Deck 4: Bipolar Junction Transistors
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Bipolar Junction Transistors
1
The NOR gate is a digital circuit that produces a
A)HIGH level signal when one or more inputs are LOW
B)LOW level signal when one or more inputs are LOW
C)LOW level signal when one or more inputs are HIGH
D)HIGH level signal when one or more inputs are HIGH
A)HIGH level signal when one or more inputs are LOW
B)LOW level signal when one or more inputs are LOW
C)LOW level signal when one or more inputs are HIGH
D)HIGH level signal when one or more inputs are HIGH
C
2
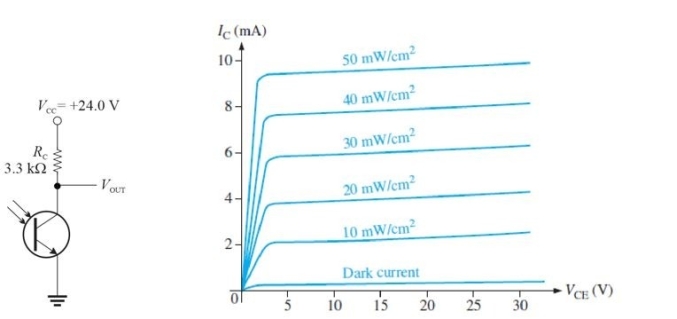 Figure 6 A phototransistor and its characteristic curve
Figure 6 A phototransistor and its characteristic curveRefer to Figure 6. Assume you measure VOUT as 11 V. From this, you can conclude that the light intensity is approximately
A)20 mW/cm2
B)10 mW/cm2
C)40 mW/cm2
D)30 mW/cm2
A
3
A 10 mV ac signal is applied to the base of a properly biased transistor with RC = 1.2 k▲ and re' = 36 ▲. The output ac voltage is
A)333 mV
B)33 mV
C)152 mV
D)105 mV
A)333 mV
B)33 mV
C)152 mV
D)105 mV
B
4
Small signal transistors are available in
A)dual in line (DIP)packs
B)plastic or metal cases
C)quad small outline (SO)packs
D)all of the above
A)dual in line (DIP)packs
B)plastic or metal cases
C)quad small outline (SO)packs
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For the characteristic curve in Figure 2, the equation IC = fiDCIB is true
A)only beyond C on the curve
B)at no place on the curve
C)only between B and C on the curve
D)only between A and B on the curve
A)only beyond C on the curve
B)at no place on the curve
C)only between B and C on the curve
D)only between A and B on the curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
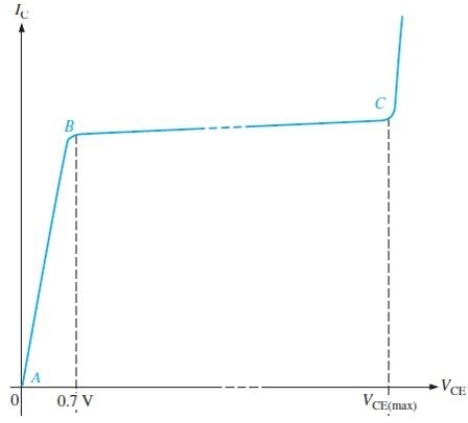 Figure 2 A characteristic curve
Figure 2 A characteristic curveFor the characteristic curve in Figure 2, the region between A and B is called the
A)active region
B)breakdown region
C)saturation region
D)cutoff region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The primary purpose of an optocoupler is to
A)couple an LED to a relay
B)amplify light
C)convert light into electrical current
D)isolate certain sections of circuits
A)couple an LED to a relay
B)amplify light
C)convert light into electrical current
D)isolate certain sections of circuits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
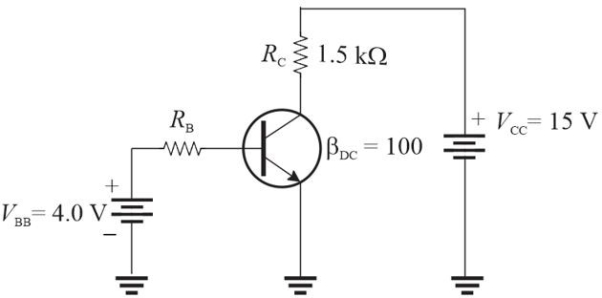 Figure 4
Figure 4Refer to Figure 4. If RB = 100 k▲, VC is approximately
A)5 V
B)7.5 V
C)12.5 V
D)10 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The NAND gate is a digital circuit that produces a
A)LOW level signal when both inputs are LOW
B)HIGH level signal when both inputs are LOW
C)HIGH level signal when both inputs are HIGH
D)LOW level signal when both inputs are HIGH
A)LOW level signal when both inputs are LOW
B)HIGH level signal when both inputs are LOW
C)HIGH level signal when both inputs are HIGH
D)LOW level signal when both inputs are HIGH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
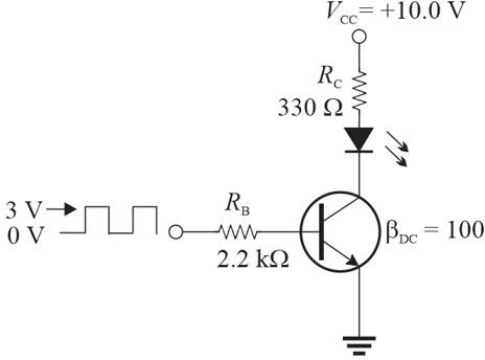 Figure 5
Figure 5Refer to Figure 5. When conducting, assume the LED drops 1.8 V and VCE(sat)= 0.2 V. If the input square wave is +3.0 V, the current in the LED will be approximately
A)30 mA
B)24 mA
C)105 mA
D)136 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A forward- biased npn transistor has a typical voltage drop from base to emitter of
A)50 V
B)10 V
C)0.7 V
D)1.5 V
A)50 V
B)10 V
C)0.7 V
D)1.5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a certain BJT, the collector current is 22.0 mA when the base current is 100 µA. The emitter current is
A)21.9 mA
B)22.1 mA
C)22.0 mA
D)2.2 mA
A)21.9 mA
B)22.1 mA
C)22.0 mA
D)2.2 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
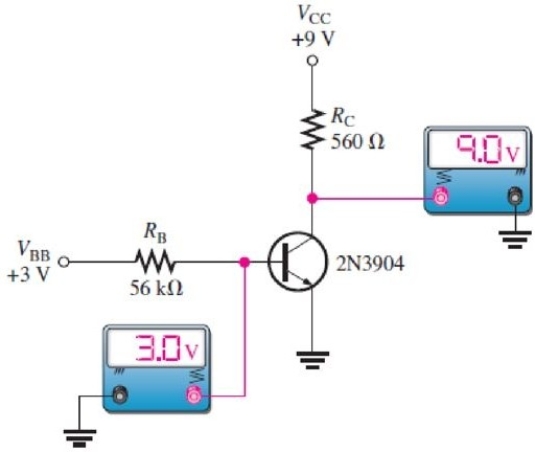 Figure 7
Figure 7Refer to Figure 7. The transistor is
A)cutoff
B)in the breakdown region
C)in the active region
D)saturated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a BJT is saturated,
A)VCC appears between the collector and emitter
B)both base current and collector current are at a maximum
C)base current is at maximum
D)collector current is at maximum
A)VCC appears between the collector and emitter
B)both base current and collector current are at a maximum
C)base current is at maximum
D)collector current is at maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
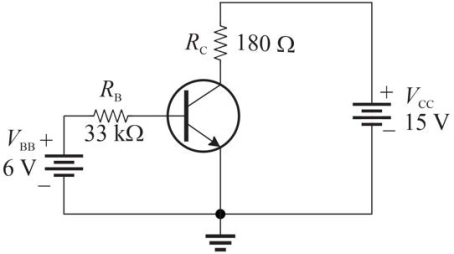 Figure 1
Figure 1Refer to Figure 1. If VCC is increased to 18 V, IB will
A)decrease
B)increase
C)not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
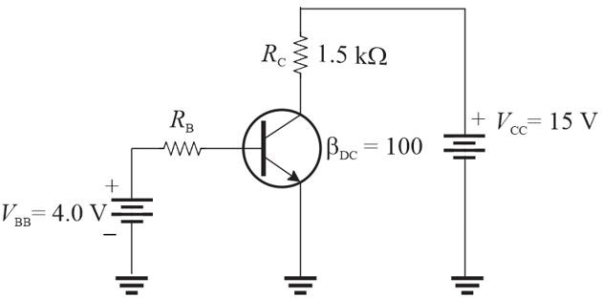 Figure 4
Figure 4Refer to Figure 4. Assume RB = 22 k▲. The collector current will be approximately
A)5 mA
B)20 mA
C)10 mA
D)27 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The symbol hFE means the same as
A)aDC
B)fiDC
C)Av
D)PD(max)
A)aDC
B)fiDC
C)Av
D)PD(max)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
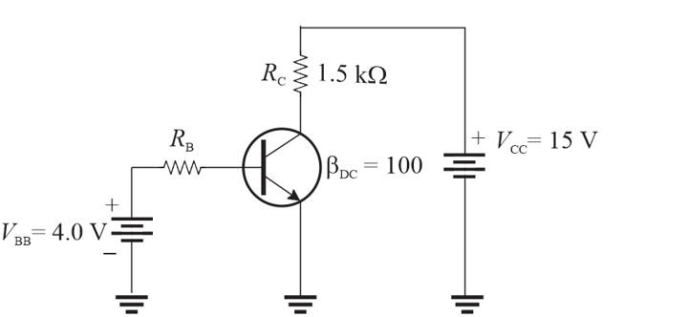 Figure 4
Figure 4Refer to Figure 4. The largest base resistor that will still saturate the transistor is approximately
A)33 k▲
B)400 k▲
C)330 k▲
D)40 k▲

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Typical values of aDC are from
A)20 to 200
B)0.95 to 0.99
C)800 to 1000
D)1.00 to 10
A)20 to 200
B)0.95 to 0.99
C)800 to 1000
D)1.00 to 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The light sensitive region of a photo transistor is the
A)base
B)substrate
C)emitter
D)collector
A)base
B)substrate
C)emitter
D)collector

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
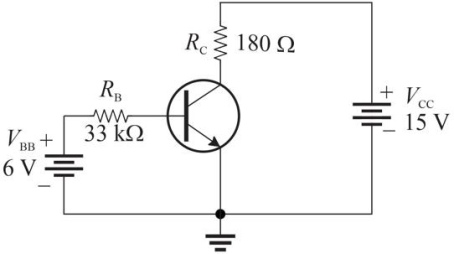 Figure 1
Figure 1Refer to Figure 1. Assume fiDC = 200. The expected value of IB is
A)200 µA
B)161 µA
C)80 µA
D)182 µA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
 Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.
Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.Refer to Fig 3. Assume VCC is lowered to 15 V. The transistor is
A)saturated
B)in the linear range
C)cutoff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When a BJT is conducting, the collector current is identical to the emitter current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
hFE varies with
A)temperature
B)collector current
C)both A and B
D)none of the above
A)temperature
B)collector current
C)both A and B
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The base region of a BJT is heavily doped and wide compared to the other two regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
 Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.
Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.Refer to Figure 3. The maximum value that VCC can be adjusted to without exceeding the VCE(max)rating is (ignore other max ratings).
A)60 V
B)45 V
C)50 V
D)40 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The fiDC for a BJT is the ratio of collector current to emitter current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assume a transistor has a maximum power rating of 1 W and VCE = 5 V. If IC = 120 mA, the power rating is not exceeded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
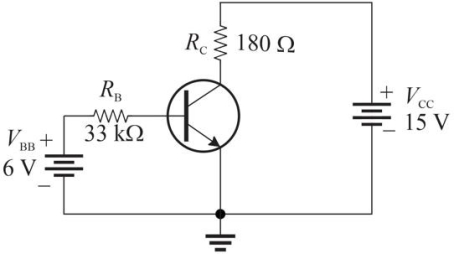 Figure 1
Figure 1Refer to Figure 1. Assume fiDC = 200. The value of VCE is approximately
A)12.4 V
B)9.2 V
C)7.5 V
D)5.8 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a BJT is saturated,
A)VCE is approximately 1/2 VCC
B)VCE is approximately equal to VCC
C)VCE is near zero
D)none of the above
A)VCE is approximately 1/2 VCC
B)VCE is approximately equal to VCC
C)VCE is near zero
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In switching circuits, a transistor operates between
A)active region and breakdown
B)cutoff and active region
C)cutoff and saturation
D)none of the above
A)active region and breakdown
B)cutoff and active region
C)cutoff and saturation
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
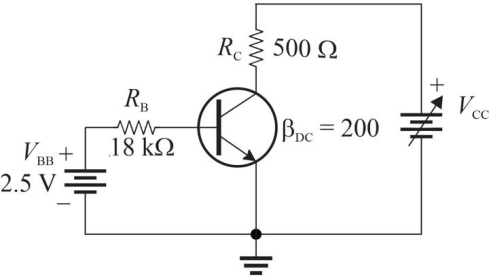 Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.
Figure 3 The transistor has the following ratings: PD(max)= 650 mW, VCE(max)= 40 V, and IC(max)= 200 mA.Refer to Figure 3. If VCC is set to 48 V, PD(max)is exceeded by
A)80 mW
B)55 mW
C)110 mW
D)310 mW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A saturated BJT has maximum collector current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The metal mounting tab or case of a power transistor is connected to the
A)base
B)emitter
C)substrate
D)collector
A)base
B)emitter
C)substrate
D)collector

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
ICEO is
A)collector current when the transistor is cutoff
B)collector current when the transistor is saturated
C)collector current when the transistor is on
D)base current when the transistor is saturated
A)collector current when the transistor is cutoff
B)collector current when the transistor is saturated
C)collector current when the transistor is on
D)base current when the transistor is saturated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Photo transistors have the greatest sensitivity to blue light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The value of fiDC is the ratio of
A)collector current to base current
B)collector current to emitter current
C)emitter current to base current
D)none of the above
A)collector current to base current
B)collector current to emitter current
C)emitter current to base current
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
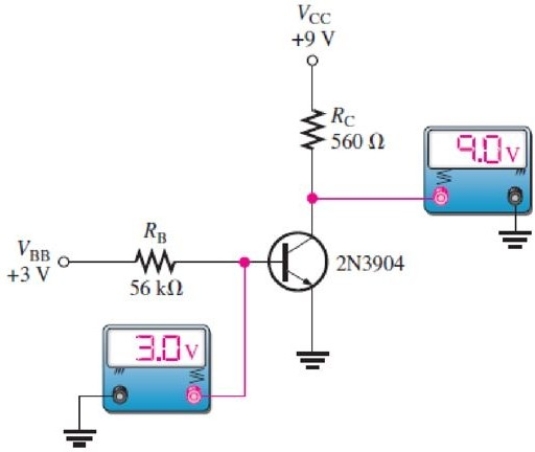 Figure 7
Figure 7Refer to Figure 7. Assume a single problem accounts for the readings. From the readings, you can conclude that
A)RB is open
B)the base- collector junction is open
C)the base- emitter junction is open
D)RC is shorted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
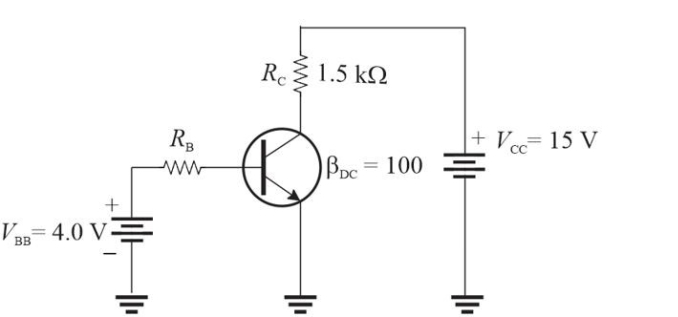 Figure 4
Figure 4Refer to Figure 4. If you wanted to change the transistor to a pnp type, you need to
A)increase the base resistor
B)increase the collector resistor
C)change both dc sources to negative supplies
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The voltage gain of a BJT amplifier is directly proportional to the internal ac emitter resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



