Deck 19: Galaxies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Galaxies
1
The dark features in the HST image in the figure shown below indicate 
A) collections of cool stars.
B) clumps of dark matter.
C) copious amounts of dark energy.
D) large amounts of dust.
E) faulty pixels on the CCD camera.

A) collections of cool stars.
B) clumps of dark matter.
C) copious amounts of dark energy.
D) large amounts of dust.
E) faulty pixels on the CCD camera.
large amounts of dust.
2
Which of the following images shows an edge-on spiral galaxy? 
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
3
What type of galaxy is shown in the figure below? 
A) a giant elliptical
B) a regular spiral galaxy
C) an irregular galaxy
D) a barred spiral
E) a dwarf spiral

A) a giant elliptical
B) a regular spiral galaxy
C) an irregular galaxy
D) a barred spiral
E) a dwarf spiral
a giant elliptical
4
Which distance indicator can be used to measure the most distant objects?
A) Cepheids
B) parallax
C) Type Ia supernovae
D) main-sequence fitting
E) RR Lyrae stars
A) Cepheids
B) parallax
C) Type Ia supernovae
D) main-sequence fitting
E) RR Lyrae stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The disks of spiral galaxies appear blue because
A) they are moving toward us.
B) they contain a relatively high concentration of low-mass stars.
C) they contain active regions of star formation.
D) they contain more metals that, when ionized, emit blue light.
E) stars collide with each other frequently in these dense regions and explode as Type Ia supernovae.
A) they are moving toward us.
B) they contain a relatively high concentration of low-mass stars.
C) they contain active regions of star formation.
D) they contain more metals that, when ionized, emit blue light.
E) stars collide with each other frequently in these dense regions and explode as Type Ia supernovae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Astronomers have known that galaxies are separate entities outside of our own for roughly the last
A) 35 years.
B) 60 years.
C) 90 years.
D) 150 years.
E) 210 years.
A) 35 years.
B) 60 years.
C) 90 years.
D) 150 years.
E) 210 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To be a standard candle, an object must have a known
A) lifetime.
B) brightness.
C) luminosity.
D) distance.
E) mass.
A) lifetime.
B) brightness.
C) luminosity.
D) distance.
E) mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In spiral galaxies, the size of the central bulge is correlated with the
A) tightness of the spiral arms.
B) luminosity of the galaxy.
C) age of the galaxy.
D) thickness of the disk.
E) presence of an active nucleus.
A) tightness of the spiral arms.
B) luminosity of the galaxy.
C) age of the galaxy.
D) thickness of the disk.
E) presence of an active nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What caused early astronomers to believe that our galaxy is only about 6,000 light-years across?
A) Telescopes were not powerful enough to observe stars farther away.
B) Interstellar dust blocked visible light from stars farther away.
C) Stars farther away could not be resolved as individual objects.
D) Astronomers miscalculated the distances to stars, believing that the stars were 50 times closer than they actually were.
E) Astronomers assumed all red stars were faint main-sequence stars, and they confused them with the more luminous red giants.
A) Telescopes were not powerful enough to observe stars farther away.
B) Interstellar dust blocked visible light from stars farther away.
C) Stars farther away could not be resolved as individual objects.
D) Astronomers miscalculated the distances to stars, believing that the stars were 50 times closer than they actually were.
E) Astronomers assumed all red stars were faint main-sequence stars, and they confused them with the more luminous red giants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You observe a reddish galaxy with stars that orbit in random directions.This galaxy is most likely a(n)
A) elliptical galaxy.
B) unbarred spiral galaxy.
C) irregular galaxy.
D) barred spiral.
E) It is none of these; more information is needed.
A) elliptical galaxy.
B) unbarred spiral galaxy.
C) irregular galaxy.
D) barred spiral.
E) It is none of these; more information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Hubble classification scheme for galaxies sorts them by their
A) evolutionary state.
B) mass.
C) amount of dust.
D) amount of dark matter.
E) visual appearance.
A) evolutionary state.
B) mass.
C) amount of dust.
D) amount of dark matter.
E) visual appearance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What did Edwin Hubble study in the Andromeda Galaxy that proved it was an individual galaxy and not part of our own Milky Way?
A) Cepheid stars
B) Type Ia supernovae
C) globular clusters
D) red giant stars
E) RR Lyrae variables
A) Cepheid stars
B) Type Ia supernovae
C) globular clusters
D) red giant stars
E) RR Lyrae variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Stars in the disks of spiral galaxies have orbits that are
A) randomly oriented.
B) constantly getting larger.
C) mostly aligned in the same plane.
D) spiral-shaped.
E) unaffected by dark matter.
A) randomly oriented.
B) constantly getting larger.
C) mostly aligned in the same plane.
D) spiral-shaped.
E) unaffected by dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the Great Debate of 1920, Curtis and Shapley argued over whether or not
A) the Big Bang occurred.
B) the age of the universe was 14 billion years.
C) the universe was contracting.
D) life existed outside Earth.
E) the spiral nebulae were located outside the Milky Way.
A) the Big Bang occurred.
B) the age of the universe was 14 billion years.
C) the universe was contracting.
D) life existed outside Earth.
E) the spiral nebulae were located outside the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Even though each item on the distance ladder is only effective within a certain distance range, the concept is still effective because
A) each technique produces exact distances on its own.
B) the distance ladder concept can be verified by looking in different wavelength ranges.
C) each step can be calibrated through its overlap with the previous step.
D) distances are ultimately relative, and not absolute.
E) the time delay due to light travel time is significant enough to limit the accuracy of distance measurements anyway.
A) each technique produces exact distances on its own.
B) the distance ladder concept can be verified by looking in different wavelength ranges.
C) each step can be calibrated through its overlap with the previous step.
D) distances are ultimately relative, and not absolute.
E) the time delay due to light travel time is significant enough to limit the accuracy of distance measurements anyway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Active star formation does not typically occur in elliptical galaxies because they
A) rotate too fast.
B) contain little cold gas.
C) are too massive.
D) are too far away.
E) usually contain active nuclei.
A) rotate too fast.
B) contain little cold gas.
C) are too massive.
D) are too far away.
E) usually contain active nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The nearest big galaxy, Andromeda, is at an estimated distance of
A) 780 Mpc.
B) 0.78 kpc.
C) 0.78 Mpc.
D) 25 kpc.
E) 250 Gpc.
A) 780 Mpc.
B) 0.78 kpc.
C) 0.78 Mpc.
D) 25 kpc.
E) 250 Gpc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following lists distance indicators from nearest to farthest?
A) Cepheids, parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Type Ia supernovae
B) parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae
C) parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Type Ia supernovae, Cepheids
D) spectroscopic parallax, parallax, Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae
E) Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae, spectroscopic parallax, parallax
A) Cepheids, parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Type Ia supernovae
B) parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae
C) parallax, spectroscopic parallax, Type Ia supernovae, Cepheids
D) spectroscopic parallax, parallax, Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae
E) Cepheids, Type Ia supernovae, spectroscopic parallax, parallax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Elliptical galaxies appear red because they
A) are moving away from us.
B) contain mostly ionized hydrogen gas.
C) contain mostly old stars.
D) contain lots of dust.
E) contain a mix of old and young stars.
A) are moving away from us.
B) contain mostly ionized hydrogen gas.
C) contain mostly old stars.
D) contain lots of dust.
E) contain a mix of old and young stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What type of galaxy is shown in the figure below? 
A) a giant elliptical
B) an ordinary spiral galaxy
C) an irregular galaxy
D) a barred spiral
E) a dwarf elliptical

A) a giant elliptical
B) an ordinary spiral galaxy
C) an irregular galaxy
D) a barred spiral
E) a dwarf elliptical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The recession speed of spiral galaxies may also render their colors ________ due to ________.
A) bluer; relativistic beaming
B) bluer; a Doppler-like effect
C) redder; relativistic beaming
D) redder; a Doppler-like effect
E) redder; galactic interactions
A) bluer; relativistic beaming
B) bluer; a Doppler-like effect
C) redder; relativistic beaming
D) redder; a Doppler-like effect
E) redder; galactic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You see a galaxy in which the H line (rest wavelength = 656.3 nm) is observed at a wavelength of 756.3 nm.What would be the observed wavelength of a particular helium line that has a rest wavelength of 1,083 nm?
A) 1,083 nm
B) 1,183 nm
C) 1,248 nm
D) 1,440 nm
E) 3,142 nm
A) 1,083 nm
B) 1,183 nm
C) 1,248 nm
D) 1,440 nm
E) 3,142 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the figure shown below, the upper spectrum is from hydrogen at rest in a laboratory, and the lower spectrum is from a galaxy.How far away is this galaxy? 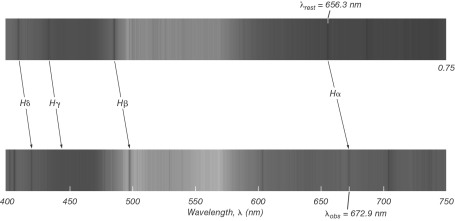
A) 110 Mpc
B) 170 Mpc
C) 230 Mpc
D) 280 Mpc
E) 340 Mpc

A) 110 Mpc
B) 170 Mpc
C) 230 Mpc
D) 280 Mpc
E) 340 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the spectrum of a distant galaxy is observed to have a calcium K absorption line that occurs at a wavelength of 500.4 nm, what is this galaxy's distance if the rest wavelength of this absorption line is 393.4 nm? Assume the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/Mpc.
A) 720 Mpc
B) 950 Mpc
C) 1,200 Mpc
D) 2,600 Mpc
E) 3,700 Mpc
A) 720 Mpc
B) 950 Mpc
C) 1,200 Mpc
D) 2,600 Mpc
E) 3,700 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a galaxy has a recessional velocity of 50,000 km/s, at what wavelength will you observe the H emission line? (Note that the rest wavelength of the H emission line is 656.3 nm.)
A) 695.7 nm
B) 719.4 nm
C) 742.3 nm
D) 765.7 nm
E) 1,750 nm
A) 695.7 nm
B) 719.4 nm
C) 742.3 nm
D) 765.7 nm
E) 1,750 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the distance of a galaxy is 50 Mpc, what is its recessional velocity if the Hubble constant is assumed to be 70 km/s/Mpc?
A) 700 km/s
B) 1,000 km/s
C) 3,500 km/s
D) 5,000 km/s
E) 7,000 km/s
A) 700 km/s
B) 1,000 km/s
C) 3,500 km/s
D) 5,000 km/s
E) 7,000 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The technique of using a star's spectrum to find its location on the H-R diagram, which provides an estimate of its luminosity, and thereby its distance, is called
A) the Tully-Fisher method.
B) spectroscopic parallax.
C) the Doppler shift.
D) Hubble's law.
E) trigonometric parallax.
A) the Tully-Fisher method.
B) spectroscopic parallax.
C) the Doppler shift.
D) Hubble's law.
E) trigonometric parallax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If you found a galaxy with an H emission line that had a wavelength of 756.3 nm, what would be the galaxy's redshift? (Note that the rest wavelength of the H emission line is 656.3 nm.)
A) 0.05
B) 0.07
C) 0.10
D) 0.13
E) 0.15
A) 0.05
B) 0.07
C) 0.10
D) 0.13
E) 0.15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Tully-Fisher method of determination of distances to galaxies is based on the correlation between
A) color and redshift.
B) star formation rate and morphological type.
C) width of emission lines and black hole accretion rate.
D) rotational speed and luminosity.
E) dark matter radial profile and X-ray brightness.
A) color and redshift.
B) star formation rate and morphological type.
C) width of emission lines and black hole accretion rate.
D) rotational speed and luminosity.
E) dark matter radial profile and X-ray brightness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A certain spectral line of rest wavelength lrest (i.e., laboratory value) is shifted by 100 nm in a quasar.A second line from the same quasar with a rest wavelength half the (rest) value of the first one would be shifted by
A) 200 nm.
B) 100 nm.
C) 500 nm.
D) 50 nm.
E) 1000 nm.
A) 200 nm.
B) 100 nm.
C) 500 nm.
D) 50 nm.
E) 1000 nm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to Hubble's law, as the distance of a galaxy ________, its ________ increases.
A) increases; luminosity
B) increases; recessional velocity
C) decreases; luminosity
D) decreases; recessional velocity
E) decreases; peculiar velocity
A) increases; luminosity
B) increases; recessional velocity
C) decreases; luminosity
D) decreases; recessional velocity
E) decreases; peculiar velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why can Type Ia supernovae be used to determine a galaxy's distance?
A) Type Ia supernovae occur only in very luminous galaxies.
B) Most Type Ia supernovae have approximately the same peak luminosity.
C) Most Type Ia supernovae have approximately the same size.
D) A Type Ia supernova occurs in a typical galaxy about once every 100 years.
E) Type Ia supernovae occur even in very small galaxies.
A) Type Ia supernovae occur only in very luminous galaxies.
B) Most Type Ia supernovae have approximately the same peak luminosity.
C) Most Type Ia supernovae have approximately the same size.
D) A Type Ia supernova occurs in a typical galaxy about once every 100 years.
E) Type Ia supernovae occur even in very small galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a galaxy has an apparent velocity of 700 km/s, what is its distance if the Hubble constant is assumed to be 70 km/s/Mpc?
A) 10 Mpc
B) 70 Mpc
C) 100 Mpc
D) 700 Mpc
E) 1,000 Mpc
A) 10 Mpc
B) 70 Mpc
C) 100 Mpc
D) 700 Mpc
E) 1,000 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The rotation curve of a galaxy is a plot of the rotation speed as a function of the
A) galaxy's luminosity.
B) mass of the dark matter halo.
C) brightness of the luminous matter in the galaxy.
D) radius from the center.
E) ages of star clusters.
A) galaxy's luminosity.
B) mass of the dark matter halo.
C) brightness of the luminous matter in the galaxy.
D) radius from the center.
E) ages of star clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Astronomers use galactic redshift to estimate
A) gravity.
B) luminosity.
C) star counts.
D) mass.
E) distance.
A) gravity.
B) luminosity.
C) star counts.
D) mass.
E) distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You read about the discovery of quasars with redshift z larger than 1.This means that
A) their host galaxies are receding at speeds exceeding the speed of light.
B) the measurements of redshift must be wrong; z cannot exceed 1.
C) the relationship between z and receding speed must account for relativistic corrections.
D) the speed of light can exceed c in the case of distant quasars.
E) quasars must contain a lot of dark matter.
A) their host galaxies are receding at speeds exceeding the speed of light.
B) the measurements of redshift must be wrong; z cannot exceed 1.
C) the relationship between z and receding speed must account for relativistic corrections.
D) the speed of light can exceed c in the case of distant quasars.
E) quasars must contain a lot of dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Type Ia supernovae have a peak luminosity of 3.7 x1036 W.If you discover a Type Ia supernovae in a distant galaxy that has a measured brightness of 9.5 x10-17 W/m2, then how far away is this galaxy? Note that 1 Mpc = 3.1 x1022 m.
A) 0.3 Mpc
B) 40 Mpc
C) 1,200 Mpc
D) 1,800 Mpc
E) 3,500 Mpc
A) 0.3 Mpc
B) 40 Mpc
C) 1,200 Mpc
D) 1,800 Mpc
E) 3,500 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The spectra of most galaxies tell us that
A) galaxies appear to be moving away from us.
B) their light comes predominantly from objects other than stars.
C) most galaxies contain clouds of gas that are absorbing their favorite wavelengths.
D) galaxies in the past rotated at a faster rate than they do today.
E) galaxies are rushing through space in all directions.
A) galaxies appear to be moving away from us.
B) their light comes predominantly from objects other than stars.
C) most galaxies contain clouds of gas that are absorbing their favorite wavelengths.
D) galaxies in the past rotated at a faster rate than they do today.
E) galaxies are rushing through space in all directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If you found a galaxy with an H emission line that had a wavelength of 756.3 nm, what would be the galaxy's distance if the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/Mpc? (Note that the rest wavelength of the H emission line is 656.3 nm.)
A) 650 Mpc
B) 760 Mpc
C) 3,200 Mpc
D) 6,400 Mpc
E) 7,600 Mpc
A) 650 Mpc
B) 760 Mpc
C) 3,200 Mpc
D) 6,400 Mpc
E) 7,600 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The nearest known quasar shows a redshift of z = 0.0516, which means it is at a distance of
A) 220 Mpc.
B) 450 Mpc.
C) 100 Mpc.
D) 15,400 Mpc.
E) 100 kpc.
A) 220 Mpc.
B) 450 Mpc.
C) 100 Mpc.
D) 15,400 Mpc.
E) 100 kpc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the galactic rotation curves in the figure below is closest to what is actually measured for galaxies? 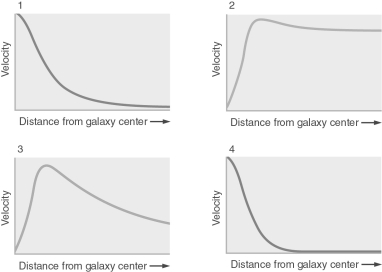
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 4 for ellipticals, 2 for spirals

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 4 for ellipticals, 2 for spirals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For which galaxies would it be easiest to measure rotation curves?
A) elliptical
B) face-on barred spirals
C) face-on normal spirals
D) face-on S0 galaxies
E) edge-on spirals
A) elliptical
B) face-on barred spirals
C) face-on normal spirals
D) face-on S0 galaxies
E) edge-on spirals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Dark matter is most likely made up of
A) elementary particles that have mass but do not interact much with normal matter.
B) supermassive black holes.
C) faint stellar remnants such as white dwarfs and neutron stars.
D) free-floating Jupiter-mass planets.
E) cold concentrations of dust.
A) elementary particles that have mass but do not interact much with normal matter.
B) supermassive black holes.
C) faint stellar remnants such as white dwarfs and neutron stars.
D) free-floating Jupiter-mass planets.
E) cold concentrations of dust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What do the broad emission lines in quasar spectra tell astronomers about these objects?
A) They are very far away.
B) They are moving away from us.
C) They have rapid internal motions.
D) They are very dense.
E) They have few heavy elements.
A) They are very far away.
B) They are moving away from us.
C) They have rapid internal motions.
D) They are very dense.
E) They have few heavy elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Quasars were first discovered in which region of the electromagnetic spectrum?
A) X-ray
B) gamma-ray
C) radio
D) infrared
E) visible
A) X-ray
B) gamma-ray
C) radio
D) infrared
E) visible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How can we measure the mass of an elliptical galaxy?
A) by measuring the speeds of stars in the nucleus
B) by observing the velocity of the hot, X-ray-emitting gas that surrounds the galaxy
C) by measuring the number of H II regions in the galaxy
D) by measuring how many supernovae go off each century
E) by measuring the amount of blue light in the galaxy
A) by measuring the speeds of stars in the nucleus
B) by observing the velocity of the hot, X-ray-emitting gas that surrounds the galaxy
C) by measuring the number of H II regions in the galaxy
D) by measuring how many supernovae go off each century
E) by measuring the amount of blue light in the galaxy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If you measure the velocity of a cloud of gas that is rotating around the center of a galaxy in a circular orbit with radius R, you can determine the
A) total mass of the galaxy.
B) mass of the stars and gas in the galaxy.
C) mass of the galaxy enclosed within the radius R.
D) mass of the galaxy located outside the radius R.
E) mass of luminous matter within the radius R.
A) total mass of the galaxy.
B) mass of the stars and gas in the galaxy.
C) mass of the galaxy enclosed within the radius R.
D) mass of the galaxy located outside the radius R.
E) mass of luminous matter within the radius R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How did astronomers determine that elliptical galaxies are composed mostly of dark matter?
A) They measured the velocities of stars in the inner regions of the galaxies.
B) They measured the rotation rates of gas as a function of distance from the centers of the galaxies.
C) They measured the amount of gravitational pull elliptical galaxies have on companion galaxies.
D) They assumed that the proportion of dark matter was roughly the same as in spiral galaxies.
E) They measured the X-ray emission from hot gas gravitationally bound to the galaxies.
A) They measured the velocities of stars in the inner regions of the galaxies.
B) They measured the rotation rates of gas as a function of distance from the centers of the galaxies.
C) They measured the amount of gravitational pull elliptical galaxies have on companion galaxies.
D) They assumed that the proportion of dark matter was roughly the same as in spiral galaxies.
E) They measured the X-ray emission from hot gas gravitationally bound to the galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
More luminous giant galaxies tend to have ________ supermassive black holes at their centers.
A) more-massive
B) radio-quiet
C) more-luminous
D) slower-rotating
E) less-massive
A) more-massive
B) radio-quiet
C) more-luminous
D) slower-rotating
E) less-massive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Quasars are most likely to be found
A) near our galaxy.
B) in the centers of elliptical galaxies.
C) at extreme distances.
D) in very old galaxies.
E) in dwarf galaxies.
A) near our galaxy.
B) in the centers of elliptical galaxies.
C) at extreme distances.
D) in very old galaxies.
E) in dwarf galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For the more distant quasars, the emission lines that would normally occur in the visible domain would be shifted into
A) UV.
B) X-rays.
C) gamma rays.
D) infrared.
E) radio.
A) UV.
B) X-rays.
C) gamma rays.
D) infrared.
E) radio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Astronomers can determine the maximum size of a distant, luminous object by
A) directly resolving it in a telescope only.
B) using trigonometric parallax.
C) timing the fluctuations in its luminosity.
D) looking for the amplitude of an oscillating Doppler shift.
E) using the phenomenon of radio wave diffraction.
A) directly resolving it in a telescope only.
B) using trigonometric parallax.
C) timing the fluctuations in its luminosity.
D) looking for the amplitude of an oscillating Doppler shift.
E) using the phenomenon of radio wave diffraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Quasars remain unresolved sources, even with the best telescopic observations, because they
A) are too luminous.
B) occupy a very small volume.
C) are quite blue.
D) produce copious amounts of radio energy.
E) host supermassive black holes.
A) are too luminous.
B) occupy a very small volume.
C) are quite blue.
D) produce copious amounts of radio energy.
E) host supermassive black holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Dust in galaxies does not count as dark matter because
A) it absorbs only some wavelengths of light but not all wavelengths as dark matter does.
B) it interacts with light.
C) it is found only in spiral disks, whereas dark matter is also found in elliptical galaxies.
D) dust is easily destroyed by dark matter.
E) there is never enough to account for all the gravity in galaxies.
A) it absorbs only some wavelengths of light but not all wavelengths as dark matter does.
B) it interacts with light.
C) it is found only in spiral disks, whereas dark matter is also found in elliptical galaxies.
D) dust is easily destroyed by dark matter.
E) there is never enough to account for all the gravity in galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In most cases it is impossible to observe the host galaxies of quasars because
A) quasars outshine the host galaxies by a few orders of magnitude.
B) the supermassive black holes have "eaten" all the stars in those galaxies.
C) the host galaxies of quasars have too much dark matter.
D) the host galaxies of quasars have too much obscuring dust.
E) the galaxies hosting quasars are much smaller than our own Milky Way.
A) quasars outshine the host galaxies by a few orders of magnitude.
B) the supermassive black holes have "eaten" all the stars in those galaxies.
C) the host galaxies of quasars have too much dark matter.
D) the host galaxies of quasars have too much obscuring dust.
E) the galaxies hosting quasars are much smaller than our own Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How have astronomers searched for evidence of MACHOs in the halo of the Milky Way?
A) They search for stars that are binary companions of MACHOs.
B) They search for rapidly moving massive gas clouds.
C) They search for disturbances in the background of gravitational waves.
D) They search for distant stars with light briefly amplified by gravitational lensing.
E) They search for close binary stars undergoing mass transfer.
A) They search for stars that are binary companions of MACHOs.
B) They search for rapidly moving massive gas clouds.
C) They search for disturbances in the background of gravitational waves.
D) They search for distant stars with light briefly amplified by gravitational lensing.
E) They search for close binary stars undergoing mass transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The term "dark" in "dark matter" refers to the fact that dark matter
A) absorbs but does not emit light.
B) emits only infrared light.
C) emits only ultraviolet ("black") light.
D) does not absorb or emit light.
E) absorbs 99 percent of all light, but emits only in radio waves.
A) absorbs but does not emit light.
B) emits only infrared light.
C) emits only ultraviolet ("black") light.
D) does not absorb or emit light.
E) absorbs 99 percent of all light, but emits only in radio waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The formation of the Solar System and the existence of AGNs both demonstrate the
A) information gained from how luminosity varies with time.
B) high efficiency of nuclear fusion.
C) effects of accretion disks.
D) importance of living in the center of a galaxy.
E) existence of dark matter.
A) information gained from how luminosity varies with time.
B) high efficiency of nuclear fusion.
C) effects of accretion disks.
D) importance of living in the center of a galaxy.
E) existence of dark matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Roughly what percentage of the total mass of a galaxy is made up of luminous, or normal, matter?
A) 5-10 percent
B) 25-30 percent
C) 40-50 percent
D) 70-75 percent
E) 90-95 percent
A) 5-10 percent
B) 25-30 percent
C) 40-50 percent
D) 70-75 percent
E) 90-95 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What makes up the majority of the mass of an individual spiral galaxy?
A) a central supermassive black hole
B) dark matter
C) massive O- and B-type stars
D) cold molecular gas clouds
E) low-mass G-, K-, and M-type stars
A) a central supermassive black hole
B) dark matter
C) massive O- and B-type stars
D) cold molecular gas clouds
E) low-mass G-, K-, and M-type stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The unified model of AGN suggests that quasars, Seyfert galaxies, and radio galaxies are
A) unrelated, although they are all very luminous galaxies at radio wavelengths.
B) powered by differring mass accretion rates onto supermassive black holes.
C) driven by violent mergers of two gas-rich spiral galaxies.
D) similar phenomena but viewed from different orientation angles.
E) all powered by high rates of star formation and supernova explosions.
A) unrelated, although they are all very luminous galaxies at radio wavelengths.
B) powered by differring mass accretion rates onto supermassive black holes.
C) driven by violent mergers of two gas-rich spiral galaxies.
D) similar phenomena but viewed from different orientation angles.
E) all powered by high rates of star formation and supernova explosions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the figure below to estimate the value of Hubble's constant.Be sure to include the appropriate units. 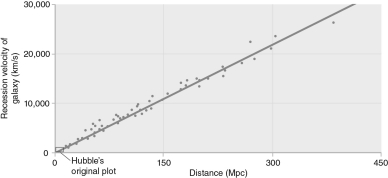


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
AGNs are most likely powered by
A) extremely dense star clusters.
B) accreting supermassive black holes.
C) ultradense molecular clouds.
D) decaying dark matter.
E) supernova explosions.
A) extremely dense star clusters.
B) accreting supermassive black holes.
C) ultradense molecular clouds.
D) decaying dark matter.
E) supernova explosions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Name two "rungs" in the distance ladder, and how distances within of these two "rungs" are measured or estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Order the following objects by the maximum distance from which they can be detected: Cepheid variables, RR Lyrae stars, Type Ia supernovae, and low-mass main-sequence stars.Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How did Edwin Hubble definitively prove that "spiral nebulae" were individual galaxies that were separate from the Milky Way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How do the current star-formation rates of spiral and elliptical galaxies compare?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
As of the writing of your textbook, what types of galaxies (not including our own Milky Way Galaxy) have been observed to have planets orbiting stars within them?
A) other spiral galaxies only
B) elliptical galaxies only
C) irregular galaxies only
D) spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies
E) no planets have been observed in other galaxies.
A) other spiral galaxies only
B) elliptical galaxies only
C) irregular galaxies only
D) spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies
E) no planets have been observed in other galaxies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a Seyfert galaxy's nucleus varies in brightness on the timescale of 10 hours, then what is the approximate upper limit for the size of the emitting region?
A) 20 AU
B) 30 AU
C) 50 AU
D) 70 AU
E) 120 AU
A) 20 AU
B) 30 AU
C) 50 AU
D) 70 AU
E) 120 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How did Hubble classify galaxies? Is there any significance to this organization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why do the light gray bands (labeled Radar, Parallax, etc.) that cover certain ranges of distances in the figure shown below overlap with one another both at the beginning and at the end? 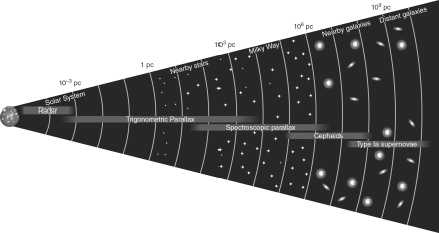


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What happens to active galaxies when their AGNs run out of fuel?
A) The black holes powering them collapse even further.
B) They simply become normal galaxies.
C) They slowly dissipate into clouds of gas and dust.
D) They eventually pull in material from farther out, starting the AGN process all over again.
E) They explode as gamma-ray bursts.
A) The black holes powering them collapse even further.
B) They simply become normal galaxies.
C) They slowly dissipate into clouds of gas and dust.
D) They eventually pull in material from farther out, starting the AGN process all over again.
E) They explode as gamma-ray bursts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What were the positions taken by Heber Curtis and Harlow Shapley in their "Great Debate," and how were both of them partially correct?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
We interpret the presence of more AGNs in the past than today to indicate that
A) there were fewer galaxy-galaxy interactions in the past.
B) there were more galaxy-galaxy interactions in the past.
C) supermassive black holes were larger in the past.
D) today's AGNs are hidden primarily by large amounts of cold gas and dust.
E) AGNs had bigger central black holes in the past.
A) there were fewer galaxy-galaxy interactions in the past.
B) there were more galaxy-galaxy interactions in the past.
C) supermassive black holes were larger in the past.
D) today's AGNs are hidden primarily by large amounts of cold gas and dust.
E) AGNs had bigger central black holes in the past.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How do we know that AGNs have sizes on the order of our Solar System?
A) Quasars and Seyfert galaxies are stellar-like sources.
B) Their brightness varies by factors of a few.
C) The emission lines in their spectra show gas rotating at speeds of thousands of km/s.
D) Their brightness varies on timescales ranging from hours to a day.
E) We can measure their angular size, which gives us the physical size when we know the distance.
A) Quasars and Seyfert galaxies are stellar-like sources.
B) Their brightness varies by factors of a few.
C) The emission lines in their spectra show gas rotating at speeds of thousands of km/s.
D) Their brightness varies on timescales ranging from hours to a day.
E) We can measure their angular size, which gives us the physical size when we know the distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In some radio galaxies, we see only one side of the jet because
A) the black hole produces a jet in only one direction.
B) of relativistic beaming.
C) the other side is inside the black hole's event horizon.
D) of dust obscuration.
E) of dark matter that blocks the light from one side of the jet.
A) the black hole produces a jet in only one direction.
B) of relativistic beaming.
C) the other side is inside the black hole's event horizon.
D) of dust obscuration.
E) of dark matter that blocks the light from one side of the jet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following functions correctly illustrates the relation between mean density and black hole mass?
A) ( M - 2 )
M - 2 )
B) ( M - 1 )
M - 1 )
C) (
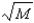 )
)
D) ( M )
M )
E) ( M 2)
M 2)
A) (
 M - 2 )
M - 2 )B) (
 M - 1 )
M - 1 )C) (

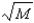 )
)D) (
 M )
M )E) (
 M 2)
M 2)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How do we know that the stellar disks in spiral galaxies are flat? How do we know that elliptical galaxies are not flat?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Explain why Hubble's law, which is linear, has no intercept (recall the standard equation for a line
is y = mx + b).
is y = mx + b).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Assume that when a supermassive black hole accretes gas, approximately 20 percent of the accreted mass is converted directly into energy, which is radiated away.If a quasar has a luminosity of 1013 LSUN, then what must be its mass accretion rate? Note that the Sun has a luminosity of 4 x1026 W, and a mass of 2 x1030 kg.
A) 1 MSUN per year
B) 3.5 MSUN per year
C) 1 MSUN per century
D) 3.5 MSUN per century
E) 1 MSUN per million years
A) 1 MSUN per year
B) 3.5 MSUN per year
C) 1 MSUN per century
D) 3.5 MSUN per century
E) 1 MSUN per million years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



