Deck 23: Large-Scale Structure in the Universe
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Large-Scale Structure in the Universe
1
What does the large-scale structure of the universe look most like?
A) a sponge with many large holes
B) a loaf of wheat bread with many tiny holes
C) a plate of flat noodles
D) a jar of marbles
E) a pizza with evenly distributed pepperoni
A) a sponge with many large holes
B) a loaf of wheat bread with many tiny holes
C) a plate of flat noodles
D) a jar of marbles
E) a pizza with evenly distributed pepperoni
a sponge with many large holes
2
The Virgo Cluster is at an estimated distance of 16.5 Mpc.What is the average recession speed of the cluster, assuming a Hubble constant of 70km/s/Mpc?
A) 1,200 km/s
B) 32,000 km/s
C) 300 km/s
D) 10,000 km/s
E) 3,800 km/s
A) 1,200 km/s
B) 32,000 km/s
C) 300 km/s
D) 10,000 km/s
E) 3,800 km/s
1,200 km/s
3
Which of the following is true about the Great Attractor?
A) It is about 5 Mpc away.
B) It is in fact a black hole the size of a galaxy.
C) It can only be detected in radio wavelengths.
D) It is at the center of the Laniakea Supercluster.
E) It has no gravitational effects.
A) It is about 5 Mpc away.
B) It is in fact a black hole the size of a galaxy.
C) It can only be detected in radio wavelengths.
D) It is at the center of the Laniakea Supercluster.
E) It has no gravitational effects.
It is at the center of the Laniakea Supercluster.
4
Astronomers estimate distances to large numbers of distant galaxies using
A) the cosmological constant.
B) Cepheid variable stars.
C) parallax.
D) Type II supernovae.
E) redshifts.
A) the cosmological constant.
B) Cepheid variable stars.
C) parallax.
D) Type II supernovae.
E) redshifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The diameter of the Local Group of galaxies is closest to which of the following distances?
A) 50 AU
B) 100,000 light-years
C) 3 million parsecs
D) 200 million light-years
E) 1 billion parsecs
A) 50 AU
B) 100,000 light-years
C) 3 million parsecs
D) 200 million light-years
E) 1 billion parsecs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following fills the space between galaxies in a cluster?
A) young blue stars
B) old red stars
C) hot gas that glows at X-ray wavelengths
D) cold, dark gas that only glows in radio wavelengths
E) supermassive black holes
A) young blue stars
B) old red stars
C) hot gas that glows at X-ray wavelengths
D) cold, dark gas that only glows in radio wavelengths
E) supermassive black holes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Our galaxy is part of the ________ Supercluster.
A) Laniakea
B) Solar
C) Milky Way
D) Great Attractor
E) Andromeda
A) Laniakea
B) Solar
C) Milky Way
D) Great Attractor
E) Andromeda

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a way in which astronomers detect dark matter in clusters of galaxies?
A) by determining the amount of mass necessary to gravitationally lens images of distant objects
B) by directly measuring the dark matter using infrared light
C) by measuring the peculiar velocity of the galaxy cluster
D) by determining the amount of mass necessary to gravitationally collapse clouds of gas to form the number of stars present
E) None of these; dark matter cannot be detected in any way.
A) by determining the amount of mass necessary to gravitationally lens images of distant objects
B) by directly measuring the dark matter using infrared light
C) by measuring the peculiar velocity of the galaxy cluster
D) by determining the amount of mass necessary to gravitationally collapse clouds of gas to form the number of stars present
E) None of these; dark matter cannot be detected in any way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Astronomers can estimate distances to the galaxies in the figure below because of 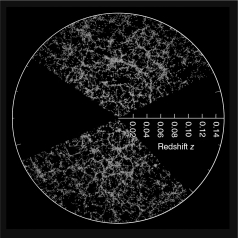
A) the expansion of the universe.
B) our location at the center of the universe.
C) dark matter.
D) peculiar velocities.
E) gravitational redshift.

A) the expansion of the universe.
B) our location at the center of the universe.
C) dark matter.
D) peculiar velocities.
E) gravitational redshift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The figure below shows a small section of the Virgo Cluster.The indicated galaxy can be classified as 
A) elliptical.
B) peculiar.
C) dwarf.
D) ultrafaint.
E) quasar.

A) elliptical.
B) peculiar.
C) dwarf.
D) ultrafaint.
E) quasar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Scientists estimate the following quantities for the Coma Cluster: the total mass of the cluster is Mtotal ~ 1.3 *1015 MSUN, the total mass of all stars is Mstars ~ 3 *1013 MSUN, and the mass of the hot X-ray-emitting gas is Mgas ~ 1 * 1014 MSUN.What is the corresponding percentage of dark matter within the Coma Cluster?
A) 4 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 72 percent
D) 90 percent
E) There is no dark matter contribution.
A) 4 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 72 percent
D) 90 percent
E) There is no dark matter contribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following provides direct evidence for the existence of dark matter?
A) the rotation curves of spiral galaxies
B) the motions of galaxies in clusters
C) the temperature of the diffuse intergalactic gas within clusters
D) the gravitational lensing produced by galaxy clusters
E) all of these
A) the rotation curves of spiral galaxies
B) the motions of galaxies in clusters
C) the temperature of the diffuse intergalactic gas within clusters
D) the gravitational lensing produced by galaxy clusters
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A galaxy has a peculiar velocity due to the effects of
A) erroneous redshifts.
B) local gravitational attraction.
C) supernovae.
D) eclipsing binary stars.
E) interstellar winds.
A) erroneous redshifts.
B) local gravitational attraction.
C) supernovae.
D) eclipsing binary stars.
E) interstellar winds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Filaments and voids are hallmarks of
A) reionization.
B) large-scale structure.
C) spiral galaxies.
D) elementary particles.
E) hot dark matter.
A) reionization.
B) large-scale structure.
C) spiral galaxies.
D) elementary particles.
E) hot dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Understanding the distribution of galaxies in the universe requires the construction of a three-dimensional map where for each galaxy we need to know its position and
A) mass.
B) redshift.
C) dust content.
D) morphological type.
E) star formation rate.
A) mass.
B) redshift.
C) dust content.
D) morphological type.
E) star formation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these is the correct order of collections of galaxies, from smallest to largest?
A) group, supercluster, cluster
B) cluster, supercluster, group
C) group, cluster, supercluster
D) cluster, group, supercluster
E) supercluster, group, cluster
A) group, supercluster, cluster
B) cluster, supercluster, group
C) group, cluster, supercluster
D) cluster, group, supercluster
E) supercluster, group, cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The most common type of galaxy found in a galaxy cluster is a ________ galaxy.
A) spiral
B) giant elliptical
C) giant irregular
D) dwarf
E) barred spiral
A) spiral
B) giant elliptical
C) giant irregular
D) dwarf
E) barred spiral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The peculiar velocity of a galaxy describes its motion relative to the
A) Local Group.
B) center of the Milky Way.
C) center of the universe.
D) Great Attractor.
E) cosmic microwave background.
A) Local Group.
B) center of the Milky Way.
C) center of the universe.
D) Great Attractor.
E) cosmic microwave background.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Dark matter constitutes ________ of the mass in galaxy clusters, while the majority of non-dark matter mass is found in ________.
A) the majority; supermassive black holes
B) a minority; supermassive black holes
C) a minority; cold gas
D) the majority; hot gas
E) none; old stars
A) the majority; supermassive black holes
B) a minority; supermassive black holes
C) a minority; cold gas
D) the majority; hot gas
E) none; old stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In order to use Hubble's law to find the distance to a galaxy, astronomers need to measure that galaxy's
A) radius.
B) rotational velocity.
C) mass.
D) peculiar velocity.
E) redshift.
A) radius.
B) rotational velocity.
C) mass.
D) peculiar velocity.
E) redshift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Structure in our universe evolved by initially forming
A) giant galaxies, some of which later fragmented into dwarf galaxies.
B) dwarf galaxies that later merged to form bigger galaxies.
C) individual, free-floating stars, that later aggregated to form galaxies.
D) hot dark matter that later cooled into cold dark matter.
E) all types and sizes of galaxies at the same time.
A) giant galaxies, some of which later fragmented into dwarf galaxies.
B) dwarf galaxies that later merged to form bigger galaxies.
C) individual, free-floating stars, that later aggregated to form galaxies.
D) hot dark matter that later cooled into cold dark matter.
E) all types and sizes of galaxies at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The expansion of the universe will eventually render the CMB invisible because its photons will
A) have wavelengths that will exceed the size of the observable universe.
B) be swamped by the light from the ever-increasing star formation rates in the universe.
C) not have enough energy to escape the gravity of degenerate stellar remnants.
D) all combine and again produce pairs of massive particles.
E) not escape the strong gravity of supermassive black holes the size of galaxy clusters.
A) have wavelengths that will exceed the size of the observable universe.
B) be swamped by the light from the ever-increasing star formation rates in the universe.
C) not have enough energy to escape the gravity of degenerate stellar remnants.
D) all combine and again produce pairs of massive particles.
E) not escape the strong gravity of supermassive black holes the size of galaxy clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Quantum fluctuations in the early universe
A) were the seeds that grew into today's galaxies.
B) are the reason dark matter exists.
C) were made of small black holes.
D) had no effect on the current structure of the universe.
E) can be observed with radio telescopes.
A) were the seeds that grew into today's galaxies.
B) are the reason dark matter exists.
C) were made of small black holes.
D) had no effect on the current structure of the universe.
E) can be observed with radio telescopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Dark matter is essential in understanding the formation of the large-scale structure in the universe in that it
A) was clumpier than normal matter in the early universe.
B) consists exclusively of antimatter particles.
C) has a repulsive effect, just like the dark energy.
D) explains the physics of black holes.
E) cannot be made of elementary particles.
A) was clumpier than normal matter in the early universe.
B) consists exclusively of antimatter particles.
C) has a repulsive effect, just like the dark energy.
D) explains the physics of black holes.
E) cannot be made of elementary particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the early universe, why were inhomogeneities in the distribution of normal matter much smaller than inhomogeneities in the dark matter?
A) Normal matter was pushed away by supernova explosions.
B) Large-scale magnetic fields smoothed the distribution of charged particles in the normal matter but not in dark matter.
C) Dark matter particles were more massive than and cooled off before normal matter, and so dark matter fluctuations had more time to grow.
D) Dark matter was 10 times more massive than normal matter.
E) Radiation pressure affected normal matter but not dark matter.
A) Normal matter was pushed away by supernova explosions.
B) Large-scale magnetic fields smoothed the distribution of charged particles in the normal matter but not in dark matter.
C) Dark matter particles were more massive than and cooled off before normal matter, and so dark matter fluctuations had more time to grow.
D) Dark matter was 10 times more massive than normal matter.
E) Radiation pressure affected normal matter but not dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What has the dominant role in defining the large-scale structure of the universe?
A) supernovae from the first generation of stars
B) the gravitational attraction of matter
C) matter/antimatter annihilation
D) magnetic fields
E) electric force
A) supernovae from the first generation of stars
B) the gravitational attraction of matter
C) matter/antimatter annihilation
D) magnetic fields
E) electric force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The best hypothesis about the nature of dark matter is that it consists of particles with no electric charge.What is one reason why dark matter particles must have zero electric charge?
A) They cannot be more massive than an electron.
B) If they did, they would emit photons as they move in external magnetic fields.
C) All charged particles would have been annihilated in particle-antiparticle collisions in the early universe.
D) No elementary particle has electric charge.
E) Charged particles formed only later inside stars.
A) They cannot be more massive than an electron.
B) If they did, they would emit photons as they move in external magnetic fields.
C) All charged particles would have been annihilated in particle-antiparticle collisions in the early universe.
D) No elementary particle has electric charge.
E) Charged particles formed only later inside stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true about neutrinos?
A) They are a possible example of cold dark matter.
B) They are a possible example of hot dark matter.
C) They have been theoretically predicted, yet never detected.
D) They must be much more massive than the dark matter candidate called photino.
E) They account for all the dark matter in the universe.
A) They are a possible example of cold dark matter.
B) They are a possible example of hot dark matter.
C) They have been theoretically predicted, yet never detected.
D) They must be much more massive than the dark matter candidate called photino.
E) They account for all the dark matter in the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Lambda-CDM model combines the properties of ________ to explain the formation of structure in the universe.
A) black holes and neutron stars
B) dark energy and cold dark matter
C) star formation and angular momentum
D) nucleosynthesis and hot dark matter
E) gravity and nuclear forces
A) black holes and neutron stars
B) dark energy and cold dark matter
C) star formation and angular momentum
D) nucleosynthesis and hot dark matter
E) gravity and nuclear forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Our current understanding of galaxy formation suggests that the visible parts of galaxies
A) form first and are incorporated into dark matter halos later.
B) form only in the densest parts of dark matter halos.
C) can tell you the total size of the dark matter halo.
D) can tell you everything about the formation history of that galaxy.
E) spread over distances larger than those of dark matter halos.
A) form first and are incorporated into dark matter halos later.
B) form only in the densest parts of dark matter halos.
C) can tell you the total size of the dark matter halo.
D) can tell you everything about the formation history of that galaxy.
E) spread over distances larger than those of dark matter halos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The figure below shows snapshots taken from the Bolshoi simulation of the formation of the large-scale structure in the universe.Which one of these images represents the state of the universe at the highest redshift? 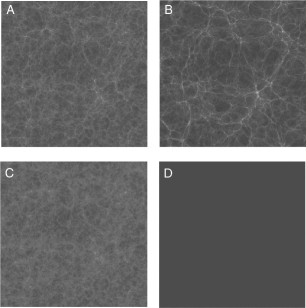
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) All of these occur at the same redshift, just in different regions of the universe.

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) All of these occur at the same redshift, just in different regions of the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How do the properties of the CMB give support to the existence of dark matter?
A) The CMB has the same temperature as the cold dark matter.
B) The faint glow of the CMB was actually produced by dark matter particles as they annihilated particles of normal matter.
C) The opaque CMB is essentially hiding the dark matter that existed earlier in the universe.
D) The CMB is too smooth to account for the structure we observe in the universe unless dark matter exists.
E) The observed spatial scale of CMB clumping perfectly matches that of the dark matter.
A) The CMB has the same temperature as the cold dark matter.
B) The faint glow of the CMB was actually produced by dark matter particles as they annihilated particles of normal matter.
C) The opaque CMB is essentially hiding the dark matter that existed earlier in the universe.
D) The CMB is too smooth to account for the structure we observe in the universe unless dark matter exists.
E) The observed spatial scale of CMB clumping perfectly matches that of the dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
You observe two galaxy clusters, cluster A and cluster B.If the outer galaxies of both clusters have the same circular velocities, but cluster A has twice the mass of cluster B, then the size of cluster A must be
A) 4 times that of cluster B.
B) one-fourth that of cluster B.
C) twice that of cluster B.
D) half that of cluster B.
E) the same as cluster B.
A) 4 times that of cluster B.
B) one-fourth that of cluster B.
C) twice that of cluster B.
D) half that of cluster B.
E) the same as cluster B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The small density variations that subsequently led to the formation of large-scale structure in the universe are thought to have formed
A) from quantum fluctuations during inflation.
B) due to the supernovae of the very first stars.
C) at the end of the recombination epoch.
D) as particle-antiparticle pairs annihilated.
E) as supermassive black holes powered the first quasars.
A) from quantum fluctuations during inflation.
B) due to the supernovae of the very first stars.
C) at the end of the recombination epoch.
D) as particle-antiparticle pairs annihilated.
E) as supermassive black holes powered the first quasars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The figure below shows snapshots taken from the Bolshoi simulation of the formation of the large-scale structure in the universe.Which one of these images shows the current structure of the universe? 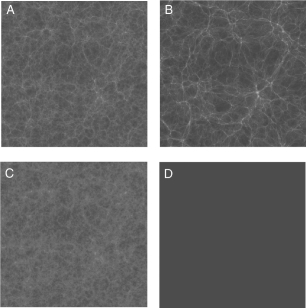
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) All of these occur at the same redshift, just in different regions of the universe.

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) All of these occur at the same redshift, just in different regions of the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Scientists think that neutrinos cannot be the dominant form of dark matter in the universe.Why?
A) Neutrinos are an example of hot dark matter that could form large superclusters but not smaller structures.
B) Neutrinos interact too strongly with ordinary matter.
C) Neutrinos would decay over time and disappear, causing galaxies to fall apart.
D) Neutrinos would not gravitationally lens background galaxies.
E) Neutrinos are charged particles.
A) Neutrinos are an example of hot dark matter that could form large superclusters but not smaller structures.
B) Neutrinos interact too strongly with ordinary matter.
C) Neutrinos would decay over time and disappear, causing galaxies to fall apart.
D) Neutrinos would not gravitationally lens background galaxies.
E) Neutrinos are charged particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Structure formation in the universe proceeds hierarchically, meaning that
A) large objects collapse and then fragment to form smaller objects.
B) large objects form at the same times as smaller objects.
C) small objects collapse and then merge to form larger objects.
D) only small objects form and are stable over time.
E) normal matter collapses first and dark matter collapses later.
A) large objects collapse and then fragment to form smaller objects.
B) large objects form at the same times as smaller objects.
C) small objects collapse and then merge to form larger objects.
D) only small objects form and are stable over time.
E) normal matter collapses first and dark matter collapses later.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why can't dark matter halos collapse to be the same size as the visible parts of galaxies?
A) Dark matter can't dissipate its energy through radiation from collisions.
B) Dark matter is made mostly of mini-black holes.
C) Dark matter has much more angular momentum.
D) Dark matter annihilates when it begins to get that dense.
E) Dark matter particles are too large to collapse that much.
A) Dark matter can't dissipate its energy through radiation from collisions.
B) Dark matter is made mostly of mini-black holes.
C) Dark matter has much more angular momentum.
D) Dark matter annihilates when it begins to get that dense.
E) Dark matter particles are too large to collapse that much.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
You observe two galaxy clusters, cluster A and cluster B.Both have the same radius, but cluster B's outer galaxies are orbiting the cluster with circular velocities that are twice that of cluster A's circular velocities.The mass of cluster B is
A) 2 times cluster A's mass
B) 4 times cluster A's mass.
C) half of cluster A's mass.
D) one-quarter of cluster A's mass.
E) equal to cluster A's mass.
A) 2 times cluster A's mass
B) 4 times cluster A's mass.
C) half of cluster A's mass.
D) one-quarter of cluster A's mass.
E) equal to cluster A's mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Reionization of the neutral gas in the universe occurred due to the
A) decay of dark matter particles.
B) emission of neutrinos by the first stars that formed.
C) heating from the motion of high-velocity black holes.
D) radiation from the first stars, supernovae, and black holes that formed.
E) positron and electron annihilations.
A) decay of dark matter particles.
B) emission of neutrinos by the first stars that formed.
C) heating from the motion of high-velocity black holes.
D) radiation from the first stars, supernovae, and black holes that formed.
E) positron and electron annihilations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The first stars formed in the universe had ________ compared with the stars formed today.
A) higher heavy-element content and higher mass
B) higher heavy-element content and lower mass
C) lower heavy-element content and higher mass
D) lower heavy-element content and lower mass
E) higher mass and longer lifetimes
A) higher heavy-element content and higher mass
B) higher heavy-element content and lower mass
C) lower heavy-element content and higher mass
D) lower heavy-element content and lower mass
E) higher mass and longer lifetimes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following best explains the difference between the heavy-element abundances seen in the first stars and those seen in stars that we observe today?
A) Stars today have more heavy elements because modern stars have higher masses, allowing them to create more heavy elements through nuclear fusion.
B) Stars today have more heavy elements because the gas that formed the current stars was enriched by the higher-mass elements formed in previous generations of stars.
C) Stars today have fewer heavy elements because they have been around long enough to use up the larger atoms.
D) Stars today have a smaller abundance of heavy elements because they haven't been around long enough to make as many of the larger atoms.
E) The stars that astronomers observe now are the first generation of stars.
A) Stars today have more heavy elements because modern stars have higher masses, allowing them to create more heavy elements through nuclear fusion.
B) Stars today have more heavy elements because the gas that formed the current stars was enriched by the higher-mass elements formed in previous generations of stars.
C) Stars today have fewer heavy elements because they have been around long enough to use up the larger atoms.
D) Stars today have a smaller abundance of heavy elements because they haven't been around long enough to make as many of the larger atoms.
E) The stars that astronomers observe now are the first generation of stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The second generation of stars
A) is indistinguishable from the first generation.
B) have all left the main sequence.
C) can only be found in galactic disks.
D) are all giant stars.
E) contain some elements heavier than lithium.
A) is indistinguishable from the first generation.
B) have all left the main sequence.
C) can only be found in galactic disks.
D) are all giant stars.
E) contain some elements heavier than lithium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
At what redshift would a quasar's emission line emitted at 121.6 nm show up at the "normal" wavelength of 486.1 nm of the Balmer H line?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 7
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The most distant galaxies detected at z  10 are best observed with ________ wavelengths of light.
10 are best observed with ________ wavelengths of light.
A) infrared
B) visible
C) X-ray
D) gamma-ray
E) radio
 10 are best observed with ________ wavelengths of light.
10 are best observed with ________ wavelengths of light.A) infrared
B) visible
C) X-ray
D) gamma-ray
E) radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is true about ultrafaint dwarf galaxies?
A) They are surrounded by dark dust and gas.
B) They are sites of active star formation.
C) They are dominated by dark matter.
D) They have been predicted but have never been observed.
E) They are more massive than most dwarf galaxies.
A) They are surrounded by dark dust and gas.
B) They are sites of active star formation.
C) They are dominated by dark matter.
D) They have been predicted but have never been observed.
E) They are more massive than most dwarf galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements about galaxy and star formation is true?
A) Star formation follows a "top-down" sequence whereas galaxy formation involves a "bottom-up" sequence.
B) Dark matter is essential in the formation of galaxies, but it is not involved in the formation of stars.
C) Galaxy angular momentum originates in gravitational interactions of clumps whereas star angular momentum is caused by the turbulence of the original molecular clouds.
D) When stars form they acquire most of the mass of the collapsing system, whereas in a Milky Way-like galaxy much of the matter remains distributed in a disk.
E) All of these statements are true.
A) Star formation follows a "top-down" sequence whereas galaxy formation involves a "bottom-up" sequence.
B) Dark matter is essential in the formation of galaxies, but it is not involved in the formation of stars.
C) Galaxy angular momentum originates in gravitational interactions of clumps whereas star angular momentum is caused by the turbulence of the original molecular clouds.
D) When stars form they acquire most of the mass of the collapsing system, whereas in a Milky Way-like galaxy much of the matter remains distributed in a disk.
E) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Telescopes like ALMA (working in the range 0.4-3.0 mm) and JWST (working in IR, in the range 0.6-28.5 micro-m) would help astronomers close a gap of observations that corresponds to the window
A) z = 2-3, when the star formation rate peaked.
B) z = 10-1,000, between the epochs of recombination and reionization.
C) z = 0-0.5, when there was a big change in the relative fraction of irregular galaxies.
D) z 1,100, to directly observe the inflation epoch.
E) Such telescopes are actually designed to only explore planetary systems within the boundaries of our Milky Way.
A) z = 2-3, when the star formation rate peaked.
B) z = 10-1,000, between the epochs of recombination and reionization.
C) z = 0-0.5, when there was a big change in the relative fraction of irregular galaxies.
D) z 1,100, to directly observe the inflation epoch.
E) Such telescopes are actually designed to only explore planetary systems within the boundaries of our Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The James Webb Space Telescope is designed to observe the most distant galaxies in the universe.It will observe them in
A) UV wavelengths.
B) IR wavelengths.
C) visible wavelengths.
D) X-ray wavelengths.
E) radio wavelengths.
A) UV wavelengths.
B) IR wavelengths.
C) visible wavelengths.
D) X-ray wavelengths.
E) radio wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Compared with what we see today, galaxies in the past were
A) more ordered and more likely to have spiral structure.
B) more ordered and less likely to have spiral structure.
C) messier and more likely to have spiral structure.
D) messier and less likely to have spiral structure.
E) exactly the same as they are today.
A) more ordered and more likely to have spiral structure.
B) more ordered and less likely to have spiral structure.
C) messier and more likely to have spiral structure.
D) messier and less likely to have spiral structure.
E) exactly the same as they are today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Each of these statements describes the steps that occur during star formation.Which of these is NOT also true for galaxy formation?
A) Angular momentum leads to the formation of a disk.
B) For both stars and galaxies, the largest objects form first, with smaller objects coming together later.
C) A gas cloud radiates energy, allowing it to collapse further than when it was hotter.
D) Gravitational instability leads to collapse.
E) The original large gas cloud splits into smaller fragments, because areas with higher density also have greater gravitational pull.
A) Angular momentum leads to the formation of a disk.
B) For both stars and galaxies, the largest objects form first, with smaller objects coming together later.
C) A gas cloud radiates energy, allowing it to collapse further than when it was hotter.
D) Gravitational instability leads to collapse.
E) The original large gas cloud splits into smaller fragments, because areas with higher density also have greater gravitational pull.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
We expect the kinds of galaxies that we see at redshift of z  4 to be
4 to be
A) much like what we see today.
B) smaller and much more irregular looking than today.
C) smaller versions of what we see today.
D) far more numerous but with fewer spiral galaxies.
E) larger versions of what we see today.
 4 to be
4 to beA) much like what we see today.
B) smaller and much more irregular looking than today.
C) smaller versions of what we see today.
D) far more numerous but with fewer spiral galaxies.
E) larger versions of what we see today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How has the fraction of galaxies with irregular morphologies evolved from 4 billion years ago to the present epoch?
A) About 10 percent of today's galaxies are peculiar, whereas 4 billion years ago more than half the galaxies were peculiar.
B) The fraction has remained at 50 percent over the last 4 billion to 5 billion years.
C) At the present epoch there are far more interacting galaxies than when the universe was about 9 billion to 10 billion years old.
D) The fraction has remained at 10 percent over the last 4 billion to 5 billion years.
E) There are no peculiar galaxies today, whereas 4 billion years ago they comprised nearly 10 percent of galaxies.
A) About 10 percent of today's galaxies are peculiar, whereas 4 billion years ago more than half the galaxies were peculiar.
B) The fraction has remained at 50 percent over the last 4 billion to 5 billion years.
C) At the present epoch there are far more interacting galaxies than when the universe was about 9 billion to 10 billion years old.
D) The fraction has remained at 10 percent over the last 4 billion to 5 billion years.
E) There are no peculiar galaxies today, whereas 4 billion years ago they comprised nearly 10 percent of galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Panel (b) of the figure below shows the enhanced infrared glow obtained after nearby stars and galaxies are subtracted from a standard Spitzer Space Telescope exposure.Scientists ascribe this faint signature to 
A) the CMB.
B) the first stars and galaxies formed.
C) GRBs and quasars.
D) supernovae.
E) our Sun.

A) the CMB.
B) the first stars and galaxies formed.
C) GRBs and quasars.
D) supernovae.
E) our Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What would be the observed wavelength for the Balmer H line emitted at 486.1 nm by a quasar at redshift z =5?
A) 2.9 µm
B) 81.0 nm
C) 21.0 cm
D) 121.6 nm
E) 1.2 µm
A) 2.9 µm
B) 81.0 nm
C) 21.0 cm
D) 121.6 nm
E) 1.2 µm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of these lists shows the correct chronological order of the events listed, starting with the earliest and ending with the most recent?
A) reionization, dark matter halos collapse, recombination, first galaxies are formed
B) dark matter halos collapse, reionization, first galaxies are formed, recombination
C) reionization, first galaxies are formed, dark matter halos collapse, recombination
D) recombination, dark matter halos collapse, first galaxies are formed, reionization
E) first galaxies are formed, dark matter halos collapse, reionization, recombination
A) reionization, dark matter halos collapse, recombination, first galaxies are formed
B) dark matter halos collapse, reionization, first galaxies are formed, recombination
C) reionization, first galaxies are formed, dark matter halos collapse, recombination
D) recombination, dark matter halos collapse, first galaxies are formed, reionization
E) first galaxies are formed, dark matter halos collapse, reionization, recombination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Where would a newly-discovered ultrafaint galaxy most likely be found?
A) on its own, away from other galaxies
B) a few billion light-years from Earth
C) at high redshift
D) in a large galaxy cluster
E) orbiting the Milky Way
A) on its own, away from other galaxies
B) a few billion light-years from Earth
C) at high redshift
D) in a large galaxy cluster
E) orbiting the Milky Way

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following must be true about the very first stars?
A) They couldn't form until billions of years after the Big Bang.
B) They were made of dark matter.
C) They all had low (less than 1 MSUN) masses.
D) They formed in large clusters of millions of stars, which became galaxies.
E) The material from which they formed contained no elements more massive than lithium.
A) They couldn't form until billions of years after the Big Bang.
B) They were made of dark matter.
C) They all had low (less than 1 MSUN) masses.
D) They formed in large clusters of millions of stars, which became galaxies.
E) The material from which they formed contained no elements more massive than lithium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Low-mass stars could form in the second generation because
A) massive elements produced in the first stars coalesced into dust grains.
B) they formed in minihalos of cold dark matter.
C) gravitational waves led to the fragmentation of dark matter minihalos into microhalos.
D) there was a lot more raw material available for star formation after the demise of the first stars.
E) different types of fundamental forces controlled the formation of the first and second generation.
A) massive elements produced in the first stars coalesced into dust grains.
B) they formed in minihalos of cold dark matter.
C) gravitational waves led to the fragmentation of dark matter minihalos into microhalos.
D) there was a lot more raw material available for star formation after the demise of the first stars.
E) different types of fundamental forces controlled the formation of the first and second generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Spiral galaxies
A) were present during the Big Bang.
B) formed immediately after recombination.
C) formed at the same time as the first stars.
D) took some time to form, after the first stars appeared.
E) can have existed only for the last billion years or so.
A) were present during the Big Bang.
B) formed immediately after recombination.
C) formed at the same time as the first stars.
D) took some time to form, after the first stars appeared.
E) can have existed only for the last billion years or so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe two ways in which you could measure the mass of a galaxy cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the expected future of our galaxy?
A) Its contents will eventually be pulled in by the supermassive black hole at its center, Sagittarius A*.
B) Eventually all its matter will be in the form of iron atoms.
C) It will eventually be made of nothing but white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes, and then will collapse in on itself in a Big Crunch.
D) It will merge with nearby galaxies and then eventually decay into photons.
E) It will expand with the universe, but will stop expanding once enough stars become black holes.
A) Its contents will eventually be pulled in by the supermassive black hole at its center, Sagittarius A*.
B) Eventually all its matter will be in the form of iron atoms.
C) It will eventually be made of nothing but white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes, and then will collapse in on itself in a Big Crunch.
D) It will merge with nearby galaxies and then eventually decay into photons.
E) It will expand with the universe, but will stop expanding once enough stars become black holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Out of all the mass and energy in the universe, ordinary matter (the stuff that makes up stars and gas, and all the things we interact with in everyday life) constitutes about
A) 4-5 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) half.
D) 85 percent.
E) 99 percent.
A) 4-5 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) half.
D) 85 percent.
E) 99 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the large-scale structure of the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which probably formed last in the course of the evolution of the universe?
A) a typical proton inside a water molecule on Earth
B) a helium atom in the surface of the Sun
C) a typical star that is a member of a globular cluster star in our Milky Way
D) the Milky Way
E) the Virgo Supercluster
A) a typical proton inside a water molecule on Earth
B) a helium atom in the surface of the Sun
C) a typical star that is a member of a globular cluster star in our Milky Way
D) the Milky Way
E) the Virgo Supercluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
By measuring the star formation rate in galaxies as a function of their redshift, we have learned that the average star formation rate in galaxies peaked approximately ________ years ago.
A) 1 billion
B) 3 billion
C) 5 billion
D) 7 billion
E) 11 billion
A) 1 billion
B) 3 billion
C) 5 billion
D) 7 billion
E) 11 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of these statements about galaxy clusters is true?
A) Galaxy clusters do not require dark matter in order to form.
B) Galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the universe.
C) Small galaxy clusters form first and then merge to form larger galaxy clusters.
D) Galaxy clusters are evenly distributed throughout the universe.
E) There are such large distances between galaxy clusters that they never actually run into each other.
A) Galaxy clusters do not require dark matter in order to form.
B) Galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the universe.
C) Small galaxy clusters form first and then merge to form larger galaxy clusters.
D) Galaxy clusters are evenly distributed throughout the universe.
E) There are such large distances between galaxy clusters that they never actually run into each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
According to the figure below, the maximum star formation rate in the past was about ________ the star formation rate today. 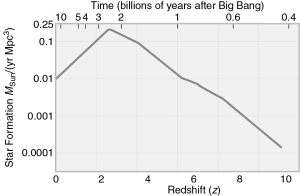
A) the same as
B) 5 times
C) 20 times
D) 100 times
E) 10,000 times

A) the same as
B) 5 times
C) 20 times
D) 100 times
E) 10,000 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If dark energy is embedded within the vacuum of space, then the best places to study it would probably be the
A) spiral galaxies.
B) interacting, irregular galaxies.
C) cosmic walls and filaments.
D) cosmic voids.
E) clusters of galaxies.
A) spiral galaxies.
B) interacting, irregular galaxies.
C) cosmic walls and filaments.
D) cosmic voids.
E) clusters of galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A galaxy cluster is measured to have a radius of 8 x1019 km, and the small outer galaxies are measured to orbit the cluster center with a circular velocity of 900 km/s.What is the mass of this cluster's core? (Recall that G = 6.67 *10-11 N m2 kg-2.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Scientists estimate that, in the distant cosmic future, before the universe becomes filled exclusively with elementary particles, the last large concentrations of mass will be
A) white dwarfs.
B) neutron stars.
C) black holes.
D) brown dwarfs.
E) ultrafaint galaxies.
A) white dwarfs.
B) neutron stars.
C) black holes.
D) brown dwarfs.
E) ultrafaint galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is likely to happen when two spiral galaxies collide?
A) A more massive elliptical galaxy might form out of the merger.
B) The two supermassive black holes at their centers could form a binary black hole system.
C) A burst of star formation will occur in the merged galaxy.
D) The cold gas in the merged galaxy might be blown away by supernovae.
E) All of these are likely.
A) A more massive elliptical galaxy might form out of the merger.
B) The two supermassive black holes at their centers could form a binary black hole system.
C) A burst of star formation will occur in the merged galaxy.
D) The cold gas in the merged galaxy might be blown away by supernovae.
E) All of these are likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What role do cosmological computer simulations play in the scientific method?
A) They create virtual observations, allowing scientists to test hypotheses without gathering data.
B) They design experiments.
C) They create predictions that can be tested with additional observations.
D) Simulations do not tie into the scientific method; they are only used to verify the math within theories.
E) Simulations do not tie into the scientific method; they only provide scientists tools to visualize concepts.
A) They create virtual observations, allowing scientists to test hypotheses without gathering data.
B) They design experiments.
C) They create predictions that can be tested with additional observations.
D) Simulations do not tie into the scientific method; they are only used to verify the math within theories.
E) Simulations do not tie into the scientific method; they only provide scientists tools to visualize concepts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In studying galaxies of various morphological types, scientists have estimated equivalent mass-to-light ratios (M/L) of about 1-30 in solar units (1 MSUN/1 LSUN), with ratios being lower for spiral galaxies and higher for elliptical galaxies.In galaxy clusters, however, the typical total mass-to-light ratio is estimated in the range 300-600 (MSUN/LSUN).What is the implication of these numbers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Ignoring the effect of redshift, we expect the galaxies that we see at a redshift of z = 3 will be ________ than galaxies today.
A) more irregular and redder
B) larger and redder
C) smaller and bluer
D) smaller and redder
E) larger and bluer
A) more irregular and redder
B) larger and redder
C) smaller and bluer
D) smaller and redder
E) larger and bluer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use Hubble's law to explain how measurements of redshift help astronomers map the large-scale structure of the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What do the arcs seen in the Hubble Space Telescope image below represent? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain why the Bullet Cluster is considered a strong example for the existence of dark matter, based on the figure below. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How do we know how fast the Milky Way is moving relative to the local universe? What are we moving toward, and what do we think is mostly responsible for this motion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Scientists quantified the following amounts of mass for the Coma Cluster: the total mass of the cluster is Mtotal ~ 1.3 * 1015 MSUN, the total mass of all stars Mstars ~ 3 * 1013 MSUN, and the mass of the hot X-ray-emitting gas Mgas ~ 1 * 1014 MSUN.What is the corresponding percentage of dark matter within the Coma Cluster?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



