Deck 6: The Acquisition, Use, and Disposal of Depreciable Property
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/8
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Acquisition, Use, and Disposal of Depreciable Property
1
Green Gardens Inc. purchased a piece of Class 8 machinery in 20X0. The cost of the machine was $5,000. In 20X2, the machine was sold for proceeds of $2,000 and there were no other purchases or disposals during the year. The UCC in the Class 8 pool was $5,500 at the beginning of 20X2. What is the UCC of this class at the end of 20X2?
A) $4,800
B) $2,800
C) $3,500
D) $700
A) $4,800
B) $2,800
C) $3,500
D) $700
B
2
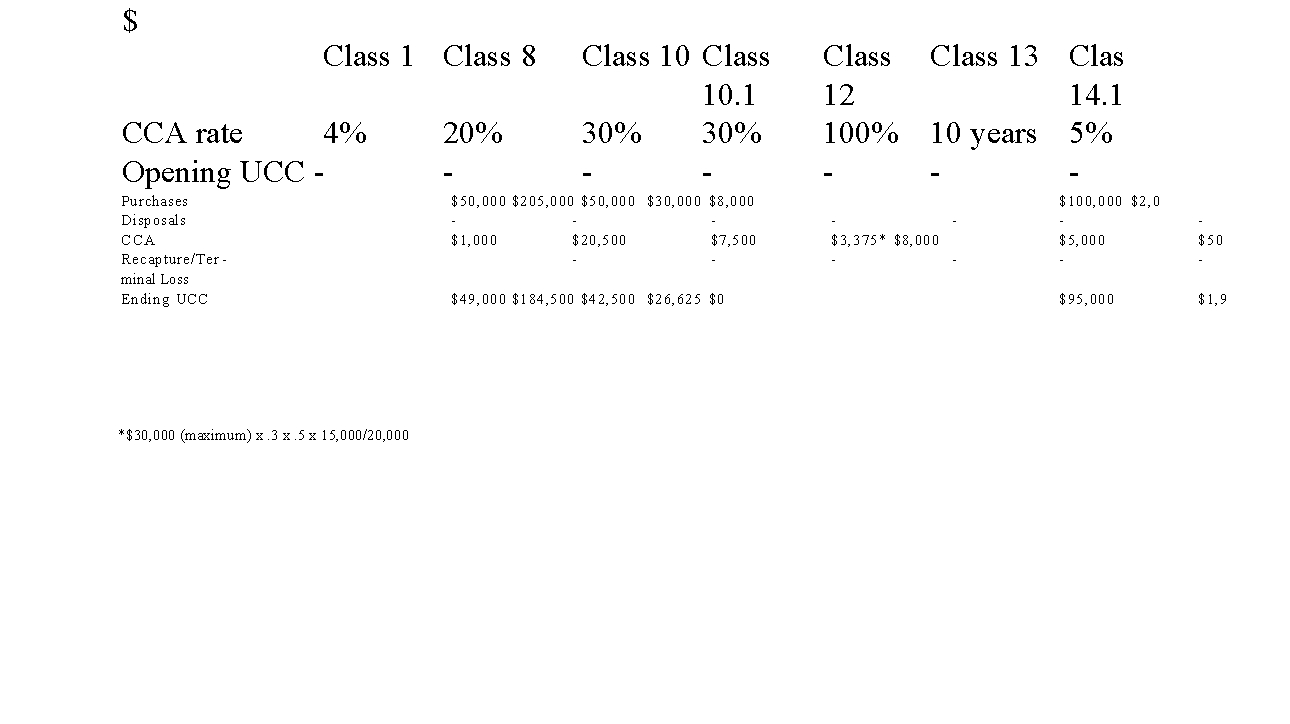
Tom's Tool Rentals began operations in 20X0. All income in the company classifies as 'business income'. The following information pertains to
transactions in 20X0:
1, Tom signed an 8 year lease for a building when he began the business. The building is in an excellent location and is estimated to be worth $500,000. Tom has an option to renew the lease for an additional 2 years.
Tom spent $100,000 in 20X0 on improvements to the leased building at the beginning of the year.
Tom purchased a small piece of adjacent land and a small building on the land for $120,000 in 20X0 (after March 18, 2007). The building was valued at
$50,000, and is used as a storage facility. Tom has chosen not to take the additional allowance on the building.
Tom's inventory of rental tools is valued at $200,000. All of the tools were purchased in 20X0 and are required to be placed in Class 8 by the CRA.
Tom purchased several small tools in 20X0 that he uses to maintain his rental
tools. The total cost of these tools was $8,000, and each tool cost under $500.
A delivery van costing a total of $50,000 was purchased in 20X0, to be used solely in the business.
Tom furnished the reception area of his business at a cost of $5000.
A computer was purchased for tracking sales and inventory. The computer cost
$1,000. (Assume the Class 50 time period applies.) Incorporation costs for the business were $5,000.
Tom purchased a $42,000 vehicle to be used to drive clients to meetings.
Business was quick to pick up in the first year so Tom chose to use all of the CC that was available to him in 20X0.
Tom is an HST registrant.
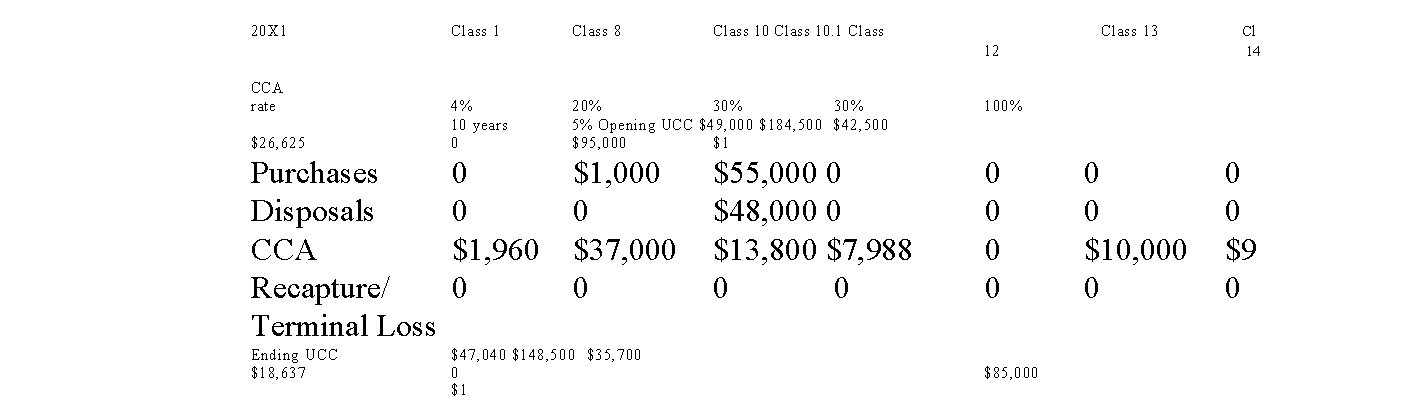
The following transactions occurred in 20X1:
Tom sold the delivery truck for $48,000, and immediately purchased a newer and larger model for $55,000.
New shelving was purchased for the reception area, at a cost of $1,000. Maximum CCA was claimed for the year.
In 20X2 the storage facility was destroyed in a fire. The market value of the
building, which was insured, was $55,000. A new building was built one year after the fire at a cost of $60,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the capital cost allowance per class claimed by the company in
20X0 and 20X1. (Assume the company began after 2016.) (Round all answers.)
B) Show the amended recapture calculation to be filed, pertaining to the storage building, in the year the new building is built.
transactions in 20X0:
1, Tom signed an 8 year lease for a building when he began the business. The building is in an excellent location and is estimated to be worth $500,000. Tom has an option to renew the lease for an additional 2 years.
Tom spent $100,000 in 20X0 on improvements to the leased building at the beginning of the year.
Tom purchased a small piece of adjacent land and a small building on the land for $120,000 in 20X0 (after March 18, 2007). The building was valued at
$50,000, and is used as a storage facility. Tom has chosen not to take the additional allowance on the building.
Tom's inventory of rental tools is valued at $200,000. All of the tools were purchased in 20X0 and are required to be placed in Class 8 by the CRA.
Tom purchased several small tools in 20X0 that he uses to maintain his rental
tools. The total cost of these tools was $8,000, and each tool cost under $500.
A delivery van costing a total of $50,000 was purchased in 20X0, to be used solely in the business.
Tom furnished the reception area of his business at a cost of $5000.
A computer was purchased for tracking sales and inventory. The computer cost
$1,000. (Assume the Class 50 time period applies.) Incorporation costs for the business were $5,000.
Tom purchased a $42,000 vehicle to be used to drive clients to meetings.
Business was quick to pick up in the first year so Tom chose to use all of the CC that was available to him in 20X0.
Tom is an HST registrant.
The following transactions occurred in 20X1:
Tom sold the delivery truck for $48,000, and immediately purchased a newer and larger model for $55,000.
New shelving was purchased for the reception area, at a cost of $1,000. Maximum CCA was claimed for the year.
In 20X2 the storage facility was destroyed in a fire. The market value of the
building, which was insured, was $55,000. A new building was built one year after the fire at a cost of $60,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the capital cost allowance per class claimed by the company in
20X0 and 20X1. (Assume the company began after 2016.) (Round all answers.)
B) Show the amended recapture calculation to be filed, pertaining to the storage building, in the year the new building is built.
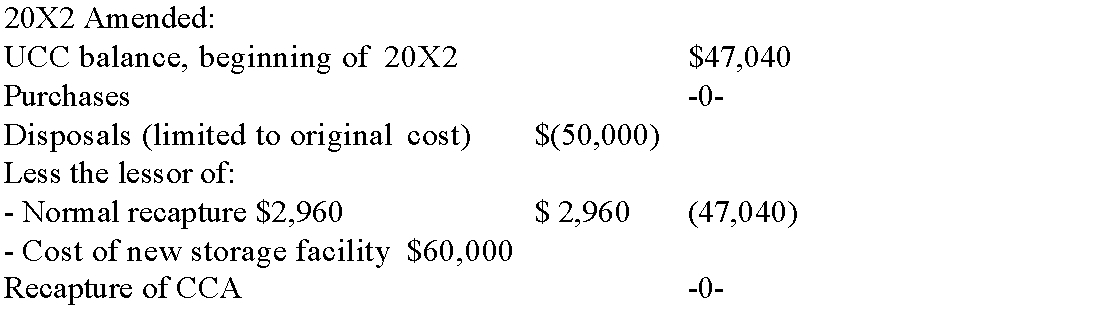
3
Which of the following statements regarding recapture is true?
A) Recapture only occurs when there is a positive balance in a class pool and that pool of assets is empty.
B) Recapture may be deducted from business income.
C) Recapture occurs when there is a negative balance in a class pool, even if there are assets remaining in that class pool.
D) Recapture occurs when there is a positive balance in a class pool, even if there are assets remaining in that class pool.
A) Recapture only occurs when there is a positive balance in a class pool and that pool of assets is empty.
B) Recapture may be deducted from business income.
C) Recapture occurs when there is a negative balance in a class pool, even if there are assets remaining in that class pool.
D) Recapture occurs when there is a positive balance in a class pool, even if there are assets remaining in that class pool.
C
4
Ben purchased Miller Co. in 2014 for $430,000, which included $35,000 of goodwill. It is now 2016 and Ben is considering selling Miller Co. which has a current goodwill value of $55,000. What was the balance in the cumulative eligible capital account at the end of 2015, assuming there were no other intangible assets in the company? (Rounded)
A) $30,272
B) $2,279
C) $1,709
D) $22,704
A) $30,272
B) $2,279
C) $1,709
D) $22,704

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Alpha Ltd. is a Canadian-controlled private corporation operating a small
land-development business. In June 20X2, the company acquired a license to manufacture pre-fab homes and began operations immediately. Financial
information for the 20X2 taxation year is outlined below:
Alpha's profit before income taxes for the year ended November 30, 20X2, was
$245,000, as follows:
 The loss on sale of property results from two transactions. On October 1, 20X2,
The loss on sale of property results from two transactions. On October 1, 20X2,
Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd., a 100% subsidiary, for $100,000. (The
shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.) Also, during the year, Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000.The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale. New vehicles were obtained
under a lease arrangement.
The 20X1 corporate tax return shows the following UCC balances:
 Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20X2. At that
Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20X2. At that
time, it acquired the following:
 Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.
Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.
Alpha normally acquires raw land, which it then develops into building lots for resale to individuals or housing contractors. In 20X2, it sold part of its
undeveloped land inventory to another developer for $400,000. The sale realized a profit of $80,000, which is included in the land-development income above.
The proceeds consisted of $40,000 in cash, with the balance payable in five annual installments beginning in 20X3.
Travel and entertainment expense includes the following:
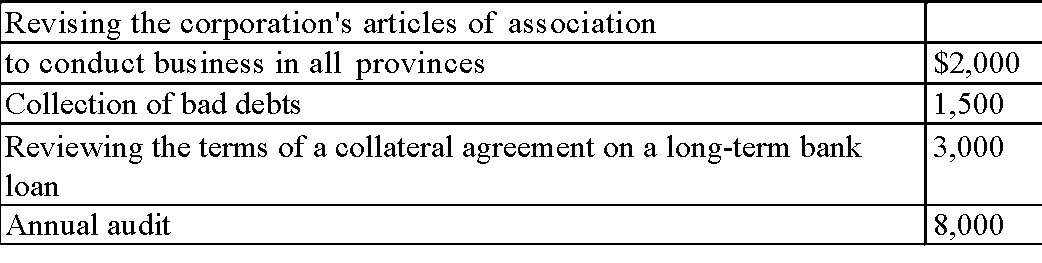
 Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
 Required:
Required:
Calculate Alpha's net income for tax purposes for the 20X2 taxation year. (Assume a 2016 tax year.)
land-development business. In June 20X2, the company acquired a license to manufacture pre-fab homes and began operations immediately. Financial
information for the 20X2 taxation year is outlined below:
Alpha's profit before income taxes for the year ended November 30, 20X2, was
$245,000, as follows:
 The loss on sale of property results from two transactions. On October 1, 20X2,
The loss on sale of property results from two transactions. On October 1, 20X2,Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd., a 100% subsidiary, for $100,000. (The
shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.) Also, during the year, Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000.The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale. New vehicles were obtained
under a lease arrangement.
The 20X1 corporate tax return shows the following UCC balances:
 Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20X2. At that
Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20X2. At thattime, it acquired the following:
 Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.
Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.Alpha normally acquires raw land, which it then develops into building lots for resale to individuals or housing contractors. In 20X2, it sold part of its
undeveloped land inventory to another developer for $400,000. The sale realized a profit of $80,000, which is included in the land-development income above.
The proceeds consisted of $40,000 in cash, with the balance payable in five annual installments beginning in 20X3.
Travel and entertainment expense includes the following:
 Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
Legal and accounting expense includes the following: Required:
Required:Calculate Alpha's net income for tax purposes for the 20X2 taxation year. (Assume a 2016 tax year.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following situations would not be permitted to defer the recognition of any recapture that might arise from the disposition of the asset?
A) A half-ton truck that belonged to a construction company was stolen in 20X0. Insurance proceeds were received which generated recapture. The truck was replaced in 20X1.
B) A building that was used for income earning purposes was destroyed in a fire. Insurance proceeds were received which generated recapture. A new building was built one and a half years later.
C) A customized half-ton truck that belonged to a construction company was sold in 20X0. The proceeds from the sale generated recapture. A new customized truck was purchased fourteen months later in order to carry out the duties of a large contract
Awarded to the company.
D) A building that was used for income earning purposes was sold in December 20X0. The proceeds from the sale generated recapture. A new building was purchased in April 20X1. The company's fiscal year-end is December 31st.
A) A half-ton truck that belonged to a construction company was stolen in 20X0. Insurance proceeds were received which generated recapture. The truck was replaced in 20X1.
B) A building that was used for income earning purposes was destroyed in a fire. Insurance proceeds were received which generated recapture. A new building was built one and a half years later.
C) A customized half-ton truck that belonged to a construction company was sold in 20X0. The proceeds from the sale generated recapture. A new customized truck was purchased fourteen months later in order to carry out the duties of a large contract
Awarded to the company.
D) A building that was used for income earning purposes was sold in December 20X0. The proceeds from the sale generated recapture. A new building was purchased in April 20X1. The company's fiscal year-end is December 31st.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following cases is not eligible for capital cost allowance in the current year?
A) A building under construction is scheduled for completion in eighteen months. The building will be used as a production facility.
B) A new engine is installed in a semi-trailer that is used to haul produce to the United States.
C) A piece of equipment was purchased during the year on a 5 year financing term.
D) An employee owns and uses an automobile in the course of her employment duties during the month of December. Her pay for December is not received until January of the following year.
A) A building under construction is scheduled for completion in eighteen months. The building will be used as a production facility.
B) A new engine is installed in a semi-trailer that is used to haul produce to the United States.
C) A piece of equipment was purchased during the year on a 5 year financing term.
D) An employee owns and uses an automobile in the course of her employment duties during the month of December. Her pay for December is not received until January of the following year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
ABC Corp. leased an office and paid $20,000 for leasehold improvements in
January of this year. This cost included dry wall, new carpets, and all new light fixtures. The term of the lease is 2 years plus an option to renew for 2 more
years.
Required:
Calculate the maximum CCA that ABC Corp. will be allowed to deduct this year
January of this year. This cost included dry wall, new carpets, and all new light fixtures. The term of the lease is 2 years plus an option to renew for 2 more
years.
Required:
Calculate the maximum CCA that ABC Corp. will be allowed to deduct this year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



