Deck 8: Gains and Losses on the Disposition of Capital Property-Capital Gains
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Gains and Losses on the Disposition of Capital Property-Capital Gains
1
When establishing whether the sale of an asset is capital income or business income, which of the following is not one of the factors which the courts take into consideration when determining the original intention of a transaction?
A) Period of ownership
B) Relation of transaction to taxpayer's business
C) Canadian residency test
D) Number and frequency of transactions
A) Period of ownership
B) Relation of transaction to taxpayer's business
C) Canadian residency test
D) Number and frequency of transactions
C
2
Mr. Yee sold a piece of land in 20X0 for $500,000. He originally paid $100,000 for the land. Selling costs totaled $15,000. The land is classified as capital
property. The purchaser of the land paid Mr. Yee $80,000 in 20X0, and will pay
$84,000 each year for the next five years.
Required:
Calculate the taxable capital gain that Mr. Yee will have to include in his income for tax purposes in 20X0 and 20X1.
property. The purchaser of the land paid Mr. Yee $80,000 in 20X0, and will pay
$84,000 each year for the next five years.
Required:
Calculate the taxable capital gain that Mr. Yee will have to include in his income for tax purposes in 20X0 and 20X1.

3
Evergreen Trees Inc. is a CCPC operating in your province. The company has a
December 31st year-end.
Three asset sales occurred prior to the end of 20X1. The following information pertains to the net gain on the sale of the assets:
Building (One of several owned by the company)
The building was previously purchased for $80,000. At the time of the sale in 20X1, the accumulated amortization on the building was $10,000. The UCC
balance was $65,000. The full payment of $110,000 was received before the end of the year.
Land
The land was purchased for $200,000 and sold in 20X1 for $250,000. Proceeds of $60,000 will be received this year. The remainder of the payment will be
received in equal installments over the next eight years.
Marketable Securities
The company sold its entire public portfolio this year. The adjusted cost base of the shares was $100,000. The market value of the shares at the time of sale in 20X1 was $135,000. Selling costs on the sale were $5,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that Evergreen Trees Inc. will have to report in 20X1.
B) Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that must be reported in 20X2.
December 31st year-end.
Three asset sales occurred prior to the end of 20X1. The following information pertains to the net gain on the sale of the assets:
Building (One of several owned by the company)
The building was previously purchased for $80,000. At the time of the sale in 20X1, the accumulated amortization on the building was $10,000. The UCC
balance was $65,000. The full payment of $110,000 was received before the end of the year.
Land
The land was purchased for $200,000 and sold in 20X1 for $250,000. Proceeds of $60,000 will be received this year. The remainder of the payment will be
received in equal installments over the next eight years.
Marketable Securities
The company sold its entire public portfolio this year. The adjusted cost base of the shares was $100,000. The market value of the shares at the time of sale in 20X1 was $135,000. Selling costs on the sale were $5,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that Evergreen Trees Inc. will have to report in 20X1.
B) Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that must be reported in 20X2.
A)
 Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X1 = $36,000 B)
Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X1 = $36,000 B)
 Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X2 = $4,000
Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X2 = $4,000
 Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X1 = $36,000 B)
Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X1 = $36,000 B) Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X2 = $4,000
Total minimum taxable capital gain for 20X2 = $4,000 4
John sold a piece of land in 20X9 for $350,000. The land was recognized as capital property. The original cost of the land was $75,000. The selling costs incurred in 20X9 were $5,000. The terms of the payment included an immediate down payment of
$50,000, with the remainder of the cost to be paid over the next three years in three equal payments. John wishes to report the minimum taxable capital gain allowed each year. How much will he report in 20X9? (Round all numbers to zero decimal places.)
A) $27,000
B) $216,000
C) $135,000
D) $0
$50,000, with the remainder of the cost to be paid over the next three years in three equal payments. John wishes to report the minimum taxable capital gain allowed each year. How much will he report in 20X9? (Round all numbers to zero decimal places.)
A) $27,000
B) $216,000
C) $135,000
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mandy holds shares in Y Co. Recently, the shares have been experiencing a decline in market value. She originally purchased 1000 shares in 20X0 at $5 per share. On September 22nd of 20X1 she sold the shares when they were trading for only $3 per share. On October 3rd she felt optimistic that the market value would rise substantially by the end of the year, so she repurchased 1000 shares of Y Co. at $2.50 per share.
Which of the following is true for Mandy?
A) Mandy can recognize a $2,000 capital loss on the sale of her shares on her 20X1 tax return.
B) Mandy can recognize a $2,000 superficial loss on the sale of her shares on her 20X1 tax return.
C) The adjusted cost base of Mandy's new shares is $2,500.
D) The adjusted cost base of Mandy's new shares is $4,500.
Which of the following is true for Mandy?
A) Mandy can recognize a $2,000 capital loss on the sale of her shares on her 20X1 tax return.
B) Mandy can recognize a $2,000 superficial loss on the sale of her shares on her 20X1 tax return.
C) The adjusted cost base of Mandy's new shares is $2,500.
D) The adjusted cost base of Mandy's new shares is $4,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Greta Snow sold the following items prior to moving to Europe:
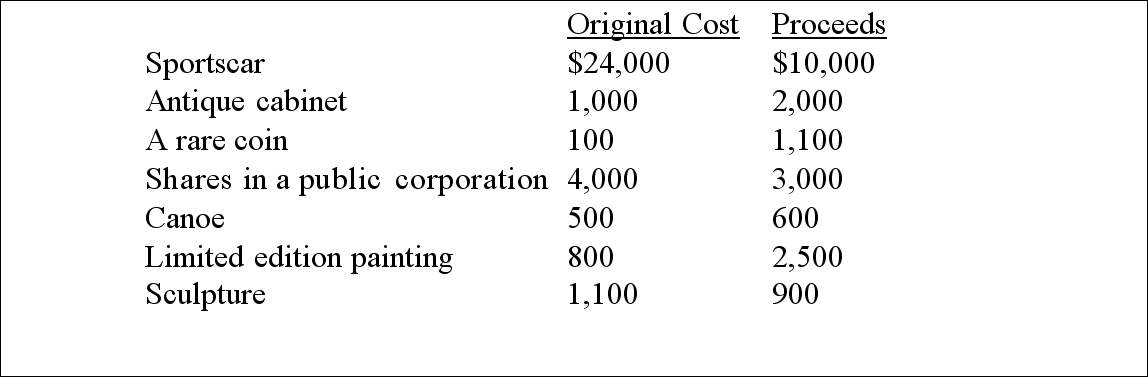
Required:
Calculate the tax consequences of Greta's sales, placing the items into the appropriate categories of capital property.

Required:
Calculate the tax consequences of Greta's sales, placing the items into the appropriate categories of capital property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following cases pertain to some of the unique aspects regarding the sale of
various types of capital properties. Next to each case, identify (from the list) the
type of capital property that applies. (Select only one category of capital property for each case and use each category only once.)
Gains are treated as business income or business losses.
The weighted average method is used to determine the adjusted cost base in order to determine the capital gain or loss.
Though typically of an inventory nature, the CRA allows gains on these
sales to be reported as capital unless the nature of the taxpayer's business is closely related.
A capital gain deferral may be recognized provided a reinvestment in common shares from the treasury of a replacement entity is made.
A gain resulting from the receipt of compensation for expropriated property may be deferred if the property is replaced before the end of the second
taxation year that begins following the year of expropriation.
The grantor must report a capital gain in the year received.
List of capital properties:
Identical properties Options and warrants
Commodities and futures transactions Goodwill and eligible capital property Voluntary and involuntary dispositions Eligible small-business investments
Gifts of Canadian public securities
various types of capital properties. Next to each case, identify (from the list) the
type of capital property that applies. (Select only one category of capital property for each case and use each category only once.)
Gains are treated as business income or business losses.
The weighted average method is used to determine the adjusted cost base in order to determine the capital gain or loss.
Though typically of an inventory nature, the CRA allows gains on these
sales to be reported as capital unless the nature of the taxpayer's business is closely related.
A capital gain deferral may be recognized provided a reinvestment in common shares from the treasury of a replacement entity is made.
A gain resulting from the receipt of compensation for expropriated property may be deferred if the property is replaced before the end of the second
taxation year that begins following the year of expropriation.
The grantor must report a capital gain in the year received.
List of capital properties:
Identical properties Options and warrants
Commodities and futures transactions Goodwill and eligible capital property Voluntary and involuntary dispositions Eligible small-business investments
Gifts of Canadian public securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Anne Smith acquired her house in 20X0 for $150,000 and her cottage in 20X4 for $100,000. Due to a rise in real estate prices, she decided to sell both
properties and backpack around the world for two years. Both properties were sold in October of 20X8. Anne received proceeds of $375,000 for the house, and
$250,000 for the cottage.
Required:
Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that Anne will report for her house and her cottage on her 20X8 tax return. Show all calculations, identifying the
taxable capital gain for each property.
properties and backpack around the world for two years. Both properties were sold in October of 20X8. Anne received proceeds of $375,000 for the house, and
$250,000 for the cottage.
Required:
Calculate the minimum taxable capital gain that Anne will report for her house and her cottage on her 20X8 tax return. Show all calculations, identifying the
taxable capital gain for each property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Sarah Green purchased a piece of land in 20X8 with plans to build and operate a greenhouse and evergreen nursery. Sarah is a full-time teacher, but has always dreamed of also running her own business. It is now 20X9 and Sarah has not yet started her
Business, and upon receiving an offer to teach on a tropical island, has decided to sell the land. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The intent of the purchase is insignificant when determining the type of income to report.
B) Sarah purchased the land with the primary intent to resell it at a profit.
C) Sarah's primary intent suggests that the income should be treated as a business transaction.
D) Sarah purchased the land with the primary intent to recognize a long-term economic benefit.
Business, and upon receiving an offer to teach on a tropical island, has decided to sell the land. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The intent of the purchase is insignificant when determining the type of income to report.
B) Sarah purchased the land with the primary intent to resell it at a profit.
C) Sarah's primary intent suggests that the income should be treated as a business transaction.
D) Sarah purchased the land with the primary intent to recognize a long-term economic benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following rules regarding the tax treatment of a principal residence is FALSE?
A) Properties can be designated to each married or common-law partner in a family for the purpose of reducing the gains on the sale of two principal residences.
B) When a taxpayer owns more than one residence, the decision to designate a particular property as the 'principal residence' occurs at the time of sale.
C) If a taxpayer only owns one residence, the 'principal residence formula' reduces any capital gain on the sale to nil.
D) A capital loss cannot be realized on the sale of a principal residence.
A) Properties can be designated to each married or common-law partner in a family for the purpose of reducing the gains on the sale of two principal residences.
B) When a taxpayer owns more than one residence, the decision to designate a particular property as the 'principal residence' occurs at the time of sale.
C) If a taxpayer only owns one residence, the 'principal residence formula' reduces any capital gain on the sale to nil.
D) A capital loss cannot be realized on the sale of a principal residence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



