Deck 11: Managing Demand and Forecasting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Managing Demand and Forecasting
1
Using sales force estimates for forecasting has the advantage that
A) confusion between customer "wants" (wish list) and customer "needs" (necessary purchases) is eliminated.
B) statistical estimates of seasonal factors are more precise than any other approach.
C) forecasts of individual sale force members can be easily combined to get regional or national sales totals.
D) no biases exist in the forecasts.
A) confusion between customer "wants" (wish list) and customer "needs" (necessary purchases) is eliminated.
B) statistical estimates of seasonal factors are more precise than any other approach.
C) forecasts of individual sale force members can be easily combined to get regional or national sales totals.
D) no biases exist in the forecasts.
forecasts of individual sale force members can be easily combined to get regional or national sales totals.
2
Demands for a newly developed salad bar at the Great Professional restaurant for the first six months of this year are shown below. What is the forecast for July if the weighted moving average method is used? (Use weights of 0.5 for the most recent demand, 0.3, and 0.2.) 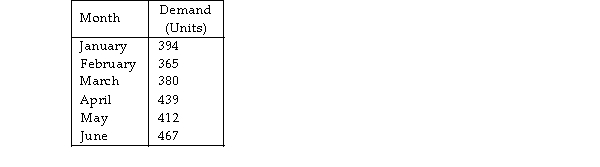
A) less than or equal to 432 units
B) greater than 432 units but less than or equal to 442 units
C) greater than 442 units but less than or equal to 452 units
D) greater than 452

A) less than or equal to 432 units
B) greater than 432 units but less than or equal to 442 units
C) greater than 442 units but less than or equal to 452 units
D) greater than 452
greater than 442 units but less than or equal to 452 units
3
Table 11.6.
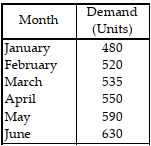
Use the information in Table 11.6. Use the exponential smoothing method with ? = 0.5 to forecast the sales for year 5.
A) less than or equal to 3
B) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
C) greater than 4 but less than or equal to 5
D) greater than 5

Use the information in Table 11.6. Use the exponential smoothing method with ? = 0.5 to forecast the sales for year 5.
A) less than or equal to 3
B) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
C) greater than 4 but less than or equal to 5
D) greater than 5
greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
4
Table 11.9.
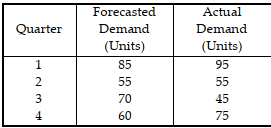
Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the mean absolute percent error for the data?
A) less than 5%
B) greater than or equal to 5%, but less than 13%
C) greater than or equal to 13%, but less than or equal to 18%
D) greater than 18%

Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the mean absolute percent error for the data?
A) less than 5%
B) greater than or equal to 5%, but less than 13%
C) greater than or equal to 13%, but less than or equal to 18%
D) greater than 18%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 11.7.
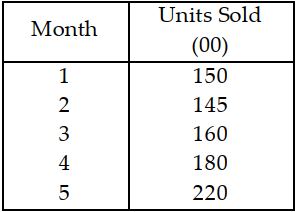
Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 5 is
A) less than or equal to 150 units.
B) greater than 150 but less than or equal to 160 units.
C) greater than 160 but less than or equal to 170 units.
D) greater than 170 units.

Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 5 is
A) less than or equal to 150 units.
B) greater than 150 but less than or equal to 160 units.
C) greater than 160 but less than or equal to 170 units.
D) greater than 170 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Delphi method of forecasting is useful when
A) historical data is available and the best basis for making projections is to use past demand patterns.
B) a systematic approach to creating and testing hypotheses is needed and the data are usually gathered by sending a questionnaire to consumers.
C) judgment and opinion are the only bases for making informed projections.
D) historical data are available and the relationship between the factor to be forecast and other external or internal factors can be identified.
A) historical data is available and the best basis for making projections is to use past demand patterns.
B) a systematic approach to creating and testing hypotheses is needed and the data are usually gathered by sending a questionnaire to consumers.
C) judgment and opinion are the only bases for making informed projections.
D) historical data are available and the relationship between the factor to be forecast and other external or internal factors can be identified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 11.1.
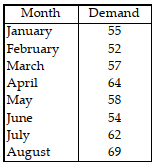
Use the information in Table 11.1. Your boss has asked you to find a good technique to forecast short- term demand for an important product. You have decided to test the following four techniques against the historical data already given: -Three- month simple moving average
-Three- month weighted moving average, with weight of 0.6 for the most recent month, 0.3 for the second- most- recent month, and 0.1 for the third- most- recent month
-Three- month weighted moving average, with weights of 0.5 for the most recent month, 0.3 for the second- most- recent month, and 0.2 for the third- most- recent month
-Exponential smoothing (a = 0.3 and the forecast for March was 55)
Use each of the four techniques to forecast April through August, and then use the five months of forecasts to calculate MAD. Round all forecasts to the nearest whole number just before doing your MAD calculations. Which of the four techniques is best in terms of MAD?
A) three- month weighted moving average (0.5, 0.3, 0.2)
B) three- month weighted moving average (0.6, 0.3, 0.1)
C) exponential smoothing (a = 0.3)
D) three- month simple moving average

Use the information in Table 11.1. Your boss has asked you to find a good technique to forecast short- term demand for an important product. You have decided to test the following four techniques against the historical data already given: -Three- month simple moving average
-Three- month weighted moving average, with weight of 0.6 for the most recent month, 0.3 for the second- most- recent month, and 0.1 for the third- most- recent month
-Three- month weighted moving average, with weights of 0.5 for the most recent month, 0.3 for the second- most- recent month, and 0.2 for the third- most- recent month
-Exponential smoothing (a = 0.3 and the forecast for March was 55)
Use each of the four techniques to forecast April through August, and then use the five months of forecasts to calculate MAD. Round all forecasts to the nearest whole number just before doing your MAD calculations. Which of the four techniques is best in terms of MAD?
A) three- month weighted moving average (0.5, 0.3, 0.2)
B) three- month weighted moving average (0.6, 0.3, 0.1)
C) exponential smoothing (a = 0.3)
D) three- month simple moving average

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A tracking signal greater than zero and a mean absolute deviation greater than zero imply that the forecast has
A) a nonzero amount of bias and a nonzero amount of forecast error variability.
B) a nonzero amount of bias and no variability of forecast error.
C) no bias and no variability of forecast error.
D) no bias and a nonzero amount of forecast error variability.
A) a nonzero amount of bias and a nonzero amount of forecast error variability.
B) a nonzero amount of bias and no variability of forecast error.
C) no bias and no variability of forecast error.
D) no bias and a nonzero amount of forecast error variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following statements about the patterns of a demand series is FALSE?
A) The trend, over an extended period of time, always increases the average level of the series.
B) The five basic patterns of most business demand series are the horizontal, trend, seasonal, cyclical, and random.
C) Estimating cyclical movement is difficult. Forecasters do not know the duration of the cycle because they cannot predict the events that cause it.
D) Every demand series has at least the following two components: horizontal and random.
A) The trend, over an extended period of time, always increases the average level of the series.
B) The five basic patterns of most business demand series are the horizontal, trend, seasonal, cyclical, and random.
C) Estimating cyclical movement is difficult. Forecasters do not know the duration of the cycle because they cannot predict the events that cause it.
D) Every demand series has at least the following two components: horizontal and random.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following statements about forecasting is FALSE?
A) The weighted moving average method allows forecasters to emphasize recent demand over earlier demand. The forecast will be more responsive to change in the underlying average of the demand series.
B) The most frequently used time series forecasting method is exponential smoothing because of its simplicity and the small amount of data needed to support it.
C) In exponential smoothing, higher alpha values place greater weight on recent demands in computing the average.
D) You should use the simple moving average method to estimate the mean demand of a time series that has a pronounced trend and seasonal influences.
A) The weighted moving average method allows forecasters to emphasize recent demand over earlier demand. The forecast will be more responsive to change in the underlying average of the demand series.
B) The most frequently used time series forecasting method is exponential smoothing because of its simplicity and the small amount of data needed to support it.
C) In exponential smoothing, higher alpha values place greater weight on recent demands in computing the average.
D) You should use the simple moving average method to estimate the mean demand of a time series that has a pronounced trend and seasonal influences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which one of the following basic patterns of demand is difficult to predict because it is affected by national or international events or because of a lack of demand history reflecting the stages of demand from product development to decline?
A) random
B) cyclical
C) horizontal
D) seasonal
A) random
B) cyclical
C) horizontal
D) seasonal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following statements about forecasting is FALSE?
A) The method for incorporating a trend in an exponentially smoothed forecast requires the estimation of three smoothing constants: one for the mean, one for the trend, and one for the error.
B) A tracking signal is a measure that indicates whether a method of forecasting has any built- in biases over a period of time.
C) The standard deviation and the mean absolute deviation measure the dispersion of forecast errors.
D) The cumulative sum of forecast errors (CFE) is useful in measuring the bias in a forecast.
A) The method for incorporating a trend in an exponentially smoothed forecast requires the estimation of three smoothing constants: one for the mean, one for the trend, and one for the error.
B) A tracking signal is a measure that indicates whether a method of forecasting has any built- in biases over a period of time.
C) The standard deviation and the mean absolute deviation measure the dispersion of forecast errors.
D) The cumulative sum of forecast errors (CFE) is useful in measuring the bias in a forecast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Acme Computer Company has recorded sales of one of its products for a six- week period:  Using the three- week moving average method, forecast sales for week 7.
Using the three- week moving average method, forecast sales for week 7.
A) 20
B) 21
C) 22
D) 23
 Using the three- week moving average method, forecast sales for week 7.
Using the three- week moving average method, forecast sales for week 7.A) 20
B) 21
C) 22
D) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A systematic increase or decrease in the mean of a demand time series is referred to as
A) a trend.
B) random variation.
C) a seasonal pattern.
D) a cyclical adjustment.
A) a trend.
B) random variation.
C) a seasonal pattern.
D) a cyclical adjustment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Table 11.9.

Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the mean absolute deviation of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 25 units
C) greater than 25, but less than or equal to 50 units
D) greater than 50 units

Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the mean absolute deviation of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 25 units
C) greater than 25, but less than or equal to 50 units
D) greater than 50 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Table 11.4.
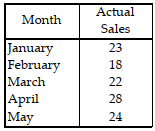
Use the information in Table 11.4. The forecasting equation for a three- month weighted moving average is: At = W1Dt + W2Dt - 1 + W3Dt - 2
If the sales for June were 40 units and the weights are W1= 1/2, W2 = 1/3, and W3 = 1/6, what is the forecast for July?
A) less than or equal to 30 units
B) greater than 30 but less than or equal to 33 units
C) greater than 33 but less than or equal to 36 units
D) greater than 36 units

Use the information in Table 11.4. The forecasting equation for a three- month weighted moving average is: At = W1Dt + W2Dt - 1 + W3Dt - 2
If the sales for June were 40 units and the weights are W1= 1/2, W2 = 1/3, and W3 = 1/6, what is the forecast for July?
A) less than or equal to 30 units
B) greater than 30 but less than or equal to 33 units
C) greater than 33 but less than or equal to 36 units
D) greater than 36 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 11.8.
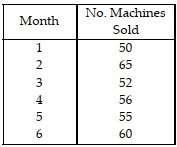
Use the information in Table 11.8. Use the weighted moving average method to calculate the forecast for month 7. The weights are 0.50, 0.30, and 0.20, where 0.50 refers to the most recent demand.
A) less than or equal to 56
B) greater than 56 but less than or equal to 58
C) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 61
D) greater than 61

Use the information in Table 11.8. Use the weighted moving average method to calculate the forecast for month 7. The weights are 0.50, 0.30, and 0.20, where 0.50 refers to the most recent demand.
A) less than or equal to 56
B) greater than 56 but less than or equal to 58
C) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 61
D) greater than 61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 11.9.
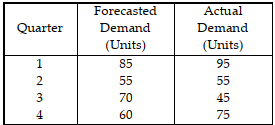
Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the standard deviation of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 10 units
C) greater than 10, but less than 20 units
D) greater than 20 units

Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the standard deviation of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 10 units
C) greater than 10, but less than 20 units
D) greater than 20 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which one of the following is an example of a time series forecasting technique?
A) trend- adjusted exponential smoothing
B) Delphi method
C) survey analysis
D) market research
A) trend- adjusted exponential smoothing
B) Delphi method
C) survey analysis
D) market research

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Table 11.1.
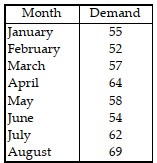
Use the information in Table 11.1. What would be the forecast for September if the exponential smoothing technique were used? (a = 0.30 and the forecast for March was 55)
A) less than or equal to 65
B) greater than 65 but less than or equal to 67
C) greater than 67 but less than or equal to 69
D) greater than 69

Use the information in Table 11.1. What would be the forecast for September if the exponential smoothing technique were used? (a = 0.30 and the forecast for March was 55)
A) less than or equal to 65
B) greater than 65 but less than or equal to 67
C) greater than 67 but less than or equal to 69
D) greater than 69

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Table 11.7.
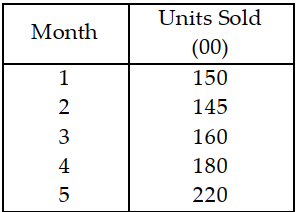
Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 3 is
A) less than or equal to 140 units.
B) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 160 units.
C) greater than 160 but less than or equal to 180 units.
D) greater than 180 units.

Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 3 is
A) less than or equal to 140 units.
B) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 160 units.
C) greater than 160 but less than or equal to 180 units.
D) greater than 180 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Classical Consultant Company provides forecasting research for clients such as a group of five doctors associated with a new hospital health maintenance program. The company has been asked to forecast the number of patients requesting blood analysis per week. The past weekly average is 38 and for the trend is 2 per week. This week's demand was 42 blood tests. How many patients Will come next week? (Suppose α = 0.10 and β = 0.30.)
A) less than or equal to 39
B) greater than 39 but less than or equal to 41
C) greater than 41 but less than or equal to 43
D) greater than 43
A) less than or equal to 39
B) greater than 39 but less than or equal to 41
C) greater than 41 but less than or equal to 43
D) greater than 43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is an example of a judgmental forecasting technique?
A) simple moving average
B) linear regression
C) market research
D) multiplicative seasonal method
A) simple moving average
B) linear regression
C) market research
D) multiplicative seasonal method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Bias is always less than MAD.
B) For projections of more stable demand patterns without trends, seasonal influences, or cyclical influences, use larger values of n in the simple moving average approach.
C) Getting a single forecast of 500 units for the month of July is better than getting a forecast that there is a 95 percent chance that demand for July will be between 450 and 550 units.
D) The ideal of zero bias and zero MAD can be accomplished by systematically searching for the best values of the smoothing constants.
A) Bias is always less than MAD.
B) For projections of more stable demand patterns without trends, seasonal influences, or cyclical influences, use larger values of n in the simple moving average approach.
C) Getting a single forecast of 500 units for the month of July is better than getting a forecast that there is a 95 percent chance that demand for July will be between 450 and 550 units.
D) The ideal of zero bias and zero MAD can be accomplished by systematically searching for the best values of the smoothing constants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Table 11.3
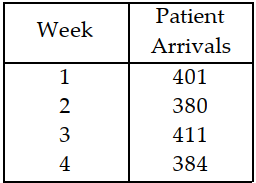
Use the information in Table 11.3. Calculate the exponential smoothing forecast for week 5 using a = 0.10 and F4 = 410.
A) less than or equal to 400
B) greater than 400 but less than or equal to 408
C) greater than 408 but less than or equal to 416
D) greater than 416

Use the information in Table 11.3. Calculate the exponential smoothing forecast for week 5 using a = 0.10 and F4 = 410.
A) less than or equal to 400
B) greater than 400 but less than or equal to 408
C) greater than 408 but less than or equal to 416
D) greater than 416

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The management of a company specializing in securities analysis has been using two forecasting methods to follow a new stock issue. Forecast Method 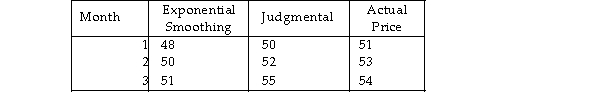 Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Based on MAD, the judgmental method is more accurate.
B) Based on CFE, the bias of the judgment forecasts is larger than the bias of the exponential smoothing forecasts.
C) Based on MAD, the exponential smoothing approach is more accurate.
D) Based on CFE, the bias of the exponential smoothing forecasts is steadily improving.
 Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?A) Based on MAD, the judgmental method is more accurate.
B) Based on CFE, the bias of the judgment forecasts is larger than the bias of the exponential smoothing forecasts.
C) Based on MAD, the exponential smoothing approach is more accurate.
D) Based on CFE, the bias of the exponential smoothing forecasts is steadily improving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the underlying mean of a time series changes frequently but there is no trend, cyclical, or seasonal influence,
A) an exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.01 should outperform a exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.30.
B) a simple moving average forecast with n = 3 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 20.
C) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should perform about the same as a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
D) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
A) an exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.01 should outperform a exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.30.
B) a simple moving average forecast with n = 3 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 20.
C) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should perform about the same as a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
D) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
With the multiplicative seasonal method of forecasting,
A) there can only be four seasons in the time series data.
B) the times series cannot exhibit a trend.
C) the seasonal amplitude is a constant, regardless of the magnitude of average demand.
D) seasonal factors are multiplied by an estimate of average demand to arrive at a seasonal forecast.
A) there can only be four seasons in the time series data.
B) the times series cannot exhibit a trend.
C) the seasonal amplitude is a constant, regardless of the magnitude of average demand.
D) seasonal factors are multiplied by an estimate of average demand to arrive at a seasonal forecast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Table 11.2
The manager of a pizza shop must forecast weekly demand for special pizzas
so that he can order pizza shells weekly. Recent demand has been:
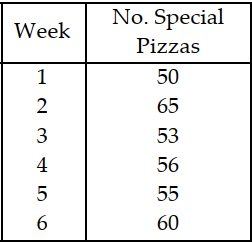
Use the information from Table 11.2. Using a four- week moving average, what is the forecast for week 7?
A) less than or equal to 58
B) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 60
C) greater than 60 but less than or equal to 62
D) greater than 62
The manager of a pizza shop must forecast weekly demand for special pizzas
so that he can order pizza shells weekly. Recent demand has been:

Use the information from Table 11.2. Using a four- week moving average, what is the forecast for week 7?
A) less than or equal to 58
B) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 60
C) greater than 60 but less than or equal to 62
D) greater than 62

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which one of the following time series forecasting methods will generate the most accurate forecasts when demands have a consistent trend pattern?
A) simple moving average method
B) weighted moving average method
C) trend- adjusted exponential smoothing method
D) exponential smoothing method
A) simple moving average method
B) weighted moving average method
C) trend- adjusted exponential smoothing method
D) exponential smoothing method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Table 11.6.
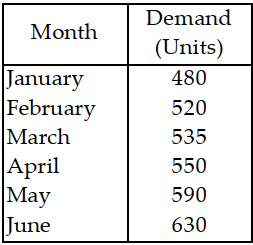
Use the information in Table 11.6. Use an exponential smoothing model with a smoothing parameter of 0.30 to forecast sales for year 5.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 3
C) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
D) greater than 4

Use the information in Table 11.6. Use an exponential smoothing model with a smoothing parameter of 0.30 to forecast sales for year 5.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 3
C) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
D) greater than 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which one of the following is an example of causal forecasting technique?
A) weighted moving average
B) exponential smoothing
C) linear regression
D) Delphi method
A) weighted moving average
B) exponential smoothing
C) linear regression
D) Delphi method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Assume that a time series forecast is generated for future demand, and subsequently it is observed that the forecast method did not accurately predict the actual demand. Specifically, the forecast errors were found to be: Mean absolute percent error = 10%
Cumulative sum of forecast errors = 0%
Which one of the statements concerning this forecast is TRUE?
A) The forecast has a positive bias and a positive standard deviation of errors.
B) The forecast has no bias and has a standard deviation of errors equal to zero.
C) The forecast has a positive bias and a standard deviation of errors equal to zero.
D) The forecast has no bias but has a positive standard deviation of errors.
Cumulative sum of forecast errors = 0%
Which one of the statements concerning this forecast is TRUE?
A) The forecast has a positive bias and a positive standard deviation of errors.
B) The forecast has no bias and has a standard deviation of errors equal to zero.
C) The forecast has a positive bias and a standard deviation of errors equal to zero.
D) The forecast has no bias but has a positive standard deviation of errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Table 11.7.
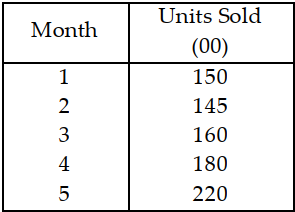
TOMBOW is a small manufacturer of pencils and has had the following sales record for the most recent five months: Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 2 is
A) less than or equal to 120 units.
B) greater than 120 but less than or equal to 140 units.
C) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 160 units.
D) greater than 160 units.

TOMBOW is a small manufacturer of pencils and has had the following sales record for the most recent five months: Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 2 is
A) less than or equal to 120 units.
B) greater than 120 but less than or equal to 140 units.
C) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 160 units.
D) greater than 160 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Table 11.2
The manager of a pizza shop must forecast weekly demand for special pizzas
so that he can order pizza shells weekly. Recent demand has been:
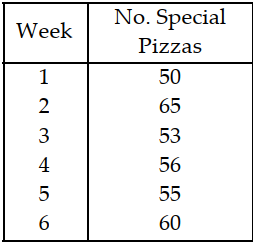
Use the information from Table 11.2. If a four- week weighted moving average were used, what would be the forecast for week 7? (The weights are 0.77, 0.11, 0.11, and 0.01.)
A) less than or equal to 58
B) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 59
C) greater than 59 but less than or equal to 60
D) greater than 60
The manager of a pizza shop must forecast weekly demand for special pizzas
so that he can order pizza shells weekly. Recent demand has been:

Use the information from Table 11.2. If a four- week weighted moving average were used, what would be the forecast for week 7? (The weights are 0.77, 0.11, 0.11, and 0.01.)
A) less than or equal to 58
B) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 59
C) greater than 59 but less than or equal to 60
D) greater than 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 11.4.
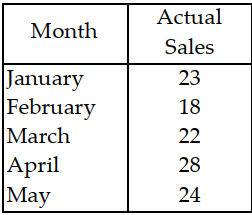
Use the information in Table 11.4. Suppose actual sales in June turn out to be 40 units. Use the three- month moving average method to forecast the sales in July.
A) less than or equal to 27
B) greater than 27 but less than or equal to 29 units
C) greater than 29 but less than or equal to 31 units
D) greater than 31 units
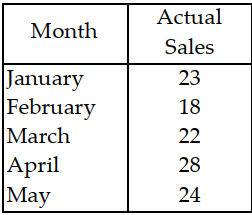
Use the information in Table 11.4. Suppose actual sales in June turn out to be 40 units. Use the three- month moving average method to forecast the sales in July.
A) less than or equal to 27
B) greater than 27 but less than or equal to 29 units
C) greater than 29 but less than or equal to 31 units
D) greater than 31 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the following data concerning the performance of a forecasting method. 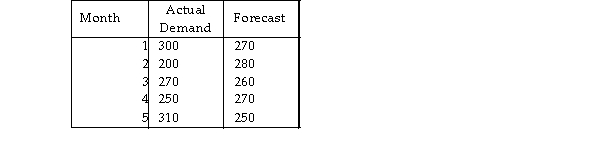
A) The CFE is less than 100, and the MAD is greater than 50.
B) The CFE is less than 100, and the MAD is less than 50.
C) The CFE is greater than 100, and the MAD is greater than 50.
D) The CFE is greater than 100, and the MAD is less than 50.

A) The CFE is less than 100, and the MAD is greater than 50.
B) The CFE is less than 100, and the MAD is less than 50.
C) The CFE is greater than 100, and the MAD is greater than 50.
D) The CFE is greater than 100, and the MAD is less than 50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which one of the following statements about forecasting is TRUE?
A) Judgment methods are designed particularly for situations when historical data are lacking.
B) Casual methods are used when historical data are available and the relationship between the factor to be forecast and other external and internal factors cannot be identified.
C) Focused forecasting is a technique that focuses on one particular component of demand and develops a forecast from it.
D) The five basic patterns of demand are the horizontal, trend, seasonal, cyclical, and the subjective judgment of forecasters.
A) Judgment methods are designed particularly for situations when historical data are lacking.
B) Casual methods are used when historical data are available and the relationship between the factor to be forecast and other external and internal factors cannot be identified.
C) Focused forecasting is a technique that focuses on one particular component of demand and develops a forecast from it.
D) The five basic patterns of demand are the horizontal, trend, seasonal, cyclical, and the subjective judgment of forecasters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Table 11.5.
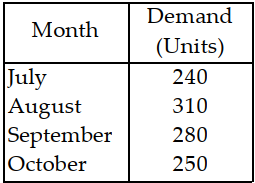
Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the exponential smoothing method, with alpha equal to 0.2, what is the forecasted demand for November? Use an initial value for the forecast (July) equal to 277 units.
A) less than or equal to 260 units
B) greater than 260 but less than or equal to 275 units
C) greater than 275 but less than or equal to 285 units
D) more than 285 units

Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the exponential smoothing method, with alpha equal to 0.2, what is the forecasted demand for November? Use an initial value for the forecast (July) equal to 277 units.
A) less than or equal to 260 units
B) greater than 260 but less than or equal to 275 units
C) greater than 275 but less than or equal to 285 units
D) more than 285 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Table 11.4.
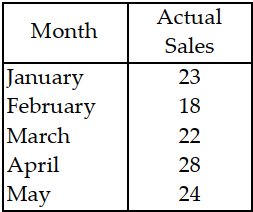
Use the information in Table 11.4. Use the three- month moving average method to forecast sales for June.
A) less than or equal to 20 units
B) greater than 20 but less than or equal to 22 units
C) greater than 22 but less than or equal to 24 units
D) greater than 24 units
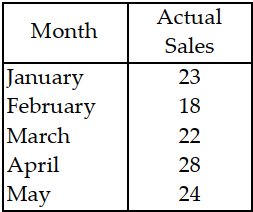
Use the information in Table 11.4. Use the three- month moving average method to forecast sales for June.
A) less than or equal to 20 units
B) greater than 20 but less than or equal to 22 units
C) greater than 22 but less than or equal to 24 units
D) greater than 24 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Table 11.8.
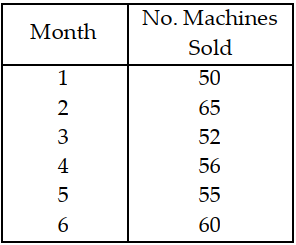
Use the information in Table 11.8. Calculate the MAD for months 4 through 6 for the three- month moving average forecasts.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 4
C) greater than 4 but less than or equal to 6
D) greater than 6

Use the information in Table 11.8. Calculate the MAD for months 4 through 6 for the three- month moving average forecasts.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 4
C) greater than 4 but less than or equal to 6
D) greater than 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The judgment methods of forecasting are to be used for purposes of
A) making adjustments to quantitative forecasts due to unusual circumstances.
B) making forecasts more variable.
C) avoiding the calculations necessary for quantitative forecasts.
D) forecasting seasonal demands in lieu of time series approaches.
A) making adjustments to quantitative forecasts due to unusual circumstances.
B) making forecasts more variable.
C) avoiding the calculations necessary for quantitative forecasts.
D) forecasting seasonal demands in lieu of time series approaches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The multiplicative seasonal method is most appropriate when the
A) demand each period is a constant multiple of the demand in the previous period.
B) seasonal influence is dependent on the level of demand.
C) seasonal influence is erratic, changing in the timing of the peaks and valleys.
D) seasonal influence is a constant regardless of the level of demand.
A) demand each period is a constant multiple of the demand in the previous period.
B) seasonal influence is dependent on the level of demand.
C) seasonal influence is erratic, changing in the timing of the peaks and valleys.
D) seasonal influence is a constant regardless of the level of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A weighted moving average method that calculates the average of a time series by giving recent demands more weight than earlier methods is called
A) seasonally adjusted smoothing.
B) exponential smoothing.
C) cumulative tracking error.
D) multiplicative seasonal method.
A) seasonally adjusted smoothing.
B) exponential smoothing.
C) cumulative tracking error.
D) multiplicative seasonal method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 11.8
A manager wants to forecast the monthly demand
for a machine the company produces.
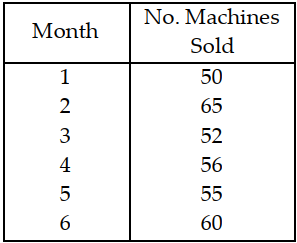
Use the information in Table 11.8. Forecast the demand for the machine for month 7, using the three- month moving average method.
A) less than or equal to 56
B) greater than 56 but less than or equal to 58
C) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 61
D) greater than 61
A manager wants to forecast the monthly demand
for a machine the company produces.

Use the information in Table 11.8. Forecast the demand for the machine for month 7, using the three- month moving average method.
A) less than or equal to 56
B) greater than 56 but less than or equal to 58
C) greater than 58 but less than or equal to 61
D) greater than 61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which one of the following statements about forecasting is FALSE?
A) Time series express the relationship between the factor to be forecast and related factors, such as promotional campaigns, economic conditions, and competitor actions.
B) To achieve the objective of developing a useful forecast from the information at hand, the forecaster must select the appropriate technique. This choice sometimes involves a trade- off between forecast accuracy and cost.
C) Three general types of forecasting techniques are used for demand forecasting: time series analysis, causal methods, and judgment methods.
D) A time series is a list of repeated observations of a phenomenon, such as demand, arranged in the order in which they actually occurred.
A) Time series express the relationship between the factor to be forecast and related factors, such as promotional campaigns, economic conditions, and competitor actions.
B) To achieve the objective of developing a useful forecast from the information at hand, the forecaster must select the appropriate technique. This choice sometimes involves a trade- off between forecast accuracy and cost.
C) Three general types of forecasting techniques are used for demand forecasting: time series analysis, causal methods, and judgment methods.
D) A time series is a list of repeated observations of a phenomenon, such as demand, arranged in the order in which they actually occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Table 11.7
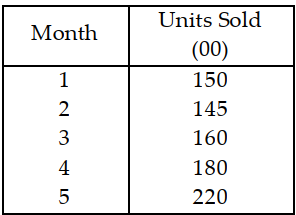
Use the information in Table 11.7. What is the MAD for months 2 through 5?
A) less than or equal to 20
B) greater than 20 but less than or equal to 25
C) greater than 25 but less than or equal to 30
D) greater than 30

Use the information in Table 11.7. What is the MAD for months 2 through 5?
A) less than or equal to 20
B) greater than 20 but less than or equal to 25
C) greater than 25 but less than or equal to 30
D) greater than 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Table 11.8
A manager wants to forecast the monthly demand
for a machine the company produces.
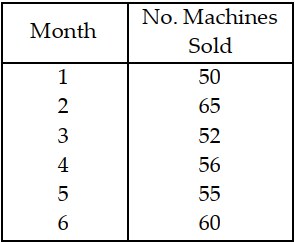
Use the information in Table 11.8. Calculate the MAD for months 4 through 6 for the weighted moving average forecasts. The weights are 0.50, 0.30, and 0.20, where 0.50 refers to the most recent demand.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 3
C) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
D) greater than 4
A manager wants to forecast the monthly demand
for a machine the company produces.

Use the information in Table 11.8. Calculate the MAD for months 4 through 6 for the weighted moving average forecasts. The weights are 0.50, 0.30, and 0.20, where 0.50 refers to the most recent demand.
A) less than or equal to 2
B) greater than 2 but less than or equal to 3
C) greater than 3 but less than or equal to 4
D) greater than 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
It is now near the end of May and you must prepare a forecast for June for a certain product. The forecast for May was 900 units. The actual demand for May was 1000 units. You are using the exponential smoothing method with a = 0.20. The forecast for June is
A) less than 925 units.
B) greater than or equal to 925 units but less than 950 units.
C) greater than or equal to 950 units but less than 1000 units.
D) greater than or equal to 1000 units.
A) less than 925 units.
B) greater than or equal to 925 units but less than 950 units.
C) greater than or equal to 950 units but less than 1000 units.
D) greater than or equal to 1000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Table 11.5.
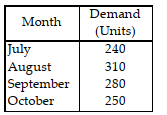
Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the weighted moving average technique and the following weights, what is the forecasted demand for November?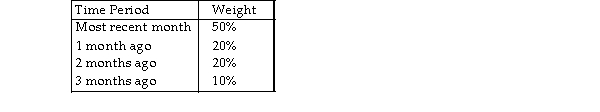
A) less than or equal to 250 units
B) greater than 250 but less than or equal to 265 units
C) greater than 265 but less than or equal to 280 units
D) more than 280 units

Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the weighted moving average technique and the following weights, what is the forecasted demand for November?

A) less than or equal to 250 units
B) greater than 250 but less than or equal to 265 units
C) greater than 265 but less than or equal to 280 units
D) more than 280 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Table 11.9
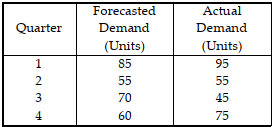
Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the cumulative sum of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 25 units
C) greater than 25, but less than or equal to 50 units
D) greater than 50 units

Use the information in Table 11.9. What is the cumulative sum of forecast errors for the data?
A) 0 units
B) greater than 0, but less than or equal to 25 units
C) greater than 25, but less than or equal to 50 units
D) greater than 50 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Table 11.3.
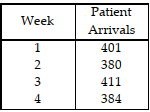
Use the information in Table 11.3. Compute a three- week moving average forecast for the arrival of medical clinic patients in week 5.
A) less than or equal to 382
B) greater than 382 but less than or equal to 389
C) greater than 389 but less than or equal to 396
D) greater than 396

Use the information in Table 11.3. Compute a three- week moving average forecast for the arrival of medical clinic patients in week 5.
A) less than or equal to 382
B) greater than 382 but less than or equal to 389
C) greater than 389 but less than or equal to 396
D) greater than 396

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which one of the following is most useful for measuring the bias in a forecast?
A) cumulative sum of forecast errors
B) standard deviation of forecast errors
C) percentage forecast error in period t
D) mean absolute deviation of forecast errors
A) cumulative sum of forecast errors
B) standard deviation of forecast errors
C) percentage forecast error in period t
D) mean absolute deviation of forecast errors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Table 11.7.
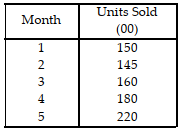
Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 4 is
A) less than or equal to 140 units.
B) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 150
C) greater than 150 but less than or equal to 160 units.
D) greater than 160 units.

Use the information in Table 11.7. The forecast for month 4 is
A) less than or equal to 140 units.
B) greater than 140 but less than or equal to 150
C) greater than 150 but less than or equal to 160 units.
D) greater than 160 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Table 11.4
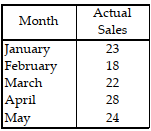
Use the information in Table 11.4. What is the forecast for July with the two- month moving average method and June sales of 40 units?
A) less than or equal to 25 units
B) greater than 25 but less than or equal to 30 units
C) greater than 30 but less than or equal to 35 units
D) greater than 35 units

Use the information in Table 11.4. What is the forecast for July with the two- month moving average method and June sales of 40 units?
A) less than or equal to 25 units
B) greater than 25 but less than or equal to 30 units
C) greater than 30 but less than or equal to 35 units
D) greater than 35 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
With the trend- adjusted exponential smoothing method,
A) the only smoothing is done on the trend estimates using exponential smoothing.
B) the forecast for the next period is simply the average computed this period.
C) an estimate of the trend is computed by taking the difference between the demand this period and the demand last period to avoid lengthy averaging calculations.
D) the forecast can be adjusted to account for changes in the trend.
A) the only smoothing is done on the trend estimates using exponential smoothing.
B) the forecast for the next period is simply the average computed this period.
C) an estimate of the trend is computed by taking the difference between the demand this period and the demand last period to avoid lengthy averaging calculations.
D) the forecast can be adjusted to account for changes in the trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When the underlying mean of a time series is very stable and there are no trend, cyclical, or seasonal influences,
A) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should perform about the same as a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
B) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
C) a simple moving average forecast with n = 3 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 20.
D) an exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.30 should outperform a exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.01.
A) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should perform about the same as a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
B) a simple moving average forecast with n = 20 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 3.
C) a simple moving average forecast with n = 3 should outperform a simple moving average forecast with n = 20.
D) an exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.30 should outperform a exponential smoothing forecast with alpha = 0.01.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Table 11.5.
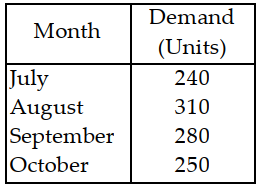
Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the simple moving average technique for the most recent three months, what will be the forecasted demand for November?
A) less than or equal to 260 units
B) greater than 260, but less than or equal to 275 units
C) greater than 275, but less than or equal to 290 units
D) more than 290 units

Use the information in Table 11.5. Using the simple moving average technique for the most recent three months, what will be the forecasted demand for November?
A) less than or equal to 260 units
B) greater than 260, but less than or equal to 275 units
C) greater than 275, but less than or equal to 290 units
D) more than 290 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Demand for a new five- inch color TV during the last six periods has been as follows: 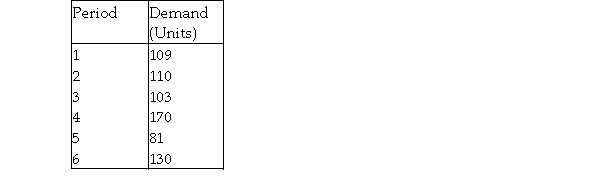 What is the forecast for period 7 if the company uses the simple moving average method with n = 4?
What is the forecast for period 7 if the company uses the simple moving average method with n = 4?
A) less than or equal to 115
B) greater than 115 but less than or equal to 120
C) greater than 120 but less than or equal to 125
D) greater than 125
 What is the forecast for period 7 if the company uses the simple moving average method with n = 4?
What is the forecast for period 7 if the company uses the simple moving average method with n = 4?A) less than or equal to 115
B) greater than 115 but less than or equal to 120
C) greater than 120 but less than or equal to 125
D) greater than 125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The owner of the Crossed Connections electronic appliance repair shop is enjoying increasing demand for her services. Total weekly demand, measured in standard labor hours, has been increasing. The owner uses trend- adjusted exponential smoothing to make forecasts for the following week so that she can plan work schedules and staffing levels. She has the following data to prepare her forecast:
At- 1 = 100 hours
α = 0.30
Tt- 1 = 10 hours
β = 0.10
Dt = 120 hours
Assuming she is now at the end of week t, what is the forecast for week t + 1?
A) less than or equal to 114 hours
B) greater than 114 hours but less than or equal to 118 hours
C) greater than 118 hours but less than or equal to 122 hours
D) greater than 122 hours
At- 1 = 100 hours
α = 0.30
Tt- 1 = 10 hours
β = 0.10
Dt = 120 hours
Assuming she is now at the end of week t, what is the forecast for week t + 1?
A) less than or equal to 114 hours
B) greater than 114 hours but less than or equal to 118 hours
C) greater than 118 hours but less than or equal to 122 hours
D) greater than 122 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The _________ is a process of gaining consensus from a group of experts while maintaining their anonymity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A(n) _________ is a customer order that cannot be filled immediately but is filled as soon as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain the coefficient of determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Table 11.7
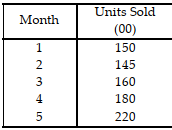
Use the information in Table 11.7. The cumulative sum of errors CFE from months 2 through 5 is
A) less than or equal to 80.
B) greater than 80 but less than or equal to 85.
C) greater than 87 but less than or equal to 90.
D) greater than 90.

Use the information in Table 11.7. The cumulative sum of errors CFE from months 2 through 5 is
A) less than or equal to 80.
B) greater than 80 but less than or equal to 85.
C) greater than 87 but less than or equal to 90.
D) greater than 90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
_________ forecasts are produced by averaging independent forecasts based on different methods or data or both.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Distinguish between a moving average model and an exponential smoothing model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_________ is a method for incorporating a trend in an exponentially smoothed forecast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe the exponential smoothing method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare seasonal effects and cyclical effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
_________ forecasting is a method that selects the best forecast from a group of forecasts generated by simple techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is focus forecasting?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
_________ is a method of incorporating a trend in an exponentially smoothed forecast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The sample _________ coefficient measures the direction and strength of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables in a linear regression equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe the judgment method technique of forecasting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is focus forecasting?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Briefly describe what the causal method of forecasting is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
_________ is a weighted moving average time- series method that gives recent demands more weight than earlier demands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
_________ is a forecasting method in which the opinions, experience, and technical knowledge of one or more managers are summarized to arrive at a single forecast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Explain the coefficient of linear correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Table 11.3
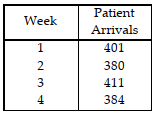
Use the information in Table 11.3. If the actual number of patients is 415 in week 5, what is the forecast for week 6 using a three- week moving average forecast?
A) less than or equal to 390
B) greater than 390 but less than or equal to 398
C) greater than 398 but less than or equal to 406
D) greater than 406

Use the information in Table 11.3. If the actual number of patients is 415 in week 5, what is the forecast for week 6 using a three- week moving average forecast?
A) less than or equal to 390
B) greater than 390 but less than or equal to 398
C) greater than 398 but less than or equal to 406
D) greater than 406

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



