Deck 17: Immunization and Immune Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Immunization and Immune Testing
1
Anti- human antibodies (specific for human IgG antibodies) with fluorescent molecules covalently attached are used for
A) direct ELISAs.
B) immunodiffusion tests.
C) direct fluorescent antibody tests.
D) indirect ELISAs.
E) indirect fluorescent antibody tests.
A) direct ELISAs.
B) immunodiffusion tests.
C) direct fluorescent antibody tests.
D) indirect ELISAs.
E) indirect fluorescent antibody tests.
C
2
The study and diagnosis of antigen- antibody interactions in the blood is known as
A) serology.
B) immunology.
C) cytology.
D) histology.
E) hematology.
A) serology.
B) immunology.
C) cytology.
D) histology.
E) hematology.
A
3
Tuberculosis may be diagnosed using
A) immunoelectrophoresis.
B) a direct fluorescent antibody test.
C) a viral hemagglutination test.
D) complement fixation.
E) an immunoblot test.
A) immunoelectrophoresis.
B) a direct fluorescent antibody test.
C) a viral hemagglutination test.
D) complement fixation.
E) an immunoblot test.
B
4
Which of the following statements regarding toxoids is FALSE?
A) They stimulate antibody- mediated immune responses.
B) They are produced against the toxin of the microorganism rather than the microorganism itself.
C) They are chemically or thermally modified.
D) They have few antigenic determinants.
E) They provide lifelong immunity.
A) They stimulate antibody- mediated immune responses.
B) They are produced against the toxin of the microorganism rather than the microorganism itself.
C) They are chemically or thermally modified.
D) They have few antigenic determinants.
E) They provide lifelong immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Titration is a serological procedure that
A) identifies the causative microbe of an infectious disease.
B) must be done before the western blot test to diagnose HIV.
C) determines the amount of an antibody in the blood.
D) has been replaced by genetic engineering in isolating the antigen of a pathogen.
E) is used for blood grouping.
A) identifies the causative microbe of an infectious disease.
B) must be done before the western blot test to diagnose HIV.
C) determines the amount of an antibody in the blood.
D) has been replaced by genetic engineering in isolating the antigen of a pathogen.
E) is used for blood grouping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A woman uses a home pregnancy test kit that tests for hCG hormone in urine. She knows this is a type of antibody assay from the kit brochure. Antibodies reacting with the hormone produce two lines on the test strip. What specific type of antibody assay does this represent?
A) a direct immunofluoresence test
B) an immunochromatographic assay
C) an ELISA
D) a complement fixation test
E) a neutralization assay
A) a direct immunofluoresence test
B) an immunochromatographic assay
C) an ELISA
D) a complement fixation test
E) a neutralization assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What type of vaccine is the hepatitis B vaccine?
A) a recombinant vaccine composed of a single antigen of the hepatitis virus
B) attenuated vaccine
C) a vaccine produced by treating the virus with formaldehyde
D) toxoid vaccine
E) inactivated whole pathogen
A) a recombinant vaccine composed of a single antigen of the hepatitis virus
B) attenuated vaccine
C) a vaccine produced by treating the virus with formaldehyde
D) toxoid vaccine
E) inactivated whole pathogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements regarding ELISAs is TRUE?
A) They are not quantitative.
B) They involve the use of membrane filters.
C) They require large amounts of serum.
D) The antibody label is a fluorescent molecule.
E) They can be used to detect antibody or antigen.
A) They are not quantitative.
B) They involve the use of membrane filters.
C) They require large amounts of serum.
D) The antibody label is a fluorescent molecule.
E) They can be used to detect antibody or antigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Killed vaccines work by stimulating
A) cytotoxic T cells.
B) an antibody mediated response.
C) lymphocyte proliferation.
D) phagocytic activity.
E) the cell- mediated immune response.
A) cytotoxic T cells.
B) an antibody mediated response.
C) lymphocyte proliferation.
D) phagocytic activity.
E) the cell- mediated immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Almost a century after Edward Jenner introduced successful vaccination, Louis Pasteur developed vaccine(s) against
A) human cholera.
B) rabies.
C) anthrax.
D) influenza.
E) both anthrax and rabies.
A) human cholera.
B) rabies.
C) anthrax.
D) influenza.
E) both anthrax and rabies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Passive immunotherapy is used when
A) the pathogen does not produce a toxin.
B) the attenuated live vaccine is too difficult to produce.
C) a representative antigen for the microbe cannot be isolated.
D) protection against a recent infection or disease is needed immediately.
E) the microorganism can be genetically manipulated.
A) the pathogen does not produce a toxin.
B) the attenuated live vaccine is too difficult to produce.
C) a representative antigen for the microbe cannot be isolated.
D) protection against a recent infection or disease is needed immediately.
E) the microorganism can be genetically manipulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In precipitation tests, maximum precipitation takes place when
A) the amount of the antigen exceeds the amount of the antibody.
B) the amount of the antibody and the amount of the antigen are at optimal proportions.
C) a toxin is present.
D) a complex solution of many antibodies is used.
E) the amount of the antibody exceeds the amount of the antigen.
A) the amount of the antigen exceeds the amount of the antibody.
B) the amount of the antibody and the amount of the antigen are at optimal proportions.
C) a toxin is present.
D) a complex solution of many antibodies is used.
E) the amount of the antibody exceeds the amount of the antigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The vaccine against smallpox developed by Edward Jenner is an example of a(n) vaccine.
A) whole inactivated
B) subunit
C) attenuated
D) toxoid
E) combination
A) whole inactivated
B) subunit
C) attenuated
D) toxoid
E) combination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Exposure to HIV can be verified using a(n) _ assay.
A) western blot
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) viral hemagglutination inhibition
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) viral neutralization
A) western blot
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) viral hemagglutination inhibition
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) viral neutralization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A person who has been exposed to rabies receives both HRIG (human rabies immunoglobulin) injected near the bite site and the rabies vaccine. What does this strategy represent?
A) active immunization
B) viral hemagglutination inhibition
C) passive immunotherapy
D) passive immunotherapy combined with viral hemagglutination inhibition
E) active immunization combined with passive immunotherapy
A) active immunization
B) viral hemagglutination inhibition
C) passive immunotherapy
D) passive immunotherapy combined with viral hemagglutination inhibition
E) active immunization combined with passive immunotherapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A(n) vaccine to prevent cervical cancer was recently developed.
A) subunit
B) recombinant
C) attenuated
D) toxoid
E) inactivated whole
A) subunit
B) recombinant
C) attenuated
D) toxoid
E) inactivated whole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be detected in specimens by the test.
A) ELISA
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) complement fixation
D) hemagglutination
E) indirect fluorescent antibody
A) ELISA
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) complement fixation
D) hemagglutination
E) indirect fluorescent antibody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements regarding variolation is FALSE?
A) It was administered to children as early as the 12th century.
B) At the time no one knew how it worked.
C) It was risk- free.
D) It involves grinding smallpox scabs.
E) It reduced the incidence of smallpox.
A) It was administered to children as early as the 12th century.
B) At the time no one knew how it worked.
C) It was risk- free.
D) It involves grinding smallpox scabs.
E) It reduced the incidence of smallpox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements regarding an inactivated vaccine is FALSE?
A) It is safer than an attenuated vaccine.
B) It is made from pathogens that cannot replicate.
C) It can be produced from antigenic fragments of a pathogen.
D) It is made from mutated forms of the pathogen.
E) It can be produced with deactivated whole microorganisms.
A) It is safer than an attenuated vaccine.
B) It is made from pathogens that cannot replicate.
C) It can be produced from antigenic fragments of a pathogen.
D) It is made from mutated forms of the pathogen.
E) It can be produced with deactivated whole microorganisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the most efficient and cost- effective way to control infectious diseases?
A) active immunization by vaccination
B) variolation
C) passive immunotherapy using immunoglobulins
D) autoimmunization
E) immune testing
A) active immunization by vaccination
B) variolation
C) passive immunotherapy using immunoglobulins
D) autoimmunization
E) immune testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Viral neutralization testing is based on the fact that
A) antibodies have different molecular weights.
B) the gene for a pathogen's antigen can be isolated and introduced into a host cell by way of a plasmid.
C) viruses introduced into appropriate cell cultures have a cytopathic effect.
D) antibodies to certain microbes can be given a fluorescent label.
E) antibodies can be produced against the toxin of a pathogen.
A) antibodies have different molecular weights.
B) the gene for a pathogen's antigen can be isolated and introduced into a host cell by way of a plasmid.
C) viruses introduced into appropriate cell cultures have a cytopathic effect.
D) antibodies to certain microbes can be given a fluorescent label.
E) antibodies can be produced against the toxin of a pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The complement fixation test uses red blood cells as the target for complement activation. Test serum containing antibodies is combined with a known amount of antigen in a tube, and then the RBCs and antibodies against the RBCs are added. A positive result for the complement fixation test would be
A) loss of color in the tube.
B) a cloudy solution in the tube.
C) a line of precipitate near the bottom of the tube.
D) a solution that is clear due to precipitation of RBCs.
E) a fluorescent precipitate.
A) loss of color in the tube.
B) a cloudy solution in the tube.
C) a line of precipitate near the bottom of the tube.
D) a solution that is clear due to precipitation of RBCs.
E) a fluorescent precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following tests is most effective in determining whether someone has been infected with the H1N1 influenza virus?
A) a viral neutralization test
B) an immunodiffusion test
C) an immunoblot
D) an antibody titer test
E) a viral hemagglutination test
A) a viral neutralization test
B) an immunodiffusion test
C) an immunoblot
D) an antibody titer test
E) a viral hemagglutination test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Antivenin is a(n)
A) vaccine made toward the endotoxin of a virus.
B) vaccine produced against the endotoxin of a bacterium.
C) antitoxin used to treat snakebites.
D) antigen produced from a virus.
E) antiserum produced from hybridomas.
A) vaccine made toward the endotoxin of a virus.
B) vaccine produced against the endotoxin of a bacterium.
C) antitoxin used to treat snakebites.
D) antigen produced from a virus.
E) antiserum produced from hybridomas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following diagnostic procedures depends on precipitation of antigen- antibody complexes?
A) blood typing
B) fluorescent antibody tests
C) immunodiffusion
D) viral hemagglutination inhibition tests used to diagnose viral infections
E) ELISA
A) blood typing
B) fluorescent antibody tests
C) immunodiffusion
D) viral hemagglutination inhibition tests used to diagnose viral infections
E) ELISA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The discovery of antibodies and the understanding of their actions lead to treatments for disease.
A) passive immunotherapy
B) recombinant
C) neutralization
D) active immunotherapy
E) serologic
A) passive immunotherapy
B) recombinant
C) neutralization
D) active immunotherapy
E) serologic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Rabies virus can be directly detected in brain tissue using a(n) _ _ assay.
A) immunodiffusion precipitation
B) immunoblot
C) viral neutralization
D) viral hemagglutination inhibition
E) direct fluorescent antibody
A) immunodiffusion precipitation
B) immunoblot
C) viral neutralization
D) viral hemagglutination inhibition
E) direct fluorescent antibody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A(n) assay is used for rapid identification of influenza infections.
A) immunochromatographic
B) viral neutralization
C) immunodiffusion precipitation
D) immunoblot
E) direct fluorescent antibody
A) immunochromatographic
B) viral neutralization
C) immunodiffusion precipitation
D) immunoblot
E) direct fluorescent antibody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An infectious disease researcher isolates the pathogen responsible for an emerging disease. The microbe is grown in the lab for many generations. A preparation of the laboratory- grown microbe is treated with ionizing radiation and then tested for its potential as a vaccine. What type of vaccine is this?
A) subunit
B) inactivated whole
C) attenuated
D) combination
E) toxoid
A) subunit
B) inactivated whole
C) attenuated
D) combination
E) toxoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following substances is commonly used to inactivate microbes?
A) aluminum
B) mineral oil
C) aluminum phosphate
D) saponin
E) formaldehyde
A) aluminum
B) mineral oil
C) aluminum phosphate
D) saponin
E) formaldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Agglutination tests can be used to
A) determine the concentration of complement proteins in serum.
B) diagnose HIV.
C) estimate the amount (titer) of antibodies in a person's serum.
D) determine the effectiveness of passive immunotherapy.
E) detect a complex mix of antigens.
A) determine the concentration of complement proteins in serum.
B) diagnose HIV.
C) estimate the amount (titer) of antibodies in a person's serum.
D) determine the effectiveness of passive immunotherapy.
E) detect a complex mix of antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
OPV, the attenuated oral poliovirus vaccine, is no longer administered in the U.S.A. because it
A) can be spread to contacts.
B) is very toxic.
C) does not provide good immunity.
D) can revert to wild- type virulence.
E) can be spread to contacts and can revert to wild- type virulence.
A) can be spread to contacts.
B) is very toxic.
C) does not provide good immunity.
D) can revert to wild- type virulence.
E) can be spread to contacts and can revert to wild- type virulence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Serologic tests may be used to detect for diagnosis of disease.
A) the proportion of plasma in a patient's blood
B) antigen- specific antibodies
C) the ability of the patient's antibodies to activate the complement system
D) the concentration of serum proteins
E) specific epitopes
A) the proportion of plasma in a patient's blood
B) antigen- specific antibodies
C) the ability of the patient's antibodies to activate the complement system
D) the concentration of serum proteins
E) specific epitopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Variolation was first used
A) to treat individuals exposed to hepatitis.
B) to protect individuals against the plague during the Middle Ages.
C) for research purposes in the 20th century.
D) to immunize the Chinese against smallpox.
E) to spread smallpox throughout the Native American populations.
A) to treat individuals exposed to hepatitis.
B) to protect individuals against the plague during the Middle Ages.
C) for research purposes in the 20th century.
D) to immunize the Chinese against smallpox.
E) to spread smallpox throughout the Native American populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Pathogens may be attenuated for use in vaccines by
A) raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells.
B) treatment with formaldehyde.
C) genetic manipulation.
D) genetic manipulation coupled with treatment with formaldehyde.
E) genetic manipulation and/or raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells.
A) raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells.
B) treatment with formaldehyde.
C) genetic manipulation.
D) genetic manipulation coupled with treatment with formaldehyde.
E) genetic manipulation and/or raising the pathogen for several generations in tissue culture cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A new virus is discovered that causes cells to clump together. Which of the following types of assay would be useful for diagnosing infection with this virus?
A) complement fixation test
B) hemagglutination
C) both agglutination and complement fixation tests
D) viral hemagglutination
E) agglutination
A) complement fixation test
B) hemagglutination
C) both agglutination and complement fixation tests
D) viral hemagglutination
E) agglutination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Infection with the fungus Coccidioides immitis can be diagnosed using a(n) assay.
A) viral neutralization
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) immunoblot
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) viral hemagglutination inhibition
A) viral neutralization
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) immunoblot
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) viral hemagglutination inhibition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
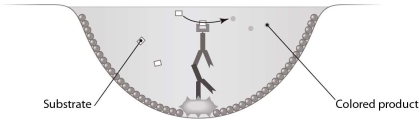 Which type of antibody assay is represented in this figure?
Which type of antibody assay is represented in this figure?A) an immunodiffusion assay
B) a western blot
C) an indirect ELISA
D) a direct ELISA
E) an indirect immunofluorescence assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following assays is dependent on the ability of antibodies to bind to and crosslink two antigens?
A) neutralization tests
B) ELISAs
C) precipitation tests
D) immunoblot tests
E) direct fluorescent antibody tests
A) neutralization tests
B) ELISAs
C) precipitation tests
D) immunoblot tests
E) direct fluorescent antibody tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When immunization levels in a population are high, _ provides protection from infection for at- risk persons who cannot be immunized.
A) active immunization
B) contact immunity
C) adjuvant therapy
D) herd immunity
E) variolation
A) active immunization
B) contact immunity
C) adjuvant therapy
D) herd immunity
E) variolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A microbe antigenically similar to human pathogen but incapable of causing disease in humans is a good candidate for use as a(n) (attenuated/inactivated/recombinant) vaccine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Modern vaccine technology can involve inserting the DNA encoding the pathogen's antigen(s) into a (plasmid/virus) and injecting it into an individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
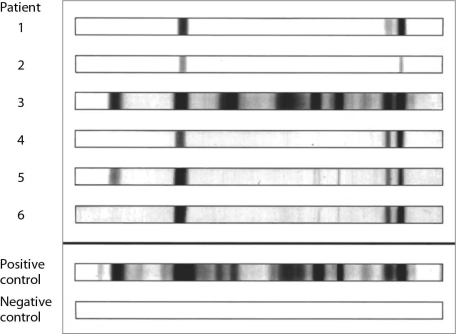 For what is the assay shown here used?
For what is the assay shown here used?A) detecting antibodies against a complex mix of antigens
B) detecting neutralizing antibodies
C) blood typing
D) determining the concentration of antibodies
E) verifying infection with a virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Hybridomas are produced by
A) combining two virus- infected cells.
B) fusing plasma cells with myeloma cells.
C) repeated culture of a pathogen until it loses its virulence.
D) combining two bacterial infected cells.
E) combining a viral infected cell with a bacterial infected cell.
A) combining two virus- infected cells.
B) fusing plasma cells with myeloma cells.
C) repeated culture of a pathogen until it loses its virulence.
D) combining two bacterial infected cells.
E) combining a viral infected cell with a bacterial infected cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A(n) (ELISA/immunofiltration/western) assay uses antibodies bound on the surface of a membrane filter to detect antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
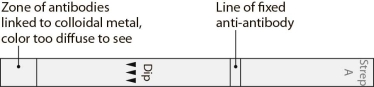 This device is used in a(n) (immunodiffusion/immunochromatographic/precipitation) test.
This device is used in a(n) (immunodiffusion/immunochromatographic/precipitation) test.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A(n)_ assay is used to detect hantavirus.
A) viral hemagglutination inhibition
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) viral neutralization
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) western blot
A) viral hemagglutination inhibition
B) direct fluorescent antibody
C) viral neutralization
D) immunodiffusion precipitation
E) western blot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Antisera directed against toxins are known as (antibodies/antitoxins/anti- antibodies).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One way to measure the antibody levels in the blood is by (turbidimitry/titration) using agglutination tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Snakebites are treated with (antisera/antitoxins/antivenins).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Materials that are added to a vaccine to increase the effective antigenicity are known as (antigens/adjuvants/antibodies).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When vaccines do not provide lifelong immunity, (adjuvants/boosters/repeats) must be given to maintain protection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Chemically or thermally modified toxins that are used for vaccination are called (adjuvants/antigens/toxoids).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Deliberate infection of young children with particles of ground smallpox scabs from children who had survived mild cases of smallpox was known as (vaccination/variolation/immunization).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which property of antibodies is the basis for complement fixation tests?
A) The Fc portion of IgG becomes enzymatically active upon antigen binding.
B) The Fc portion can trigger the classical complement system upon antigen binding.
C) The Fc portion of the molecule can be modified without interfering with antigen binding.
D) Antibodies can bind two antigens simultaneously.
E) Antibodies can neutralize the ability of viruses to infect cells.
A) The Fc portion of IgG becomes enzymatically active upon antigen binding.
B) The Fc portion can trigger the classical complement system upon antigen binding.
C) The Fc portion of the molecule can be modified without interfering with antigen binding.
D) Antibodies can bind two antigens simultaneously.
E) Antibodies can neutralize the ability of viruses to infect cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Raising viruses for numerous generations can produce an (attenuated/inactivated) form of the virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Genetic manipulation of a microbe to remove one or more virulence factors is a method for producing a(n) _ vaccine.
A) toxoid
B) combination
C) attenuated
D) inactived
E) DNA
A) toxoid
B) combination
C) attenuated
D) inactived
E) DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The fusion of antibody- producing plasma cells with cancerous cells produces (hybridomas/lymphocytes/cancers) that divide continuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Immunization with (attenuated/recombinant/inactivated) vaccines results in primarily an antibody- mediated immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Fluorescent antibody, ELISA, and immunoblotting tests involve the use of (labeled/unlabeled) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Edward Jenner was the physician who first used cowpox to vaccinate individuals against smallpox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The "sandwich" ELISA is used to quantify the amount of antibody in a serum sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
ELISAs require less reaction time than do immunofiltration assays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The virulence of the rabies virus is increased by prolonged culture in rabbit spinal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Agglutination tests are used to detect soluble antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Anti- antibodies are used in indirect antibody assays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How has modern technology helped to produce new types of vaccines?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Discuss the similarities and differences between immunodiffusion and immunochromatographic assays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Passive immunotherapy does not result in immunological memory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Complement fixation is a more sensitive test for the presence of specific antibodies than are agglutination tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For some bacterial diseases such as tetanus, it is more effective to produce an immune response against the bacterial toxin than against the bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss the concept of herd immunity and its importance in creating and maintaining a healthy population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Because attenuated live vaccines contain viruses that are less virulent, many booster vaccines must be given to produce an effective immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Two types of vaccines for polio have been developed, an inactivated whole (Salk) and a live attenuated (Sabin) vaccine. Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of the two polio vaccines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Compare and contrast viral neutralization and viral hemagglutination tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



