Deck 22: The Industrial Era Dawns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: The Industrial Era Dawns
1
Identify and state the historical significance of Alexander Graham Bell.
Inventor credited with the invention of the telephone.
2
Much of the investment funds that enabled America to industrialize in the late 19th century came from
A) surplus wealth generated by agriculture.
B) the state governments.
C) private foreign investors.
D) individual Americans' savings.
E) the sale of confiscated Confederate land and property.
A) surplus wealth generated by agriculture.
B) the state governments.
C) private foreign investors.
D) individual Americans' savings.
E) the sale of confiscated Confederate land and property.
private foreign investors.
3
The national government helped to finance transcontinental railroad construction in the late 19th century by providing railroad corporations with
A) cash grants from new taxes.
B) land grants and loans.
C) cash grants from higher tariffs.
D) reduced prices for iron and steel.
E) aid for construction of railroad stations.
A) cash grants from new taxes.
B) land grants and loans.
C) cash grants from higher tariffs.
D) reduced prices for iron and steel.
E) aid for construction of railroad stations.
land grants and loans.
4
Identify and state the historical significance of Terence Powderly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify and state the historical significance of James J. Hill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The greatest economic consequence of the transcontinental railroad network was that it
A) enabled farmers to make a highly profitable living by shipping their goods across the country.
B) enabled people from farms and small towns to visit the big cities.
C) united the nation into a single, integrated national market.
D) made it possible for some immigrants to settle in the West.
E) developed a skilled industrial workforce.
A) enabled farmers to make a highly profitable living by shipping their goods across the country.
B) enabled people from farms and small towns to visit the big cities.
C) united the nation into a single, integrated national market.
D) made it possible for some immigrants to settle in the West.
E) developed a skilled industrial workforce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify and state the historical significance of Collis P. Huntington.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify and state the historical significance of Mary Harris "Mother" Jones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match each railroad company below with the correct entrepreneur.

A) A-4, B-2, C-1
B) A-3, B-4, C-2
C) A-2, B-1, C-3
D) A-4, B-3, C-1
E) A-1, B-3, C-4

A) A-4, B-2, C-1
B) A-3, B-4, C-2
C) A-2, B-1, C-3
D) A-4, B-3, C-1
E) A-1, B-3, C-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify and state the historical significance of John D. Rockefeller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify and state the historical significance of John P. Altgeld.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify and state the historical significance of Cornelius Vanderbilt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify and state the historical significance of Thomas Edison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The only transcontinental railroad built without government aid was the
A) New York Central.
B) Northern Pacific.
C) Union Pacific.
D) Central Pacific Railroad.
E) Great Northern.
A) New York Central.
B) Northern Pacific.
C) Union Pacific.
D) Central Pacific Railroad.
E) Great Northern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify and state the historical significance of J. Pierpont Morgan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify and state the historical significance of Andrew Carnegie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following was NOT among the technological improvements that made the modern transcontinental railroad network possible?
A) steel rails
B) air brakes
C) standard gauge tracks
D) the block signal
E) the electric engine
A) steel rails
B) air brakes
C) standard gauge tracks
D) the block signal
E) the electric engine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The greatest single factor helping to spur the amazing industrialization of the post-Civil War years was
A) agriculture.
B) mining.
C) the steel industry.
D) the railroad network
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) agriculture.
B) mining.
C) the steel industry.
D) the railroad network
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify and state the historical significance of Jay Gould.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify and state the historical significance of Leland Stanford.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When Europeans owned or invested in private companies in the United States, they generally
A) appointed European managers to key positions in the company.
B) let Americans manage the business unless there was an economic crisis.
C) made American banks issue regular reports on the profitability of their companies.
D) steered most of the profits back into European investments.
E) insisted that the companies hire a portion of immigrants from the nation owning the company.
A) appointed European managers to key positions in the company.
B) let Americans manage the business unless there was an economic crisis.
C) made American banks issue regular reports on the profitability of their companies.
D) steered most of the profits back into European investments.
E) insisted that the companies hire a portion of immigrants from the nation owning the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Agreements between railroad corporations to divide the business in a given area and share the profits were called
A) pools.
B) trusts.
C) rebates.
D) interlocking directorates.
E) kickbacks.
A) pools.
B) trusts.
C) rebates.
D) interlocking directorates.
E) kickbacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following was NOT among the critical U.S. raw materials, delivered by railroads to factories, that fueled early American industrialization?
A) rubber
B) iron
C) coal
D) copper
E) oil
A) rubber
B) iron
C) coal
D) copper
E) oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Match each entrepreneur below with the field of enterprise with which he is historically identified.
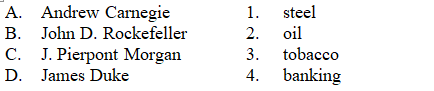
A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
D) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3
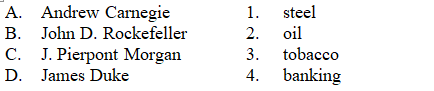
A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
D) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two technological innovations that greatly expanded the industrial employment of women in the late 19th century were the
A) typewriter and the telephone.
B) electric light and the phonograph.
C) Bessemer steel process and the internal combustion engine.
D) streetcar and the bicycle.
E) electric refrigerator and stove.
A) typewriter and the telephone.
B) electric light and the phonograph.
C) Bessemer steel process and the internal combustion engine.
D) streetcar and the bicycle.
E) electric refrigerator and stove.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the case of Wabash, St. Louis, and Pacific Railroad Company v. Illinois, the U.S. Supreme Court held that state legislatures could NOT regulate railroads because
A) the U.S. Constitution did not permit the government to regulate private industry.
B) the state legislatures were acting on behalf of private interest, Illinois farmers.
C) the state legislatures had provided the railroad company with state regulatory exemptions when land grant legislation was enacted to help create the railroad.
D) railroad executives had committed no illegal acts in their business.
E) railroads were interstate businesses and could not be regulated by any single state.
A) the U.S. Constitution did not permit the government to regulate private industry.
B) the state legislatures were acting on behalf of private interest, Illinois farmers.
C) the state legislatures had provided the railroad company with state regulatory exemptions when land grant legislation was enacted to help create the railroad.
D) railroad executives had committed no illegal acts in their business.
E) railroads were interstate businesses and could not be regulated by any single state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Match each entrepreneur below with the field of enterprise with which he is historically identified.

A) A-2, B-4, C-1
B) A-3, B-2, C-4
C) A-3, B-2, C-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-4, B-1, C-3

A) A-2, B-4, C-1
B) A-3, B-2, C-4
C) A-3, B-2, C-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-4, B-1, C-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The United States changed to standard time zones when
A) Congress passed a law establishing this system.
B) the major rail lines decreed common fixed times so that they could keep schedules and avoid wrecks.
C) factories demanded standard time schedules.
D) long-distance telephones required standard time coordination.
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) Congress passed a law establishing this system.
B) the major rail lines decreed common fixed times so that they could keep schedules and avoid wrecks.
C) factories demanded standard time schedules.
D) long-distance telephones required standard time coordination.
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Efforts to regulate the monopolizing practices of railroad corporations FIRST came in the form of action by
A) Congress.
B) the Supreme Court.
C) state referendums and initiatives.
D) President Cleveland's anti-trust activities.
E) state legislatures.
A) Congress.
B) the Supreme Court.
C) state referendums and initiatives.
D) President Cleveland's anti-trust activities.
E) state legislatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following was NOT among the technologies invented or improved by Thomas A. Edison?
A) the electric light bulb
B) the phonograph
C) the mimeograph
D) the electric dynamo
E) the motion picture
A) the electric light bulb
B) the phonograph
C) the mimeograph
D) the electric dynamo
E) the motion picture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The major incentive that drove captains of industry to invent machines was
A) lucrative government grants that were offered to would-be inventors.
B) a chance to strike it rich via technological innovation.
C) that machines would enable them to replace expensive skilled workers with cheap unskilled workers.
D) that machines could do the work five times faster than humans did.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) lucrative government grants that were offered to would-be inventors.
B) a chance to strike it rich via technological innovation.
C) that machines would enable them to replace expensive skilled workers with cheap unskilled workers.
D) that machines could do the work five times faster than humans did.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The American system of mass manufacture of standardized, interchangeable parts provided strong incentives for U.S. capitalists to
A) lay off tens of thousands of American workers from factories.
B) hire American workers rather than foreign immigrants.
C) replace skilled labor with machinery.
D) build extremely large factories in dedicated industrial districts.
E) pay higher wages to retain a steady workforce.
A) lay off tens of thousands of American workers from factories.
B) hire American workers rather than foreign immigrants.
C) replace skilled labor with machinery.
D) build extremely large factories in dedicated industrial districts.
E) pay higher wages to retain a steady workforce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All of the following were important factors in post-Civil War industrial expansion EXCEPT
A) a large pool of unskilled labor.
B) an abundance of natural resources.
C) American ingenuity and inventiveness.
D) immigration restrictions.
E) a political climate favoring business.
A) a large pool of unskilled labor.
B) an abundance of natural resources.
C) American ingenuity and inventiveness.
D) immigration restrictions.
E) a political climate favoring business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following was NOT among the common forms of corruption practiced by the wealthy railroad barons?
A) bribing judges and state legislatures
B) forcing their employees to buy railroad company stock
C) providing free railroad passes to journalists and politicians
D) watering railroad stocks and bonds in order to sell them at inflated prices
E) receiving kickbacks from powerful shippers
A) bribing judges and state legislatures
B) forcing their employees to buy railroad company stock
C) providing free railroad passes to journalists and politicians
D) watering railroad stocks and bonds in order to sell them at inflated prices
E) receiving kickbacks from powerful shippers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Among the countries that provided the largest amounts of foreign capital investment in American industry were
A) Sweden, Denmark, and Norway.
B) Italy, Spain, and Greece.
C) Argentina, Brazil, and Chile.
D) Britain, France, and the Netherlands.
E) Canada and Mexico.
A) Sweden, Denmark, and Norway.
B) Italy, Spain, and Greece.
C) Argentina, Brazil, and Chile.
D) Britain, France, and the Netherlands.
E) Canada and Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The vast, integrated, continental U.S. market greatly enhanced the American inclination toward
A) reducing imports of manufactured goods from abroad.
B) specialized goods produced by skilled labor.
C) government certification and regulation of consumer products.
D) mass manufacturing of standardized industrial products.
E) importing raw materials from overseas.
A) reducing imports of manufactured goods from abroad.
B) specialized goods produced by skilled labor.
C) government certification and regulation of consumer products.
D) mass manufacturing of standardized industrial products.
E) importing raw materials from overseas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The first federal regulatory agency designed to protect the public interest from business combinations was the
A) Federal Trade Commission.
B) Interstate Commerce Commission.
C) Consumer Affairs Commission.
D) Federal Anti-Trust Commission.
E) Federal Communications Commission.
A) Federal Trade Commission.
B) Interstate Commerce Commission.
C) Consumer Affairs Commission.
D) Federal Anti-Trust Commission.
E) Federal Communications Commission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The single largest source of a critical raw material that fueled early American industrialization was/were the
A) copper mines of Montana and Arizona.
B) oil wells of Oklahoma and Texas.
C) lead mines of Wisconsin.
D) coal mines of Kansas and Nebraska.
E) Mesabi iron range of Minnesota.
A) copper mines of Montana and Arizona.
B) oil wells of Oklahoma and Texas.
C) lead mines of Wisconsin.
D) coal mines of Kansas and Nebraska.
E) Mesabi iron range of Minnesota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One of the methods by which post-Civil War business leaders increased their profits was
A) increased competition.
B) supporting a centrally planned economy.
C) funding research on new technologies.
D) elimination of the tactic of vertical integration.
E) elimination of as much competition as possible.
A) increased competition.
B) supporting a centrally planned economy.
C) funding research on new technologies.
D) elimination of the tactic of vertical integration.
E) elimination of as much competition as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The two industries that the transcontinental railroads MOST significantly expanded were
A) textiles and fishing.
B) mining and agriculture.
C) banking and finance.
D) shipping and fishing.
E) electricity and telecommunications.
A) textiles and fishing.
B) mining and agriculture.
C) banking and finance.
D) shipping and fishing.
E) electricity and telecommunications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Believers in the doctrine of "survival of the fittest" argued that
A) only a few large corporations were fit to survive in the industrial jungle.
B) society owed a basic standard of living to even its weakest members.
C) there should be mental and physical competitions to determine fitness to survive and succeed in society.
D) fitness to survive and thrive could be proven only through physical competition.
E) the wealthy deserved their riches because they had demonstrated greater abilities than the poor.
A) only a few large corporations were fit to survive in the industrial jungle.
B) society owed a basic standard of living to even its weakest members.
C) there should be mental and physical competitions to determine fitness to survive and succeed in society.
D) fitness to survive and thrive could be proven only through physical competition.
E) the wealthy deserved their riches because they had demonstrated greater abilities than the poor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
To help corporations, the courts ingeniously interpreted the Fourteenth Amendment, which was designed to protect the rights of ex-slaves, so as to
A) help freedmen to work in factories.
B) incorporate big businesses.
C) allow the captains of industry to avoid paying taxes.
D) avoid corporate regulation by the states.
E) protect the civil rights of business people.
A) help freedmen to work in factories.
B) incorporate big businesses.
C) allow the captains of industry to avoid paying taxes.
D) avoid corporate regulation by the states.
E) protect the civil rights of business people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Sherman Anti-Trust Act was at first primarily used to curb the power of
A) mining companies.
B) labor unions.
C) oil companies.
D) railroad corporations.
E) banking syndicates.
A) mining companies.
B) labor unions.
C) oil companies.
D) railroad corporations.
E) banking syndicates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
America's first billion-dollar corporation was
A) General Electric (GE).
B) Standard Oil.
C) American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T).
D) The Union Pacific Railroad.
E) United States Steel.
A) General Electric (GE).
B) Standard Oil.
C) American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T).
D) The Union Pacific Railroad.
E) United States Steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
John D. Rockefeller's organizational technique of horizontal integration involved
A) franchising Standard Oil gasoline stations to independent operators.
B) combining and controlling all phases of the oil industry from drilling to commercial retailing.
C) creating standardized job assignments and fixed production and sales quotas for all employees.
D) forcing small competitors to assign stock to Standard Oil, then consolidating and integrating the operations of the previously competing enterprises, or lose their business.
E) developing multiple uses for oil in transportation, lighting, and industry.
A) franchising Standard Oil gasoline stations to independent operators.
B) combining and controlling all phases of the oil industry from drilling to commercial retailing.
C) creating standardized job assignments and fixed production and sales quotas for all employees.
D) forcing small competitors to assign stock to Standard Oil, then consolidating and integrating the operations of the previously competing enterprises, or lose their business.
E) developing multiple uses for oil in transportation, lighting, and industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The ____ Amendment was especially helpful to giant corporations when defending themselves against regulation by state governments.
A) Fifth
B) Fourteenth
C) Fifteenth
D) Sixteenth
E) Seventeenth
A) Fifth
B) Fourteenth
C) Fifteenth
D) Sixteenth
E) Seventeenth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Although they were commonly called "Social Darwinists," advocates of economic, national, or racial "survival of the fittest" ideas actually drew less on biologist Charles Darwin than on
A) English philosopher Herbert Spencer and Yale professor William Graham Sumner.
B) German philosophers like G.W.F. Hegel and Friedrich Nietzsche.
C) American literary figures like Jack London and Theodore Dreiser.
D) European scientists like Gregor Mendel and Louis Pasteur.
E) racist theorists like Arthur Gobineau and Houston Stewart Chamberlain.
A) English philosopher Herbert Spencer and Yale professor William Graham Sumner.
B) German philosophers like G.W.F. Hegel and Friedrich Nietzsche.
C) American literary figures like Jack London and Theodore Dreiser.
D) European scientists like Gregor Mendel and Louis Pasteur.
E) racist theorists like Arthur Gobineau and Houston Stewart Chamberlain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
J.P. Morgan undermined competition by placing officers of his bank on the boards of supposedly independent companies that he wanted to control. This method was known as a(n)
A) interlocking directorates
B) trust.
C) vertical integration.
D) pool.
E) fraudulent assignment.
A) interlocking directorates
B) trust.
C) vertical integration.
D) pool.
E) fraudulent assignment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Many Southerners saw employment in the textile mills as
A) high-wage positions.
B) strictly short-term or temporary employment.
C) a poor alternative to farming.
D) institutions that broke up families.
E) the only steady jobs and wages available.
A) high-wage positions.
B) strictly short-term or temporary employment.
C) a poor alternative to farming.
D) institutions that broke up families.
E) the only steady jobs and wages available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The South's major attraction for potential investors was
A) readily available raw materials.
B) a warm climate.
C) good transportation.
D) cheap labor.
E) ethnic diversity.
A) readily available raw materials.
B) a warm climate.
C) good transportation.
D) cheap labor.
E) ethnic diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Sherman Anti-Trust Act prohibited
A) companies from signing contracts without competitive bidding.
B) the federal government from favoring one business corporation over another.
C) competing companies from having interlocking corporate boards of directors.
D) private corporations or organizations from engaging in "combinations in restraint of trade."
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) companies from signing contracts without competitive bidding.
B) the federal government from favoring one business corporation over another.
C) competing companies from having interlocking corporate boards of directors.
D) private corporations or organizations from engaging in "combinations in restraint of trade."
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The steel industry owed much to the inventive genius of
A) Jay Gould.
B) Henry Bessemer.
C) J.P. Morgan
D) Thomas Edison.
E) Alexander Graham Bell.
A) Jay Gould.
B) Henry Bessemer.
C) J.P. Morgan
D) Thomas Edison.
E) Alexander Graham Bell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The "Gospel of Wealth" endorsed by Andrew Carnegie
A) based its theology on the teachings of Jesus.
B) held that the wealthy should display moral responsibility in the use of their God-given money.
C) stimulated efforts to help minorities.
D) was opposed by most late nineteenth century clergymen.
E) asserted that the wealthy should spend and invest their money in any way they felt was best.
A) based its theology on the teachings of Jesus.
B) held that the wealthy should display moral responsibility in the use of their God-given money.
C) stimulated efforts to help minorities.
D) was opposed by most late nineteenth century clergymen.
E) asserted that the wealthy should spend and invest their money in any way they felt was best.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During the age of industrialization, the South
A) was not targeted by northern industrialists who sought to introduce factories into the region.
B) received preferential treatment from the railroads.
C) turned away from agriculture
D) made major efforts to industrialize that ultimately transformed the economic culture of the South, making the region much more industrial.
E) remained overwhelmingly rural and agricultural.
A) was not targeted by northern industrialists who sought to introduce factories into the region.
B) received preferential treatment from the railroads.
C) turned away from agriculture
D) made major efforts to industrialize that ultimately transformed the economic culture of the South, making the region much more industrial.
E) remained overwhelmingly rural and agricultural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
John D. Rockefeller used all of the following tactics to achieve his domination of the oil industry EXCEPT
A) employing spies.
B) extorting rebates from railroads.
C) using federal agents to break his competitors.
D) acquiring control of 95 percent of all the oil refineries in the country.
E) using high-pressure sales methods.
A) employing spies.
B) extorting rebates from railroads.
C) using federal agents to break his competitors.
D) acquiring control of 95 percent of all the oil refineries in the country.
E) using high-pressure sales methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the late 19th century, tax and other benefits especially attracted ____ manufacturing to the new South.
A) textile
B) steel
C) train and railroad track
D) electrical appliance
E) farm equipment
A) textile
B) steel
C) train and railroad track
D) electrical appliance
E) farm equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The largest southern-based monopolistic corporation was the one founded by James Duke to produce
A) steel.
B) oil.
C) textiles.
D) cigarettes.
E) alcohol.
A) steel.
B) oil.
C) textiles.
D) cigarettes.
E) alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The first major product of the oil industry was
A) kerosene.
B) gasoline.
C) propane.
D) natural gas.
E) heating oil.
A) kerosene.
B) gasoline.
C) propane.
D) natural gas.
E) heating oil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Andrew Carnegie's system of vertical integration
A) combined all facets of an industry, from raw material to final product, within a single company.
B) created an industrial association through which member companies could wield much power.
C) embraced the notion of buying up competitors and forming a monopoly interest.
D) required smaller competitors to agree to standardized rates set by larger firms.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) combined all facets of an industry, from raw material to final product, within a single company.
B) created an industrial association through which member companies could wield much power.
C) embraced the notion of buying up competitors and forming a monopoly interest.
D) required smaller competitors to agree to standardized rates set by larger firms.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The oil industry became a huge business
A) with the building of kerosene-fueled electric generators.
B) when the federal government granted a monopoly to Standard Oil.
C) with the invention of the internal combustion engine.
D) when diesel engines were perfected.
E) when oil shipping tankers were constructed on a massive scale.
A) with the building of kerosene-fueled electric generators.
B) when the federal government granted a monopoly to Standard Oil.
C) with the invention of the internal combustion engine.
D) when diesel engines were perfected.
E) when oil shipping tankers were constructed on a massive scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Women were drawn into industry by
A) the promise of wages on par with those of men.
B) inventions like the typewriter and telephone switchboard.
C) economic downturns, which hit rural families hardest.
D) the lure of city life.
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) the promise of wages on par with those of men.
B) inventions like the typewriter and telephone switchboard.
C) economic downturns, which hit rural families hardest.
D) the lure of city life.
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is least like the other four?
A) closed shop
B) lockout
C) yellow dog contract
D) blacklist
E) company town
A) closed shop
B) lockout
C) yellow dog contract
D) blacklist
E) company town

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Reformers' efforts to raise public awareness about the hazards of child labor
A) made progress with the help of photography.
B) pertained only to native born children.
C) were focused primarily on the plight of new immigrants.
D) focused on blacklisting the most abusive companies.
E) focused mostly on girls working in textile mills.
A) made progress with the help of photography.
B) pertained only to native born children.
C) were focused primarily on the plight of new immigrants.
D) focused on blacklisting the most abusive companies.
E) focused mostly on girls working in textile mills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Most women workers of the 1890s worked
A) to achieve financial independence.
B) for the cultural glamour of being a working woman in American society.
C) for economic necessity.
D) to accumulate their retirement savings.
E) because their husbands preferred that they work.
A) to achieve financial independence.
B) for the cultural glamour of being a working woman in American society.
C) for economic necessity.
D) to accumulate their retirement savings.
E) because their husbands preferred that they work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
One of the major reasons the Knights of Labor failed was
A) its racial exclusiveness.
B) its support of unskilled workers.
C) its failure to admit women to its ranks.
D) its abandonment of the concept of independent producers.
E) the absence of "class consciousness" that caused the Knights to neglect focusing their energies on agitating and negotiating for what economic benefits they could gain from the existing capitalist system.
A) its racial exclusiveness.
B) its support of unskilled workers.
C) its failure to admit women to its ranks.
D) its abandonment of the concept of independent producers.
E) the absence of "class consciousness" that caused the Knights to neglect focusing their energies on agitating and negotiating for what economic benefits they could gain from the existing capitalist system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Leftists scholars who found fault with the post-Civil War era captains of industry mostly argued that these men
A) had no real business ability.
B) built their corporate wealth and power by exploiting workers.
C) tried to take the United States back to an earlier age of aristocracy.
D) were environmentally insensitive.
E) were insufficiently philanthropic in donating considerable sums of personal wealth to cultural institutions such as libraries that benefited the masses.
A) had no real business ability.
B) built their corporate wealth and power by exploiting workers.
C) tried to take the United States back to an earlier age of aristocracy.
D) were environmentally insensitive.
E) were insufficiently philanthropic in donating considerable sums of personal wealth to cultural institutions such as libraries that benefited the masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Historians critical of the captains of industry and capitalism in the post-Civil War era generally concede that class-based protest
A) was a more galvanizing and more violent phenomenon among the lower classes in the United States than it was in Europe.
B) was less than in Europe because of America's greater level of social mobility.
C) was dampened by the fact large numbers of Americans in post-Civil War era made small improvements in their economic and social status.
D) was diluted by differences in social mobility, according to race and ethnicity.
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) was a more galvanizing and more violent phenomenon among the lower classes in the United States than it was in Europe.
B) was less than in Europe because of America's greater level of social mobility.
C) was dampened by the fact large numbers of Americans in post-Civil War era made small improvements in their economic and social status.
D) was diluted by differences in social mobility, according to race and ethnicity.
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Despite generally rising wages in the late nineteenth century, industrial workers were extremely vulnerable to all of the following EXCEPT
A) economic swings and depressions.
B) employers' whims.
C) new educational requirements for jobs.
D) sudden unemployment.
E) illness and accident.
A) economic swings and depressions.
B) employers' whims.
C) new educational requirements for jobs.
D) sudden unemployment.
E) illness and accident.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
One group barred from membership in the Knights of Labor was
A) African Americans.
B) "nonproducers" such as liquor dealers, professional gamblers, lawyers, bankers, and stockbrokers.
C) women.
D) immigrants.
E) unskilled workers.
A) African Americans.
B) "nonproducers" such as liquor dealers, professional gamblers, lawyers, bankers, and stockbrokers.
C) women.
D) immigrants.
E) unskilled workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Railroading in the late 19th century provided a significant stimulus to
A) agriculture.
B) urbanization.
C) feminism.
D) immigration.
E) industrialization.
A) agriculture.
B) urbanization.
C) feminism.
D) immigration.
E) industrialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Vital improvements in railroading in the late 19th century included
A) standard gauge of track width.
B) air brakes.
C) steel rails.
D) Pullman cars.
E) the block signal.
A) standard gauge of track width.
B) air brakes.
C) steel rails.
D) Pullman cars.
E) the block signal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The image of the "Gibson Girl" represented a(n)
A) revival of the early American feminine ideal of republican motherhood.
B) portrayal of the modern corporate business woman.
C) exploitative image of the woman as a sex object.
D) romantic ideal of the independent and athletic new woman.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) revival of the early American feminine ideal of republican motherhood.
B) portrayal of the modern corporate business woman.
C) exploitative image of the woman as a sex object.
D) romantic ideal of the independent and athletic new woman.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One of the greatest changes that industrialization brought about in the lives of workers was
A) their movement to the suburbs.
B) the need for them to adjust their lives to the time clock.
C) enjoying less physical comforts and a declining standard of living.
D) the narrowing of class divisions.
E) the encounter with other races.
A) their movement to the suburbs.
B) the need for them to adjust their lives to the time clock.
C) enjoying less physical comforts and a declining standard of living.
D) the narrowing of class divisions.
E) the encounter with other races.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Knights of Labor believed that republican traditions and institutions could be preserved from corrupt monopolies
A) when American workers achieved a greater degree of class consciousness.
B) by strengthening the economic and political independence of the workers.
C) through the destruction of the American Federation of Labor.
D) by the development of strong craft unions.
E) by forming an independent political movement.
A) when American workers achieved a greater degree of class consciousness.
B) by strengthening the economic and political independence of the workers.
C) through the destruction of the American Federation of Labor.
D) by the development of strong craft unions.
E) by forming an independent political movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Generally, the Supreme Court in the late 19th century interpreted the Constitution in such a way as to favor
A) labor unions.
B) corporations.
C) state regulatory agencies.
D) individual entrepreneurs.
E) independent workers and craftsmen.
A) labor unions.
B) corporations.
C) state regulatory agencies.
D) individual entrepreneurs.
E) independent workers and craftsmen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
By 1900, American attitudes toward labor began to change as the public came to recognize the right of workers to bargain collectively and strike. Nevertheless,
A) labor unions continued to decline in membership.
B) the American Federation of Labor failed to take advantage of the situation.
C) the vast majority of employers continued to fight organized labor.
D) Congress declared the AFL illegal.
E) workers began to turn to the Socialist party.
A) labor unions continued to decline in membership.
B) the American Federation of Labor failed to take advantage of the situation.
C) the vast majority of employers continued to fight organized labor.
D) Congress declared the AFL illegal.
E) workers began to turn to the Socialist party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The most effective and most enduring labor union of the post-Civil War period was the
A) National Labor Union.
B) Knights of Labor.
C) American Federation of Labor.
D) United Steel Workers of America.
E) Congress of Industrial Organizations.
A) National Labor Union.
B) Knights of Labor.
C) American Federation of Labor.
D) United Steel Workers of America.
E) Congress of Industrial Organizations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the textiles mills of the industrializing South, all of the following are true statements EXCEPT
A) rural black and white southerners landed plumb jobs in the new mills.
B) entire families worked long hours in the mills.
C) most workers were paid half the rate received by northern workers for the same tasks.
D) payment was typically made in credit to the company store.
E) workers were called "hillbillies" or "lintheads" by employers.
A) rural black and white southerners landed plumb jobs in the new mills.
B) entire families worked long hours in the mills.
C) most workers were paid half the rate received by northern workers for the same tasks.
D) payment was typically made in credit to the company store.
E) workers were called "hillbillies" or "lintheads" by employers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The first transcontinental railroad was completed by the construction efforts of which of the following railroads?
A) Union Pacific
B) Northern Pacific
C) Central Pacific
D) Southern Pacific
E) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe
A) Union Pacific
B) Northern Pacific
C) Central Pacific
D) Southern Pacific
E) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The factors promoting the growth of manufacturing in post-Civil War America included
A) plentiful cheap labor.
B) available investment capital.
C) abundant natural resources.
D) effective government planning.
E) massive immigration.
A) plentiful cheap labor.
B) available investment capital.
C) abundant natural resources.
D) effective government planning.
E) massive immigration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



