Deck 20: Domestic and International Business Expansion
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/8
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Domestic and International Business Expansion
1
In the Canada-U.S. tax treaty, the definition of a 'permanent establishment' does not include:
A) a storage facility
B) a place of management
C) an office
D) a factory
A) a storage facility
B) a place of management
C) an office
D) a factory
A
2
Andy Griffin would like to invest $150,000 in his friend Ernie's company, which was founded and operates in a foreign country. This investment would give Andy 25% ownership of the company. An annual dividend of $15,000 (Canadian
funds) is anticipated.
Andy's personal marginal tax rate is 45% on regular income, 28% on eligible
dividends, and 36% on non-eligible dividends. The foreign company is subject to a tax rate of 38% on all business income. Any dividends received by Andy,
personally, will be subject to a 15% withholding tax. Required:
1) Determine a) the total tax liability (foreign and Canadian) that Andy will be subject to upon receiving dividends from the foreign company, and b) the
after-tax proceeds.
2) How would your answer in part 1 change if Andy established a Canadian holding company to purchase the shares, (subject to a 5% withholding tax on dividends received)?
3) What would Andy's after-tax proceeds be if he received eligible dividend income from the holding company?
funds) is anticipated.
Andy's personal marginal tax rate is 45% on regular income, 28% on eligible
dividends, and 36% on non-eligible dividends. The foreign company is subject to a tax rate of 38% on all business income. Any dividends received by Andy,
personally, will be subject to a 15% withholding tax. Required:
1) Determine a) the total tax liability (foreign and Canadian) that Andy will be subject to upon receiving dividends from the foreign company, and b) the
after-tax proceeds.
2) How would your answer in part 1 change if Andy established a Canadian holding company to purchase the shares, (subject to a 5% withholding tax on dividends received)?
3) What would Andy's after-tax proceeds be if he received eligible dividend income from the holding company?
1. The combination of foreign and Canadian taxes that Andy will be subject to is $6,750.
a)
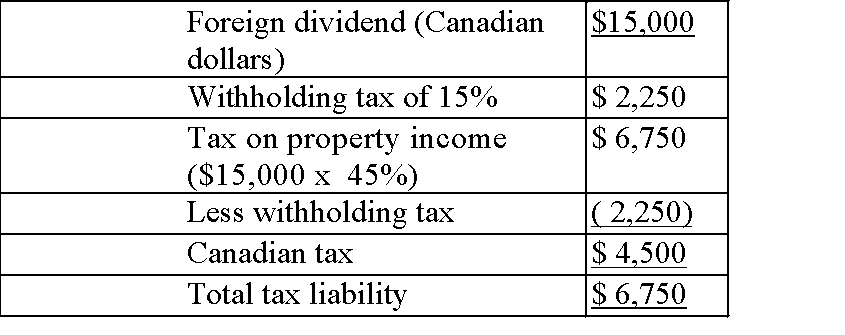 b)
b)
 2. Ernie's corporation would qualify as a foreign affiliate, therefore, there is no tax on the dividends received by Andy's corporation. The only tax
2. Ernie's corporation would qualify as a foreign affiliate, therefore, there is no tax on the dividends received by Andy's corporation. The only tax
liability is the withholding tax at source.
 3.
3.

a)
 b)
b) 2. Ernie's corporation would qualify as a foreign affiliate, therefore, there is no tax on the dividends received by Andy's corporation. The only tax
2. Ernie's corporation would qualify as a foreign affiliate, therefore, there is no tax on the dividends received by Andy's corporation. The only taxliability is the withholding tax at source.
 3.
3.
3
Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning domestic expansion of a business?
A) The main advantage of incorporating an expansion activity is the use of start-up losses against income from other divisions of the founding corporation.
B) Cash funding requirements will be lower for a corporation than a corporate division if the expansion activity incurs start-up losses.
C) Obligations of a new division are separate from the parent company due to the limited liability of the division.
D) Cash funding requirements will be higher for a corporation than a corporate division if the expansion activity incurs start-up losses.
A) The main advantage of incorporating an expansion activity is the use of start-up losses against income from other divisions of the founding corporation.
B) Cash funding requirements will be lower for a corporation than a corporate division if the expansion activity incurs start-up losses.
C) Obligations of a new division are separate from the parent company due to the limited liability of the division.
D) Cash funding requirements will be higher for a corporation than a corporate division if the expansion activity incurs start-up losses.
D
4
The Sweater Corp. is a Canadian corporation which plans to expand internationally. The company has decided to establish a foreign subsidiary corporation in another country. Which of the following is FALSE?
A) The subsidiary will be subject to taxes in the foreign country.
B) The subsidiary's profits will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.
C) Dividends received by the Canadian corporation from the foreign subsidiary may be subject to a withholding tax in the foreign jurisdiction.
D) Dividends received by the Canadian corporation from the foreign subsidiary will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.
A) The subsidiary will be subject to taxes in the foreign country.
B) The subsidiary's profits will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.
C) Dividends received by the Canadian corporation from the foreign subsidiary may be subject to a withholding tax in the foreign jurisdiction.
D) Dividends received by the Canadian corporation from the foreign subsidiary will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Crispy Chips Inc. is considering an expansion into the United States. Jeff Arthur, the CEO, is not sure how to structure this new venture and would like some
general information before he meets with his accountant and lawyer.
Required:
Write a memo to Jeff informing him of the two fundamental approaches he can take to conduct his foreign operations (branch and subsidiary corporation),
listing two advantages and two disadvantages of each approach.
general information before he meets with his accountant and lawyer.
Required:
Write a memo to Jeff informing him of the two fundamental approaches he can take to conduct his foreign operations (branch and subsidiary corporation),
listing two advantages and two disadvantages of each approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following lists are acceptable methods that may be used in adopting a reasonable transfer price between a Canadian parent and its foreign subsidiary corporations?
A) Cost-plus method; resale price method; profit-margin method
B) Comparable arm's-length selling price method; lowest tax rate method; profit-margin method
C) Comparable arm's-length selling price method; cost-plus method; resale price method
D) Lowest tax rate method; resale price method; comparable arm's-length selling price method
A) Cost-plus method; resale price method; profit-margin method
B) Comparable arm's-length selling price method; lowest tax rate method; profit-margin method
C) Comparable arm's-length selling price method; cost-plus method; resale price method
D) Lowest tax rate method; resale price method; comparable arm's-length selling price method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Running Shoe Corp. is a Canadian corporation which plans to expand internationally. The company has decided to establish a foreign branch in another country. Which of the following is FALSE?
A) The branch profits will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.
B) If the foreign country has a lower tax rate, a tax benefit will be recognized.
C) Provided a treaty is in place with the foreign country, a foreign tax credit will reduce the Canadian taxes payable by the amount paid in foreign taxes.
D) The branch will be subject to branch taxes in the foreign country.
A) The branch profits will be included in the Canadian corporation's worldwide income.
B) If the foreign country has a lower tax rate, a tax benefit will be recognized.
C) Provided a treaty is in place with the foreign country, a foreign tax credit will reduce the Canadian taxes payable by the amount paid in foreign taxes.
D) The branch will be subject to branch taxes in the foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Great Big Company (GBC) is a CCPC located in Saskatchewan. GBC owns a foreign subsidiary, The Little Company (TLC), which is located in a foreign country. GBC manufactures electronic component parts which are then sold to TLC for assembly. GBC is subject to a 27% corporate tax rate and TLC is
subject to a 19% corporate tax rate. Fiona Big, the CEO of GBC, has mentioned that due to the lower tax rate in the foreign country, the profits of GBC could be shifted to TLC by adjusting the selling price of the component parts.
Required:
A) Can Fiona Big adjust the selling price of the component parts in order to take advantage of the lower tax rate? Why or why not?
B) What are three methods used to establish transfer prices for non-arm's length transactions?
subject to a 19% corporate tax rate. Fiona Big, the CEO of GBC, has mentioned that due to the lower tax rate in the foreign country, the profits of GBC could be shifted to TLC by adjusting the selling price of the component parts.
Required:
A) Can Fiona Big adjust the selling price of the component parts in order to take advantage of the lower tax rate? Why or why not?
B) What are three methods used to establish transfer prices for non-arm's length transactions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



