Deck 14: Multiple Corporations and Their Reorganization
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/8
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Multiple Corporations and Their Reorganization
1
Jack Grey is the sole shareholder of Grey's Garden tools. He owns one class of common shares which have a value of $200,000. Jack is approaching retirement age and would like his two key employees to take over his company someday. At this point in time, the employees do not have enough excess cash to buy Jack's shares. Which of the following statements is true with regard to a corporate reorganization that would allow the
Employees to take over the ownership?
A) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in a continual growth of the new preferred shares.
B) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in an immediate tax consequence for himself.
C) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in the conversion of his common shares to preferred shares.
D) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in an immediate tax consequence for his employees.
Employees to take over the ownership?
A) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in a continual growth of the new preferred shares.
B) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in an immediate tax consequence for himself.
C) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in the conversion of his common shares to preferred shares.
D) Section 86 of the Income Tax Act would allow Jack to restructure the ownership of his company and would result in an immediate tax consequence for his employees.
C
2
Which of the following is one of the conditions necessary for an amalgamation to result in a tax-free combination?
A) At least one of the corporations must be Canadian.
B) All of the shareholders of the old corporations must become shareholders of the new corporations.
C) The two corporations must be in a similar line of business.
D) 50 percent of the assets and liabilities of the old corporation must become assets and liabilities of the new corporation.
A) At least one of the corporations must be Canadian.
B) All of the shareholders of the old corporations must become shareholders of the new corporations.
C) The two corporations must be in a similar line of business.
D) 50 percent of the assets and liabilities of the old corporation must become assets and liabilities of the new corporation.
B
3
Stan is the sole shareholder of Hardware Ltd. Hardware purchased all of the shares of Tools Inc. in 20X4 for $500,000. Tools incurred a non-capital loss of
$25,000 in the year ended December 31, 20X3. Stan has decided to initiate a
Section 88 wind-up of Tools Inc. into Hardware Ltd. on June 23, 20X7. Due to the seasonal nature of his sales, Stan would like to maintain the April 30th year end that he has used since beginning his business.
Stan's accountant has prepared the following balance sheet for Tools Inc. as of
June 22, 20X7. The fair market value of the assets on both June 22, 20X7 and the date of acquisition in 20X4 are presented in the following table:
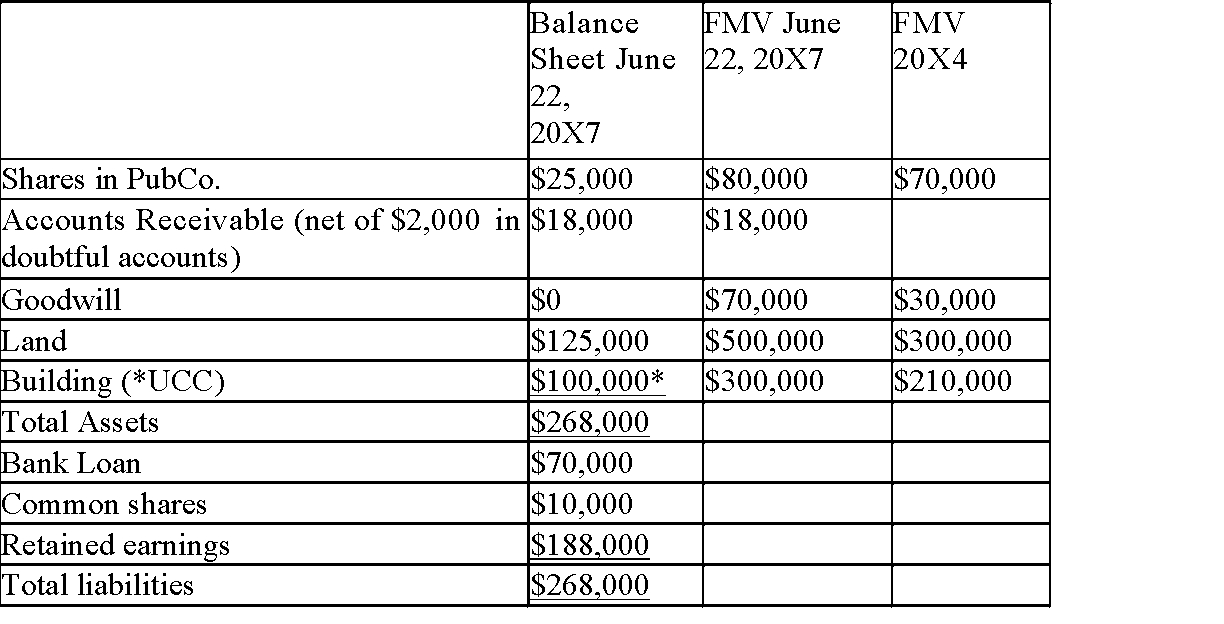 Tools paid dividends of $8,000 to Hardware in 20X7. Required:
Tools paid dividends of $8,000 to Hardware in 20X7. Required:
Answer the following questions (filling in the charts where provided):
1) Immediately following the windup, Hardware will report the following assets at what values?

2) Calculate the value of the "bump" available on the ACB for the non-depreciable capital property.
3) Identify the assets which may use the bump, and the amount of the bump available for each asset identified. Identify any unusable bump amount.
4) Explain when Hardware will be able to use the non-capital loss from Tools.
$25,000 in the year ended December 31, 20X3. Stan has decided to initiate a
Section 88 wind-up of Tools Inc. into Hardware Ltd. on June 23, 20X7. Due to the seasonal nature of his sales, Stan would like to maintain the April 30th year end that he has used since beginning his business.
Stan's accountant has prepared the following balance sheet for Tools Inc. as of
June 22, 20X7. The fair market value of the assets on both June 22, 20X7 and the date of acquisition in 20X4 are presented in the following table:
 Tools paid dividends of $8,000 to Hardware in 20X7. Required:
Tools paid dividends of $8,000 to Hardware in 20X7. Required:Answer the following questions (filling in the charts where provided):
1) Immediately following the windup, Hardware will report the following assets at what values?

2) Calculate the value of the "bump" available on the ACB for the non-depreciable capital property.
3) Identify the assets which may use the bump, and the amount of the bump available for each asset identified. Identify any unusable bump amount.
4) Explain when Hardware will be able to use the non-capital loss from Tools.
1)

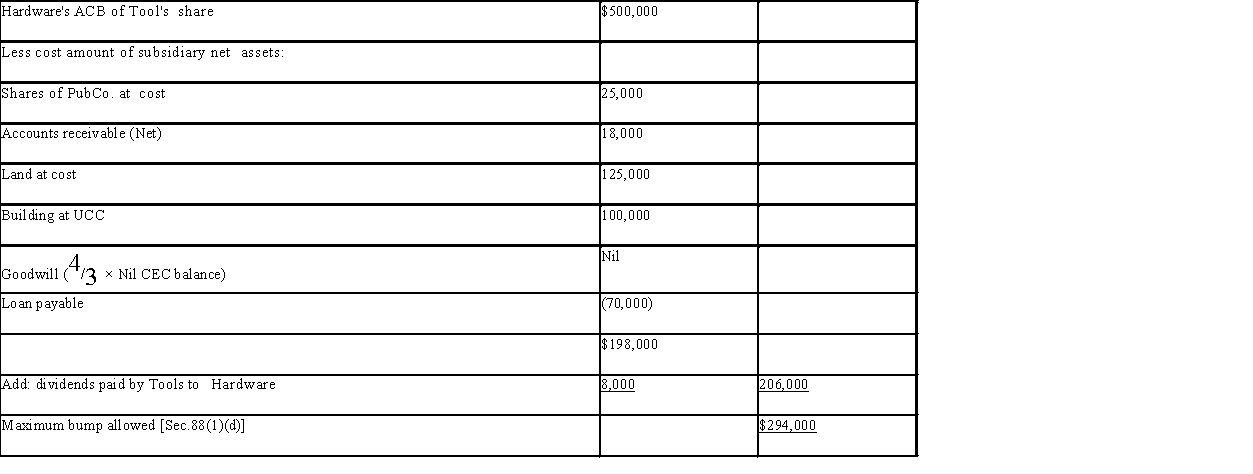
1) The bump available to the public shares is $45,000 ($70,000 - $25,000). The bump available to the land is $175,000 ($300,000 - $125,000).
The bump cannot be allocated to the depreciable assets.
$294,000 - 45,000 - 175,000 = $74,000 of the bump is unusable.
2) The $25,000 loss will be available for use in the first tax year that begin after the windup. Since the windup is taking place in 20X7 in the tax year ending 20X8, the loss will be available in the year ending in 20X9.


1) The bump available to the public shares is $45,000 ($70,000 - $25,000). The bump available to the land is $175,000 ($300,000 - $125,000).
The bump cannot be allocated to the depreciable assets.
$294,000 - 45,000 - 175,000 = $74,000 of the bump is unusable.
2) The $25,000 loss will be available for use in the first tax year that begin after the windup. Since the windup is taking place in 20X7 in the tax year ending 20X8, the loss will be available in the year ending in 20X9.
4
Hold Co. is a Canadian controlled private corporation that acquired 100% of the shares of Small Co. in 20X5. Hold Co. paid $50,000 for the shares. Big Co., an arm's length corporation, is now interested in purchasing Hold Co.'s investment in Small Co. Small Co.'s shares are currently worth $500,000 and the retained earnings of the company are $200,000. In order to reduce the fair market value of the shares, Small Co. will pay a dividend of $450,000 to Hold Co., and then
sell the shares for $50,000.
Required:
Presuming Subsection 55(2) applies, how much is the capital gain that Hold Co. will have to realize on this sale? (Ignore Part IV tax.)
sell the shares for $50,000.
Required:
Presuming Subsection 55(2) applies, how much is the capital gain that Hold Co. will have to realize on this sale? (Ignore Part IV tax.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The shareholders of Parent Co. and Sub Co. wish to combine the business
activities of the two companies through a business combination. Both companies have assets that have appreciated in value above their capital cost. Parent Co.
owns 85% of the shares of Sub Co.
Required:
Suggest a business combination (amalgamation or wind-up) that would defer the tax consequences associated with the increased value of the assets, and explain why you did not choose the other option.
activities of the two companies through a business combination. Both companies have assets that have appreciated in value above their capital cost. Parent Co.
owns 85% of the shares of Sub Co.
Required:
Suggest a business combination (amalgamation or wind-up) that would defer the tax consequences associated with the increased value of the assets, and explain why you did not choose the other option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Mr. Chan has created a holding company between himself and his corporation which earns only active business income. This will permit which of the following?
A) The holding company will receive dividends from the corporation, free of tax.
B) Mr. Chan will receive dividends from the holding company, free of tax.
C) The corporation's income will not be taxed.
D) Mr. Chan will receive dividends from the corporation, free of tax.
A) The holding company will receive dividends from the corporation, free of tax.
B) Mr. Chan will receive dividends from the holding company, free of tax.
C) The corporation's income will not be taxed.
D) Mr. Chan will receive dividends from the corporation, free of tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Browns have owned and operated The Tile Company Inc. for thirty years and are ready to retire. Their long-time employee wishes to buy the company but does not have the funds available to do so at this time. Which section of the Income Tax Act would
Allow the Browns to transfer the value of their common shares to preferred shares on a tax-deferred basis while issuing new common shares to the employee for a nominal
Value?
A) Section 88
B) Section 87
C) This transaction is not within the spirit of the Income Tax Act and would be subject to GAAR.
D) Section 86
Allow the Browns to transfer the value of their common shares to preferred shares on a tax-deferred basis while issuing new common shares to the employee for a nominal
Value?
A) Section 88
B) Section 87
C) This transaction is not within the spirit of the Income Tax Act and would be subject to GAAR.
D) Section 86

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Tom and Bob are equal shareholders of a profitable company with only active business income. The company is growing and dividend payouts are increasing. The two men have heard that 'holding corporations' might suit their needs. Which of the following would apply?
A) The holding companies would receive the dividends from the operating company, free of tax, to be invested in ventures of Tom and Bob's separate choices.
B) Dividends would flow from the operating company to Tom and Bob, and then to the holding corporations.
C) Dividends received by the holding companies from the operating company must be invested in the same ventures.
D) The establishment of holding corporations would allow Tom and Bob to access the profits of the operating company for personal expenditures without paying a second level of tax.
A) The holding companies would receive the dividends from the operating company, free of tax, to be invested in ventures of Tom and Bob's separate choices.
B) Dividends would flow from the operating company to Tom and Bob, and then to the holding corporations.
C) Dividends received by the holding companies from the operating company must be invested in the same ventures.
D) The establishment of holding corporations would allow Tom and Bob to access the profits of the operating company for personal expenditures without paying a second level of tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 8 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



