Deck 4: Income From Employment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/9
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Income From Employment
1
Steven is employed by Big Rigs Inc., a Canadian controlled private corporation. Steven earned $85,000 in 20X1. During the year, the following occurred:
A cash bonus of $8,000 was announced on December 3rd, to be paid to Steven o January 10th of the following year.
Steven was provided with a company car which he drove all year. The cost of the car (including taxes) was $42,000. All operating costs were paid by the employer Steven drove the car 21,000 kilometres in 20X1, of which 10,000 kilometres
were for personal use.
Big Rigs contributed $5,000 towards Steven's registered pension plan.
Steven contributed $5,000 towards his registered pension plan.
Steven was presented with a watch valued at $200 on his birthday.
The company provided Steven with a $200 cell phone to be used for business purposes.
In January of 20X1, Big Rigs loaned Steven $15,000 at a rate of 1% interest. The CRA's prescribed rate of interest during the year was 3%.
In January, Steven was offered a stock option to purchase 2000 shares in Big Rig at a cost of $8.00 per share. At that time, the fair market value per share was
$9.00. Steven exercised his option in February when the market value had risen to $9.50 per share. At the end of the year, Steven had not sold any of the shares,
and he was hoping to purchase more shares in the company in the upcoming year
Big Rigs provided Steven with a $25 meal allowance every week due to the two hours of overtime that he was required to work each Wednesday immediately
following his eight hours of regular work.
10.Steven's annual union dues totaled $850, which was deducted from his pay. Required:
Calculate Steven's minimum employment income for tax purposes. Explain why any items have been omitted in your calculations.
A cash bonus of $8,000 was announced on December 3rd, to be paid to Steven o January 10th of the following year.
Steven was provided with a company car which he drove all year. The cost of the car (including taxes) was $42,000. All operating costs were paid by the employer Steven drove the car 21,000 kilometres in 20X1, of which 10,000 kilometres
were for personal use.
Big Rigs contributed $5,000 towards Steven's registered pension plan.
Steven contributed $5,000 towards his registered pension plan.
Steven was presented with a watch valued at $200 on his birthday.
The company provided Steven with a $200 cell phone to be used for business purposes.
In January of 20X1, Big Rigs loaned Steven $15,000 at a rate of 1% interest. The CRA's prescribed rate of interest during the year was 3%.
In January, Steven was offered a stock option to purchase 2000 shares in Big Rig at a cost of $8.00 per share. At that time, the fair market value per share was
$9.00. Steven exercised his option in February when the market value had risen to $9.50 per share. At the end of the year, Steven had not sold any of the shares,
and he was hoping to purchase more shares in the company in the upcoming year
Big Rigs provided Steven with a $25 meal allowance every week due to the two hours of overtime that he was required to work each Wednesday immediately
following his eight hours of regular work.
10.Steven's annual union dues totaled $850, which was deducted from his pay. Required:
Calculate Steven's minimum employment income for tax purposes. Explain why any items have been omitted in your calculations.
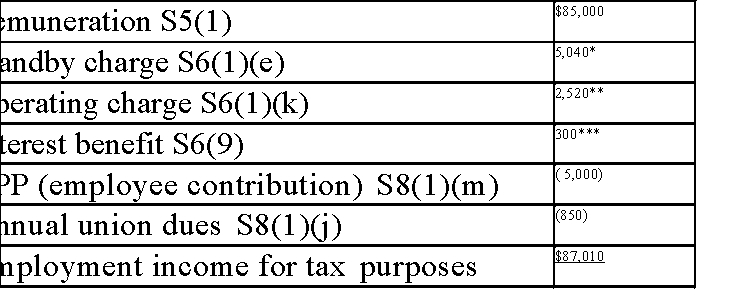 *($42,000 × 2% × 12) × 10,000/(1667 × 12) = $5,040
*($42,000 × 2% × 12) × 10,000/(1667 × 12) = $5,040**Lessor of: a) .26 × 10,000 kms = $2,600 and b) $5,040 × .5 = $2,520
***$15,000 × (.03 - .01)
Omitted items:
Cash bonus - received in the following year; therefore not taxable in current year
RPP - employer contribution is a deferred benefit Watch - non-cash gift within non-taxable limit
Cell phone - used for work, therefore, not taxable
Stock option - CCPC shares, therefore, the benefit may be deferred until the year of sale.
Meal allowance for "infrequent" overtime of two hours worked immediately following his scheduled shift
2
Which of the following, when provided by an employer, is NOT a tax-deferred or tax-free benefit for the employee?
A) A near-cash gift for the employee's wedding.
B) Counselling services to prepare the employee for retirement.
C) Contributions to the employee's registered pension plan.
D) Premiums for private health care plans.
A) A near-cash gift for the employee's wedding.
B) Counselling services to prepare the employee for retirement.
C) Contributions to the employee's registered pension plan.
D) Premiums for private health care plans.
A
3
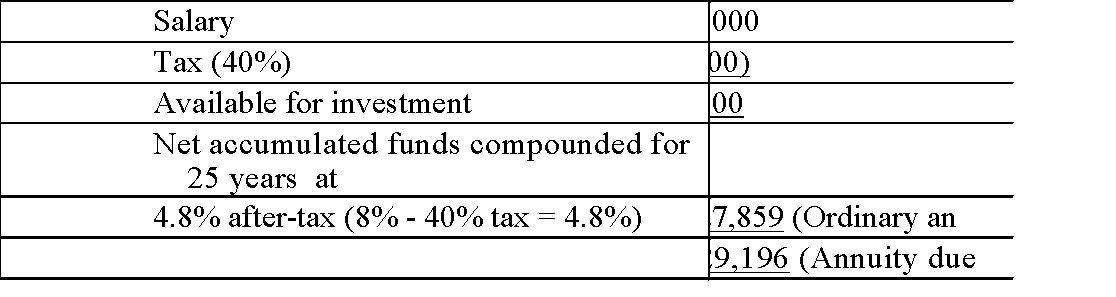
An individual has the option to receive a $1000 annual bonus and invest the after-tax amount for 25 years, or receive $1000 per annum in a registered
pension plan for the next 25 years. Assuming a constant rate of return of 8% and a tax rate of 40%, what will be the total after-tax difference between the two
plans? Show all of your work.
pension plan for the next 25 years. Assuming a constant rate of return of 8% and a tax rate of 40%, what will be the total after-tax difference between the two
plans? Show all of your work.
Salary
 RPP
RPP
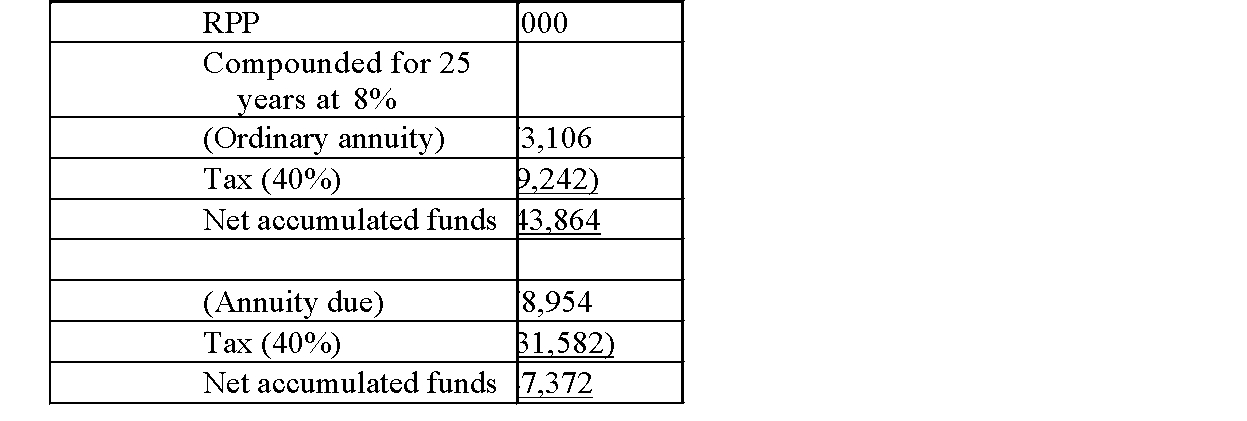 The RPP nets an increase of $16,005 under the ordinary annuity method, and $18,176 under the annuity due method.
The RPP nets an increase of $16,005 under the ordinary annuity method, and $18,176 under the annuity due method.
 RPP
RPP The RPP nets an increase of $16,005 under the ordinary annuity method, and $18,176 under the annuity due method.
The RPP nets an increase of $16,005 under the ordinary annuity method, and $18,176 under the annuity due method. 4
Which of the following factors are used by the courts in order to determine a taxpayer's status as an employee or a self-employed contractor?
A) control test, ownership of tools test, chance of profit and loss, integration test
B) control test, ownership of tools test, chance of lawsuit, integration test
C) control test, employer test, chance of lawsuit, integration test
D) control test, employer test, chance of profit and loss, integration test
A) control test, ownership of tools test, chance of profit and loss, integration test
B) control test, ownership of tools test, chance of lawsuit, integration test
C) control test, employer test, chance of lawsuit, integration test
D) control test, employer test, chance of profit and loss, integration test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Andy worked for High Speed Bikes Inc. from March 1st - December 31st during 20X1. He earned a monthly salary of $4,000 plus 1% commission on all of his
sales. During 20X1, Andy's sales totaled $800,000. Andy was required to pay for his employment expenses. He traveled out of his city most days in order to sell
to customers in surrounding towns. He received an allowance of $500 per month to cover his traveling costs. Andy and his employer each contributed $2,000 to
the company's registered pension plan.
Andy provided you with the following receipts for 20X1:
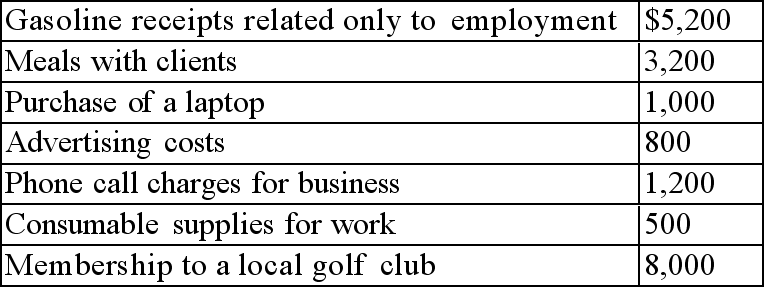 Andy purchased a new vehicle for work during the year, and drove it a total of 25,000 kms while employed at High Speed Bikes. 12,000 of these kilometres were for business. The vehicle cost Andy $32,000 plus GST of 5% and PST of 5%. Work-related interest payments on the car loan totaled $200 per month.
Andy purchased a new vehicle for work during the year, and drove it a total of 25,000 kms while employed at High Speed Bikes. 12,000 of these kilometres were for business. The vehicle cost Andy $32,000 plus GST of 5% and PST of 5%. Work-related interest payments on the car loan totaled $200 per month.
Required:
Calculate Andy's employment income for 20X1.
sales. During 20X1, Andy's sales totaled $800,000. Andy was required to pay for his employment expenses. He traveled out of his city most days in order to sell
to customers in surrounding towns. He received an allowance of $500 per month to cover his traveling costs. Andy and his employer each contributed $2,000 to
the company's registered pension plan.
Andy provided you with the following receipts for 20X1:
 Andy purchased a new vehicle for work during the year, and drove it a total of 25,000 kms while employed at High Speed Bikes. 12,000 of these kilometres were for business. The vehicle cost Andy $32,000 plus GST of 5% and PST of 5%. Work-related interest payments on the car loan totaled $200 per month.
Andy purchased a new vehicle for work during the year, and drove it a total of 25,000 kms while employed at High Speed Bikes. 12,000 of these kilometres were for business. The vehicle cost Andy $32,000 plus GST of 5% and PST of 5%. Work-related interest payments on the car loan totaled $200 per month.Required:
Calculate Andy's employment income for 20X1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Susan was provided with a company car to drive from March 1st to December 31st of the current year. The car cost the company $22,000 plus GST and PST totalling 11%. Susan drove the car a total of 15,000 kilometres during the year. 11,000 kilometres were for business purposes and the other 4,000 kilometres were for personal use. Susan's
Employer pays for all of the vehicle's operating costs which totaled $1,100. What is the minimum that Susan will report in total taxable benefits as result of the above
Information? (Round your answer.)
A) $5,924
B) $2,212
C) $1,758
D) $1,172
Employer pays for all of the vehicle's operating costs which totaled $1,100. What is the minimum that Susan will report in total taxable benefits as result of the above
Information? (Round your answer.)
A) $5,924
B) $2,212
C) $1,758
D) $1,172

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Simon Stevens is a high school history teacher. Simon is a national expert in ancient Mayan ruins. In July of 20X1, he was hired by the local university to
teach an elective course in ancient Mayan history. Simon then conducted a field trip of the ruins in Guatemala with some of the local students from July 27th to August 7th. He recruited another local expert to teach his last class that fell
during the dates of the trip.
Simon earned $55,000 from his teaching job. He negotiated a contract price of
$5,000 to teach the university elective and $7,000 to conduct the tour. The
university provided Simon with office space during the month of July. He used his laptop computer to prepare his lectures and the tour material. Additionally, Simon used his extensive collection of books to prepare his notes. He was not provided any benefits or insurance by the university. Simon was paid on July
31st and August 31st.
Simon is not sure how to prepare his tax return. He has a number of expenses
from his university job, and wants to know if he can use them to reduce his taxes payable.
Required:
Determine the tax treatment of Simon's income for 20X1. Apply the four tests within the guidelines used by the courts to determine whether a taxpayer is an employee or an independent contractor.
teach an elective course in ancient Mayan history. Simon then conducted a field trip of the ruins in Guatemala with some of the local students from July 27th to August 7th. He recruited another local expert to teach his last class that fell
during the dates of the trip.
Simon earned $55,000 from his teaching job. He negotiated a contract price of
$5,000 to teach the university elective and $7,000 to conduct the tour. The
university provided Simon with office space during the month of July. He used his laptop computer to prepare his lectures and the tour material. Additionally, Simon used his extensive collection of books to prepare his notes. He was not provided any benefits or insurance by the university. Simon was paid on July
31st and August 31st.
Simon is not sure how to prepare his tax return. He has a number of expenses
from his university job, and wants to know if he can use them to reduce his taxes payable.
Required:
Determine the tax treatment of Simon's income for 20X1. Apply the four tests within the guidelines used by the courts to determine whether a taxpayer is an employee or an independent contractor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sarah borrowed $25,000 from her employer at a rate of 1% interest. At the time the loan was made, the CRA's prescribed rate of interest was 3%. Sarah is in a 40% income tax bracket. What is the actual cost (rate) of Sarah's loan? (Assume there are no fluctuations in the prescribed rate of interest.)
A) 1.2%
B) 1.8%
C) 1%
D) 2%
A) 1.2%
B) 1.8%
C) 1%
D) 2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cindy works for Sky Manufacturers, a public corporation. In 20X1 she was offered an option to purchase shares at $15 per share from her employer. The fair market value on that day was $17 per share. The option had a four year exercise time-limit. Cindy exercised her option in 20X3 and purchased 500 shares. The fair market value at that
Time was $21 per share. What is Cindy's tax treatment of this option in the year 20X3?
A) $3,000 taxable benefit and no security option deduction
B) $3,000 taxable benefit and a 50% security option deduction
C) $2,000 taxable benefit and no security option deduction
D) $2,000 taxable benefit and a 50% security option deduction
Time was $21 per share. What is Cindy's tax treatment of this option in the year 20X3?
A) $3,000 taxable benefit and no security option deduction
B) $3,000 taxable benefit and a 50% security option deduction
C) $2,000 taxable benefit and no security option deduction
D) $2,000 taxable benefit and a 50% security option deduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



