Deck 9: Atmospheres of the Terrestrial Planets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Atmospheres of the Terrestrial Planets
1
Why did the terrestrial planets lose the majority of the gases in their primary atmospheres?
A) They were too hot and their escape velocities too low to hold onto them.
B) The solar wind was too strong and destroyed the planets' magnetospheres.
C) Their high surface temperatures made the gas chemically react with the rock.
D) The initial gases were so heavy when the planet differentiated that they sank to the core.
E) There wasn't much gas to begin with.
A) They were too hot and their escape velocities too low to hold onto them.
B) The solar wind was too strong and destroyed the planets' magnetospheres.
C) Their high surface temperatures made the gas chemically react with the rock.
D) The initial gases were so heavy when the planet differentiated that they sank to the core.
E) There wasn't much gas to begin with.
They were too hot and their escape velocities too low to hold onto them.
2
We do not find asteroids with thick atmospheres because
A) they are too close to the Sun, on average.
B) they are too far from the Sun, on average.
C) they do not have volcanoes.
D) they are too small.
E) they rotate too quickly.
A) they are too close to the Sun, on average.
B) they are too far from the Sun, on average.
C) they do not have volcanoes.
D) they are too small.
E) they rotate too quickly.
they are too small.
3
What makes carbon dioxide a highly effective greenhouse gas?
A) It easily absorbs UV radiation.
B) It easily absorbs visible light.
C) It easily absorbs infrared radiation.
D) It easily reacts chemically with rock.
E) It easily photodissociates in the upper atmosphere.
A) It easily absorbs UV radiation.
B) It easily absorbs visible light.
C) It easily absorbs infrared radiation.
D) It easily reacts chemically with rock.
E) It easily photodissociates in the upper atmosphere.
It easily absorbs infrared radiation.
4
If it were not for the greenhouse effect on Earth,
A) there would be no liquid water on Earth.
B) life as we know it would not have developed on Earth.
C) it would be a much colder planet.
D) there would be no oxygen in Earth's atmosphere.
E) All of these are results of the greenhouse effect.
A) there would be no liquid water on Earth.
B) life as we know it would not have developed on Earth.
C) it would be a much colder planet.
D) there would be no oxygen in Earth's atmosphere.
E) All of these are results of the greenhouse effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The terrestrial planets, ranked in order of decreasing atmospheric density, are
A) Venus, Earth, Mars, Mercury
B) Venus, Mars, Earth, Mercury
C) Mercury, Mars, Earth, Venus
D) Mars, Venus, Mercury, Earth
E) Mars, Earth, Venus, Mercury
A) Venus, Earth, Mars, Mercury
B) Venus, Mars, Earth, Mercury
C) Mercury, Mars, Earth, Venus
D) Mars, Venus, Mercury, Earth
E) Mars, Earth, Venus, Mercury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The greenhouse effect is the
A) trapping of infrared radiation by the atmosphere.
B) accentuated growth of plants near the equator, compared to other regions.
C) capturing of visible and UV radiation from the Sun by the atmosphere.
D) shielding of life-forms from solar UV radiation by the ozone layer.
E) process of plants generating oxygen.
A) trapping of infrared radiation by the atmosphere.
B) accentuated growth of plants near the equator, compared to other regions.
C) capturing of visible and UV radiation from the Sun by the atmosphere.
D) shielding of life-forms from solar UV radiation by the ozone layer.
E) process of plants generating oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the absence of a greenhouse effect, what would happen to Earth's oceans?
A) They would evaporate.
B) They would freeze over.
C) They would be rapidly absorbed into the surface rocks.
D) They would dissociate into ozone and hydrogen.
E) Nothing would change.
A) They would evaporate.
B) They would freeze over.
C) They would be rapidly absorbed into the surface rocks.
D) They would dissociate into ozone and hydrogen.
E) Nothing would change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The majority of the nitrogen in the air we breathe today was originally in what form?
A) amino acids
B) ammonia
C) hydrocarbons
D) halogens
E) atomic nitrogen gas emitted by the Sun.
A) amino acids
B) ammonia
C) hydrocarbons
D) halogens
E) atomic nitrogen gas emitted by the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The nitrogen in Earth's atmosphere primarily came from
A) ammonia delivered by comet impacts.
B) photosynthesis done by algae and plants.
C) oxidation of silicate-rich minerals.
D) rock delivered by asteroid impacts.
E) its primary atmosphere.
A) ammonia delivered by comet impacts.
B) photosynthesis done by algae and plants.
C) oxidation of silicate-rich minerals.
D) rock delivered by asteroid impacts.
E) its primary atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why does Mercury have so little gas in its atmosphere?
A) Its mass is small.
B) It has a high maximum temperature.
C) It is close to the Sun.
D) Its escape velocity is low.
E) all of these
A) Its mass is small.
B) It has a high maximum temperature.
C) It is close to the Sun.
D) Its escape velocity is low.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which molecule moves with the fastest average speed while being bound in Earth's atmosphere in thermal equilibrium?
A) water, H2O (atomic mass = 18)
B) carbon dioxide, CO2 (atomic mass =44)
C) nitrogen (atomic mass= 28)
D) oxygen (atomic mass = 32)
E) hydrogen, H2 (atomic mass = 2)
A) water, H2O (atomic mass = 18)
B) carbon dioxide, CO2 (atomic mass =44)
C) nitrogen (atomic mass= 28)
D) oxygen (atomic mass = 32)
E) hydrogen, H2 (atomic mass = 2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Based solely on mass and distance from the Sun, which of the following terrestrial planets would you expect to be unable to retain a secondary atmosphere?
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Earth
D) Mars
E) Venus and Earth
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Earth
D) Mars
E) Venus and Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Earth has roughly ________ times more atmospheric pressure than Mars and ________ times less than Venus.
A) 10; 10
B) 200; 100
C) 2,000; 2
D) 2; 10
E) 1,000; 200
A) 10; 10
B) 200; 100
C) 2,000; 2
D) 2; 10
E) 1,000; 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When learning about light, we predicted that Venus should have a temperature of 230 K based on its albedo and distance from the Sun.Why is Venus's observed average surface temperature equal to 740 K, which is hot enough to melt lead?
A) Venus has slow retrograde rotation, and its seasons are very long.
B) Venus has many active volcanoes that release heat into its atmosphere.
C) Venus has a very thin atmosphere, and so more sunlight falls onto its surface.
D) Venus has a strong greenhouse effect.
E) Venus has a highly eccentric orbit and is sometimes much closer to the Sun than other times.
A) Venus has slow retrograde rotation, and its seasons are very long.
B) Venus has many active volcanoes that release heat into its atmosphere.
C) Venus has a very thin atmosphere, and so more sunlight falls onto its surface.
D) Venus has a strong greenhouse effect.
E) Venus has a highly eccentric orbit and is sometimes much closer to the Sun than other times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The greenhouse effect raises Earth's surface temperature by roughly
A) 0 K.
B) 0.35 K.
C) 3.5 K.
D) 35 K.
E) 350 K.
A) 0 K.
B) 0.35 K.
C) 3.5 K.
D) 35 K.
E) 350 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The main greenhouse gases in the atmosphere of the terrestrial planets are
A) oxygen and nitrogen.
B) methane and ozone.
C) carbon dioxide and water vapor.
D) hydrogen and helium.
E) methane and ammonia.
A) oxygen and nitrogen.
B) methane and ozone.
C) carbon dioxide and water vapor.
D) hydrogen and helium.
E) methane and ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The presence of gases such as carbon dioxide and water vapor in a planet's atmosphere is direct evidence of ________ in a planet's history.
A) high surface temperatures
B) volcanic activity
C) cometary impacts
D) a lack of asteroid impacts
E) the greenhouse effect
A) high surface temperatures
B) volcanic activity
C) cometary impacts
D) a lack of asteroid impacts
E) the greenhouse effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the carbon dioxide in Earth's rocks were suddenly released into its atmosphere, what would happen?
A) It would rapidly escape into space.
B) It would dissociate into carbon and oxygen.
C) It would collect as ice on the north and south poles.
D) It would cause a runaway greenhouse effect.
E) There would be no effect.
A) It would rapidly escape into space.
B) It would dissociate into carbon and oxygen.
C) It would collect as ice on the north and south poles.
D) It would cause a runaway greenhouse effect.
E) There would be no effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Earth releases the energy it receives from the Sun by emitting ________ radiation.
A) infrared
B) visible
C) ultraviolet (UV)
D) radio
E) microwave
A) infrared
B) visible
C) ultraviolet (UV)
D) radio
E) microwave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following processes did NOT contribute gas to Earth's secondary atmosphere?
A) volcanism
B) accretion
C) oxidation
D) comet impacts
E) All of these contributed gases to Earth's secondary atmosphere.
A) volcanism
B) accretion
C) oxidation
D) comet impacts
E) All of these contributed gases to Earth's secondary atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If you found absorption from ________ in the spectrum of a planet, you could conclude that it might contain some form of life.
A) oxygen only
B) methane only
C) water vapor only
D) oxygen, methane, or water vapor
E) carbon dioxide
A) oxygen only
B) methane only
C) water vapor only
D) oxygen, methane, or water vapor
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For the first 1 billion years of Earth's evolution, the fraction of oxygen in its atmosphere was approximately
A) zero.
B) half of what it is today.
C) 2 times what it is today.
D) 10 times what it is today.
E) the same as it is today.
A) zero.
B) half of what it is today.
C) 2 times what it is today.
D) 10 times what it is today.
E) the same as it is today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How does the fraction of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere today compare to what it was 3 billion years ago?
A) It has significantly declined.
B) It has significantly increased.
C) It increased up to 2 billion years ago but has been declining ever since.
D) It declined up to 2 billion years ago but has been increasing ever since.
E) It hasn't changed.
A) It has significantly declined.
B) It has significantly increased.
C) It increased up to 2 billion years ago but has been declining ever since.
D) It declined up to 2 billion years ago but has been increasing ever since.
E) It hasn't changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to the figure below, approximately how many years ago did oxygen finally get to half its current abundance in Earth's atmosphere? 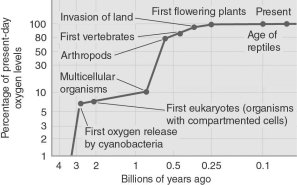
A) 3 billion years ago
B) 1 billion years ago
C) 0.6 billion years ago
D) 0.25 billion years ago
E) 0.1 billion years ago

A) 3 billion years ago
B) 1 billion years ago
C) 0.6 billion years ago
D) 0.25 billion years ago
E) 0.1 billion years ago

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Approximately how long after the Solar System formed did it take for oxygen to get to within 80 percent of its present abundance in Earth's atmosphere?
A) 4 billion years
B) 1 billion years
C) 400 million years
D) 1 million years
E) Oxygen was always a primary component of Earth's atmosphere.
A) 4 billion years
B) 1 billion years
C) 400 million years
D) 1 million years
E) Oxygen was always a primary component of Earth's atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A gas eventually will escape from a planet's atmosphere if the average velocity of the atoms exceeds 1/6 times the escape velocity of the planet.If the average velocity of water vapor in Venus's atmosphere is 0.9 km/s, would it eventually escape into outer space? Note that Venus's mass is 5 *1024 kg, its radius is 6,050 km, and G = 6.67 *10 - 11 N m 2 /kg 2 .
A) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 0.51 km/s.
B) Water vapor would not escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 1.7 km/s.
C) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 0.42 km/s.
D) Water vapor would not escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 2.6 km/s.
E) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 1.3 km/s.
A) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 0.51 km/s.
B) Water vapor would not escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 1.7 km/s.
C) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 0.42 km/s.
D) Water vapor would not escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 2.6 km/s.
E) Water vapor would escape because 1/6 times the escape velocity is 1.3 km/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If an average hydrogen atom in Earth's atmosphere has a velocity of 2.5 km/s, what would be the average velocity of an oxygen molecule in Earth's atmosphere? Note that the atomic mass of an oxygen atom is 16 times that of a hydrogen atom.
A) 0.16 km/s
B) 2.5 km/s
C) 0.62 km/s
D) 0.44 km/s
E) 0.25 km/s
A) 0.16 km/s
B) 2.5 km/s
C) 0.62 km/s
D) 0.44 km/s
E) 0.25 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If photosynthesis were to disappear on Earth,
A) the atmosphere would become less dense.
B) oxygen would disappear from the atmosphere.
C) the atmosphere would become hotter.
D) nitrogen would disappear from the atmosphere.
E) the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere would decrease.
A) the atmosphere would become less dense.
B) oxygen would disappear from the atmosphere.
C) the atmosphere would become hotter.
D) nitrogen would disappear from the atmosphere.
E) the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
By examining the three images in the following figure, what can you conclude? 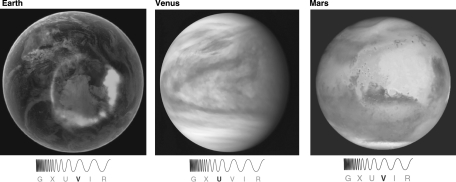
A) Venus is covered with clouds.
B) Earth has a large amount of liquid water.
C) Some form of ice does exist on Mars, but it does not have large amounts of liquid water.
D) The planets in order from the least to most dense atmospheres are Mars, Earth, and Venus.
E) all of these

A) Venus is covered with clouds.
B) Earth has a large amount of liquid water.
C) Some form of ice does exist on Mars, but it does not have large amounts of liquid water.
D) The planets in order from the least to most dense atmospheres are Mars, Earth, and Venus.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The best way to use a telescope to look for life on other planets is to
A) search for absorption from nitrogen in their atmospheres.
B) search for absorption from oxygen in their atmospheres.
C) search for emission lines from water vapor in their atmospheres.
D) search for carbon dioxide on their moons.
E) look for artificial satellites.
A) search for absorption from nitrogen in their atmospheres.
B) search for absorption from oxygen in their atmospheres.
C) search for emission lines from water vapor in their atmospheres.
D) search for carbon dioxide on their moons.
E) look for artificial satellites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Would a nitrogen atom in Venus's atmosphere, whose temperature is 740 K, eventually escape into outer space? Note that a nitrogen atom has a mass that is 14 times that of a hydrogen atom.Recall that atoms eventually will escape if their average velocity is greater than 1/6 times the escape velocity of the planet.The escape velocity of Venus is 10 km/s.For comparison, a hydrogen atom has an average velocity of 2.5 km/s at a temperature of 300 K.
A) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 0.4 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
B) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 1.0 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
C) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 1.0 km/s, and nitrogen escapes.
D) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 4.5 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
E) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 4.5 km/s, and nitrogen escapes.
A) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 0.4 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
B) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 1.0 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
C) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 1.0 km/s, and nitrogen escapes.
D) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 4.5 km/s, and nitrogen does not escape.
E) The average velocity of nitrogen atoms is 4.5 km/s, and nitrogen escapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ________ in our atmosphere is a direct consequence of the emergence of life.
A) carbon dioxide
B) water vapor
C) nitrogen
D) oxygen
E) helium
A) carbon dioxide
B) water vapor
C) nitrogen
D) oxygen
E) helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Like Mars and Venus, Earth originally had a significant amount of carbon dioxide in its atmosphere.Where is the majority of the carbon now?
A) It has escaped into outer space.
B) It is bound up in the plant life on Earth.
C) It is bound up in rocks.
D) It is dissolved into the oceans.
E) It is still in the atmosphere in the form of complex molecules.
A) It has escaped into outer space.
B) It is bound up in the plant life on Earth.
C) It is bound up in rocks.
D) It is dissolved into the oceans.
E) It is still in the atmosphere in the form of complex molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Venus and Earth probably formed with similar amounts of carbon dioxide in their secondary atmospheres.Which of the following is true?
A) The majority of Earth's carbon dioxide escaped into space because of its hotter temperature, whereas Venus's carbon dioxide remains gravitationally bound to Venus.
B) The majority of Earth's carbon is now bound up in rock, whereas Venus's remains in its atmosphere.
C) Earth lost more of its secondary atmosphere because it was bombarded by more planetesimals than Venus.
D) The majority of Earth's carbon was absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
E) Earth and Venus still have equal amounts of carbon dioxide in their atmospheres.
A) The majority of Earth's carbon dioxide escaped into space because of its hotter temperature, whereas Venus's carbon dioxide remains gravitationally bound to Venus.
B) The majority of Earth's carbon is now bound up in rock, whereas Venus's remains in its atmosphere.
C) Earth lost more of its secondary atmosphere because it was bombarded by more planetesimals than Venus.
D) The majority of Earth's carbon was absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
E) Earth and Venus still have equal amounts of carbon dioxide in their atmospheres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The major difference in the composition of Earth's atmosphere compared to the atmospheres of Venus and Mars is a direct consequence of
A) life on Earth.
B) Earth's plate tectonics.
C) differences in the greenhouse effect.
D) the presence of liquid water.
E) differing distances from the Sun.
A) life on Earth.
B) Earth's plate tectonics.
C) differences in the greenhouse effect.
D) the presence of liquid water.
E) differing distances from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
By approximately ________ years ago, ________ had produced oxygen in enough amounts for it to make up a significant fraction of Earth's atmosphere.
A) 100 million; trees and plants
B) 1 billion; trees and plants
C) 250 million; bacteria and algae
D) 2.5 billion; bacteria and algae
E) 2,000; animals and humans
A) 100 million; trees and plants
B) 1 billion; trees and plants
C) 250 million; bacteria and algae
D) 2.5 billion; bacteria and algae
E) 2,000; animals and humans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If water vapor were released from Venus's surface because of tectonic activity into its upper atmosphere, what would most likely happen to it?
A) The water vapor would relieve the greenhouse effect and decrease Venus's surface temperature.
B) Water droplets would condense into rain and form lakes on Venus's surface.
C) The water vapor would chemically react with carbon dioxide and form acid rain.
D) UV light would break apart the water molecules, and the hydrogen would be lost into space.
E) It would rise into the atmosphere and form hurricane-like storms.
A) The water vapor would relieve the greenhouse effect and decrease Venus's surface temperature.
B) Water droplets would condense into rain and form lakes on Venus's surface.
C) The water vapor would chemically react with carbon dioxide and form acid rain.
D) UV light would break apart the water molecules, and the hydrogen would be lost into space.
E) It would rise into the atmosphere and form hurricane-like storms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If sunlight broke up water molecules in Venus's atmosphere, would the hydrogen atoms escape into outer space? Note that Venus's temperature is 740 K.Recall that gas eventually will escape if the average velocity of its atoms is greater than 1/6 times the escape velocity of the planet.The escape velocity of Venus is 10 km/s.
A) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 0.8 km/s.
B) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 3.9 km/s.
C) Yes, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 3.9 km/s.
D) Yes, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 25 km/s.
E) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 25 km/s.
A) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 0.8 km/s.
B) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 3.9 km/s.
C) Yes, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 3.9 km/s.
D) Yes, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 25 km/s.
E) No, the average velocity of hydrogen atoms would be 25 km/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
According to the following figure, about how long ago did oxygen reach its current abundance in Earth's atmosphere? 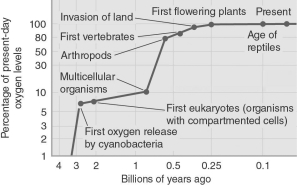
A) 3 billion years ago
B) 1 billion years ago
C) 0.5 billion years ago
D) 0.25 billion years ago
E) 0.1 billion years ago

A) 3 billion years ago
B) 1 billion years ago
C) 0.5 billion years ago
D) 0.25 billion years ago
E) 0.1 billion years ago

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Would water molecules in Venus's atmosphere, whose temperature is 740 K, eventually escape into outer space? Note that a water molecule has a mass that is 18 times that of a hydrogen atom.The escape velocity of Venus is 10 km/s.For comparison, a hydrogen atom has an average velocity of 2.5 km/s at a temperature of 300 K.
A) No, the average velocity of water molecules is 0.9 km/s.
B) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 0.9 km/s.
C) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 2.1 km/s.
D) No, the average velocity of water molecules is 2.1 km/s.
E) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 19 km/s.
A) No, the average velocity of water molecules is 0.9 km/s.
B) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 0.9 km/s.
C) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 2.1 km/s.
D) No, the average velocity of water molecules is 2.1 km/s.
E) Yes, the average velocity of water molecules is 19 km/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Earth's magnetosphere affects
A) charged particles.
B) blue photons of light.
C) red photons of light.
D) all photons of light.
E) neutrinos only.
A) charged particles.
B) blue photons of light.
C) red photons of light.
D) all photons of light.
E) neutrinos only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Large-scale winds are generated on Earth primarily because of
A) strong updrafts from the equator and air sinking near the poles.
B) uneven heating of the surface and rotation of the planet.
C) water condensation onto mountains.
D) hot air rising and cool air sinking.
E) charged particles interacting with the magnetosphere.
A) strong updrafts from the equator and air sinking near the poles.
B) uneven heating of the surface and rotation of the planet.
C) water condensation onto mountains.
D) hot air rising and cool air sinking.
E) charged particles interacting with the magnetosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Without the ozone layer, life on Earth would be in danger from increased levels of ________ radiation.
A) UV
B) X-ray
C) gamma ray
D) infrared
E) microwave
A) UV
B) X-ray
C) gamma ray
D) infrared
E) microwave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
According to the way the layers of Earth's atmosphere are defined in the left figure below, the atmosphere of Venus has only ________ distinct layer(s). 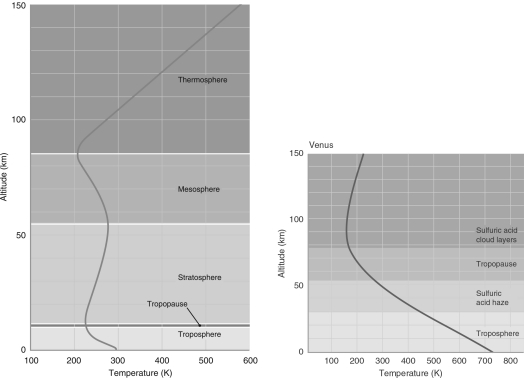
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why are auroras produced only near the northern and southern magnetic poles of a planet?
A) Those are the locations where the atmosphere is thinner, letting particles penetrate.
B) The poles are pointing toward the Sun, so they receive more solar wind particles.
C) The oxygen atoms responsible for auroral emission only exist near the poles.
D) Charged particles are forced to flow along Earth's magnetic field lines, which come out of Earth's poles.
E) Auroras require large amounts of reflective ice or snow in order to be visible.
A) Those are the locations where the atmosphere is thinner, letting particles penetrate.
B) The poles are pointing toward the Sun, so they receive more solar wind particles.
C) The oxygen atoms responsible for auroral emission only exist near the poles.
D) Charged particles are forced to flow along Earth's magnetic field lines, which come out of Earth's poles.
E) Auroras require large amounts of reflective ice or snow in order to be visible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Auroras are caused by
A) gases fluorescing in the atmosphere because of collisions with solar wind particles.
B) the magnetosphere of Earth touching its atmosphere.
C) the ozone layer being destroyed by UV light.
D) the atmospheric greenhouse effect.
E) the scattering of sunlight from particles in Earth's stratosphere.
A) gases fluorescing in the atmosphere because of collisions with solar wind particles.
B) the magnetosphere of Earth touching its atmosphere.
C) the ozone layer being destroyed by UV light.
D) the atmospheric greenhouse effect.
E) the scattering of sunlight from particles in Earth's stratosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the following figure, the different layers of Earth's atmosphere are defined by 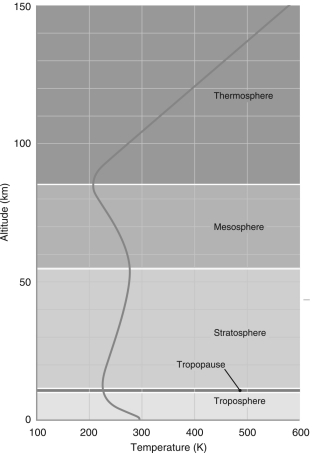
A) how the temperature varies with altitude.
B) how the pressure varies with altitude.
C) how the density varies with altitude.
D) different temperature ranges.
E) different pressure ranges.

A) how the temperature varies with altitude.
B) how the pressure varies with altitude.
C) how the density varies with altitude.
D) different temperature ranges.
E) different pressure ranges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The variations in sulfuric acid in Venus's atmosphere are thought to be evidence that
A) it has a liquid surface.
B) it is volcanically active.
C) it has a strong magnetosphere.
D) there are strong winds on the surface.
E) there is life on Venus's surface.
A) it has a liquid surface.
B) it is volcanically active.
C) it has a strong magnetosphere.
D) there are strong winds on the surface.
E) there is life on Venus's surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the main reason Hadley circulation in a planet's atmosphere breaks up into zonal winds?
A) convection driven by solar heating
B) heating from the solar wind
C) hurricanes developing along the planet's equator
D) a planet's rapid rotation
E) heating from the greenhouse effect
A) convection driven by solar heating
B) heating from the solar wind
C) hurricanes developing along the planet's equator
D) a planet's rapid rotation
E) heating from the greenhouse effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Runaway convection in Earth's atmosphere can lead to
A) snow.
B) destruction of ozone.
C) auroras.
D) acid rain.
E) violent storms.
A) snow.
B) destruction of ozone.
C) auroras.
D) acid rain.
E) violent storms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Hurricanes are powered by
A) Hadley circulation.
B) the Coriolis effect.
C) the heat of vaporization of water.
D) electrical conductivity of water.
E) the greenhouse effect.
A) Hadley circulation.
B) the Coriolis effect.
C) the heat of vaporization of water.
D) electrical conductivity of water.
E) the greenhouse effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The shape of Earth's magnetosphere is modified by
A) the Moon's tidal force.
B) the solar wind.
C) Earth's own gravity.
D) asymmetries in the shape of Earth's core.
E) Earth's elliptical orbit.
A) the Moon's tidal force.
B) the solar wind.
C) Earth's own gravity.
D) asymmetries in the shape of Earth's core.
E) Earth's elliptical orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The only two layers of Earth's atmosphere that have temperature gradients that allow convection to take place are 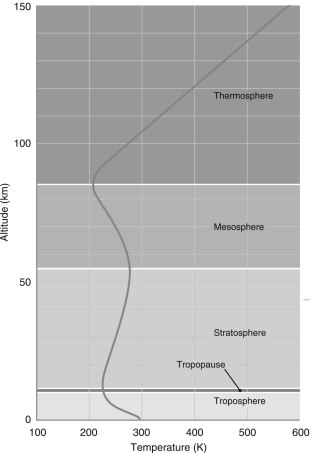
A) the troposphere and the thermosphere.
B) the mesosphere and the stratosphere.
C) the thermosphere and the stratosphere.
D) the troposphere and the mesosphere.
E) the troposphere and the stratosphere.

A) the troposphere and the thermosphere.
B) the mesosphere and the stratosphere.
C) the thermosphere and the stratosphere.
D) the troposphere and the mesosphere.
E) the troposphere and the stratosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Venus's rotation is such that the dominant form of atmospheric circulation is powered by
A) winds moving from its equator to its poles.
B) heated air escaping from its volcanoes moving along the equator.
C) winds moving from its poles to its equator.
D) heated air escaping from active tectonic plates.
E) radioisotope decays.
A) winds moving from its equator to its poles.
B) heated air escaping from its volcanoes moving along the equator.
C) winds moving from its poles to its equator.
D) heated air escaping from active tectonic plates.
E) radioisotope decays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Given the thickness and chemical composition of Venus's atmosphere, by how much would you expect its average surface temperature to change between day and night?
A) There should be almost no change in temperature.
B) by tens of K (like Earth)
C) by hundreds of K (like Mercury)
D) The answer depends on where Venus is in its orbit around the Sun.
E) The answer depends on how many volcanoes are currently active.
A) There should be almost no change in temperature.
B) by tens of K (like Earth)
C) by hundreds of K (like Mercury)
D) The answer depends on where Venus is in its orbit around the Sun.
E) The answer depends on how many volcanoes are currently active.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to the following figure, as you increase in altitude in Earth's atmosphere, the atmospheric pressure ________ dramatically at a(n) ________ rate. 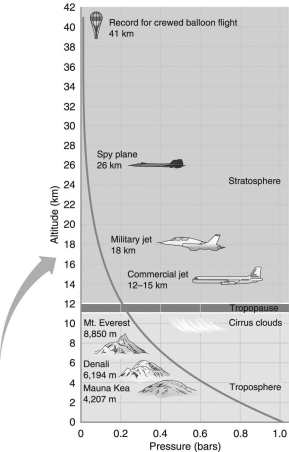
A) increases; increasing
B) increases; decreasing
C) decreases; decreasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant

A) increases; increasing
B) increases; decreasing
C) decreases; decreasing
D) decreases; increasing
E) decreases; constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the Southern Hemisphere, hurricanes ________ compared to hurricanes in the Northern Hemisphere because of the Coriolis effect.
A) rotate in the same direction
B) rotate in the opposite direction
C) move from east to west
D) have larger wind speeds
E) cause more damage
A) rotate in the same direction
B) rotate in the opposite direction
C) move from east to west
D) have larger wind speeds
E) cause more damage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
All direct weather and wind on Earth are a result of convection in the
A) troposphere.
B) stratosphere.
C) mesosphere.
D) ionosphere.
E) thermosphere.
A) troposphere.
B) stratosphere.
C) mesosphere.
D) ionosphere.
E) thermosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The planet-wide flow of air from Earth's equator to the colder poles is called Hadley circulation.An example of this effect is also seen
A) on Mars.
B) on Mercury.
C) on Venus.
D) on Pluto.
E) nowhere else in the solar system.
A) on Mars.
B) on Mercury.
C) on Venus.
D) on Pluto.
E) nowhere else in the solar system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Heating from ________ causes the top of Earth's stratosphere to be warmer than the bottom.
A) higher-energy particles in the solar wind
B) convection
C) the ozone layer absorbing UV light
D) charged particles trapped by magnetic fields
E) the greenhouse effect
A) higher-energy particles in the solar wind
B) convection
C) the ozone layer absorbing UV light
D) charged particles trapped by magnetic fields
E) the greenhouse effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Anthropogenic climate change refers to climate change caused by
A) solar activity.
B) Earth's rotation.
C) precession of Earth's axis.
D) human activity.
E) fluctuations in the magnetosphere.
A) solar activity.
B) Earth's rotation.
C) precession of Earth's axis.
D) human activity.
E) fluctuations in the magnetosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The absence of oxygen on Mars means that it has very little
A) carbon dioxide.
B) methane.
C) ozone.
D) helium.
E) ammonia
A) carbon dioxide.
B) methane.
C) ozone.
D) helium.
E) ammonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Weather is the ________ state of the atmosphere, while climate is the ________ state of the atmosphere.
A) average; day-to-day
B) day-to-day; average
C) year-to-year; millennium-to-millennium
D) average; average
E) current; past
A) average; day-to-day
B) day-to-day; average
C) year-to-year; millennium-to-millennium
D) average; average
E) current; past

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Each halogen atom, such as chlorine, fluorine, and bromine, in Earth's atmosphere contributes to
A) the production of carbon dioxide.
B) the production of acid rain.
C) the destruction of ozone over decades and centuries.
D) the destruction of water in the upper atmosphere.
E) the production of limestone.
A) the production of carbon dioxide.
B) the production of acid rain.
C) the destruction of ozone over decades and centuries.
D) the destruction of water in the upper atmosphere.
E) the production of limestone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The primary atmospheres of the terrestrial planets formed from hydrogen and helium.Why? What happened to this gas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the Martian springtime arrives and the daytime temperature reaches 20°C, what occurs?
A) Water melts and forms large pools of liquid.
B) The polar ice caps disappear.
C) large planet-wide dust storms
D) The planet's surface changes color.
E) Small plants bloom in direct sunlight.
A) Water melts and forms large pools of liquid.
B) The polar ice caps disappear.
C) large planet-wide dust storms
D) The planet's surface changes color.
E) Small plants bloom in direct sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Humans cannot survive on the surface of Mars for long periods of time because
A) there is not enough oxygen in the atmosphere.
B) the range in temperature between day and night is too large.
C) the flux of UV radiation reaching the surface is too high.
D) the atmospheric pressure would be too low.
E) all of these reasons
A) there is not enough oxygen in the atmosphere.
B) the range in temperature between day and night is too large.
C) the flux of UV radiation reaching the surface is too high.
D) the atmospheric pressure would be too low.
E) all of these reasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A gas eventually will escape from a planet's atmosphere if the average velocity of its atoms exceeds 1/6 times the escape velocity of the planet.If the average velocity of water vapor in Venus's atmosphere is 0.5 km/s, what would be the average velocity of a single hydrogen atom? If Venus's escape velocity is 11 km/s, will hydrogen atoms eventually escape?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The amount of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere has been increasing over the last 50 years because of
A) global warming.
B) the growth of the ozone hole.
C) the burning of fossil fuels.
D) increased energy output from the Sun.
E) increased magnetic activity in the Sun.
A) global warming.
B) the growth of the ozone hole.
C) the burning of fossil fuels.
D) increased energy output from the Sun.
E) increased magnetic activity in the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the average CO2 molecule in Venus's atmosphere has a velocity of 0.6 km/s, what would be the velocity for a hydrogen atom in Venus's atmosphere? Note the mass of a CO2 molecule is 44 times that of a hydrogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Where is most of Earth's supply of carbon today?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Global temperature variations on Earth driven by the Milankovitch cycle differ from those driven by the anthropogenic greenhouse effect in that
A) they are very small in magnitude, less than 1°C.
B) they occur at irregular time intervals.
C) they are driven by volcanic activity.
D) they occur over much longer timescales (thousands of years).
E) they are driven by emissions of methane gas rather than carbon dioxide.
A) they are very small in magnitude, less than 1°C.
B) they occur at irregular time intervals.
C) they are driven by volcanic activity.
D) they occur over much longer timescales (thousands of years).
E) they are driven by emissions of methane gas rather than carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Most of Earth's present-day atmosphere comes from a combination of what three sources?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe how the closer location of Venus to the Sun compared to Earth led to the runaway greenhouse effect observed on Venus today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the greenhouse effect, and what causes it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
List the three planets shown in the following figure in order of decreasing surface temperature, and cite evidence that can be seen in the images that supports your choice. 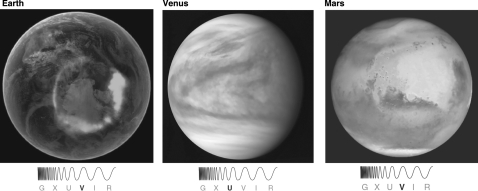


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Venus's surface temperature is fairly uniform from the equator to the poles because
A) Venus rotates very rapidly, which causes strong zonal winds.
B) Venus is covered by a thick cloud layer that absorbs most of the sunlight that falls on it.
C) the carbon dioxide in Venus's atmosphere efficiently emits infrared radiation.
D) Venus rotates slowly so Coriolis forces do not disrupt Hadley circulation.
E) Venus's orbit is nearly perfectly circular.
A) Venus rotates very rapidly, which causes strong zonal winds.
B) Venus is covered by a thick cloud layer that absorbs most of the sunlight that falls on it.
C) the carbon dioxide in Venus's atmosphere efficiently emits infrared radiation.
D) Venus rotates slowly so Coriolis forces do not disrupt Hadley circulation.
E) Venus's orbit is nearly perfectly circular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How does a planet's mass affect its atmosphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the origin of Earth's water?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When frozen water on the surface of Mars heats up during summertime, the water
A) melts and forms liquid pools on the surface.
B) boils off the surface and escapes into outer space.
C) sublimates and goes directly into the gaseous phase.
D) remains frozen because the temperature remains below the freezing point.
E) melts and creates flowing rivers that erode the landscape.
A) melts and forms liquid pools on the surface.
B) boils off the surface and escapes into outer space.
C) sublimates and goes directly into the gaseous phase.
D) remains frozen because the temperature remains below the freezing point.
E) melts and creates flowing rivers that erode the landscape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



