Deck 14: Synthetic Polymers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Synthetic Polymers
1
An example of a polyurethane is
A)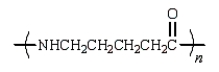
B)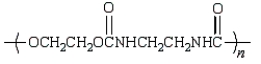
C)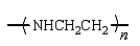
D)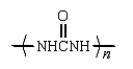
E)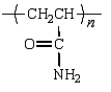
A)
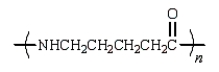
B)
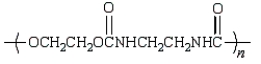
C)
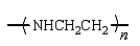
D)
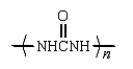
E)

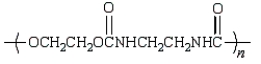
2
The repeating unit of polypropylene is:
A)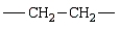
B)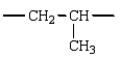
C)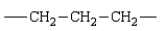
D)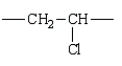
E)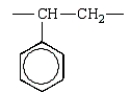
A)
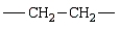
B)
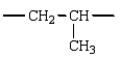
C)
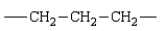
D)
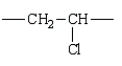
E)

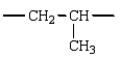
3
Dacron is an example of a
A) polyamide.
B) polyacrylate.
C) polyol.
D) polyester.
E) polyurethane.
A) polyamide.
B) polyacrylate.
C) polyol.
D) polyester.
E) polyurethane.
polyester.
4
Which of the following structures would represent the repeating unit of an alternating styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer? 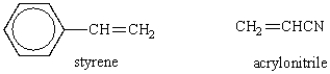
A)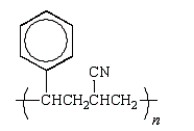
B)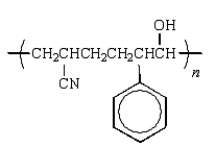
C)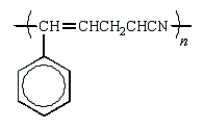
D)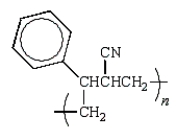
E) None of these represent the copolymer unit.
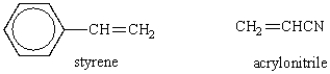
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of these represent the copolymer unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The repeating monomer unit in styrofoam cups is:
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The polymer that is not formed by the step-growth mechanism is:
A) polyethylene
B) nylon
C) kevlar
D) dacron
E) polyurethane
A) polyethylene
B) nylon
C) kevlar
D) dacron
E) polyurethane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following arrangements indicate a crosslinked homopolymer?
A)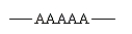
B)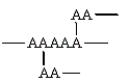
C)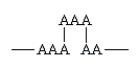
D)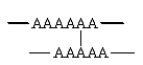
E) both B and C
A)
B)

C)

D)
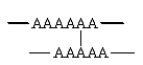
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Step-growth polymers differ from chain-growth polymers in that they
A) are more water soluble.
B) are generally prepared from difunctional monomers.
C) have more highly branched structures.
D) are thermosetting whereas chain-growth polymers are thermoplastic.
E) are formed by 1,4- instead of 1,2-addition.
A) are more water soluble.
B) are generally prepared from difunctional monomers.
C) have more highly branched structures.
D) are thermosetting whereas chain-growth polymers are thermoplastic.
E) are formed by 1,4- instead of 1,2-addition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The arrangement -AAAAABBBBB- of monomers A and B in a copolymer represents
A) an alternating copolymer.
B) a random copolymer.
C) a block copolymer.
D) a graft copolymer.
E) a syndiotactic copolymer.
A) an alternating copolymer.
B) a random copolymer.
C) a block copolymer.
D) a graft copolymer.
E) a syndiotactic copolymer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What determines the density of a polyurethane foam?
A) the amount of ammonia gas released
B) the amount of carbon dioxide released
C) the amount of oxygen absorbed
D) the solubility of the reactants
E) the amount of nitrogen absorbed
A) the amount of ammonia gas released
B) the amount of carbon dioxide released
C) the amount of oxygen absorbed
D) the solubility of the reactants
E) the amount of nitrogen absorbed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An example of a polyamide repeating unit is:
A)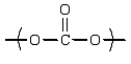
B)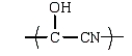
C)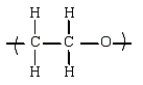
D)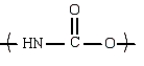
E)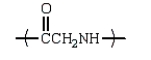
A)

B)

C)

D)
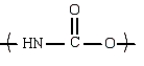
E)
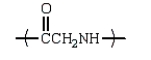

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Nylon 6 is a polymer of caprolactam.What is the structure of caprolactam?
A)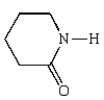
B)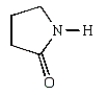
C)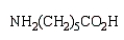
D)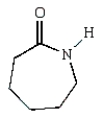
E)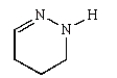
A)

B)

C)
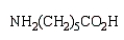
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A polymer has the repeating unit drawn below: 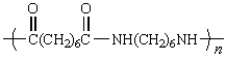 From what two monomers is this polymer made?
From what two monomers is this polymer made?
A)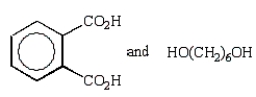
B)
C)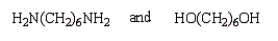
D)
E)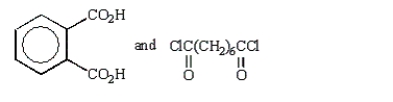
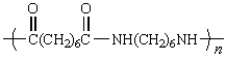 From what two monomers is this polymer made?
From what two monomers is this polymer made?A)
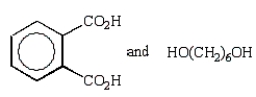
B)

C)
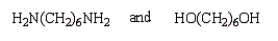
D)

E)
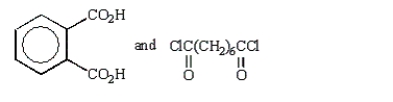

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The isoprene unit is common in many synthetic and natural polymers.Isoprene is:
A)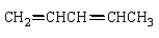
B)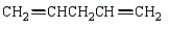
C)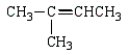
D)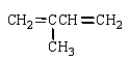
E)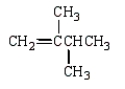
A)
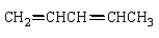
B)
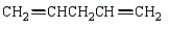
C)

D)
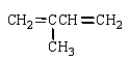
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The monomer unit of the synthetic polymer teflon is:
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An example of a synthetic polymer is:
A) RNA
B) nylon
C) starch
D) silk
E) cellulose
A) RNA
B) nylon
C) starch
D) silk
E) cellulose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The use of Superglue involves a polymerization of methyl 2-cyanopropenoate and water.What is the structure of methyl 2-cyanopropenoate?
A)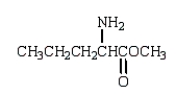
B)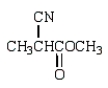
C)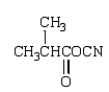
D)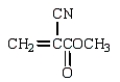
E)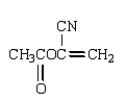
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Toluene-2,4-diisocyanate (2,4-TDI) is a very important chemical in the synthesis of polyurethanes used in foam pillows and freezer insulation.What is the structure of 2,4-TDI?
A)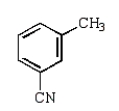
B)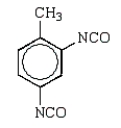
C)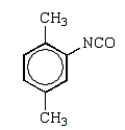
D)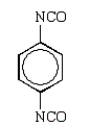
E)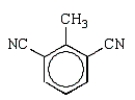
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The monomer unit of PVC pipe is:
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene
A) ethylene
B) vinyl chloride
C) styrene
D) tetrafluoroethylene
E) propene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following arrangements would indicate a graft copolymer?
A)
B)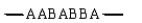
C)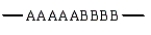
D)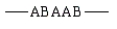
E)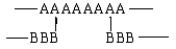
A)

B)
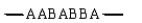
C)
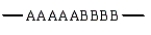
D)
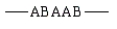
E)
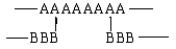

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What two families of compounds react in a step growth polymerization to give a polyester?
A) alcohol/carboxylic acid
B) carboxylic acid/amine
C) alcohol/amine
D) alcohol/ether
E) carboxylic acid/ether
A) alcohol/carboxylic acid
B) carboxylic acid/amine
C) alcohol/amine
D) alcohol/ether
E) carboxylic acid/ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Free radical polymerization is dependent on radical stabilities.Which of the following is the most stable free radical?
A)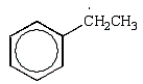
B)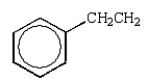
C)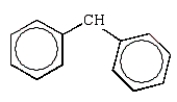
D)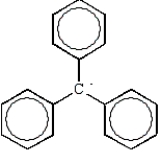
E)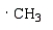
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
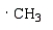

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Termination events in free radical addition polymerization involve:
A) radical decay
B) radical disproportionation
C) radical propagation
D) radical coupling
E) both b and d
A) radical decay
B) radical disproportionation
C) radical propagation
D) radical coupling
E) both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which monomer can be used to prepare the following polymer? 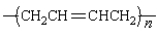
A)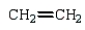
B)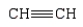
C)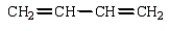
D)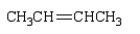
E)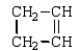
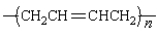
A)
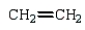
B)
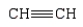
C)
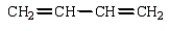
D)
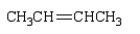
E)
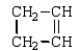

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A step growth polymer has the following repeating unit: 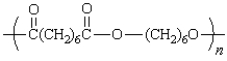 From what two monomer units is this made?
From what two monomer units is this made?
A)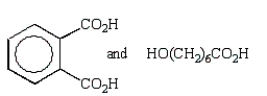
B)
C)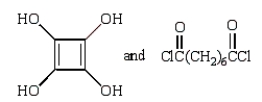
D)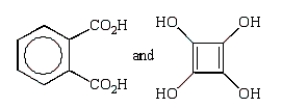
E)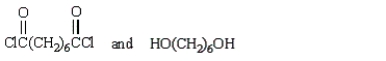
 From what two monomer units is this made?
From what two monomer units is this made?A)
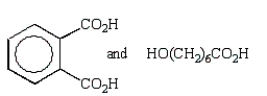
B)

C)

D)

E)
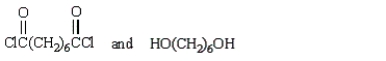

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A reactive intermediate in the base-mediated polymerization of methyl acrylate (CH2=CHCO2CH3) is:
A)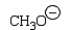
B)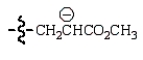
C)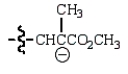
D)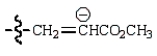
E)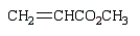
A)
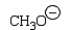
B)
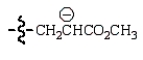
C)

D)
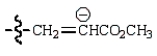
E)
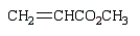

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A good initiator for a free radical addition polymerization is:
A) bromine
B) oxygen
C) benzene
D) benzoyl peroxide
E) acetyl chloride
A) bromine
B) oxygen
C) benzene
D) benzoyl peroxide
E) acetyl chloride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH2=CHCH3) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C6H5C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C6H5] is:
A)![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_89d6_a3bf_130db9aa1b9d_TB7360_00.jpg)
B)![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e7_a3bf_5198802aed91_TB7360_00.jpg)
C)![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e8_a3bf_2321f5867b6c_TB7360_00.jpg)
D)![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e9_a3bf_9b9516129b6a_TB7360_00.jpg)
E)![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_d7fa_a3bf_1342cc17f829_TB7360_00.jpg)
A)
![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_89d6_a3bf_130db9aa1b9d_TB7360_00.jpg)
B)
![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e7_a3bf_5198802aed91_TB7360_00.jpg)
C)
![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e8_a3bf_2321f5867b6c_TB7360_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_b0e9_a3bf_9b9516129b6a_TB7360_00.jpg)
E)
![<strong>An intermediate in the free radical polymerization of propylene (CH<sub>2</sub>=CHCH<sub>3</sub>) initiated by benzoyl peroxide [C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>C(=O)-O-O-C(=O)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>] is:</strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7360/11eadbaf_29ad_d7fa_a3bf_1342cc17f829_TB7360_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A compound that can be used to crosslink poly(vinyl alcohol) by ester linkages is:
A)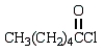
B)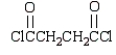
C)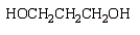
D)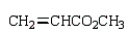
E)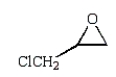
A)
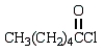
B)
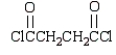
C)
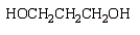
D)
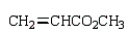
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An example of a polyether that can be prepared from the epoxide ethylene oxide is:
A)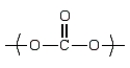
B)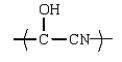
C)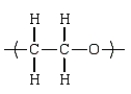
D)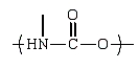
E)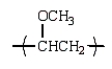
A)

B)

C)

D)
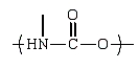
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A urethane is produced by reacting an alcohol with:
A) an isocyanate
B) an anhydride
C) styrene
D) a nitrile
E) an amide
A) an isocyanate
B) an anhydride
C) styrene
D) a nitrile
E) an amide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The following polymer would be best prepared from: 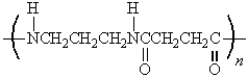
A)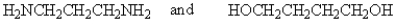
B)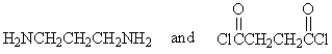
C)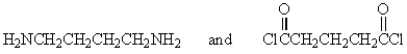
D)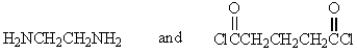
E)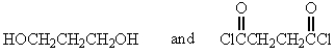
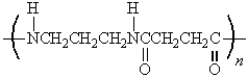
A)
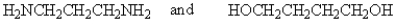
B)
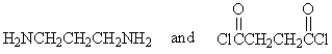
C)
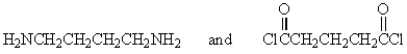
D)
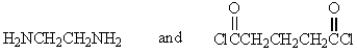
E)
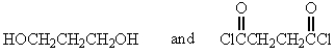

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Ziegler-Natta catalysts, used to prepare linear polymer molecules, consist of:
A) Lewis acids and bases
B) alkali metal salts and organolithiums
C) organomagnesium and alcohols
D) organoaluminums and transition metal salts
E) benzoyl peroxides and linear radicals
A) Lewis acids and bases
B) alkali metal salts and organolithiums
C) organomagnesium and alcohols
D) organoaluminums and transition metal salts
E) benzoyl peroxides and linear radicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The polymer poly(vinyl alcohol) is best prepared from which of the following monomers: 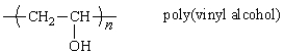
A)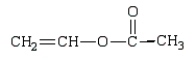
B)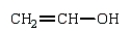
C)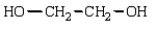
D)
E)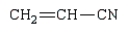
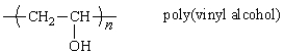
A)
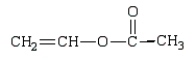
B)
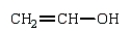
C)
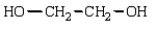
D)

E)
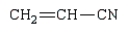

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What two families of compounds react to give a polyurethane?
A) alcohol/isocyanate
B) acid/ester
C) amine/amide
D) amine/ester
E) isocyanate/amine
A) alcohol/isocyanate
B) acid/ester
C) amine/amide
D) amine/ester
E) isocyanate/amine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The step responsible for chain-branching in free-radical polymerizations is the
A) initiation step.
B) radical coupling.
C) radical disproportionation.
D) chain transfer.
E) radical addition.
A) initiation step.
B) radical coupling.
C) radical disproportionation.
D) chain transfer.
E) radical addition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The preparation of which step-growth polymer does not involve elimination of a small molecule during the course of its formation?
A) urea-formaldehyde
B) polyamides
C) bakelite
D) polyurethanes
E) polyesters
A) urea-formaldehyde
B) polyamides
C) bakelite
D) polyurethanes
E) polyesters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Kodel can be prepared most directly from: 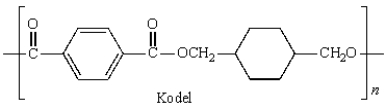
A)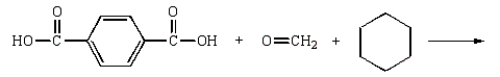
B)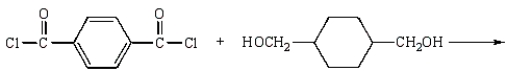
C)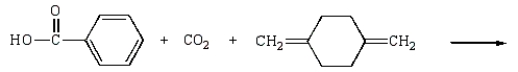
D)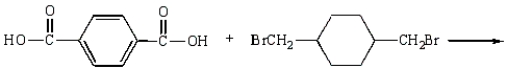
E)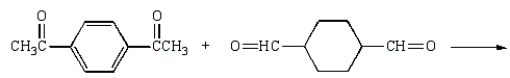

A)
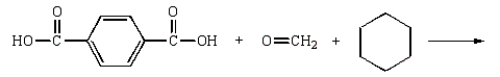
B)
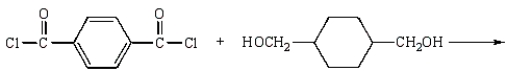
C)
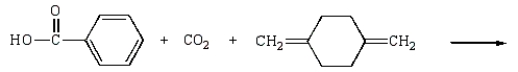
D)
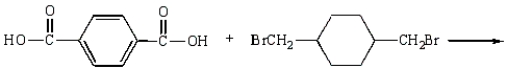
E)
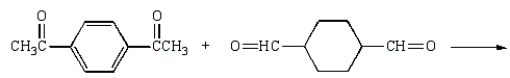

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Kel-F is the trade name for a copolymer used for rocket motors.Which monomer units will produce this copolymer? 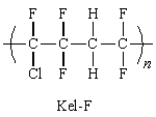
A) CH2=CF2 and Cl2C=CF2
B) CH2=CH2 and CF2=CCl2
C) ClFC=CF2 and CH2=CF2
D) CF2=CF2 and CH2=CHF
E) CHCl=CH2 and CH2=CF2

A) CH2=CF2 and Cl2C=CF2
B) CH2=CH2 and CF2=CCl2
C) ClFC=CF2 and CH2=CF2
D) CF2=CF2 and CH2=CHF
E) CHCl=CH2 and CH2=CF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The configurations of stereogenic centers in an atactic polymer are:
A) regular
B) random
C) alternate
D) the same
E) opposite
A) regular
B) random
C) alternate
D) the same
E) opposite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What type of polymer continues to crosslink on heating to produce a hard, infusible material?
A) thermosetting
B) vulcanized
C) thermoplastic
D) linear
E) copolymer
A) thermosetting
B) vulcanized
C) thermoplastic
D) linear
E) copolymer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Vulcanization is a process to strengthen natural rubber by crosslinking polymer chains with what element?
A) sodium
B) titanium
C) sulfur
D) aluminum
E) phosphorus
A) sodium
B) titanium
C) sulfur
D) aluminum
E) phosphorus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A cross-linked polymer
A) is a better elastomer than a linear polymer.
B) has a more rigid structure than a linear polymer.
C) cannot be prepared by linking chains of a linear polymer.
D) is generally more soluble in organic solvents than a linear polymer.
E) is a thermoplastic polymer.
A) is a better elastomer than a linear polymer.
B) has a more rigid structure than a linear polymer.
C) cannot be prepared by linking chains of a linear polymer.
D) is generally more soluble in organic solvents than a linear polymer.
E) is a thermoplastic polymer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An example of a syndiotactic polymer is: 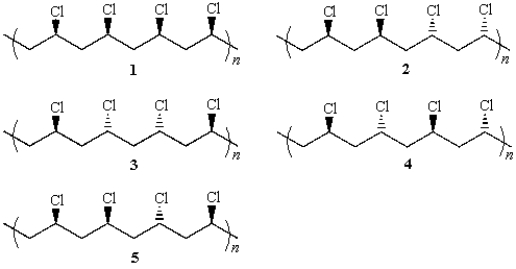
A) 5
B) 4
C) 3
D) 2
E) 1

A) 5
B) 4
C) 3
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The process by which rubber is cross-linked is called
A) polymerization.
B) epimerization.
C) saponification.
D) vulcanization.
E) solidification.
A) polymerization.
B) epimerization.
C) saponification.
D) vulcanization.
E) solidification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following polymers can be classified as a thermoplastic?
A) bakelite
B) polyurethane
C) urea-formaldehyde
D) polystyrene
E) none of these
A) bakelite
B) polyurethane
C) urea-formaldehyde
D) polystyrene
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The configurations of all stereocenters in an isotactic polymer are:
A) regular
B) random
C) alternate
D) the same
E) the opposite
A) regular
B) random
C) alternate
D) the same
E) the opposite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The stereochemistry of the following polymer is referred to as: 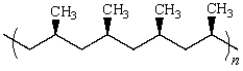
A) isomeric
B) syndiotactic
C) atactic
D) isotactic
E) barbaric

A) isomeric
B) syndiotactic
C) atactic
D) isotactic
E) barbaric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a thermosetting polymer?
A) polypropylene
B) teflon
C) dacron
D) polyester
E) bakelite
A) polypropylene
B) teflon
C) dacron
D) polyester
E) bakelite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



