Deck 7: Foundation Skills
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Foundation Skills
1
____________________ is done by using visual observation.
Inspection
2
The pulse can be counted by listening to the heart through a ____________________ placed on the chest.
Stethoscope
3
The rhythm and character of ____________________ are important observations.
Respiration
4
Risk factors that can be controlled by cardiac patients include:
A) Lack of exercise
B) High-fat diet
C) Heredity
D) Gender and age
E) a and b
A) Lack of exercise
B) High-fat diet
C) Heredity
D) Gender and age
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The diastolic reading occurs when the ventricles are ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The pulse is usually assessed using:
A) The radial artery near the wrist
B) A sphygmomanometer
C) The force of the blood
D) The systolic measurement
E) A thermometer
A) The radial artery near the wrist
B) A sphygmomanometer
C) The force of the blood
D) The systolic measurement
E) A thermometer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Basic math may be used in health care to:
A) Convert medicine dosages
B) Measure time
C) Measure temperature
D) Measure capacity and mass
E) All of the above
A) Convert medicine dosages
B) Measure time
C) Measure temperature
D) Measure capacity and mass
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The systolic reading occurs while the ventricles of the heart are ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Blood pressure reflects:
A) The number of heartbeats
B) The force of the blood against the walls of arteries
C) The systolic rate
D) The diastolic rate
E) The pulse
A) The number of heartbeats
B) The force of the blood against the walls of arteries
C) The systolic rate
D) The diastolic rate
E) The pulse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The weight recommended by health professionals usually is determined by using charts developed by:
A) The American Medical Association
B) Insurance companies
C) Hospitals
D) Physicians
E) The Food and Drug Administration
A) The American Medical Association
B) Insurance companies
C) Hospitals
D) Physicians
E) The Food and Drug Administration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Examples of rational numbers include all of the following except:
A) 10
B)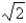
C) 7/16
D) -45
A) 10
B)
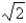
C) 7/16
D) -45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The type of graph used to chart vital signs is a:
A) Bar graph
B) Pie chart
C) Pictograph
D) Line graph
A) Bar graph
B) Pie chart
C) Pictograph
D) Line graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The basic health assessment may include an interview and physical examination to determine:
A) Functional characteristics
B) Cultural characteristics
C) Spiritual characteristics
D) Physical characteristics
E) All of the above
A) Functional characteristics
B) Cultural characteristics
C) Spiritual characteristics
D) Physical characteristics
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
____________________ is the use of the hands to evaluate structures by touch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
____________________ is the measurement of the balance between heat produced and lost by the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Four sites used to measure the temperature are:
A) Mouth, under the arm, rectum, knee
B) Mouth, under the arm, rectum, ear
C) Mouth, rectum, knee
D) Ear, mouth, rectum, knee
E) Ear, knee, mouth, under the arm
A) Mouth, under the arm, rectum, knee
B) Mouth, under the arm, rectum, ear
C) Mouth, rectum, knee
D) Ear, mouth, rectum, knee
E) Ear, knee, mouth, under the arm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ____________________ is the heartbeat that can be palpated on surface arteries as the artery walls expand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The normal rate of an adult pulse can range between:
A) 60 and 110
B) 60 and 100
C) 50 and 90
D) 80 and 110
E) 70 and 110
A) 60 and 110
B) 60 and 100
C) 50 and 90
D) 80 and 110
E) 70 and 110

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An example of a computer operating system that interprets and displays data is:
A) Unix/Linux
B) Dell's Inspiron
C) Apple's Mac
D) a and c
E) b and c
A) Unix/Linux
B) Dell's Inspiron
C) Apple's Mac
D) a and c
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Vital signs are values that can be used to measure changes in:
A) Body function and response to treatment
B) General health and response to treatment
C) Response to treatment, diagnosis, and body function
D) Body function, general health, and response to treatment
E) General health, body function, and diagnosis
A) Body function and response to treatment
B) General health and response to treatment
C) Response to treatment, diagnosis, and body function
D) Body function, general health, and response to treatment
E) General health, body function, and diagnosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
Define pulse and explain the usual method of assessing the pulse.
Define pulse and explain the usual method of assessing the pulse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Write an expository outlining the various steps in a patient health assessment; explain how a physician might use the assessment information in the health care plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
How are computers used in health care?
How are computers used in health care?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Match the numbered word below with the best definition.
a.The blood pressure during ventricular contraction
b.The pressure of circulating blood against the walls of the arteries
c.Necessary to life
d.The blood pressure at maximum cardiac relaxation
e.The technique of tapping with the fingertips to evaluate the size, borders, and consistency of internal body structures
f.The balance between heat produced and heat lost by the body
g.Pertaining to the apex, or pointed end, of the heart
h.The act of listening for sounds in the body
i.The sudden stopping of heart action
j.The technique used to feel the texture, size, consistency, and location of parts of the body with the hands
1.Apical
2.Auscultation
3.Blood pressure
4.Cardiac arrest
5.Diastolic
6.Palpation
7.Percussion
8.Systolic
9.Temperature
10.Vital
a.The blood pressure during ventricular contraction
b.The pressure of circulating blood against the walls of the arteries
c.Necessary to life
d.The blood pressure at maximum cardiac relaxation
e.The technique of tapping with the fingertips to evaluate the size, borders, and consistency of internal body structures
f.The balance between heat produced and heat lost by the body
g.Pertaining to the apex, or pointed end, of the heart
h.The act of listening for sounds in the body
i.The sudden stopping of heart action
j.The technique used to feel the texture, size, consistency, and location of parts of the body with the hands
1.Apical
2.Auscultation
3.Blood pressure
4.Cardiac arrest
5.Diastolic
6.Palpation
7.Percussion
8.Systolic
9.Temperature
10.Vital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
____________________ is striking the body to assess the sound made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain how computers can be used in health care.What might happen when a computer system crashes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Describe the early warning signs of a heart attack and explain what steps a person who has such signs should take.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For years mercury was used in thermometers.Explain the rationale for its removal and replacement with nontoxic liquids.Explain the environmental and safety risks involved in this decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
What does a basic health assessment help determine?
What does a basic health assessment help determine?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain how computer literacy plays a key role in health care.Discuss three specific tests that rely on computerized equipment to support the role of computers in health care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Health care workers use abbreviations and symbols for what purpose? What might happen if incorrect abbreviations or symbols are marked on a patient's chart?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
What is a sphygmomanometer?
What is a sphygmomanometer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What situations might call for an axillary, an oral, a rectal, or a temporal temperature measurement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
Describe what measures are included in vital signs.
Describe what measures are included in vital signs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
Explain the two values of blood pressure.
Explain the two values of blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
What is considered "normal" blood pressure?
What is considered "normal" blood pressure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What actions should be taken when vital signs fall out of the normal parameters?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
Define temperature and list the four common sites used to assess body temperature.
Define temperature and list the four common sites used to assess body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
_________________________ may result from blockage of an artery that supplies the heart or from an insufficient supply of oxygen to the heart tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
What systems of measurement can be used in health care?
What systems of measurement can be used in health care?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Using two or three sentences, answer the following questions as concisely as possible.
What techniques are used in a physical assessment?
What techniques are used in a physical assessment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



