Deck 6: The Tools of the Astronomer
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Tools of the Astronomer
1
The telescope was invented by
A) Galileo Galilei, an Italian inventor.
B) Hans Lippershey, an eyeglass maker in the Netherlands.
C) Leonardo da Vinci, an Italian polymath.
D) Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer.
E) Johannes Kepler, a German mathematician.
A) Galileo Galilei, an Italian inventor.
B) Hans Lippershey, an eyeglass maker in the Netherlands.
C) Leonardo da Vinci, an Italian polymath.
D) Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer.
E) Johannes Kepler, a German mathematician.
Hans Lippershey, an eyeglass maker in the Netherlands.
2
The angular resolution of a large ground-based telescope (without adaptive optics) is typically
A) 30 arcseconds (arcsec).
B) 1 arcminute (arcmin).
C) 10 arcsec.
D) 30 arcmin.
E) limited by atmospheric seeing.
A) 30 arcseconds (arcsec).
B) 1 arcminute (arcmin).
C) 10 arcsec.
D) 30 arcmin.
E) limited by atmospheric seeing.
limited by atmospheric seeing.
3
According to the law of reflection, if a beam of light strikes a flat mirror at an angle of 30 relative to a plane perpendicular to the surface of the mirror, at what angle will it reflect, relative to a plane perpendicular to the surface of the mirror?
A) 0
B) 30
C) 60
D) 90
E) 120
A) 0
B) 30
C) 60
D) 90
E) 120
30
4
Why can a compound lens combat a refracting telescope's chromatic aberration?
A) Red light is absorbed by a larger amount than blue light.
B) Red light is refracted by a larger amount than blue light, and different types of glass have different indexes of refraction.
C) Blue light is refracted by a larger amount than red light, and different types of glass have different indexes of refraction.
D) Blue light is absorbed by a larger amount than red light.
E) A compound lens cannot combat chromatic aberration.
A) Red light is absorbed by a larger amount than blue light.
B) Red light is refracted by a larger amount than blue light, and different types of glass have different indexes of refraction.
C) Blue light is refracted by a larger amount than red light, and different types of glass have different indexes of refraction.
D) Blue light is absorbed by a larger amount than red light.
E) A compound lens cannot combat chromatic aberration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What optical phenomenon is pictured in the figure below? 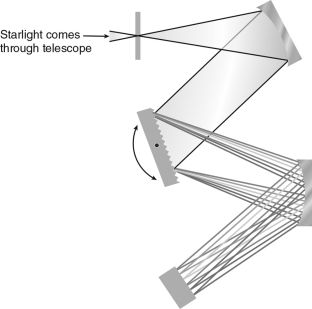
A) reflection
B) refraction
C) diffraction
D) interference
E) chromatic aberration

A) reflection
B) refraction
C) diffraction
D) interference
E) chromatic aberration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following phenomena is shown in the figure below? 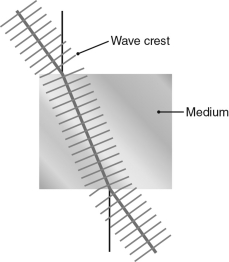
A) reflection
B) chromatic aberration
C) refraction
D) magnification
E) interference

A) reflection
B) chromatic aberration
C) refraction
D) magnification
E) interference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
As a beam of light travels from one medium to another, the change in direction of the beam of light depends on
A) the wavelength of the light.
B) the index of refraction of the outgoing medium.
C) the index of refraction of the incoming medium.
D) the angle of incidence.
E) all of these
A) the wavelength of the light.
B) the index of refraction of the outgoing medium.
C) the index of refraction of the incoming medium.
D) the angle of incidence.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a valid reason to prefer a reflecting over a refracting telescopes?
A) its lack of chromatic aberration
B) its shorter length for the same aperture size
C) its lack of an aperture limit
D) its lighter weight for larger apertures
E) all of these
A) its lack of chromatic aberration
B) its shorter length for the same aperture size
C) its lack of an aperture limit
D) its lighter weight for larger apertures
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Large reflecting telescopes have mirrors that are ________ in shape.
A) spherical
B) parabolic
C) convex
D) hyperbolic
E) cylindrical
A) spherical
B) parabolic
C) convex
D) hyperbolic
E) cylindrical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The aperture of a telescope is which of the following?
A) the length of the telescope
B) the diameter of the telescope tube
C) the diameter of the primary lens/mirror
D) the radius of the primary lens/mirror
E) the diameter of the secondary mirror
A) the length of the telescope
B) the diameter of the telescope tube
C) the diameter of the primary lens/mirror
D) the radius of the primary lens/mirror
E) the diameter of the secondary mirror

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following phenomena is shown in the figure below? 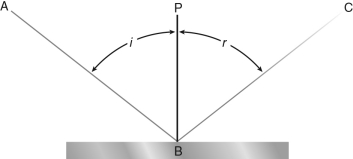
A) reflection
B) refraction
C) magnification
D) diffraction
E) interference

A) reflection
B) refraction
C) magnification
D) diffraction
E) interference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which property of light is responsible for chromatic aberration?
A) reflection
B) interference
C) dispersion
D) diffraction
E) magnification
A) reflection
B) interference
C) dispersion
D) diffraction
E) magnification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Cameras that use adaptive optics provide higher-spatial-resolution images primarily because
A) they operate above Earth's atmosphere.
B) they capture infrared light, which has a longer wavelength than visible light.
C) deformable mirrors are used to correct the blurring due to Earth's atmosphere.
D) composite lenses correct for chromatic aberration.
E) they simulate a much larger telescope.
A) they operate above Earth's atmosphere.
B) they capture infrared light, which has a longer wavelength than visible light.
C) deformable mirrors are used to correct the blurring due to Earth's atmosphere.
D) composite lenses correct for chromatic aberration.
E) they simulate a much larger telescope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Chromatic aberration results from
A) blue light being reflected more than red light.
B) red light being reflected more than blue light.
C) red light being refracted more than blue light.
D) blue light being refracted more than red light.
E) a lens being polished incorrectly.
A) blue light being reflected more than red light.
B) red light being reflected more than blue light.
C) red light being refracted more than blue light.
D) blue light being refracted more than red light.
E) a lens being polished incorrectly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Telescopes revolutionized astronomy because they
A) bring objects closer to us to study.
B) make very small things look very big.
C) gather more light than the human eye, and magnify the image.
D) allow us to run tests on distant objects.
E) make large objects look small enough to study.
A) bring objects closer to us to study.
B) make very small things look very big.
C) gather more light than the human eye, and magnify the image.
D) allow us to run tests on distant objects.
E) make large objects look small enough to study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following phenomena is shown in the figure below? 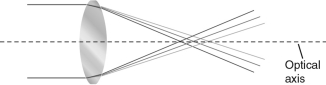
A) reflection
B) chromatic aberration
C) diffraction
D) magnification
E) interference

A) reflection
B) chromatic aberration
C) diffraction
D) magnification
E) interference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why do reflecting telescopes usually have a secondary mirror in addition to a primary mirror?
A) to increase the light-gathering power
B) to make the telescope shorter
C) to increase the magnification
D) to eliminate the focal length
E) to combat chromatic aberration
A) to increase the light-gathering power
B) to make the telescope shorter
C) to increase the magnification
D) to eliminate the focal length
E) to combat chromatic aberration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A prism is able to spread white light out into a spectrum of colors based on the property of
A) reflection.
B) refraction.
C) magnification.
D) resolution.
E) aberration.
A) reflection.
B) refraction.
C) magnification.
D) resolution.
E) aberration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An object sits infinitely far away from a parabolic mirror.At what distance from the mirror will its image be created?
A) It will be imaged at half the focal length.
B) It will be imaged at the focal length.
C) It will be imaged at twice the focal length.
D) No image will be created (the beams would be reflected parallel to each other).
E) The image is created on the other side of the mirror.
A) It will be imaged at half the focal length.
B) It will be imaged at the focal length.
C) It will be imaged at twice the focal length.
D) No image will be created (the beams would be reflected parallel to each other).
E) The image is created on the other side of the mirror.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following phenomena is shown in the figure below? 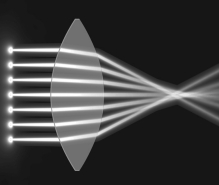
A) reflection
B) refraction
C) magnification
D) diffraction
E) interference

A) reflection
B) refraction
C) magnification
D) diffraction
E) interference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The angular resolution of the largest single-dish radio telescope in the United States, the 100-m Green Bank Telescope, is ________ when it operates at a wavelength of 20 cm.
A) 41 arcmin
B) 6.9 arcmin
C) 4.1 arcmin
D) 6.9 arcsec
E) 4.1 arcsec
A) 41 arcmin
B) 6.9 arcmin
C) 4.1 arcmin
D) 6.9 arcsec
E) 4.1 arcsec

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You are observing the Andromeda Galaxy using both photographic plates and a CCD.If you double the exposure time for both detectors, you
A) double the amount of light recorded by both the photographic plate and the CCD.
B) double the amount of light recorded by the CCD only.
C) double the amount of light recorded by the photographic plate, but the CCD records less.
D) double the amount of light recorded by the photographic plate, but the CCD records more.
E) record less than twice the amount of light on both the photographic plate and the CCD.
A) double the amount of light recorded by both the photographic plate and the CCD.
B) double the amount of light recorded by the CCD only.
C) double the amount of light recorded by the photographic plate, but the CCD records less.
D) double the amount of light recorded by the photographic plate, but the CCD records more.
E) record less than twice the amount of light on both the photographic plate and the CCD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why are large telescopes often placed on top of mountains?
A) Mountaintops are among the few places with enough open space.
B) to be physically closer to objects in space
C) to get above most of the atmosphere
D) Astronomers prefer remote locations in order to avoid distractions.
E) to avoid the noise of major roadways
A) Mountaintops are among the few places with enough open space.
B) to be physically closer to objects in space
C) to get above most of the atmosphere
D) Astronomers prefer remote locations in order to avoid distractions.
E) to avoid the noise of major roadways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) project's Allen Telescope Array will have 350 radio dishes, each with an individual diameter of 6 m, spread out over a circle whose
Diameter is 1 km.What would this array's spatial resolution be when it operates at 6,000 MHz?
A) 10 arcsec
B) 0.10 arcsec
C) 1 arcsec
D) 10 arcmin
E) 1.0 arcmin
Diameter is 1 km.What would this array's spatial resolution be when it operates at 6,000 MHz?
A) 10 arcsec
B) 0.10 arcsec
C) 1 arcsec
D) 10 arcmin
E) 1.0 arcmin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The 305-meter (-m) Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico has a resolution that is closest to that of
A) the Hubble Space Telescope (0.1 arcsec).
B) a human eye (1 arcmin).
C) the Chandra X-ray telescope (0.5 arcsec).
D) a 1-m optical telescope (1 arcsec).
E) one of the 10-m Keck telescopes (0.0133 arcsec).
A) the Hubble Space Telescope (0.1 arcsec).
B) a human eye (1 arcmin).
C) the Chandra X-ray telescope (0.5 arcsec).
D) a 1-m optical telescope (1 arcsec).
E) one of the 10-m Keck telescopes (0.0133 arcsec).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imagine that you could build a telescope of any size in your backyard.Ultimately, the smallest angular size that could be resolved by this telescope would be governed by the
A) blurring caused by Earth's atmosphere.
B) diffraction limit of the telescope.
C) size of the primary mirror.
D) motion of the night sky.
E) magnification of the telescope.
A) blurring caused by Earth's atmosphere.
B) diffraction limit of the telescope.
C) size of the primary mirror.
D) motion of the night sky.
E) magnification of the telescope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If we could increase the quantum efficiency of the human eye, it would
A) allow humans to see a larger range of wavelengths.
B) allow humans to see better at night or other low-light conditions.
C) increase the resolution of the human eye.
D) decrease the resolution of the human eye.
E) not make a difference in the sight of the human eye.
A) allow humans to see a larger range of wavelengths.
B) allow humans to see better at night or other low-light conditions.
C) increase the resolution of the human eye.
D) decrease the resolution of the human eye.
E) not make a difference in the sight of the human eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The magnification of a telescope depends on the focal length of the telescope and
A) the size of the aperture.
B) the type of telescope (refracting vs.reflecting).
C) the wavelengths being observed.
D) the focal length of the eyepiece.
E) the angular resolution of the telescope.
A) the size of the aperture.
B) the type of telescope (refracting vs.reflecting).
C) the wavelengths being observed.
D) the focal length of the eyepiece.
E) the angular resolution of the telescope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The aperture of a telescope partially or totally determines its
A) focal length and magnification.
B) light-gathering power.
C) focal length.
D) light-gathering power and magnification.
E) light-gathering power and diffraction limit.
A) focal length and magnification.
B) light-gathering power.
C) focal length.
D) light-gathering power and magnification.
E) light-gathering power and diffraction limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The two Keck 10-m telescopes, separated by a distance of 85 m, can operate as an optical interferometer.What is its resolution when it observes in the infrared at a wavelength of 2 microns?
A) 0.01 arcsec
B) 0.005 arcsec
C) 0.4 arcsec
D) 0.06 arcsec
E) 0.2 arcsec
A) 0.01 arcsec
B) 0.005 arcsec
C) 0.4 arcsec
D) 0.06 arcsec
E) 0.2 arcsec

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Typically, video is shot using 24-30 frames per second (one frame each 33-42 ms).If a filmmaker shot new experimental video at 100 frames per second (one frame each 10 ms), how would it look during playback to the human eye if played at 100 frames per second?
A) It would look like the video was being fast-forwarded.
B) It would look like the video was about the same as normal video.
C) It would look like the video was being played back in slow motion.
D) It would look like a slideshow, a series of pictures on the screen each for a perceptible amount of time.
E) It would look like the video was about the same speed as normal video, but blurry.
A) It would look like the video was being fast-forwarded.
B) It would look like the video was about the same as normal video.
C) It would look like the video was being played back in slow motion.
D) It would look like a slideshow, a series of pictures on the screen each for a perceptible amount of time.
E) It would look like the video was about the same speed as normal video, but blurry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What part(s) of the human eye is responsible for detecting light?
A) cornea
B) lens
C) pupil
D) rods and cones
E) iris
A) cornea
B) lens
C) pupil
D) rods and cones
E) iris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When we determine the angular resolution of an interferometric array of radio telescopes using the formula /D, the variable D stands for the
A) diameter of the telescopes.
B) separation between the telescopes.
C) magnification of the telescopes.
D) number of telescopes.
E) focal length of the telescopes.
A) diameter of the telescopes.
B) separation between the telescopes.
C) magnification of the telescopes.
D) number of telescopes.
E) focal length of the telescopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which telescope would collect 100 times more light than a 1-m telescope?
A) 100-m telescope
B) 80-m telescope
C) 50-m telescope
D) 30-m telescope
E) 10-m telescope
A) 100-m telescope
B) 80-m telescope
C) 50-m telescope
D) 30-m telescope
E) 10-m telescope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is the best location for an infrared telescope on the on Earth's surface?
A) at sea level, on land
B) at sea level, in the ocean
C) below sea level, on land
D) 5,000 ft above sea level
E) 10,000 ft above sea level
A) at sea level, on land
B) at sea level, in the ocean
C) below sea level, on land
D) 5,000 ft above sea level
E) 10,000 ft above sea level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The diffraction limit of a 4-m telescope is ________ than that of a 2-m telescope.
A) two times larger
B) four times larger
C) four times smaller
D) two times smaller
E) It depends on the type of telescope.
A) two times larger
B) four times larger
C) four times smaller
D) two times smaller
E) It depends on the type of telescope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Before charge-coupled devices (CCDs) were invented, what was the device most commonly used for imaging with optical telescopes?
A) Polaroid cameras
B) photographic glass plates
C) 35-mm film
D) high-speed film
E) video cameras
A) Polaroid cameras
B) photographic glass plates
C) 35-mm film
D) high-speed film
E) video cameras

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The first astronomical detector was
A) the CCD.
B) photoelectric tubes.
C) the human eye.
D) photographic plates.
E) 35-mm film.
A) the CCD.
B) photoelectric tubes.
C) the human eye.
D) photographic plates.
E) 35-mm film.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why can you see fainter stars with an 8-inch telescope than you can see with your naked eye?
A) The telescope collects light over a larger area.
B) The telescope magnifies the field of view.
C) The telescope collects light over a wider range of wavelengths than your eye.
D) The telescope has a wider field of view.
E) The telescope has a longer integration time than your eyes.
A) The telescope collects light over a larger area.
B) The telescope magnifies the field of view.
C) The telescope collects light over a wider range of wavelengths than your eye.
D) The telescope has a wider field of view.
E) The telescope has a longer integration time than your eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The image of a star in the figure below does not look like a single dot due to 
A) refraction.
B) chromatic aberration.
C) spectral dispersion.
D) segmented mirrors.
E) diffraction.

A) refraction.
B) chromatic aberration.
C) spectral dispersion.
D) segmented mirrors.
E) diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A large region of ________ wavelengths are not affected in any way by Earth's atmosphere, and so astronomers can effectively observe at these wavelengths even at sea level.
A) X-ray
B) ultraviolet
C) gamma-ray
D) infrared
E) radio
A) X-ray
B) ultraviolet
C) gamma-ray
D) infrared
E) radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You hear a news story about an X-ray telescope being built on Earth.You know this can't be possible because
A) X-rays do not travel very far through Earth's atmosphere.
B) X-ray telescopes are impossible to build.
C) X-ray telescopes would receive too much interference from hospitals.
D) it would cost too much money.
E) X-rays see through things, making them pointless for observations.
A) X-rays do not travel very far through Earth's atmosphere.
B) X-ray telescopes are impossible to build.
C) X-ray telescopes would receive too much interference from hospitals.
D) it would cost too much money.
E) X-rays see through things, making them pointless for observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why do astronomers use monochromatic CCDs instead of color CCDs like your cell phone does?
A) Color CCDs have worse angular resolution.
B) They don't make color CCDs large enough.
C) Monochromatic CCDs last longer.
D) Monochromatic CCDs have smaller angular resolution.
E) Color CCDs can't detect infrared light.
A) Color CCDs have worse angular resolution.
B) They don't make color CCDs large enough.
C) Monochromatic CCDs last longer.
D) Monochromatic CCDs have smaller angular resolution.
E) Color CCDs can't detect infrared light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An atmospheric window is
A) a giant glass dome.
B) a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can reach the ground.
C) a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot reach the ground.
D) ultraviolet.
E) X-rays.
A) a giant glass dome.
B) a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that can reach the ground.
C) a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot reach the ground.
D) ultraviolet.
E) X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A diffraction grating is
A) a filter for imaging.
B) a device that uses interference to spread light out into different wavelengths.
C) a complicated series of prisms.
D) a device that counteracts the effects of chromatic aberration.
E) the pattern of light resulting from the spectrum of a star.
A) a filter for imaging.
B) a device that uses interference to spread light out into different wavelengths.
C) a complicated series of prisms.
D) a device that counteracts the effects of chromatic aberration.
E) the pattern of light resulting from the spectrum of a star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Astronomers can use ground-based telescopes to observe large portions of what regions of the electromagnetic spectrum?
A) visible and infrared
B) visible and ultraviolet
C) visible and radio
D) visible, ultraviolet, and infrared
E) infrared and radio
A) visible and infrared
B) visible and ultraviolet
C) visible and radio
D) visible, ultraviolet, and infrared
E) infrared and radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The figure below illustrates 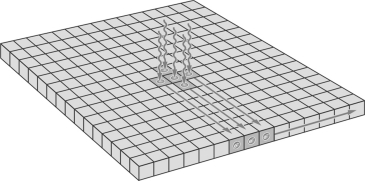
A) a technique for sorting stars.
B) quantum efficiency.
C) a CCD chip recording incident photons.
D) diffraction.
E) a grid of photographic plates.

A) a technique for sorting stars.
B) quantum efficiency.
C) a CCD chip recording incident photons.
D) diffraction.
E) a grid of photographic plates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Grote Reber conducted the first radio survey of the sky in the 1930s and 1940s with his 9-m-diameter radio telescope.Why did his telescope need to be so large?
A) He needed a large light-collecting area because radio sources are notoriously dim.
B) He needed better angular resolution to identify sources because radio waves are so long.
C) He needed a higher magnification to identify sources because radio sources are quite small.
D) He needed a longer focal length because radio sources are so far away.
E) He needed a shorter focal length because radio sources are so far away.
A) He needed a large light-collecting area because radio sources are notoriously dim.
B) He needed better angular resolution to identify sources because radio waves are so long.
C) He needed a higher magnification to identify sources because radio sources are quite small.
D) He needed a longer focal length because radio sources are so far away.
E) He needed a shorter focal length because radio sources are so far away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Water vapor in Earth's atmosphere primarily absorbs which type of photons?
A) radio
B) infrared
C) visible
D) ultraviolet
E) X-ray
A) radio
B) infrared
C) visible
D) ultraviolet
E) X-ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the biggest disadvantage of putting a telescope in space?
A) Astronomers don't have as much control in choosing what to observe.
B) Astronomers have to wait until the telescopes come back to Earth to get their images.
C) Space telescopes can only observe in certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
D) Space telescopes don't last long before they fall back to Earth.
E) Space telescopes are much more expensive than similar ground-based telescopes.
A) Astronomers don't have as much control in choosing what to observe.
B) Astronomers have to wait until the telescopes come back to Earth to get their images.
C) Space telescopes can only observe in certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
D) Space telescopes don't last long before they fall back to Earth.
E) Space telescopes are much more expensive than similar ground-based telescopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A spectrograph is
A) a device used for clearly resolving physical details of distant objects.
B) typically made from two ordinary pieces of glass.
C) a device used to measure the intensity of light at each wavelength.
D) a radio telescope.
E) a visible-light telescope.
A) a device used for clearly resolving physical details of distant objects.
B) typically made from two ordinary pieces of glass.
C) a device used to measure the intensity of light at each wavelength.
D) a radio telescope.
E) a visible-light telescope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Most modern spectrographs use a ________ to disperse the light from an object.
A) spherical mirror
B) lens
C) glass prism
D) diffraction grating
E) parabolic mirror
A) spherical mirror
B) lens
C) glass prism
D) diffraction grating
E) parabolic mirror

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An interferometer requires a minimum of how many telescopes?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 10
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Ultraviolet radiation with a wavelength shorter than about 200 nm is hard to observe primarily because
A) Earth's atmosphere easily absorbs it.
B) no space-based telescopes operate at ultraviolet wavelengths.
C) only the lowest-mass stars emit ultraviolet light.
D) very few objects emit at ultraviolet wavelengths.
E) Earth emits too much ultraviolet background light.
A) Earth's atmosphere easily absorbs it.
B) no space-based telescopes operate at ultraviolet wavelengths.
C) only the lowest-mass stars emit ultraviolet light.
D) very few objects emit at ultraviolet wavelengths.
E) Earth emits too much ultraviolet background light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Photographic plates provide an improvement over naked-eye observations because
A) it is possible to observe a larger field of view.
B) the quantum efficiency is higher.
C) the image resolution is much better.
D) it is possible to detect fainter objects.
E) the integration time is much shorter.
A) it is possible to observe a larger field of view.
B) the quantum efficiency is higher.
C) the image resolution is much better.
D) it is possible to detect fainter objects.
E) the integration time is much shorter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Arrays of radio telescopes can produce much better resolution than single-dish telescopes because they work based on the principle of
A) reflection.
B) refraction.
C) dispersion.
D) diffraction.
E) interference.
A) reflection.
B) refraction.
C) dispersion.
D) diffraction.
E) interference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What property of light allows a grating to disperse the light from an object into a spectrum?
A) interference
B) reflection
C) refraction
D) aberration
E) magnification
A) interference
B) reflection
C) refraction
D) aberration
E) magnification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The major advantage CCDs have over other imaging techniques is that
A) they have a higher quantum efficiency.
B) they have a linear response to light.
C) they yield output in digital format.
D) they operate at visible and near-infrared wavelengths.
E) all of these are correct.
A) they have a higher quantum efficiency.
B) they have a linear response to light.
C) they yield output in digital format.
D) they operate at visible and near-infrared wavelengths.
E) all of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In order to observe gamma rays from space, astronomers must first
A) observe gamma rays, as they are still theoretical.
B) place a gamma ray telescope above Earth's atmosphere.
C) place a gamma ray filter on a visible light telescope.
D) build a very large diffraction grating.
E) build a very small telescope in order to detect such small wavelengths.
A) observe gamma rays, as they are still theoretical.
B) place a gamma ray telescope above Earth's atmosphere.
C) place a gamma ray filter on a visible light telescope.
D) build a very large diffraction grating.
E) build a very small telescope in order to detect such small wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
NASA's Kuiper Airborne Observatory and the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) are two examples of telescopes placed in high-flying aircraft.Why would astronomers put telescopes in airplanes?
A) to get the telescopes closer to the stars
B) to get the telescopes away from the light pollution of cities
C) to get the telescopes above the majority of the water vapor in Earth's atmosphere
D) to be able to observe one object for more than 24 hours without stopping
E) to allow the telescopes to observe the full spectrum of light
A) to get the telescopes closer to the stars
B) to get the telescopes away from the light pollution of cities
C) to get the telescopes above the majority of the water vapor in Earth's atmosphere
D) to be able to observe one object for more than 24 hours without stopping
E) to allow the telescopes to observe the full spectrum of light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain why stars "twinkle" when viewed from the ground.Would they twinkle if they were viewed from outer space?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Particle accelerators that smash atoms or particles together at high speeds, such as the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), are important tools used for simulating conditions in
A) the early universe.
B) the solar wind.
C) red giants.
D) brown dwarf stars.
E) planetary nebula.
A) the early universe.
B) the solar wind.
C) red giants.
D) brown dwarf stars.
E) planetary nebula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Label the eyepiece, lens, focus, and focal length of the telescope shown in the figure below. 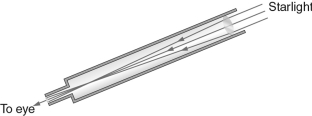


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Remote-sensing instruments have been used to
A) map surfaces hidden beneath thick atmospheres.
B) measure the composition of atmospheres.
C) identify geological features.
D) watch weather patterns develop.
E) All of these are correct.
A) map surfaces hidden beneath thick atmospheres.
B) measure the composition of atmospheres.
C) identify geological features.
D) watch weather patterns develop.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Landers, rovers, and/or atmospheric probes have visited which object(s) listed below in an effort to gain new information about our Solar System?
A) Jupiter
B) Titan, Saturn's moon
C) Mars
D) Eros, an asteroid
E) all of these
A) Jupiter
B) Titan, Saturn's moon
C) Mars
D) Eros, an asteroid
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Using robotic probes to fly by other planets is advantageous as compared to orbiting or landing probes on those planets because
A) cameras work best at high altitudes.
B) flybys are easier and cheaper.
C) planetary atmospheres cause orbiters and rovers to burn up quickly.
D) maintaining an orbit or landing requires too much energy.
E) flyby probes return to Earth and return samples of distant objects.
A) cameras work best at high altitudes.
B) flybys are easier and cheaper.
C) planetary atmospheres cause orbiters and rovers to burn up quickly.
D) maintaining an orbit or landing requires too much energy.
E) flyby probes return to Earth and return samples of distant objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
LIGO and VIRGO are facilities that detect
A) neutrinos
B) gravitational waves.
C) green photons.
D) short wavelengths of light.
E) long wavelengths of light.
A) neutrinos
B) gravitational waves.
C) green photons.
D) short wavelengths of light.
E) long wavelengths of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In 2008, the Cassini spacecraft made a flyby of Enceladus, one of the icy moons of Saturn.If the spacecraft's high-resolution camera had an angular resolution of 3 arcsec and it flew at an altitude of 23 km above Enceladus's surface, approximately how large an object could be resolved on the surface?
A) 3 m
B) 30 cm
C) 30 km
D) 5 cm
E) 50 m
A) 3 m
B) 30 cm
C) 30 km
D) 5 cm
E) 50 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What geographic properties should be considered when choosing a location on Earth for a ground-based research telescope, in order to get the best possible resolution and view of the sky? Name and discuss the reasoning behind at least two such properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following cannot be directly detected using a telescope?
A) X-rays
B) visible light
C) infrared light
D) neutrinos
E) ultraviolet light
A) X-rays
B) visible light
C) infrared light
D) neutrinos
E) ultraviolet light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why do reflecting telescopes use curved mirrors instead of flat mirrors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A small backyard refracting telescope might have an aperture of 50 mm, a focal length of
600 mm, and three eyepieces with a focal lengths of 20 mm, 12 mm, and 4 mm, respectively.
What magnification(s) is (or are) possible with this equipment?
600 mm, and three eyepieces with a focal lengths of 20 mm, 12 mm, and 4 mm, respectively.
What magnification(s) is (or are) possible with this equipment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Telescopes and satellites such as Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE), Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), and Planck are designed to detect microwave radiation emitted by
A) galaxies.
B) black holes.
C) planets.
D) the Big Bang.
E) stars.
A) galaxies.
B) black holes.
C) planets.
D) the Big Bang.
E) stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Label the eyepiece, primary mirror, secondary mirror, focus, and focal length of the telescope shown in the figure below. 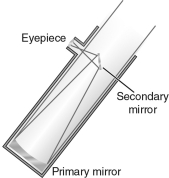


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain why the largest telescopes are not refracting telescopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Of the following, the best location for a neutrino detector is
A) in orbit around Earth.
B) on a mountaintop.
C) far from Earth.
D) at sea level.
E) deep underground.
A) in orbit around Earth.
B) on a mountaintop.
C) far from Earth.
D) at sea level.
E) deep underground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Explain why chromatic aberration is a problem for refracting lenses but not for reflecting mirrors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain how adaptive optics help compensate for atmospheric seeing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Samples of which celestial object(s) have been brought back to Earth to be studied in detail?
A) a comet
B) the solar wind
C) an asteroid
D) the Moon
E) all of these are correct.
A) a comet
B) the solar wind
C) an asteroid
D) the Moon
E) all of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How much larger is the light-gathering power of a 10-inch telescope than the human eye?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



