Deck 14: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
1
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in the thiosulfate ion, S2O32-?
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
+2
2
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in sulfur trioxide, SO3?
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
+6
3
Which statement is TRUE?
A) Hydrogen atom to hydrogen ion (H+) is reduction.
B) Oxygen atom to oxide ion (O2-) is reduction.
C) Tin atom to tin(IV) ion is reduction.
D) Fluoride ion (F-) to fluorine atom is reduction.
A) Hydrogen atom to hydrogen ion (H+) is reduction.
B) Oxygen atom to oxide ion (O2-) is reduction.
C) Tin atom to tin(IV) ion is reduction.
D) Fluoride ion (F-) to fluorine atom is reduction.
Oxygen atom to oxide ion (O2-) is reduction.
4
In the context of chemical reactions, oxidation refers to the:
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) loss of oxygen.
D) loss of water.
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) loss of oxygen.
D) loss of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element(s) can reduce zinc ion to elemental zinc?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) copper
D) nickel, iron, and copper
E) None of these elements can reduce zinc ion to elemental zinc.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) copper
D) nickel, iron, and copper
E) None of these elements can reduce zinc ion to elemental zinc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The major credit for creating the first "battery" goes to:
A) James Watt.
B) Andre Ampere.
C) Alessandro Volta.
D) Georg Ohm.
A) James Watt.
B) Andre Ampere.
C) Alessandro Volta.
D) Georg Ohm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Given the accompanying partial activity series, predict which element or ion will react with cobalt, Co.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn
B) Fe2+
C) Ni
D) Cu2+
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn
B) Fe2+
C) Ni
D) Cu2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Given the accompanying partial activity series, predict which element or ion will react with the cobalt ion, Co2+.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn
B) Fe2+
C) Ni
D) Cu2+
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn
B) Fe2+
C) Ni
D) Cu2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Considering the following net ionic equation: Mg + Fe2+ Mg2+ + Fe
The species REDUCED is _____, and the REDUCING AGENT is _____.
A) Mg; Mg
B) Mg; Fe2+
C) Fe2+; Fe2+
D) Fe2+; Mg
The species REDUCED is _____, and the REDUCING AGENT is _____.
A) Mg; Mg
B) Mg; Fe2+
C) Fe2+; Fe2+
D) Fe2+; Mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the oxidation number of carbon in carbon dioxide, CO2?
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement is FALSE?
A) Silver ion (Ag+) to silver atom is reduction.
B) Chloride (Cl-) ion to chlorine atom is reduction.
C) Hydrogen atom to hydride ion (H-) is reduction.
D) Sulfur atom to sulfide ion (S2-) is reduction.
A) Silver ion (Ag+) to silver atom is reduction.
B) Chloride (Cl-) ion to chlorine atom is reduction.
C) Hydrogen atom to hydride ion (H-) is reduction.
D) Sulfur atom to sulfide ion (S2-) is reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in the sulfite ion, SO32-?
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Given the accompanying partial activity series, predict which reaction(s) will occur as written.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn + Fe2+ Zn2+ + Fe
B) Fe + Ni2+ Fe2+ + Ni
C) Co + Cu2+ Cu + Co2+
D) Zn + Fe2+ Zn2+ + Fe, Fe + Ni2+ Fe2+ + Ni , and Co + Cu2+ Cu + Co2+
E) None of these reactions will occur as written.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Zn + Fe2+ Zn2+ + Fe
B) Fe + Ni2+ Fe2+ + Ni
C) Co + Cu2+ Cu + Co2+
D) Zn + Fe2+ Zn2+ + Fe, Fe + Ni2+ Fe2+ + Ni , and Co + Cu2+ Cu + Co2+
E) None of these reactions will occur as written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the context of chemical reactions, reduction refers to the:
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) gain of oxygen.
D) loss of water.
A) gain of electrons.
B) loss of electrons.
C) gain of oxygen.
D) loss of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the oxidation number of carbon in carbon monoxide, CO?
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4
A) -2
B) +2
C) +6
D) +4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in the nitrate ion, NO3-?
A) -1
B) -3
C) +6
D) +5
A) -1
B) -3
C) +6
D) +5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element CANNOT reduce nickel(II) to elemental nickel?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) zinc
B) iron
C) cobalt
D) copper
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) zinc
B) iron
C) cobalt
D) copper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which example illustrates a redox reaction?
A) metal and nonmetal
B) double displacement
C) neutralization
D) precipitation
A) metal and nonmetal
B) double displacement
C) neutralization
D) precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Considering the following net ionic equation: Mg + Fe2+ Mg2+ + Fe
The species that is OXIDIZED is _____, and the OXIDIZING AGENT is _____.
A) Mg; Mg
B) Mg; Fe2+
C) Fe2+; Fe2+
D) Fe2+; Mg
The species that is OXIDIZED is _____, and the OXIDIZING AGENT is _____.
A) Mg; Mg
B) Mg; Fe2+
C) Fe2+; Fe2+
D) Fe2+; Mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which example does NOT illustrate a redox reaction?
A) metal and nonmetal
B) double displacement
C) single displacement
D) combustion
A) metal and nonmetal
B) double displacement
C) single displacement
D) combustion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which example BEST represents the reaction between copper and hydrochloric acid?
A) Cu + 2 HCl CuCl2 + H2
B) Cu + 2 HCl CuH2 + Cl2
C) Cu + H2Cl CuCl + H2
D) Copper and hydrochloric acid do not react.
A) Cu + 2 HCl CuCl2 + H2
B) Cu + 2 HCl CuH2 + Cl2
C) Cu + H2Cl CuCl + H2
D) Copper and hydrochloric acid do not react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which example represents the reduction half-reaction for cobalt/cobalt(II)?
A) Co Co2+ + 2 e-
B) Co + 2 e- Co2-
C) Co2+ + 2 e- Co
D) Co2+ Co + 2 e-
A) Co Co2+ + 2 e-
B) Co + 2 e- Co2-
C) Co2+ + 2 e- Co
D) Co2+ Co + 2 e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the coefficients of the balanced equation that represents the reaction in a magnesium/aluminum electrochemical cell?
Mg (s) + Al3+ (aq) Al (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 3, 2, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 3, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 3
Mg (s) + Al3+ (aq) Al (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 3, 2, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 3, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element(s) will NOT react with acid?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) silver
D) nickel, iron, and silver
E) All of these elements will react with acid.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) silver
D) nickel, iron, and silver
E) All of these elements will react with acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider an electrochemical cell consisting of zinc and cobalt half-cells. Use the partial activity series included to determine the direction in which the electrons in the wire will flow.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) from the zinc anode to the cobalt cathode
B) from the zinc cathode to the cobalt anode
C) from the cobalt anode to the zinc cathode
D) from the cobalt cathode to the zinc anode
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) from the zinc anode to the cobalt cathode
B) from the zinc cathode to the cobalt anode
C) from the cobalt anode to the zinc cathode
D) from the cobalt cathode to the zinc anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The reduction half-reaction for the reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid is:
A) Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn.
B) Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-.
C) H2 2 H+ + 2 e-.
D) 2 H+ + 2 e- H2.
A) Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn.
B) Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-.
C) H2 2 H+ + 2 e-.
D) 2 H+ + 2 e- H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element(s) will react with acid?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) nickel
B) copper
C) silver
D) nickel, copper, and silver
E) None of these elements will react with acid.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) nickel
B) copper
C) silver
D) nickel, copper, and silver
E) None of these elements will react with acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell represents an iron-nickel cell, use the partial activity series included to describe the component labeled 2. 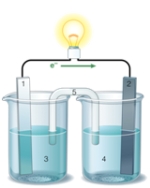 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron anode
B) nickel anode
C) iron cathode
D) nickel cathode
 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron anode
B) nickel anode
C) iron cathode
D) nickel cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell represents an iron-nickel cell, use the partial activity series included to select the half-reaction represented by the RIGHT side of the cell. 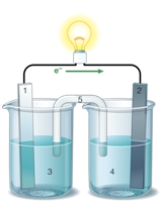 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
B) Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
C) Fe2+ + 2e- Fe
D) Ni2+ + 2e- Ni
 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
B) Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
C) Fe2+ + 2e- Fe
D) Ni2+ + 2e- Ni

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which example BEST represents the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid?
A) Mg + 2 HCl MgCl2 + H2
B) Mg + 2 HCl MgH2 + Cl2
C) Mg + H2Cl MgCl + H2
D) Magnesium and hydrochloric acid do not react.
A) Mg + 2 HCl MgCl2 + H2
B) Mg + 2 HCl MgH2 + Cl2
C) Mg + H2Cl MgCl + H2
D) Magnesium and hydrochloric acid do not react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell, identify the components labeled 1, 2, and 5, respectively. 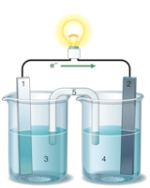
A) salt bridge, anode, cathode
B) salt bridge, cathode, anode
C) cathode, anode, salt bridge
D) anode, cathode, salt bridge

A) salt bridge, anode, cathode
B) salt bridge, cathode, anode
C) cathode, anode, salt bridge
D) anode, cathode, salt bridge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider an electrochemical cell consisting of zinc and nickel half-cells. Use the partial activity series included to determine the direction in which the electrons in the wire will flow.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) from the zinc anode to the nickel cathode
B) from the zinc cathode to the nickel anode
C) from the nickel anode to the zinc cathode
D) from the nickel cathode to the zinc anode
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) from the zinc anode to the nickel cathode
B) from the zinc cathode to the nickel anode
C) from the nickel anode to the zinc cathode
D) from the nickel cathode to the zinc anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element(s) can reduce copper(II) to elemental copper?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) zinc
D) nickel, iron, and zinc
E) None of these elements can reduce copper(II) to elemental copper.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) nickel
B) iron
C) zinc
D) nickel, iron, and zinc
E) None of these elements can reduce copper(II) to elemental copper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which example represents the oxidation half-reaction for cobalt/cobalt(II)?
A) Co Co2+ + 2 e-
B) Co + 2 e- Co2-
C) Co2+ + 2 e- Co
D) Co2+ Co + 2 e-
A) Co Co2+ + 2 e-
B) Co + 2 e- Co2-
C) Co2+ + 2 e- Co
D) Co2+ Co + 2 e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell represents an iron-nickel cell, use the partial activity series included to select the half-reaction represented by the LEFT side of the cell. 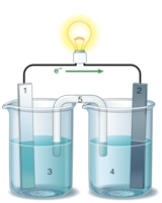 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
B) Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
C) Fe2+ + 2e- Fe
D) Ni2+ + 2e- Ni
 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
B) Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
C) Fe2+ + 2e- Fe
D) Ni2+ + 2e- Ni

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given the accompanying partial activity series, which element(s) will react with acid?
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) iron
B) nickel
C) zinc
D) iron, nickel, and zinc
E) None of these elements will react with acid.
Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
H2 2H+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Ag Ag+ + e-
A) iron
B) nickel
C) zinc
D) iron, nickel, and zinc
E) None of these elements will react with acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell represents an iron-nickel cell, use the partial activity series included to identify the components labeled 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. 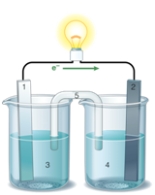 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron, nickel, iron ion solution, nickel ion solution
B) nickel, iron, iron ion solution, nickel ion solution
C) nickel, iron, nickel ion solution, iron ion solution
D) iron, nickel, nickel ion solution, iron ion solution
 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron, nickel, iron ion solution, nickel ion solution
B) nickel, iron, iron ion solution, nickel ion solution
C) nickel, iron, nickel ion solution, iron ion solution
D) iron, nickel, nickel ion solution, iron ion solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The oxidation half-reaction for the reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid is:
A) Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn.
B) Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-.
C) H2 2 H+ + 2 e-.
D) 2 H+ + 2 e- H2.
A) Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn.
B) Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-.
C) H2 2 H+ + 2 e-.
D) 2 H+ + 2 e- H2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Knowing that sodium and potassium react violently with water, predict which element will also react with water.
A) cesium
B) aluminum
C) zinc
D) It is impossible to predict accurately from the information given.
A) cesium
B) aluminum
C) zinc
D) It is impossible to predict accurately from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the accompanying drawing of an electrochemical cell represents an iron-nickel cell, use the partial activity series included to determine the component labeled 1. 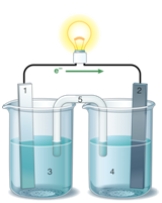 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron anode
B) nickel anode
C) iron cathode
D) nickel cathode
 Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Zn Zn2+ + 2e- Fe Fe2+ + 2e-Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) iron anode
B) nickel anode
C) iron cathode
D) nickel cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction consisting of the two half-reactions given.
Cu Cu2+ + 2 e-
Ag+ + e- Ag
A) Cu (s) + Ag+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Ag (s)
B) Cu (s) + 2 Ag+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
C) Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ag+ (aq) + Cu (s)
D) 2 Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) 2 Ag+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Cu Cu2+ + 2 e-
Ag+ + e- Ag
A) Cu (s) + Ag+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Ag (s)
B) Cu (s) + 2 Ag+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Ag (s)
C) Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ag+ (aq) + Cu (s)
D) 2 Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) 2 Ag+ (aq) + Cu (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction consisting of the two half-reactions given. Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-
Pb4+ + 4 e- Pb
A) Pb (s) + Mg2+ (aq) Pb4+ (aq) + Mg (s)
B) Mg (s) + Pb4+ (aq) Pb (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
C) 2 Mg (s) + Pb4+ (aq) Pb (s) + 2 Mg2+ (aq)
D) Pb (s) + 2 Mg2+ (aq) Pb4+ (aq) + 2 Mg (s)
Pb4+ + 4 e- Pb
A) Pb (s) + Mg2+ (aq) Pb4+ (aq) + Mg (s)
B) Mg (s) + Pb4+ (aq) Pb (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
C) 2 Mg (s) + Pb4+ (aq) Pb (s) + 2 Mg2+ (aq)
D) Pb (s) + 2 Mg2+ (aq) Pb4+ (aq) + 2 Mg (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which pair of half-reactions takes place in a fuel cell?
A) reduction: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2H2O; oxidation: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-
B) reduction: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-; oxidation: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2 H2O
C) reduction: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2H2O; oxidation: 2 H+ + 2 e- H2
D) reduction: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-; oxidation: 2 H2O O2 + 4H+ + 4 e-
A) reduction: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2H2O; oxidation: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-
B) reduction: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-; oxidation: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2 H2O
C) reduction: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- 2H2O; oxidation: 2 H+ + 2 e- H2
D) reduction: H2 2 H+ + 2 e-; oxidation: 2 H2O O2 + 4H+ + 4 e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which reaction could be used to electroplate nickel with gold?
A) Ni (s) + 2 Au+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
B) Zn (s) + 2 Au+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
C) 2 Au (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Ni (s) + 2 Au+ (aq)
D) 2 Au (s) + Zn2+ (aq) Zn (s) + 2 Au+ (aq)
A) Ni (s) + 2 Au+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
B) Zn (s) + 2 Au+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
C) 2 Au (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Ni (s) + 2 Au+ (aq)
D) 2 Au (s) + Zn2+ (aq) Zn (s) + 2 Au+ (aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the partial activity series included to determine which reaction will NOT occur spontaneously. Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe (s) + Co2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Co (s)
B) Zn (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + Ni (s)
C) Cu (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D) Ni (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe (s) + Co2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Co (s)
B) Zn (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + Ni (s)
C) Cu (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D) Ni (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + Cu (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which pair of half-reactions could be used to electroplate silver onto iron?
A) reduction: Ag+ + e- Ag; oxidation: Ag Ag+ + e-
B) reduction: Ag Ag+ + e-; oxidation: Ag+ + e- Ag
C) reduction: Fe2+ + 2 e- Fe; oxidation: Fe Fe2+ + 2 e-
D) reduction: Fe Fe2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Fe2+ + 2 e- Fe
A) reduction: Ag+ + e- Ag; oxidation: Ag Ag+ + e-
B) reduction: Ag Ag+ + e-; oxidation: Ag+ + e- Ag
C) reduction: Fe2+ + 2 e- Fe; oxidation: Fe Fe2+ + 2 e-
D) reduction: Fe Fe2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Fe2+ + 2 e- Fe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the partial activity series included to determine which reaction will NOT occur spontaneously. Zn Zn2+ + 2e-
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe (s) + Co2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Co (s)
B) Zn (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + Ni (s)
C) Co (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Co2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D) Ni (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Fe Fe2+ + 2e-
Co Co2+ + 2e-
Ni Ni2+ + 2e-
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
A) Fe (s) + Co2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Co (s)
B) Zn (s) + Ni2+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + Ni (s)
C) Co (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Co2+ (aq) + Fe (s)
D) Ni (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Ni2+ (aq) + Cu (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What are the coefficients of the balanced equation that represents the reaction in a magnesium/iron electrochemical cell?
Mg (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Fe (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 1, 2, 2, 1
C) 2, 1, 1, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 2
Mg (s) + Fe2+ (aq) Fe (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 1, 2, 2, 1
C) 2, 1, 1, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction consisting of the two half-reactions given.
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Au3+ + 3e- Au
A) Cu (s) + Au3+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Au (s)
B) 3 Cu (s) + 2 Au3+ (aq) 3 Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
C) 2 Au (s) + 3 Cu2+ (aq) 2 Au3+ (aq) + 3 Cu (s)
D) Au (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Au3+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Cu Cu2+ + 2e-
Au3+ + 3e- Au
A) Cu (s) + Au3+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + Au (s)
B) 3 Cu (s) + 2 Au3+ (aq) 3 Cu2+ (aq) + 2 Au (s)
C) 2 Au (s) + 3 Cu2+ (aq) 2 Au3+ (aq) + 3 Cu (s)
D) Au (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Au3+ (aq) + Cu (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given the following net ionic equation, select the correct pairing of half-reactions. Mg (s) + Zn2+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + Zn (s)
A) reduction: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn
B) reduction: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn; oxidation: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-
C) reduction: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn; oxidation: Mg2+ + 2 e- Mg
D) reduction: Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-
A) reduction: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn
B) reduction: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn; oxidation: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-
C) reduction: Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn; oxidation: Mg2+ + 2 e- Mg
D) reduction: Zn Zn2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Mg Mg2+ + 2 e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the coefficients of the balanced equation that represents the reaction in a magnesium/chromium electrochemical cell?
Mg (s) + Cr3+ (aq) Cr (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 3, 2, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 3, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 3
Mg (s) + Cr3+ (aq) Cr (s) + Mg2+ (aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 3, 2, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 3, 2
D) 1, 2, 1, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Given the following net ionic equation, select the CORRECT pairing of half-reactions. 2 Al (s) + 3 Pb2+ (aq) 2 Al3+ (aq) + 3 Pb (s)
A) reduction: Al Al3+ + 3 e-; oxidation: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb
B) reduction: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb; oxidation: Al Al3+ + 3 e-
C) reduction: Al3+ + 3 e- Al; oxidation: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb
D) reduction: Pb Pb2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Al Al3+ + 3 e-
A) reduction: Al Al3+ + 3 e-; oxidation: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb
B) reduction: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb; oxidation: Al Al3+ + 3 e-
C) reduction: Al3+ + 3 e- Al; oxidation: Pb2+ + 2 e- Pb
D) reduction: Pb Pb2+ + 2 e-; oxidation: Al Al3+ + 3 e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



