Deck 16: Adaptive Immunity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Adaptive Immunity
1
The Fc portion of an antibody is formed by
A) the variable regions of the heavy chains.
B) one heavy chain.
C) portions of both of the heavy chains only.
D) the light chains only.
E) the variable regions of the light chains.
A) the variable regions of the heavy chains.
B) one heavy chain.
C) portions of both of the heavy chains only.
D) the light chains only.
E) the variable regions of the light chains.
C
2
 The type of immunoglobulin illustrated here is
The type of immunoglobulin illustrated here isA) IgE.
B) IgM.
C) IgG.
D) IgD.
E) IgA.
B
3
Which of the following statements concerning plasma cells is TRUE?
A) They live for many years and function as memory cells.
B) They are descended from activated T cells.
C) They secrete a variety of antibody molecules specific for multiple epitopes.
D) The antibodies they produce can remain in circulation for years.
E) They can produce large quantities of antibodies on a daily basis.
A) They live for many years and function as memory cells.
B) They are descended from activated T cells.
C) They secrete a variety of antibody molecules specific for multiple epitopes.
D) The antibodies they produce can remain in circulation for years.
E) They can produce large quantities of antibodies on a daily basis.
E
4
Which of the following function in agglutination?
A) IgG antibodies
B) IgD antibodies
C) IgE antibodies
D) IgA antibodies
E) IgA and IgG antibodies
A) IgG antibodies
B) IgD antibodies
C) IgE antibodies
D) IgA antibodies
E) IgA and IgG antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is correct concerning interleukin 4 (IL- 4)?
A) It stimulates phagocytes.
B) It is needed for B lymphocyte activation and differentiation.
C) It ensures production of enough leukocytes.
D) Virally infected cells produce it.
E) It is a chemotactic factor for leukocytes.
A) It stimulates phagocytes.
B) It is needed for B lymphocyte activation and differentiation.
C) It ensures production of enough leukocytes.
D) Virally infected cells produce it.
E) It is a chemotactic factor for leukocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The immunological synapse refers to the
A) interaction between lymphocytes and foreign antigens to produce memory cells.
B) interaction of the many cytokines produced by different immunological cells.
C) interaction between a T cell and an antigen- presenting cell to produce a specialized contact area for communication between these cells.
D) activation of a B cell to become a plasma cell.
E) binding of a monocyte or macrophage to antigen so that it can act as an antigen- presenting cell.
A) interaction between lymphocytes and foreign antigens to produce memory cells.
B) interaction of the many cytokines produced by different immunological cells.
C) interaction between a T cell and an antigen- presenting cell to produce a specialized contact area for communication between these cells.
D) activation of a B cell to become a plasma cell.
E) binding of a monocyte or macrophage to antigen so that it can act as an antigen- presenting cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What types of antigens are bound to Class I MHC (major histocompatibility complex) proteins?
A) exogenous antigens
B) endogenous antigens
C) autoantigens
D) both autoantigens and endogenous antigens
E) autoantigens, endogenous, and exogenous antigens
A) exogenous antigens
B) endogenous antigens
C) autoantigens
D) both autoantigens and endogenous antigens
E) autoantigens, endogenous, and exogenous antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements about T lymphocytes is FALSE?
A) There are three types of T lymphocytes.
B) T lymphocytes are called such because they mature in the thymus.
C) T lymphocytes have TCRs that recognize antigen only if it is bound to MHC.
D) T lymphocytes produce antibody molecules.
E) T lymphocytes directly attack cells and produce the cell- mediated immune response.
A) There are three types of T lymphocytes.
B) T lymphocytes are called such because they mature in the thymus.
C) T lymphocytes have TCRs that recognize antigen only if it is bound to MHC.
D) T lymphocytes produce antibody molecules.
E) T lymphocytes directly attack cells and produce the cell- mediated immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the role of interleukins?
A) ensuring production of enough leukocytes
B) complement activation
C) production of virally infected cells
D) signaling between leukocytes
E) chemotaxis of leukocytes
A) ensuring production of enough leukocytes
B) complement activation
C) production of virally infected cells
D) signaling between leukocytes
E) chemotaxis of leukocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements concerning the chemical structure of an antibody is FALSE?
A) Antibodies have two short peptide chains known as light chains.
B) Antibodies are formed of four polypeptide chains.
C) The stem and arm are connected by a hinge.
D) The heavy and light chains are connected by hydrogen bonds.
E) Antibodies have two long peptide chains known as heavy chains.
A) Antibodies have two short peptide chains known as light chains.
B) Antibodies are formed of four polypeptide chains.
C) The stem and arm are connected by a hinge.
D) The heavy and light chains are connected by hydrogen bonds.
E) Antibodies have two long peptide chains known as heavy chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Clonal deletion of developing T lymphocytes takes place in which location(s) in the body?
A) the thymus
B) the liver
C) the bone marrow
D) both the bone marrow and the spleen
E) the spleen
A) the thymus
B) the liver
C) the bone marrow
D) both the bone marrow and the spleen
E) the spleen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements concerning specific immunity is FALSE?
A) It is the body's ability to respond to specific invading pathogens.
B) It is the third line of defense.
C) It is acquired.
D) It has memory.
E) It changes little with repeated exposure to the same pathogen.
A) It is the body's ability to respond to specific invading pathogens.
B) It is the third line of defense.
C) It is acquired.
D) It has memory.
E) It changes little with repeated exposure to the same pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an exogenous antigen?
A) a bacterium inside a cell
B) a noninfected human cell
C) a bacterium outside a cell
D) a virus inside a cell
E) the malaria parasite inside a red blood cell
A) a bacterium inside a cell
B) a noninfected human cell
C) a bacterium outside a cell
D) a virus inside a cell
E) the malaria parasite inside a red blood cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements regarding the cell- mediated immune response is TRUE?
A) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes do not require antigen presentation to become activated.
B) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes kill by producing hydrogen peroxide.
C) A single cytotoxic T lymphocyte can kill many target cells.
D) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes interact with antibodies that have bound antigen to identify their target.
E) Helper T lymphocytes have no role in the activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
A) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes do not require antigen presentation to become activated.
B) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes kill by producing hydrogen peroxide.
C) A single cytotoxic T lymphocyte can kill many target cells.
D) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes interact with antibodies that have bound antigen to identify their target.
E) Helper T lymphocytes have no role in the activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Secretory IgA antibodies are unique because they
A) are Y- shaped molecules.
B) have unique light chains.
C) are present in the plasma.
D) are connected with J chains and short polypeptides to form dimers.
E) are present in lymph nodes.
A) are Y- shaped molecules.
B) have unique light chains.
C) are present in the plasma.
D) are connected with J chains and short polypeptides to form dimers.
E) are present in lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following best describes IgM antibodies?
A) They cause basophils and eosinophils to degranulate.
B) They are the most common type of antibody in the blood during the initial phases of an immune response.
C) They interact with phagocytes and NK cells.
D) They can cross the placenta to provide passive immunity.
E) They are the antibody class found in body secretions.
A) They cause basophils and eosinophils to degranulate.
B) They are the most common type of antibody in the blood during the initial phases of an immune response.
C) They interact with phagocytes and NK cells.
D) They can cross the placenta to provide passive immunity.
E) They are the antibody class found in body secretions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
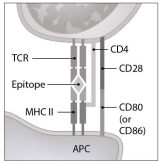 What will be the direct result of the interaction shown in this figure? (This interaction is occurring in a lymph node.)
What will be the direct result of the interaction shown in this figure? (This interaction is occurring in a lymph node.)A) clonal deletion of a T lymphocyte
B) activation of a helper T lymphocyte
C) activation of a B lymphocyte
D) activation of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte
E) clonal deletion of a B lymphocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT included in the MALT?
A) the appendix
B) the spleen
C) lymphoid tissue in the respiratory tract
D) Peyer's patches
E) lymphoid tissue in the small intestine
A) the appendix
B) the spleen
C) lymphoid tissue in the respiratory tract
D) Peyer's patches
E) lymphoid tissue in the small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following cytokines helps regulate inflammation?
A) chemokines
B) alpha interferon
C) IL- 12
D) tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
E) IL- 4 (interleukin- 4)
A) chemokines
B) alpha interferon
C) IL- 12
D) tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
E) IL- 4 (interleukin- 4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following molecules would contain T- independent antigens?
A) steroids
B) polysaccharides
C) glycoproteins
D) phospholipids
E) lipoproteins
A) steroids
B) polysaccharides
C) glycoproteins
D) phospholipids
E) lipoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Antigens are
A) proteins the body produces against invading substances.
B) proteins on the surface of our cells to which pathogens attach.
C) enzymes secreted to destroy a pathogen's cell wall.
D) specific molecules, or parts of molecules, that the body recognizes as foreign.
E) cells that protect the body against invaders.
A) proteins the body produces against invading substances.
B) proteins on the surface of our cells to which pathogens attach.
C) enzymes secreted to destroy a pathogen's cell wall.
D) specific molecules, or parts of molecules, that the body recognizes as foreign.
E) cells that protect the body against invaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The white blood cells primarily responsible for adaptive immunity are
A) macrophages and neutrophils.
B) neutrophils and dendritic cells.
C) NK lymphocytes and neutrophils.
D) macrophages and eosinophils.
E) B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.
A) macrophages and neutrophils.
B) neutrophils and dendritic cells.
C) NK lymphocytes and neutrophils.
D) macrophages and eosinophils.
E) B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is the function of gamma interferon (INF- y)?
A) activates and differentiates B lymphocytes
B) ensures production of enough leukocytes
C) activates complement
D) causes basophils and eosinophils to degranulate
E) stimulates phagocytes
A) activates and differentiates B lymphocytes
B) ensures production of enough leukocytes
C) activates complement
D) causes basophils and eosinophils to degranulate
E) stimulates phagocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true of chemokines?
A) They are involved in B lymphocyte activation and differentiation.
B) They ensure production of enough leukocytes.
C) They are chemotactic factors for leukocytes.
D) They are substances used to signal between leukocytes.
E) They cause basophils and eosinophils to degranulate.
A) They are involved in B lymphocyte activation and differentiation.
B) They ensure production of enough leukocytes.
C) They are chemotactic factors for leukocytes.
D) They are substances used to signal between leukocytes.
E) They cause basophils and eosinophils to degranulate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following cytokines act as a signal between leukocytes?
A) interleukins
B) chemokines
C) interferons
D) growth factors
E) tumor necrosis factors
A) interleukins
B) chemokines
C) interferons
D) growth factors
E) tumor necrosis factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements concerning B cell receptors (BCRs) is FALSE?
A) They are bound to the surface of B lymphocytes and have two antigen- binding sites.
B) They are complementary in shape to a specific antigenic determinant that they may or may not encounter.
C) Scientists estimate that each person forms at least 1011 different types of B lymphocytes with distinct BCRs.
D) They are formed in response to an encounter with an antigen.
E) Each B lymphocyte is randomly generated with antibody variable regions that determine its BCR.
A) They are bound to the surface of B lymphocytes and have two antigen- binding sites.
B) They are complementary in shape to a specific antigenic determinant that they may or may not encounter.
C) Scientists estimate that each person forms at least 1011 different types of B lymphocytes with distinct BCRs.
D) They are formed in response to an encounter with an antigen.
E) Each B lymphocyte is randomly generated with antibody variable regions that determine its BCR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What type of immunity is produced by the body when a person contracts a disease?
A) artificially acquired passive immunity
B) artificially acquired active immunity
C) naturally acquired passive immunity
D) innate immunity
E) naturally acquired active immunity
A) artificially acquired passive immunity
B) artificially acquired active immunity
C) naturally acquired passive immunity
D) innate immunity
E) naturally acquired active immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the result when a dendritic cell phagocytizes a microbe and processes it?
A) display of epitope- MHC I complexes on the surface of the cell
B) activation of the dendritic cell to become a plasma cell
C) display of microbial epitope- MHC II complexes on the cell surface
D) display of microbial fragments with CD8 glycoproteins
E) suppression of the immune response to the microbe
A) display of epitope- MHC I complexes on the surface of the cell
B) activation of the dendritic cell to become a plasma cell
C) display of microbial epitope- MHC II complexes on the cell surface
D) display of microbial fragments with CD8 glycoproteins
E) suppression of the immune response to the microbe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Class II MHC are found on
A) cytoplasmic membranes of nucleated cells.
B) the skin.
C) professional antigen- presenting cells.
D) red blood cells.
E) muscle.
A) cytoplasmic membranes of nucleated cells.
B) the skin.
C) professional antigen- presenting cells.
D) red blood cells.
E) muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The most prevalent type of antibody in the blood is
A) IgA.
B) IgM.
C) IgE.
D) IgD.
E) IgG.
A) IgA.
B) IgM.
C) IgE.
D) IgD.
E) IgG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The perforin- granzyme pathway involves
A) presenting the foreign antigen to B cells.
B) the production of antibodies toward the invading pathogen.
C) binding CD95L to infected cells, which eventually leads to cell apoptosis.
D) the synthesis of special cell- killing proteins that act on infected or abnormal cells.
E) the production of fever, which kills the pathogen.
A) presenting the foreign antigen to B cells.
B) the production of antibodies toward the invading pathogen.
C) binding CD95L to infected cells, which eventually leads to cell apoptosis.
D) the synthesis of special cell- killing proteins that act on infected or abnormal cells.
E) the production of fever, which kills the pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Large accumulations of unactivated self- tolerant lymphocytes conducting surveillance for specific antigenic determinants are found in
A) the MALT, lymph nodes, and thymus.
B) the MALT and lymph nodes.
C) the thymus.
D) the MALT.
E) lymph nodes.
A) the MALT, lymph nodes, and thymus.
B) the MALT and lymph nodes.
C) the thymus.
D) the MALT.
E) lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following recognizes and binds to MHC II antigens and helps stabilize the binding of epitopes to T cell receptors?
A) MHC I
B) CD26
C) CCR3
D) CD4
E) CCR5
A) MHC I
B) CD26
C) CCR3
D) CD4
E) CCR5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Vaccination triggers an immune response which produces immunity.
A) artificial passive
B) natural active
C) natural passive
D) artificial active
E) both active and passive
A) artificial passive
B) natural active
C) natural passive
D) artificial active
E) both active and passive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Major histocompatibility antigens are
A) glycoproteins found in the cytoplasmic membranes of most vertebrate animal cells.
B) antigens attached to foreign invaders.
C) antigens that provoke allergic reactions.
D) not really antigens, but rather antibodies produced to mask foreign antigens.
E) antigens that must be processed by cells called histiocytes in order to be recognized by the immune system.
A) glycoproteins found in the cytoplasmic membranes of most vertebrate animal cells.
B) antigens attached to foreign invaders.
C) antigens that provoke allergic reactions.
D) not really antigens, but rather antibodies produced to mask foreign antigens.
E) antigens that must be processed by cells called histiocytes in order to be recognized by the immune system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements regarding antibody function is FALSE?
A) They can penetrate host cells to bind intracellular antigens.
B) They can prevent virus attachment to host cells.
C) They can bind more than one pathogen at a time, forming complexes.
D) They can facilitate phagocyte attack on bacteria with a capsule (glycocalyx).
E) They can facilitate cytotoxic attack by natural killer lymphocytes.
A) They can penetrate host cells to bind intracellular antigens.
B) They can prevent virus attachment to host cells.
C) They can bind more than one pathogen at a time, forming complexes.
D) They can facilitate phagocyte attack on bacteria with a capsule (glycocalyx).
E) They can facilitate cytotoxic attack by natural killer lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A sick child may have influenza or RSV. These virus infections have different treatment options, so the physician requests antibody titer tests. The results are as follows: anti- influenza antibodies are primarily IgM, and anti- RSV antibodies are all IgA and IgG. Which of the following is the most appropriate interpretation?
A) The results do not provide sufficient data to draw a conclusion.
B) The child currently has influenza and has previously been exposed to RSV.
C) The child has a current RSV infection and was previously exposed to influenza.
D) The child has concurrent influenza and RSV infections.
E) The child has neither influenza nor RSV.
A) The results do not provide sufficient data to draw a conclusion.
B) The child currently has influenza and has previously been exposed to RSV.
C) The child has a current RSV infection and was previously exposed to influenza.
D) The child has concurrent influenza and RSV infections.
E) The child has neither influenza nor RSV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
IgE antibodies are best described as
A) a cause of basophil and eosinophil degranulation.
B) the trigger for antibody- dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC).
C) the antibodies found in body secretions.
D) the most common type of antibody in the blood during the initial phases of an immune response.
E) those involved in complement activation.
A) a cause of basophil and eosinophil degranulation.
B) the trigger for antibody- dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC).
C) the antibodies found in body secretions.
D) the most common type of antibody in the blood during the initial phases of an immune response.
E) those involved in complement activation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Adaptive immunity is sometimes also called acquired immunity. Which of the following statements provides a basis for the alternative name?
A) Activated lymphocytes produce daughter cells that are identical in specificity and function.
B) Lymphocytes of the adaptive immune system are highly specific for a single antigenic determinant.
C) To become activated, lymphocytes require exposure to the antigenic determinant for which they are specific.
D) Activated lymphocytes may persist for years in the body.
E) Lymphocytes reactive to normal body components are removed.
A) Activated lymphocytes produce daughter cells that are identical in specificity and function.
B) Lymphocytes of the adaptive immune system are highly specific for a single antigenic determinant.
C) To become activated, lymphocytes require exposure to the antigenic determinant for which they are specific.
D) Activated lymphocytes may persist for years in the body.
E) Lymphocytes reactive to normal body components are removed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The protozoan that causes malaria is an intracellular parasite of red blood cells (RBCs). An adaptive immune response to this parasite is problematic because
A) RBCs never enter lymphoid tissue.
B) complement cannot effectively destroy RBCs.
C) the parasite damages leukocytes along with RBCs.
D) red blood cells do not produce MHC and therefore do not display the fact that they have been infected by presenting antigen.
E) RBCs normally produce cytokines necessary for adaptive immune response, which this infection prevents.
A) RBCs never enter lymphoid tissue.
B) complement cannot effectively destroy RBCs.
C) the parasite damages leukocytes along with RBCs.
D) red blood cells do not produce MHC and therefore do not display the fact that they have been infected by presenting antigen.
E) RBCs normally produce cytokines necessary for adaptive immune response, which this infection prevents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A(n) (antibody/cell- mediated) immune response occurs when an APC binds to a Th2 lymphocyte and IL- 4 is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
B lymphocytes can bind directly to large antigens with repeating polysaccharide subunits, such as a bacterial capsule that has antigenic determinants known as T- independent (receptors/antigens).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How is the development of autoimmunity normally prevented?
A) T lymphocytes that respond to autoantigens in the thymus undergo clonal deletion.
B) Clonal deletion of T cells and regulatory T cell suppression prevent autoreactive T cell activation.
C) Regulatory T cells suppress autoimmune responses.
D) T lymphocytes require a specific set of cytokine signals to become activated.
E) Clonal deletion of T cells, lack of necessary cytokine signals, and regulatory T cell suppression prevent activation of autoreactive T cells.
A) T lymphocytes that respond to autoantigens in the thymus undergo clonal deletion.
B) Clonal deletion of T cells and regulatory T cell suppression prevent autoreactive T cell activation.
C) Regulatory T cells suppress autoimmune responses.
D) T lymphocytes require a specific set of cytokine signals to become activated.
E) Clonal deletion of T cells, lack of necessary cytokine signals, and regulatory T cell suppression prevent activation of autoreactive T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
TCRs only recognize antigens presented by APC; therefore, (BCR/MHC/Th1) molecules ultimately determine which epitopes elicit an immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Enhanced immune responses to subsequent exposures to an antigen to which the body has already been exposed are known as responses.
A) allergic
B) memory
C) third- degree immune
D) autoimmune
E) primary immune
A) allergic
B) memory
C) third- degree immune
D) autoimmune
E) primary immune

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The antibody immune response is attributed to the action of
A) monocytes.
B) macrophages.
C) B lymphocytes.
D) neutrophils.
E) T lymphocytes.
A) monocytes.
B) macrophages.
C) B lymphocytes.
D) neutrophils.
E) T lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Professional antigen- presenting cells (APCs) include B cells, macrophages, and (dendritic/plasma/T) cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An antigen produced by a pathogen while living inside a cell is known as an (auto- /endogenous/exogenous) antigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You step on something in the yard resulting in a puncture wound that does not bleed freely. Antigens from any microbes that entered the wound will most likely end up in the
A) appendix.
B) spleen.
C) lymph nodes of the groin.
D) lymph nodes of the neck (cervical).
E) lymph nodes of the armpit (axilla).
A) appendix.
B) spleen.
C) lymph nodes of the groin.
D) lymph nodes of the neck (cervical).
E) lymph nodes of the armpit (axilla).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The ability of the body to respond faster and more effectively to a second exposure to pathogens is called immunologic (memory/synapse/tolerance).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The (constant/end/variable) regions from the light and heavy chains of an antibody combine to form antigen- binding sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When a T cell and an antigen- presenting cell interact, a specialized contact called an immunological (connection/bond/synapse) forms between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The process of (apoptosis/autolysis/differentiation) is a critical event in the development of self- tolerance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The surface of each B lymphocyte is covered with about 250,000 to 500,000 identical copies of (BCR/MHC/TCR).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Antigen processing is required for helper T cells to respond to (antigen/cytokines/MHC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Antibody molecules are produced by (B/plasma/T) cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An APC presents antigen to an unactivated T lymphocyte on an MHC I molecule and secretes IL- 12 at the same time. As a result the T lymphocyte differentiates into a (Th1/Th2/Tr) lymphocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements about lymphocytes is FALSE?
A) The glycoproteins on the surface of a lymphocyte are designated with the prefix CD, for "cluster of differentiation."
B) Once they are mature, they migrate to secondary lymphoid organs.
C) B and T lymphocytes can be differentiated under the microscope.
D) Lymphocytes have different types of CD molecules in their cytoplasmic membranes.
E) Lymphocytes have integral surface proteins by which they can be recognized.
A) The glycoproteins on the surface of a lymphocyte are designated with the prefix CD, for "cluster of differentiation."
B) Once they are mature, they migrate to secondary lymphoid organs.
C) B and T lymphocytes can be differentiated under the microscope.
D) Lymphocytes have different types of CD molecules in their cytoplasmic membranes.
E) Lymphocytes have integral surface proteins by which they can be recognized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
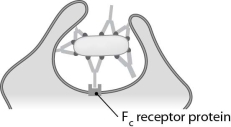 The antibody function known as (agglutination/neutralization/opsonization) is illustrated here.
The antibody function known as (agglutination/neutralization/opsonization) is illustrated here.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The body recognizes antigens by the three dimensional shapes of regions known as (antigenic/antibody/immunologic) determinants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Immature B lymphocytes undergo clonal deletion in the bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Some plasma cells persist long after an infection and contribute to secondary immune responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast clonal deletion and clonal selection of B lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Large molecules such as polymers make good antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe the mechanisms of action of antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Discuss the importance of there being two types of adaptive immune responses (antibody and cell- mediated).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During an infection with Listeria, an intracellular bacterium, APCs will present antigen on MHC II molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The MALT lacks the tough outer capsule of a lymph node but functions in the same way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A variety of molecular components of the adaptive immune system bind epitopes (antigenic determinants). Compare and contrast the binding of epitopes by antibody molecules, T cell receptors (TCRs), and MHC molecules, and describe the consequences of the different interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What are the steps involved in B cell activation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When a T cell's CD95L binds to the CD95 on a target cell, antibodies are formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Cytokines are soluble regulatory proteins that act as intercellular signals and include substances such as interleukins, interferon, and growth factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
IgG antibodies have a variety of mechanisms for acting on antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A single B lymphocyte can recognize multiple antigenic determinants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Molecules with a molecular mass less than 5000 daltons can become antigens when they bind to carrier molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



