Deck 3: Cell Structure and Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cell Structure and Function
1
A bacterial cell moving toward light would be an example of
A) tumbles.
B) positive chemotaxis.
C) negative phototaxis.
D) positive phototaxis.
E) negative chemotaxis.
A) tumbles.
B) positive chemotaxis.
C) negative phototaxis.
D) positive phototaxis.
E) negative chemotaxis.
D
2
Which of the following is found only in eukaryotic cells?
A) cytoplasm
B) cytoplasmic membrane
C) DNA
D) nuclear envelope
E) ribosomes
A) cytoplasm
B) cytoplasmic membrane
C) DNA
D) nuclear envelope
E) ribosomes
D
3
Which of the following bacterial cell structures plays an important role in the creation of biofilms?
A) fimbriae
B) pili
C) glycocalyces
D) flagella
E) both fimbriae and glycocalyces
A) fimbriae
B) pili
C) glycocalyces
D) flagella
E) both fimbriae and glycocalyces
E
4
What anchors the bacterial flagellum to the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane?
A) the hook
B) the filament
C) a pilus
D) the basal body
E) fimbriae
A) the hook
B) the filament
C) a pilus
D) the basal body
E) fimbriae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning the fluid mosaic model?
A) The phospholipids rotate across the bilayer from one face to the other.
B) Small water soluble molecules move freely across the bilayer.
C) The phospholipids form a rigid structure.
D) The integrated proteins are firmly cemented in place relative to each other.
E) Membrane proteins are free to move in two dimensions in the bilayer.
A) The phospholipids rotate across the bilayer from one face to the other.
B) Small water soluble molecules move freely across the bilayer.
C) The phospholipids form a rigid structure.
D) The integrated proteins are firmly cemented in place relative to each other.
E) Membrane proteins are free to move in two dimensions in the bilayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
ATP is expended in which of the following processes?
A) diffusion
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) group translocation
E) both active transport and group translocation
A) diffusion
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) group translocation
E) both active transport and group translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
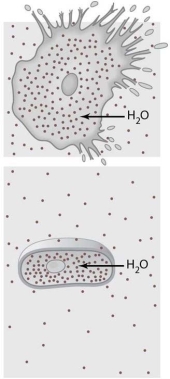 The cells illustrated in Figure 3-1 are in a(n) environment.
The cells illustrated in Figure 3-1 are in a(n) environment.A) hypertonic
B) hypotonic
C) passive
D) isotonic
E) fluid mosaic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is unique to archaea?
A) LPS
B) pili
C) hami
D) fimbriae
E) peptidoglycan
A) LPS
B) pili
C) hami
D) fimbriae
E) peptidoglycan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following may be a component of bacterial cell walls?
A) carrageenan
B) tubulin
C) both lipoteichoic and mycolic acids
D) mycolic acid
E) lipoteichoic acids
A) carrageenan
B) tubulin
C) both lipoteichoic and mycolic acids
D) mycolic acid
E) lipoteichoic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The flagella of archaea are similar to bacterial flagella but differ in that they
A) move like a whip.
B) are anchored in the cytoplasm.
C) are driven by the flow of hydrogen ions.
D) are smaller in diameter and are not hollow.
E) lack a basal body.
A) move like a whip.
B) are anchored in the cytoplasm.
C) are driven by the flow of hydrogen ions.
D) are smaller in diameter and are not hollow.
E) lack a basal body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements concerning prokaryotic flagella is TRUE?
A) Prokaryotic flagella rotate like a drive shaft.
B) Treponema is an example of a bacterium that has a tuft of polar flagella.
C) Prokaryotic flagella are anchored in the cytoplasm.
D) A ʺrunʺ results from clockwise movement of the flagellum.
E) Prokaryotic flagella are composed of tubulin.
A) Prokaryotic flagella rotate like a drive shaft.
B) Treponema is an example of a bacterium that has a tuft of polar flagella.
C) Prokaryotic flagella are anchored in the cytoplasm.
D) A ʺrunʺ results from clockwise movement of the flagellum.
E) Prokaryotic flagella are composed of tubulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Endospores survive a variety of harsh conditions in part because of the presence of
A) mycolic acid.
B) hopanoids.
C) dipicolinic acid.
D) lipopolysaccharide.
E) glycoproteins.
A) mycolic acid.
B) hopanoids.
C) dipicolinic acid.
D) lipopolysaccharide.
E) glycoproteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Lipid A is a component of
A) cytoplasmic membranes.
B) mycolic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharides.
D) plant cell walls.
E) bacterial glycocalyces.
A) cytoplasmic membranes.
B) mycolic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharides.
D) plant cell walls.
E) bacterial glycocalyces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements concerning fimbriae is TRUE?
A) Fimbriae facilitate the transfer of DNA among bacterial cells.
B) All bacteria have fimbriae.
C) A bacterial cell will usually have only one or two fimbriae.
D) Fimbriae are about as long as flagella.
E) Bacteria use fimbriae to attach to surfaces.
A) Fimbriae facilitate the transfer of DNA among bacterial cells.
B) All bacteria have fimbriae.
C) A bacterial cell will usually have only one or two fimbriae.
D) Fimbriae are about as long as flagella.
E) Bacteria use fimbriae to attach to surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Some bacteria have an outer layer composed of that protects them from desiccation and allows them to adhere to surfaces.
A) polysaccharides
B) polypeptides
C) nucleotides
D) waxes
E) either polypeptides or polysaccharides
A) polysaccharides
B) polypeptides
C) nucleotides
D) waxes
E) either polypeptides or polysaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Using a microscope, you observe an amoeba moving toward a food source. This is an example of
A) cellular structure.
B) growth.
C) responsiveness.
D) metabolism.
E) reproduction.
A) cellular structure.
B) growth.
C) responsiveness.
D) metabolism.
E) reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements concerning the characteristics of life is FALSE?
A) Reproduction is defined as an increase in the size of an organism.
B) Organisms may not exhibit all of the characteristics of life at all times.
C) Reproduction can occur asexually or sexually in living things.
D) Viruses have some, but not all, of the characteristics of living things.
E) Living things store metabolic energy in the form of chemicals such as ATP.
A) Reproduction is defined as an increase in the size of an organism.
B) Organisms may not exhibit all of the characteristics of life at all times.
C) Reproduction can occur asexually or sexually in living things.
D) Viruses have some, but not all, of the characteristics of living things.
E) Living things store metabolic energy in the form of chemicals such as ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Bacterial cell walls that are resistant to drying contain
A) tubulin.
B) waxes.
C) amino acids.
D) lipopolysaccharide.
E) carbohydrates.
A) tubulin.
B) waxes.
C) amino acids.
D) lipopolysaccharide.
E) carbohydrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lipid-soluble molecules would be expected to cross the cytoplasmic membrane by which of the following processes?
A) group translocation
B) osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion
D) active transport
E) diffusion
A) group translocation
B) osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion
D) active transport
E) diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Bacteria of the genus Mycoplasma lack cell walls. What sort of environment do they require for survival?
A) hypotonic
B) hypertonic
C) a biofilm
D) isotonic
E) low temperature
A) hypotonic
B) hypertonic
C) a biofilm
D) isotonic
E) low temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Hopanoids are found in cytoplasmic membranes.
A) bacterial
B) eukaryotic
C) no
D) archaeal
E) prokaryotic
A) bacterial
B) eukaryotic
C) no
D) archaeal
E) prokaryotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cytoplasmic membranes of contain phospholipids and proteins.
A) bacterial cells
B) archaeal cells
C) eukaryotic cells
D) both bacterial and eukaryotic cells
E) archaeal, bacterial, and eukaryotic cells
A) bacterial cells
B) archaeal cells
C) eukaryotic cells
D) both bacterial and eukaryotic cells
E) archaeal, bacterial, and eukaryotic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following processes powers the rotation of the flagella of archaea?
A) a sodium ion gradient
B) contraction of cytoskeletal proteins
C) a hydrogen ion gradient
D) assembly and disassembly of microtubules
E) ATP
A) a sodium ion gradient
B) contraction of cytoskeletal proteins
C) a hydrogen ion gradient
D) assembly and disassembly of microtubules
E) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a CORRECT pairing?
A) bacterial flagellum: microtubule protein
B) eukaryotic flagellum: flagellin protein
C) eukaryotic flagellum: hydrogen ion gradient driven
D) bacterial flagellum: ATP driven
E) eukaryotic flagellum: enclosed in cytoplasmic membrane
A) bacterial flagellum: microtubule protein
B) eukaryotic flagellum: flagellin protein
C) eukaryotic flagellum: hydrogen ion gradient driven
D) bacterial flagellum: ATP driven
E) eukaryotic flagellum: enclosed in cytoplasmic membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Endocytosis and exocytosis are means of transport used by
A) eukaryotes.
B) bacteria.
C) all prokaryotes.
D) archaea.
E) nothing; no cells use both processes.
A) eukaryotes.
B) bacteria.
C) all prokaryotes.
D) archaea.
E) nothing; no cells use both processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Membrane rafts are found in the cytoplasmic membranes of
A) bacteria only.
B) archaea only.
C) eukaryotes only.
D) both archaea and bacteria.
E) both archaea and eukaryotes.
A) bacteria only.
B) archaea only.
C) eukaryotes only.
D) both archaea and bacteria.
E) both archaea and eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is paired INCORRECTLY?
A) plants; cellulose cell wall
B) algae; glycocalyx present
C) fungi; chitin, glucomannan and/or cellulose cell wall
D) archaea; polysaccharide cell wall
E) bacteria; peptidoglycan cell wall
A) plants; cellulose cell wall
B) algae; glycocalyx present
C) fungi; chitin, glucomannan and/or cellulose cell wall
D) archaea; polysaccharide cell wall
E) bacteria; peptidoglycan cell wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements concerning the endosymbiotic theory is FALSE?
A) Mitochondria and chloroplasts can divide independently of the cell.
B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes.
C) The cristae of mitochondria evolved from the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes.
D) The endosymbiotic theory is widely accepted.
E) Eukaryotes were formed from the union of small anaerobic cells by larger aerobic cells.
A) Mitochondria and chloroplasts can divide independently of the cell.
B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes.
C) The cristae of mitochondria evolved from the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes.
D) The endosymbiotic theory is widely accepted.
E) Eukaryotes were formed from the union of small anaerobic cells by larger aerobic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Functions of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton include giving shape to the cell and
A) separating chromosomes during mitosis.
B) anchoring organelles.
C) moving cellular contents.
D) anchoring organelles and moving cellular contents.
E) anchoring organelles, moving cellular contents, and separating chromosomes during mitosis.
A) separating chromosomes during mitosis.
B) anchoring organelles.
C) moving cellular contents.
D) anchoring organelles and moving cellular contents.
E) anchoring organelles, moving cellular contents, and separating chromosomes during mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Chloroplasts differ from mitochondria in that the former have
A) thylakoids.
B) cristae.
C) two lipid bilayers.
D) 70S ribosomes.
E) DNA.
A) thylakoids.
B) cristae.
C) two lipid bilayers.
D) 70S ribosomes.
E) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following processes requires a carrier protein?
A) active transport only
B) facilitated diffusion only
C) diffusion only
D) endocytosis only
E) both facilitated diffusion and active transport
A) active transport only
B) facilitated diffusion only
C) diffusion only
D) endocytosis only
E) both facilitated diffusion and active transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements concerning endocytosis and exocytosis is TRUE?
A) Endocytosis produces a structure called a food vesicle.
B) Waste products and secretions are exported from the cell during endocytosis.
C) Endocytosis is a form of passive transport, whereas exocytosis is a form of active transport.
D) Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis in which liquids are brought into the cell.
E) These processes occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
A) Endocytosis produces a structure called a food vesicle.
B) Waste products and secretions are exported from the cell during endocytosis.
C) Endocytosis is a form of passive transport, whereas exocytosis is a form of active transport.
D) Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis in which liquids are brought into the cell.
E) These processes occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The lipids that are NOT generally components of cell membranes are
A) fatty acids.
B) phospholipids.
C) sterols.
D) triglycerides.
E) hopanoids.
A) fatty acids.
B) phospholipids.
C) sterols.
D) triglycerides.
E) hopanoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is classified as a nonmembranous organelle of eukaryotic cells?
A) endoplasmic reticulum
B) peroxisome
C) centriole
D) mitochondrion
E) Golgi body
A) endoplasmic reticulum
B) peroxisome
C) centriole
D) mitochondrion
E) Golgi body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements about the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is CORRECT?
A) The ER is a transport system within the cytoplasm.
B) The ER is a lipid storage organelle.
C) The rough ER is the site of lipid synthesis.
D) The smooth ER has ribosomes associated with it.
E) The smooth ER is a site of ATP synthesis.
A) The ER is a transport system within the cytoplasm.
B) The ER is a lipid storage organelle.
C) The rough ER is the site of lipid synthesis.
D) The smooth ER has ribosomes associated with it.
E) The smooth ER is a site of ATP synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following chemical substances contributes to the unique characteristics of acid -fast bacteria?
A) lipoteichoic acid
B) mycolic acid
C) peptidoglycan
D) endotoxin
E) N-acetylglucosamine
A) lipoteichoic acid
B) mycolic acid
C) peptidoglycan
D) endotoxin
E) N-acetylglucosamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following cellular components facilitate(s) the process of bacterial binary fission?
A) nucleoid
B) inclusions
C) centrioles
D) fimbriae
E) cytoskeleton
A) nucleoid
B) inclusions
C) centrioles
D) fimbriae
E) cytoskeleton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following molecules would be expected to cross the cytoplasmic membrane rapidly and without the use of transport proteins?
A) small hydrophilic molecules only
B) ions only
C) small hydrophobic molecules only
D) large molecules only
E) both ions and hydrophilic molecules
A) small hydrophilic molecules only
B) ions only
C) small hydrophobic molecules only
D) large molecules only
E) both ions and hydrophilic molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Some use group translocation as a means of transport.
A) protozoa
B) bacteria
C) eukaryotes and prokaryotes
D) eukaryotes
E) archaea
A) protozoa
B) bacteria
C) eukaryotes and prokaryotes
D) eukaryotes
E) archaea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate inside a bacterial cell via phosphorylation of glucose is an example of
A) diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) group translocation.
E) plasmolysis.
A) diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) group translocation.
E) plasmolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
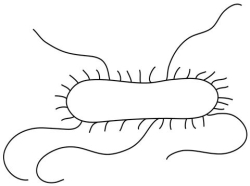 The short structures on the surface of the cell in Figure 3 -5 are cilia.
The short structures on the surface of the cell in Figure 3 -5 are cilia.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Several cellular structures of eukaryotes facilitate movement: flagella, cilia, the cytoskeleton and centrioles. Which of the following is a feature common to all of them?
A) enclosed in a lipid bilayer
B) composed of glycoproteins
C) powered by a proton (hydrogen ion) gradient
D) composed of tubulin microtubules
E) composed of flagellar proteins
A) enclosed in a lipid bilayer
B) composed of glycoproteins
C) powered by a proton (hydrogen ion) gradient
D) composed of tubulin microtubules
E) composed of flagellar proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Some members of have hami.
A) archaea
B) eukaryotes
C) bacteria
D) archaea and bacteria
E) bacteria and eukaryotes
A) archaea
B) eukaryotes
C) bacteria
D) archaea and bacteria
E) bacteria and eukaryotes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The cell walls of some are composed of proteins.
A) prokaryotes
B) bacteria
C) eukaryotes
D) archaea
E) bacteria and eukaryotes
A) prokaryotes
B) bacteria
C) eukaryotes
D) archaea
E) bacteria and eukaryotes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following prokaryotic cells contain an outer membrane?
A) both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
B) all prokaryotes
C) Gram-negative bacteria only
D) Gram-positive bacteria only
E) archaea
A) both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
B) all prokaryotes
C) Gram-negative bacteria only
D) Gram-positive bacteria only
E) archaea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is a function of the periplasmic space?
A) external digestion of large biological molecules
B) photosynthesis
C) production of proteins for secretion
D) protection from dehydration
E) create a hydrogen ion gradient to power ATP synthesis
A) external digestion of large biological molecules
B) photosynthesis
C) production of proteins for secretion
D) protection from dehydration
E) create a hydrogen ion gradient to power ATP synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Lysosomes result from the endocytosis of food particles by eukaryotic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following may have cell walls containing teichoic acids?
A) both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
B) archaea
C) all prokaryotes
D) Gram-positive bacteria only
E) Gram-negative bacteria only
A) both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
B) archaea
C) all prokaryotes
D) Gram-positive bacteria only
E) Gram-negative bacteria only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A layer of polysaccharides external to the bacterial cell but firmly attached to it is called a slime layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
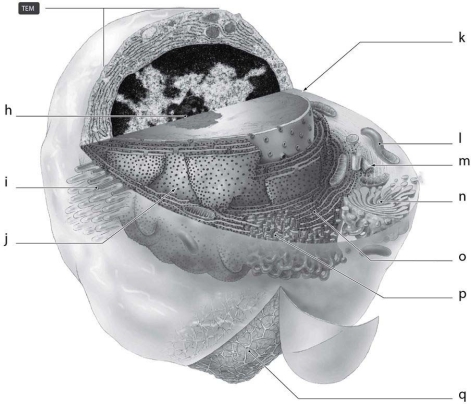 What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by ʺnʺ in Figure 3-3?
What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by ʺnʺ in Figure 3-3?A) synthesis of lipids
B) protein synthesis
C) ATP synthesis
D) cell movement
E) packaging of materials for export

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Extensively folded lipid bilayers are sites of photosynthesis in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
All cell membranes contain phospholipids and a wide variety of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Bacterial protein synthesis can begin before the reading of the gene is complete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
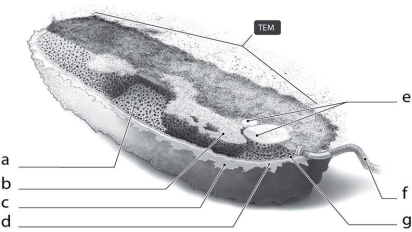 What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by ʺcʺ in Figure 3-2?
What is the function of the cellular structure indicated by ʺcʺ in Figure 3-2?A) attach to surfaces only
B) protect from dehydration only
C) provide shape only
D) attach to surfaces and protect from dehydration
E) provide shape, attach to surfaces, and protect from dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Chromatin is composed of DNA and special packaging proteins called hopanoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Eukaryotic ribosomes are composed of 50S and 30S subunits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Formation of a biofilm may contribute to bacteriaʹs ability to cause disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Cell walls composed of polysaccharide are found in
A) archaea only.
B) archaea and eukaryotes only.
C) eukaryotes only.
D) archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes.
E) bacteria only.
A) archaea only.
B) archaea and eukaryotes only.
C) eukaryotes only.
D) archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes.
E) bacteria only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A function of the cytoskeleton unique to bacteria is
A) anchoring cytoplasmic contents.
B) orienting the assembly of the cell wall.
C) providing shape to the cell.
D) cellular motility.
E) both cellular motility and orienting the assembly of the cell wall.
A) anchoring cytoplasmic contents.
B) orienting the assembly of the cell wall.
C) providing shape to the cell.
D) cellular motility.
E) both cellular motility and orienting the assembly of the cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
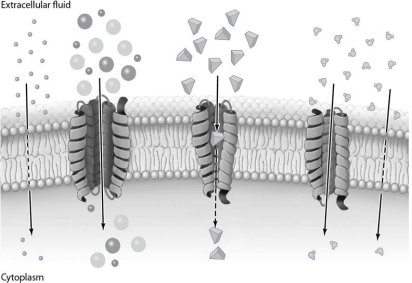 The processes illustrated in Figure 3-4 do not require energy input.
The processes illustrated in Figure 3-4 do not require energy input.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe how the structure of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane relates to its function of selective permeability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Golgi bodies are examples of a (membranous/non-membranous/cellular) organelle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The semiliquid matrix of the nucleus is called the (cytoplasm/nucleoid/nucleoplasm).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A structural molecule found in eukaryotic cytoskeletons, flagella, cilia, and centrioles is (flagellin/tubulin/fibrin).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Fibrous structures some archaea use for attachment to surfaces are (hami/fimbriae/flagella).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A new bacterium is discovered that has a unique ability to metabolize a compound toxic to most other organisms. The microbiologists researching this bacterium do not know how the bacterium takes up the compound from the environment. Design an experiment to determine whether uptake is passive or active.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
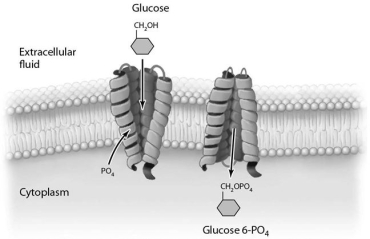 The process illustrated in Figure 3-6 occurs in (eukaryotic/bacterial/archaeal) cells.
The process illustrated in Figure 3-6 occurs in (eukaryotic/bacterial/archaeal) cells.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Most antibacterial drugs disrupt or destroy bacterial cellular characteristics that are different from those of eukaryotic cells or that may not even be present in eukaryotic cells, an idea termed ʺselective toxicity.ʺ List and describe at least three cellular features of bacteria that could be targeted to inhibit or kill a bacterial pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Lipid (LPS/NAM/A/NAG) is a part of the Gram-negative cell outer membrane that can produce fever, inflammation, and shock when it is released into the bloodstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The presence of a cell (wall/membrane) enables bacterial and plant cells to resist the effects of hypotonic solutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Enzymes which degrade toxic materials in eukaryotic cells are stored in (endosomes/lysosomes/peroxisomes).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A (capsule/slime layer/matrix) is a type of glycocalyx that is firmly attached to the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A(n) (hypertonic/isotonic/hypotonic) solution will result in crenation of animal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Eukaryotic cells use a process known as (endocytosis/pinocytosis/phagocytosis) to obtain liquids from their environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The reserve deposits of starch or other compounds found in many prokaryotic cells are called (vacuoles/inclusions/nucleoid).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts have inner membranes with much greater surface area than their outer membranes. Discuss the contribution of the extensive inner membranes to the roles of these organelles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Compare and contrast archaea and bacteria, with particular attention to the features that lead to their placement in separate taxa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A(n) (symport/antiport/uniport) is a carrier protein that transports two substances in the same direction across a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Eukaryotic flagella are anchored by the basal body in the (cytoplasm/wall/membrane).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the site of (protein/lipid/carbohydrate) synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



