Deck 16: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Nuclear Chemistry
1
Which example is, by definition, an isotope of carbon-12?
A) a nuclide with atomic number 5 and mass number 12
B) a nuclide with 8 protons and 9 neutrons
C) a nuclide with 6 protons and 8 neutrons
D) a nuclide with 12 nucleons
A) a nuclide with atomic number 5 and mass number 12
B) a nuclide with 8 protons and 9 neutrons
C) a nuclide with 6 protons and 8 neutrons
D) a nuclide with 12 nucleons
a nuclide with 6 protons and 8 neutrons
2
Complete the following nuclear equation. 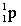 +
+ 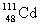
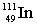 + _____
+ _____
A)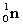
B)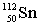
C)
D)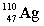
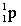 +
+ 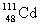
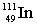 + _____
+ _____A)
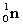
B)
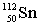
C)

D)
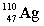
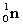
3
A nuclide is defined as an atom or nucleus containing a particular number of:
A) electrons and protons.
B) protons and neutrons.
C) electrons and neutrons.
D) electrons, protons, and neutrons.
A) electrons and protons.
B) protons and neutrons.
C) electrons and neutrons.
D) electrons, protons, and neutrons.
protons and neutrons.
4
Which atomic symbol describes an atom with 16 protons and 17 neutrons?
A)
B)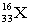
C)
D)
A)

B)
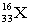
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Complete the following nuclear equation. 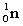 +
+ 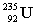
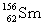 + _____ +
+ _____ + 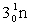
A)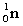
B)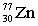
C)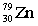
D)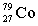
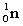 +
+ 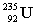
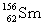 + _____ +
+ _____ + 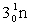
A)
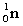
B)
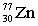
C)
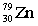
D)
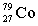

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which nuclide is represented by the atomic symbol 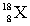 ?
?
A) oxygen-18
B) argon-18
C) neon-18
D) oxygen-10
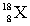 ?
?A) oxygen-18
B) argon-18
C) neon-18
D) oxygen-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Isotopes, by definition, have the same _____ but a different _____, respectively.
A) number of electrons; number of protons
B) number of electrons; number of neutrons
C) atomic number; mass number
D) number of neutrons; number of electrons
A) number of electrons; number of protons
B) number of electrons; number of neutrons
C) atomic number; mass number
D) number of neutrons; number of electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The mass number is defined as the number of:
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons and neutrons together.
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons and neutrons together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The atomic symbol 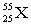 represents an element with _____ protons and _____ neutrons, respectively.
represents an element with _____ protons and _____ neutrons, respectively.
A) 25; 30
B) 25; 55
C) 55; 25
D) 55; 30
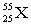 represents an element with _____ protons and _____ neutrons, respectively.
represents an element with _____ protons and _____ neutrons, respectively.A) 25; 30
B) 25; 55
C) 55; 25
D) 55; 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Complete the following example of beta decay. 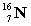 _____ +
_____ + 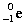 .
.
A)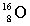
B)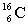
C)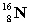
D)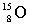
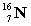 _____ +
_____ + 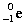 .
.A)
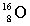
B)
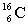
C)
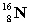
D)
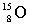

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Complete the following nuclear equation. 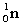 +
+ 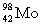 _____
_____
A)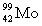
B)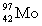
C)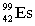
D)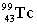
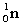 +
+ 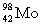 _____
_____A)
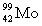
B)
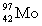
C)
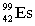
D)
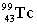

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which factor determines the elemental identity of an atom?
A) the number of electrons
B) the number of protons
C) the number of neutrons
D) the number of protons and neutrons together
A) the number of electrons
B) the number of protons
C) the number of neutrons
D) the number of protons and neutrons together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When an atom undergoes beta decay:
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Complete the following nuclear equation. 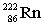
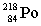 + _____
+ _____
A)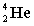
B)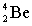
C)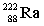
D)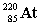
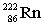
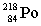 + _____
+ _____A)
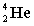
B)
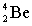
C)
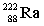
D)
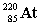

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When an atom undergoes gamma decay:
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Complete the following example of alpha decay. 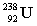 _____ +
_____ + 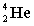
A)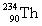
B)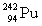
C)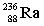
D)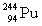
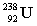 _____ +
_____ + 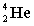
A)
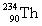
B)
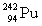
C)
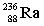
D)
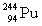

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Complete the following nuclear equation. 
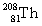 + _____
+ _____
A)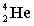
B)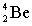
C)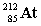
D)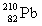

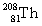 + _____
+ _____A)
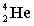
B)
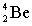
C)
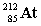
D)
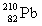

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The atomic number is defined as the number of:
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons and neutrons together.
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons and neutrons together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A nucleon can be:
A) any subatomic particle.
B) an electron.
C) an alpha particle.
D) any particle in the nucleus.
A) any subatomic particle.
B) an electron.
C) an alpha particle.
D) any particle in the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When an atom undergoes alpha decay:
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
A) the atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4.
B) the atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.
C) the atomic number and the mass number remain the same.
D) the atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number doesn't change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which form of radioactive emission is a form of electromagnetic radiation?
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Select the BEST definition for the binding energy of a nucleus.
A) the energy released when nucleons combine to form a nucleus
B) the energy required to break a nucleus into its component parts
C) both the energy released when nucleons combine to form a nucleus and the energy required to break a nucleus into its component parts
D) neither of the above
A) the energy released when nucleons combine to form a nucleus
B) the energy required to break a nucleus into its component parts
C) both the energy released when nucleons combine to form a nucleus and the energy required to break a nucleus into its component parts
D) neither of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The concentration of carbon-14 in living plants is about 240 Bq/kg C. If a tree dies today, what concentration of carbon-14 would still be present after 2 half-lives?
A) 240 Bq/kg C
B) 120 Bq/kg C
C) 60 Bq/kg C
D) none
A) 240 Bq/kg C
B) 120 Bq/kg C
C) 60 Bq/kg C
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Cobalt-58 has a half-life of 71 days. How much of a 48- g sample would remain after 284 days?
A) 24 g
B) 12 g
C) 6 g
D) 3 g
A) 24 g
B) 12 g
C) 6 g
D) 3 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which unit is NOT a measure of radiation?
A) dosimeter
B) becquerel
C) sievert
D) rem
A) dosimeter
B) becquerel
C) sievert
D) rem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which device is NOT used to measure radiation?
A) Geiger counter
B) scintillation counter
C) dosimeter
D) sievert
A) Geiger counter
B) scintillation counter
C) dosimeter
D) sievert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Lead-210 decays through the pathway , , , , , . What is the final nucleus formed after these decays?
A)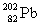
B)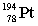
C)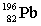
D)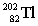
A)
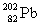
B)
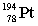
C)
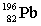
D)
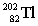

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The half-life of carbon-14 is about 5,730 years. If an ancient cave painting was found to have about 25% of the carbon-14 of a now-living object, about how old is the cave painting?
A) 5,730 years
B) 11,500 years
C) 17,200 years
D) Not enough information is given to determine the age.
A) 5,730 years
B) 11,500 years
C) 17,200 years
D) Not enough information is given to determine the age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Complete the following example of gamma decay. 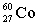 _____ +
_____ + 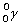
A)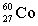
B)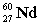
C)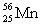
D)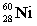
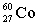 _____ +
_____ + 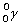
A)
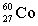
B)
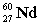
C)
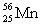
D)
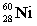

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which form of radioactive emission is the same as an electron?
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Iodine-131 has a half-life of 8 days. How much of a 16- g sample would remain after 16 days?
A) 16 g
B) 8 g
C) 4 g
D) none
A) 16 g
B) 8 g
C) 4 g
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If after 15 years, 10 mg of an original 320-mg sample of a radioactive isotope remain, how long is the half-life of this isotope?
A) 3 years
B) 5 years
C) 15 years
D) 0.5 years
A) 3 years
B) 5 years
C) 15 years
D) 0.5 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In general, how does the neutron-proton ratio change from small nuclides to larger nuclides?
A) The ratio increases.
B) The ratio decreases
C) The ratio remains the same.
A) The ratio increases.
B) The ratio decreases
C) The ratio remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Relate mass defect and binding energy and stability.
A) The greater the mass defect, the greater the binding energy and the more stable the nucleus.
B) The greater the mass defect, the greater the binding energy and the less stable the nucleus.
C) The greater the mass defect, the less the binding energy and the less stable the nucleus.
D) The less the mass defect, the less the binding energy and the more stable the nucleus.
A) The greater the mass defect, the greater the binding energy and the more stable the nucleus.
B) The greater the mass defect, the greater the binding energy and the less stable the nucleus.
C) The greater the mass defect, the less the binding energy and the less stable the nucleus.
D) The less the mass defect, the less the binding energy and the more stable the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
List the three common forms of radioactive emission by penetrating ability from least to most.
A) alpha, beta, gamma
B) beta, alpha, gamma
C) gamma, beta, alpha
D) gamma, alpha, beta
A) alpha, beta, gamma
B) beta, alpha, gamma
C) gamma, beta, alpha
D) gamma, alpha, beta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Samarium-153 has a half-life of 2 days. How much of this radioisotope remains after 10 days?
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 20%
D) about 3%
A) 50%
B) 25%
C) 20%
D) about 3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The half-life of carbon-14 is about 5,730 years. If an ancient leather strap is about 11,500 years old, what percentage of carbon-14 in a now-living object remains in the strap?
A) 100%
B) 50%
C) 25%
D) none
A) 100%
B) 50%
C) 25%
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which form of radioactive emission is the same as a helium nucleus?
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Radium-224 decays through the pathway , , , , , . What is the final stable nucleus formed?
A)
B)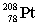
C)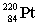
D)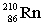
A)

B)
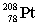
C)
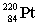
D)
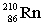

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the relationship between the mass defect and energy released in a nuclear reaction?
A) The greater the mass defect, the greater the energy released.
B) The greater the mass defect ,the less the energy released.
C) There is no relationship between the mass defect and the energy released.
A) The greater the mass defect, the greater the energy released.
B) The greater the mass defect ,the less the energy released.
C) There is no relationship between the mass defect and the energy released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Complete the following fusion reaction;
_____ +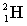
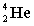 +
+ 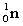
A)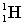
B)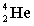
C)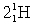
D)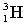
_____ +
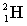
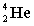 +
+ 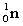
A)
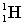
B)
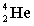
C)
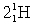
D)
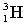

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The control rods in a nuclear reactor regulate the chain reaction by:
A) absorbing the neutrons.
B) absorbing the protons.
C) absorbing the uranium or plutonium atoms.
D) raising or lowering the temperature.
A) absorbing the neutrons.
B) absorbing the protons.
C) absorbing the uranium or plutonium atoms.
D) raising or lowering the temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The sequence of energy changes for a nuclear reactor to produce electricity is:
A) nuclear - heat - mechanical - electricity.
B) nuclear - mechanical - heat - electricity.
C) nuclear - chemical - heat - electricity.
D) nuclear - chemical - heat - mechanical - electricity.
A) nuclear - heat - mechanical - electricity.
B) nuclear - mechanical - heat - electricity.
C) nuclear - chemical - heat - electricity.
D) nuclear - chemical - heat - mechanical - electricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The reaction in which neutrons from the fission of one nucleus cause the fission of another nucleus is called:
A) a chain reaction.
B) fusion.
C) radioactive decay.
D) an endothermic reaction.
A) a chain reaction.
B) fusion.
C) radioactive decay.
D) an endothermic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Complete the fission reaction of plutonium-239: 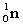 +
+ 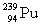
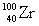 + _____ +
+ _____ + 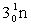 .
.
A)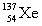
B)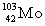
C)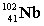
D)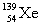
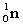 +
+ 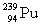
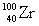 + _____ +
+ _____ + 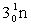 .
.A)
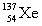
B)
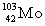
C)
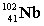
D)
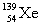

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The most stable isotope is iron-56. What kind of nuclear emission would be expected from much lighter nuclei and from much heavier nuclei, respectively?
A) beta, alpha
B) alpha, beta
C) both beta
D) both alpha
A) beta, alpha
B) alpha, beta
C) both beta
D) both alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Complete the following fusion reaction.
_____ +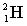
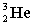
A)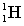
B)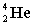
C)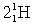
D)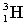
_____ +
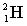
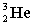
A)
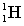
B)
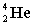
C)
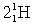
D)
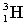

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following nuclear reaction absorbs energy. Which has more mass, the reactants or the products?
energy +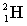 +
+ 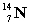
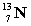 +
+ 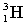
A) neither because of the law of conservation of mass
B) the reactants because some of the energy is converted to mass
C) the products because some of the energy is converted to mass
D) the reactants because some of the mass is converted to energy
energy +
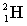 +
+ 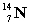
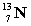 +
+ 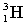
A) neither because of the law of conservation of mass
B) the reactants because some of the energy is converted to mass
C) the products because some of the energy is converted to mass
D) the reactants because some of the mass is converted to energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Complete the fission reaction of plutonium-239: 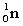 +
+ 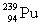
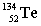 + _____ +
+ _____ + 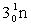 .
.
A)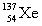
B)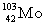
C)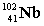
D)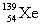
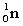 +
+ 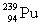
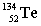 + _____ +
+ _____ + 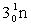 .
.A)
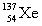
B)
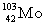
C)
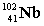
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Complete the fission reaction of plutonium-239: 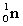 +
+ 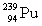
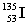 + _____ +
+ _____ + 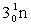 .
.
A)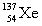
B)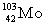
C)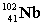
D)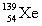
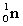 +
+ 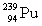
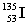 + _____ +
+ _____ + 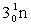 .
.A)
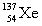
B)
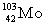
C)
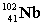
D)
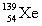

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Complete the following fusion reaction.
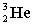 +
+ 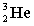 ___ + 2
___ + 2 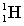
A)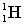
B)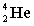
C)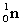
D)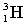
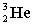 +
+ 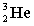 ___ + 2
___ + 2 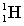
A)
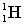
B)
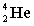
C)
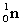
D)
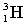

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The following nuclear reaction releases energy. Which has more mass, the reactants or the products?
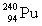
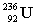 +
+ 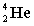 + energy
+ energy
A) neither because of the law of conservation of mass
B) the reactant because some of the mass is converted to energy
C) the products because some of the energy is converted to mass
D) the products because some of the mass is converted to energy
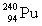
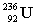 +
+ 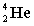 + energy
+ energyA) neither because of the law of conservation of mass
B) the reactant because some of the mass is converted to energy
C) the products because some of the energy is converted to mass
D) the products because some of the mass is converted to energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



