formula for the pyranose form of -D-galactose is: 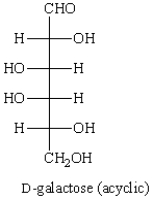
A)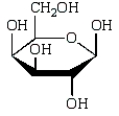
B)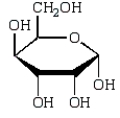
C)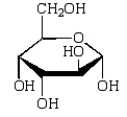
D)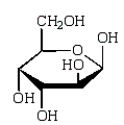
E)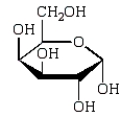

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
D-Glucose can exist in how many isomeric cyclic hemiacetal forms?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following can be considered reducing sugars? 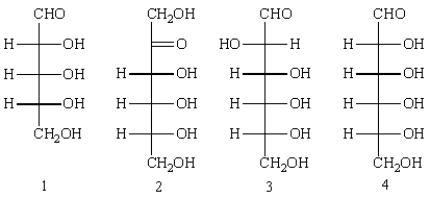
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 1, 2, 3, and 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 1, 2, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The product of the reaction below is: 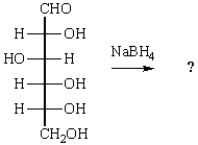
A)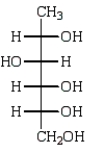
B)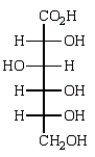
C)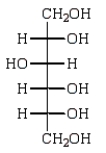
D)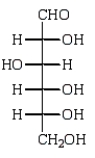
E)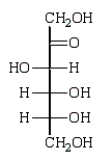

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many stereogenic centers are in the -cyclic form of glucose?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of 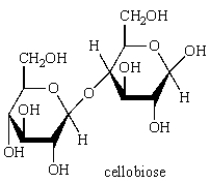 gives:
gives:
A)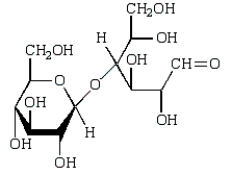
B)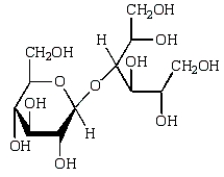
C)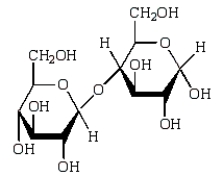
D)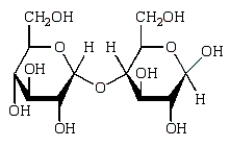
E)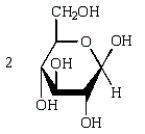
 gives:
gives:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The anomeric carbon in the structure below is numbered: 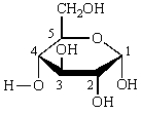
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The term that best describes the relationship between 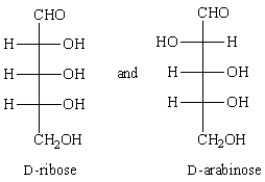 is
is
A) conformers.
B) epimers.
C) enantiomers.
D) meso forms.
E) constitutional isomers.
 is
isA) conformers.
B) epimers.
C) enantiomers.
D) meso forms.
E) constitutional isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The product of 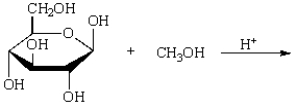 is:
is:
A)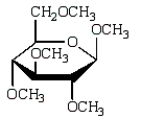
B)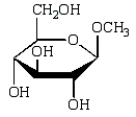
C)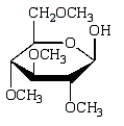
D)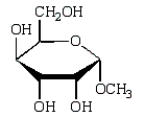
E)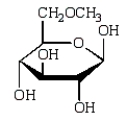
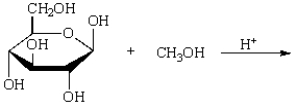 is:
is:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Reduction of which of the following aldoses provides an optically active alditol? 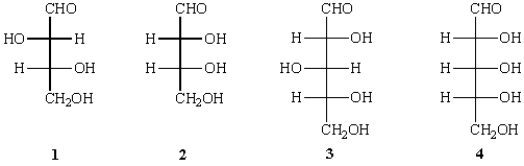
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 3 and 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 2
E) 3 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The following monosaccharide has ________ equatorial hydroxyl groups. 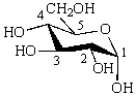 _
_
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
 _
_A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
D-Glucose reacts with acetic anhydride to produce:
A) ethers
B) esters
C) carboxylic acids
D) alcohols
E) aldehydes
A) ethers
B) esters
C) carboxylic acids
D) alcohols
E) aldehydes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Starch is a polysaccharide that is found in many food sources.When starch is completely hydrolyzed, the monosaccharide that is produced is:
A) glucose
B) mannose
C) maltose
D) galactose
E) amylose
A) glucose
B) mannose
C) maltose
D) galactose
E) amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The equilibrium rotation of an aqueous solution of - and -D-glucose is +50°, and the rotations of the pure and forms are +102° and +24°, respectively. Assuming no other forms are present, the percent form at equilibrium is:
A) 66.7%
B) 50.0%
C) 22.5%
D) 33.3%
E) 24.0%
A) 66.7%
B) 50.0%
C) 22.5%
D) 33.3%
E) 24.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Treatment of D-(+)-mannose with Fehling's reagent (Cu+2) gives: 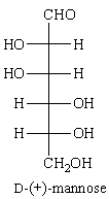
A) an aldose
B) a ketose
C) an alditol
D) an aldonic acid
E) an aldaric acid

A) an aldose
B) a ketose
C) an alditol
D) an aldonic acid
E) an aldaric acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Oxidation of optically active D-erythrose with nitric acid produces optically inactive meso-tartaric acid (below).What is the structure of D-erythrose? 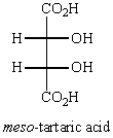
A)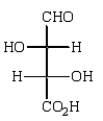
B)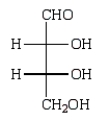
C)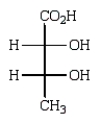
D)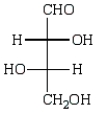
E)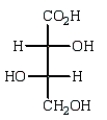

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The configurations at C2, C3, and C4 of 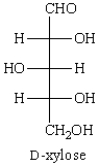 are:
are:
A) 2R, 3R, 4R
B) 2R, 3S, 4R
C) 2S, 3R, 4S
D) 2S, 3R, 4R
E) 2R, 3S, 4S
 are:
are:A) 2R, 3R, 4R
B) 2R, 3S, 4R
C) 2S, 3R, 4S
D) 2S, 3R, 4R
E) 2R, 3S, 4S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The pyranose form of glucose is a(n):
A) linear aldehyde
B) cyclic hemiacetal
C) cyclic acetal
D) acyclic acetal
E) acyclic hemiacetal
A) linear aldehyde
B) cyclic hemiacetal
C) cyclic acetal
D) acyclic acetal
E) acyclic hemiacetal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Hydrolysis of lactose gives:
A) glucose and galactose
B) glucose and fructose
C) mannose and fructose
D) galactose and fructose
E) allose and mannose
A) glucose and galactose
B) glucose and fructose
C) mannose and fructose
D) galactose and fructose
E) allose and mannose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A glycoside is formed upon reaction of glucopyranose with:
A) KMnO4
B) HNO3
C) Cu+2/OH-
D) CH3OH/H+
E) NaBH4
A) KMnO4
B) HNO3
C) Cu+2/OH-
D) CH3OH/H+
E) NaBH4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following reagents will convert the hydroxyl groups of a monosaccharide to methyl ethers?
A) H2/Ni
B) Ag2O/CH3I
C) HNO3
D) NaBH4/H2O
E) Br2/H2O
A) H2/Ni
B) Ag2O/CH3I
C) HNO3
D) NaBH4/H2O
E) Br2/H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The difference between and -glucopyranose is:
A) the stereochemistry at the anomeric carbon
B) the number of carbons in the ring
C) the position of all the OH's on the ring
D) all of these reasons
E) none of these reasons
A) the stereochemistry at the anomeric carbon
B) the number of carbons in the ring
C) the position of all the OH's on the ring
D) all of these reasons
E) none of these reasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A Newman projection formula for 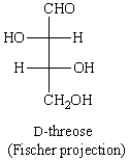 is:
is:
A)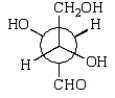
B)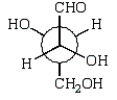
C)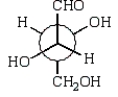
D)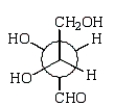
E)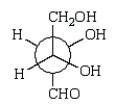
 is:
is:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The product of the following reaction sequence is: 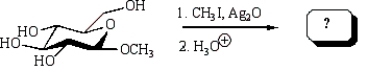
A)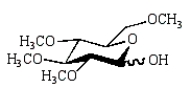
B)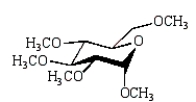
C)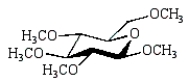
D)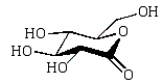
E)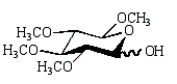
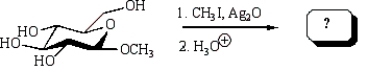
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following compounds will give a positive Tollens' test (silver mirror)?
A)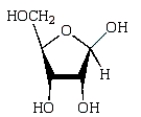
B)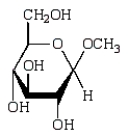
C)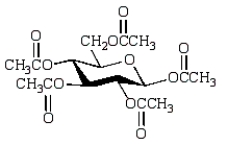
D)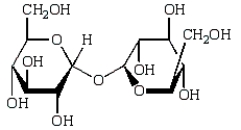
E)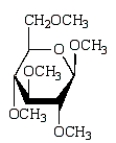
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following reagents will oxidize an aldose to an aldaric acid?
A) HNO3
B) Br2, H2O
C) NaBH4
D) PCC
E) Tollens' reagent
A) HNO3
B) Br2, H2O
C) NaBH4
D) PCC
E) Tollens' reagent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The structure of an L-aldotetrose that would give an optically inactive alditol upon reduction with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is:
A)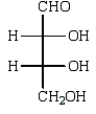
B)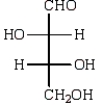
C)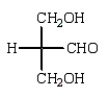
D)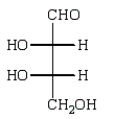
E)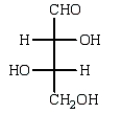
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Treatment of methyl -D-glucopyranose with silver oxide and iodomethane (Ag2O, CH3I) followed by hydrolysis (H3O+) 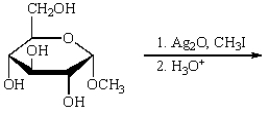 gives:
gives:
A)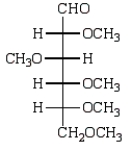
B)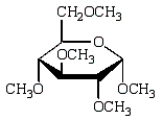
C)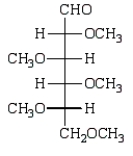
D)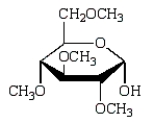
E)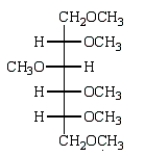
 gives:
gives:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An intermediate in the following glycoside hydrolysis is: 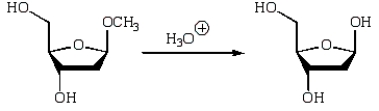
A)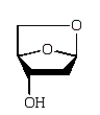
B)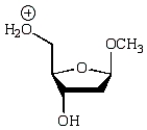
C)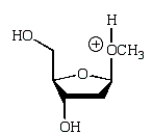
D)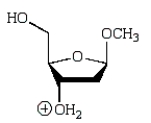
E)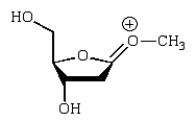

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



