Deck 7: Alcohols, Phenols Thiols
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Alcohols, Phenols Thiols
1
The formula for 2-pentanethiol is:
A)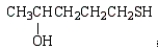
B)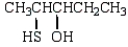
C)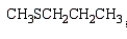
D)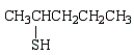
E)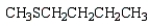
A)
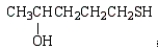
B)
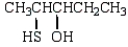
C)
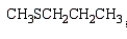
D)
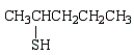
E)
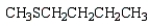
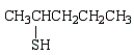
2
Which of the following molecules would have the highest boiling point?
A) CH3CH2OH
B) CH3OCH3
C) CH3CH2Cl
D) CH3CH2CH3
E) CH3CH2I
A) CH3CH2OH
B) CH3OCH3
C) CH3CH2Cl
D) CH3CH2CH3
E) CH3CH2I
CH3CH2OH
3
Which of the following molecules is classified as a tertiary (3°) alcohol? 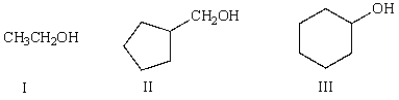
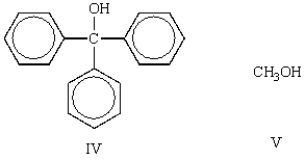
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
IV
4
What is the IUPAC name for isobutyl alcohol?
A) 1-butanol
B) 2-butanol
C) 2-methyl-2-butanol
D) 2-methyl-1-propanol
A) 1-butanol
B) 2-butanol
C) 2-methyl-2-butanol
D) 2-methyl-1-propanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following phenols is the strongest acid?
A)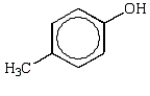
B)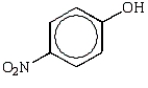
C)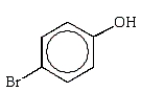
D)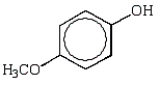
E)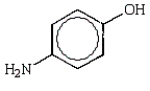
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Phenols are stronger acids than alcohols because of the
A) resonance stabilization of phenoxide ions.
B) resonance stabilization of phenols.
C) resonance stabilization of alkoxide ions.
D) resonance stabilization of alcohols.
E) hydrogen bonding in phenols.
A) resonance stabilization of phenoxide ions.
B) resonance stabilization of phenols.
C) resonance stabilization of alkoxide ions.
D) resonance stabilization of alcohols.
E) hydrogen bonding in phenols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Electron-withdrawing substituents
A) increase acidity by increasing the stability of acids.
B) decrease acidity by increasing the stability of a conjugate base.
C) increase acidity by increasing the stability of a conjugate base.
D) decrease acidity by increasing the stability of acids.
E) can only have a slight effect on acidity.
A) increase acidity by increasing the stability of acids.
B) decrease acidity by increasing the stability of a conjugate base.
C) increase acidity by increasing the stability of a conjugate base.
D) decrease acidity by increasing the stability of acids.
E) can only have a slight effect on acidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the correct name for the following molecule? 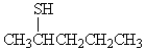
A) 2-pentanol
B) 3-thiopentanol
C) 2-pentanethiol
D) 4-pentanethiol
E) pentylsulfide
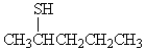
A) 2-pentanol
B) 3-thiopentanol
C) 2-pentanethiol
D) 4-pentanethiol
E) pentylsulfide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is 3-pentyn-1-ol?
A)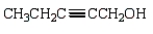
B)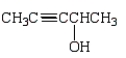
C)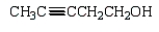
D)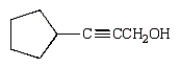
E)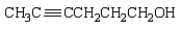
A)
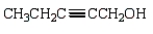
B)

C)
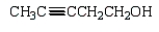
D)
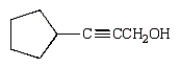
E)
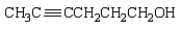

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following molecules would be the strongest Brønsted-Lowry acid?
A) H2O
B) CH4
C) HF
D) HCl
E) NH3
A) H2O
B) CH4
C) HF
D) HCl
E) NH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What would be the IUPAC name for the following alcohol? 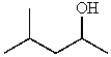
A) 2-methyl-4-pentanol
B) 2-methyl-4-hydroxypentane
C) 4-methyl-2-pentanol
D) 4-hydroxy-2-methylpentane
E) 2-hydroxy-4-methylpentane

A) 2-methyl-4-pentanol
B) 2-methyl-4-hydroxypentane
C) 4-methyl-2-pentanol
D) 4-hydroxy-2-methylpentane
E) 2-hydroxy-4-methylpentane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following molecules would be the best hydrogen bond donor?
A) CH3CH2OCH3
B) CH3CN
C) CH3OH
D) CH3SH
E) CH3CH2NH2
A) CH3CH2OCH3
B) CH3CN
C) CH3OH
D) CH3SH
E) CH3CH2NH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The conjugate base of carbonic acid, H2CO3, is:
A) H3CO3+
B) CO2
C) HCO3-
D) CO32-
E) CO3-
A) H3CO3+
B) CO2
C) HCO3-
D) CO32-
E) CO3-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The expected order of boiling points of the following is: 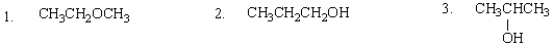
A) 3 > 2 > 1
B) 1 > 2 > 3
C) 1 > 3 > 2
D) 2 > 3 > 1
E) 2 > 1 > 3
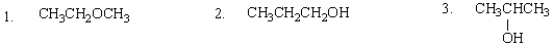
A) 3 > 2 > 1
B) 1 > 2 > 3
C) 1 > 3 > 2
D) 2 > 3 > 1
E) 2 > 1 > 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is a correct name for (CH3)3CO- Na+??
A) sodium alkoxide
B) sodium trimethyloxide
C) sodium butoxide
D) sodium trimethylethoxide
E) sodium tert-butoxide
A) sodium alkoxide
B) sodium trimethyloxide
C) sodium butoxide
D) sodium trimethylethoxide
E) sodium tert-butoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A Lewis acid is a:
A) proton donor
B) electron pair donor
C) electron pair acceptor
D) proton acceptor
A) proton donor
B) electron pair donor
C) electron pair acceptor
D) proton acceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the name of the following alcohol? 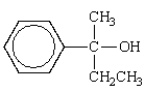
A) 1-ethyl-2-methylbenzyl alcohol
B) methylphenylpropanol
C) 2-methyl-2-phenyl-1-propanol
D) 2-phenyl-2-butanol

A) 1-ethyl-2-methylbenzyl alcohol
B) methylphenylpropanol
C) 2-methyl-2-phenyl-1-propanol
D) 2-phenyl-2-butanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the strongest base?
A)
B)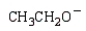
C)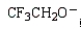
D)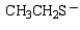
E)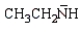
A)

B)
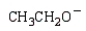
C)
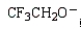
D)
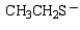
E)
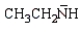

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The correct name for 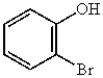 is
is
A) 2-hydroxybromobenzene.
B) 2-bromobenzyl alcohol.
C) 2-bromobenzol.
D) o-bromophenol.
E) 2-bromohexanol
 is
isA) 2-hydroxybromobenzene.
B) 2-bromobenzyl alcohol.
C) 2-bromobenzol.
D) o-bromophenol.
E) 2-bromohexanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a secondary (2°) alcohol? 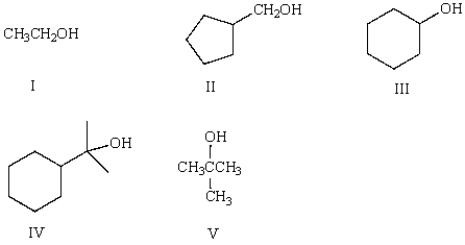
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following alcohols would react most rapidly under SN1 conditions?
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) (CH3)2CHCH2OH
D) (CH3)3COH
E) CH3CH2CH2OH
A) CH3OH
B) CH3CH2OH
C) (CH3)2CHCH2OH
D) (CH3)3COH
E) CH3CH2CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following mixtures would NOT react? 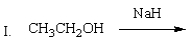
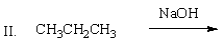
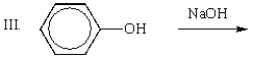
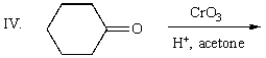
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) II and IV
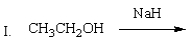
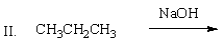


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The pKa of an acid whose Ka = 10-11 is
A) 1011
B) 11
C) -11
D) 3
E) -3
A) 1011
B) 11
C) -11
D) 3
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which reagent will accomplish the following transformation? 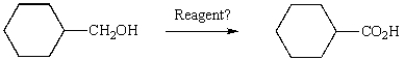
A) pyridinium chlorochromate
B) K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
C) H2O2, NaOH, H2O
D) Ag(NH3)2+, NaOH (Tollen's reagent)
E) all of the above
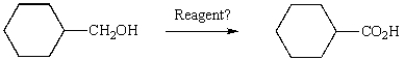
A) pyridinium chlorochromate
B) K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
C) H2O2, NaOH, H2O
D) Ag(NH3)2+, NaOH (Tollen's reagent)
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the major product of the following reaction? 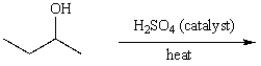
A) CH3CH2CH=CH2
B) cis-CH3CH=CHCH3
C) trans-CH3CH=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2C=CH2
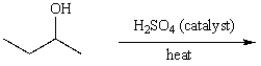
A) CH3CH2CH=CH2
B) cis-CH3CH=CHCH3
C) trans-CH3CH=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2C=CH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What type of compound is formed when a secondary (2°) alcohol is treated with Jones' reagent?
A) an alkene
B) an alkyne
C) an aldehyde
D) a ketone
E) a carboxylic acid
A) an alkene
B) an alkyne
C) an aldehyde
D) a ketone
E) a carboxylic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which reagents would you use to accomplish the following transformation? 
A) H2SO4, H2O, acetone
B) CrO3, H2SO4, acetone
C) PCC/CH2Cl2
D) Zn, HCl, acetone
E) H2, Pd, acetone

A) H2SO4, H2O, acetone
B) CrO3, H2SO4, acetone
C) PCC/CH2Cl2
D) Zn, HCl, acetone
E) H2, Pd, acetone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the product of the following reaction sequence? 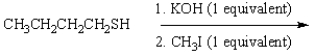
A) CH3CH2CH2CH2SCH3
B) CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH3
C) (CH3CH2CH2CH2S)2
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

A) CH3CH2CH2CH2SCH3
B) CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH3
C) (CH3CH2CH2CH2S)2
D) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
is the major product from the E1 dehydration of 2-methyl-2-hexanol?
A) 4-methyl-1-hexene
B) 4-methyl-3-hexene
C) 2-methyl-2-hexene
D) 2-methyl-1-hexene
E) 2-methylhexane
A) 4-methyl-1-hexene
B) 4-methyl-3-hexene
C) 2-methyl-2-hexene
D) 2-methyl-1-hexene
E) 2-methylhexane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which statement is false? Tert-Butyl alcohol reacts
A) with HCl to give 2-methylpropene by an E1 mechanism.
B) with HCl to give 2-chloro-2-methylpropane by an SN1 mechanism.
C) with HCl and HBr at very different rates.
D) with HCl or HBr to give a carbocation intermediate.
E) with HCl to give both 2-methylpropene and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
A) with HCl to give 2-methylpropene by an E1 mechanism.
B) with HCl to give 2-chloro-2-methylpropane by an SN1 mechanism.
C) with HCl and HBr at very different rates.
D) with HCl or HBr to give a carbocation intermediate.
E) with HCl to give both 2-methylpropene and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The rate-determining step in the following reaction is: 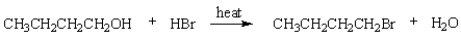
A) protonation of the alcohol
B) ionization of the alcohol to give a carbocation.
C) loss of water from the protonated alcohol to give a carbocation
D) capture of a carbocation by bromide ion.
E) displacement of water from the protonated alcohol by bromide ion.
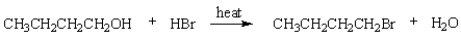
A) protonation of the alcohol
B) ionization of the alcohol to give a carbocation.
C) loss of water from the protonated alcohol to give a carbocation
D) capture of a carbocation by bromide ion.
E) displacement of water from the protonated alcohol by bromide ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The rate-determining step in the following reaction is: 
A) protonation of the alcohol.
B) ionization of the alcohol to give a carbocation.
C) loss of water from the protonated alcohol to give a carbocation.
D) capture of a carbocation by bromide ion.
E) displacement of water from the protonated alcohol by bromide ion.

A) protonation of the alcohol.
B) ionization of the alcohol to give a carbocation.
C) loss of water from the protonated alcohol to give a carbocation.
D) capture of a carbocation by bromide ion.
E) displacement of water from the protonated alcohol by bromide ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



