Deck 11: Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Characterizing and Classifying Prokaryotes
1
The current taxonomy of the bacteria as described in Bergeyʹs Manual of Systematic Bacteriology
A) is based largely on physical and metabolic characteristics.
B) includes three domains.
C) is primarily based on genetic sequences.
D) can be considered complete.
E) is universally agreed upon.
A) is based largely on physical and metabolic characteristics.
B) includes three domains.
C) is primarily based on genetic sequences.
D) can be considered complete.
E) is universally agreed upon.
C
2
The psychrophilic Gram-positive bacillus can become an intracellular parasite of white blood cells.
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Bacillus polymyxa
C) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
D) Enterococcus
E) Listeria monocytogenes
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Bacillus polymyxa
C) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
D) Enterococcus
E) Listeria monocytogenes
E
3
The Gram-positive obligate anaerobe causes a severe diarrhea.
A) Clostridium botulinum
B) Clostridium perfringens
C) Bacillus anthracis
D) Clostridium difficile
E) Selenomonas
A) Clostridium botulinum
B) Clostridium perfringens
C) Bacillus anthracis
D) Clostridium difficile
E) Selenomonas
D
4
Which of the following types of microbes might be found in a boiling hot spring?
A) halophiles
B) actinomycetes
C) hyperthermophiles
D) phototrophic bacteria
E) methanogens
A) halophiles
B) actinomycetes
C) hyperthermophiles
D) phototrophic bacteria
E) methanogens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Low G + C bacilli in the genus are beneficial to humans as probiotics.
A) Staphylococcus
B) Listeria
C) Mycobacterium
D) Corynebacterium
E) Lactobacillus
A) Staphylococcus
B) Listeria
C) Mycobacterium
D) Corynebacterium
E) Lactobacillus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
High G + C Gram-positive filamentous bacteria of the genus are capable of metabolizing a diverse range of environmental contaminants.
A) Corynebacterium
B) Actinomyces
C) Rhizobium
D) Nocardia
E) Streptomyces
A) Corynebacterium
B) Actinomyces
C) Rhizobium
D) Nocardia
E) Streptomyces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Mycoplasmas are pleomorphic because they
A) are low G + C content Gram-positive bacteria.
B) produce endospores.
C) exhibit snapping division.
D) have no cell walls.
E) have sterols in their cytoplasmic membranes.
A) are low G + C content Gram-positive bacteria.
B) produce endospores.
C) exhibit snapping division.
D) have no cell walls.
E) have sterols in their cytoplasmic membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Some obligately anaerobic are used in sewage treatment, and produce a fuel that can be used to produce electricity.
A) halophiles
B) hyperthermophiles
C) thermophiles
D) methanogens
E) cyanobacteria
A) halophiles
B) hyperthermophiles
C) thermophiles
D) methanogens
E) cyanobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What bacterial structure is responsible for separating the daughter DNA molecules after replication?
A) cross wall
B) spindle
C) fimbria
D) cytoplasmic membrane
E) cytoskeleton
A) cross wall
B) spindle
C) fimbria
D) cytoplasmic membrane
E) cytoskeleton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When conditions become inhospitable, members of the genus Clostridium produce an internal durable, dormant form by the process of
A) sporulation.
B) vegetation.
C) budding.
D) conjugation.
E) binary fission.
A) sporulation.
B) vegetation.
C) budding.
D) conjugation.
E) binary fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Pleomorphic bacteria
A) are flexible.
B) reproduce by snapping division.
C) have a slightly curved rod shape.
D) vary in size and shape.
E) are roughly spherical.
A) are flexible.
B) reproduce by snapping division.
C) have a slightly curved rod shape.
D) vary in size and shape.
E) are roughly spherical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The archaea known as halophiles
A) require temperatures above 45∘C to survive.
B) are members of the phylum Euryarchaeota.
C) require salt concentrations of 9% or greater to survive.
D) are members of the Euryarchaeota and require temperatures above 45∘C.
E) are members of the Euryarchaeota and require salt concentrations above 9%.
A) require temperatures above 45∘C to survive.
B) are members of the phylum Euryarchaeota.
C) require salt concentrations of 9% or greater to survive.
D) are members of the Euryarchaeota and require temperatures above 45∘C.
E) are members of the Euryarchaeota and require salt concentrations above 9%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following characteristics distinguish(es) the archaea from the bacteria?
A) cell wall composition
B) 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences
C) cytoplasmic membrane lipids
D) the deoxyribonucleotides in the DNA
E) cell wall composition, cytoplasmic membrane lipids, and 16S rRNA sequences
A) cell wall composition
B) 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequences
C) cytoplasmic membrane lipids
D) the deoxyribonucleotides in the DNA
E) cell wall composition, cytoplasmic membrane lipids, and 16S rRNA sequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 The arrangement represented in the figure is typical of which of the following genera of bacteria?
The arrangement represented in the figure is typical of which of the following genera of bacteria?A) Bacillus
B) Streptococcus
C) Actinomyces
D) Escherichia
E) Corynebacterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Cocci which divide along alternating planes may stick together to form
A) staphylococci.
B) palisades.
C) streptococci.
D) sarcinae.
E) tetrads.
A) staphylococci.
B) palisades.
C) streptococci.
D) sarcinae.
E) tetrads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The are autotrophs which live in anaerobic environments thought to be similar to conditions on the early Earth, and may have diverged from other bacteria far back in time.
A) thermophiles
B) mycoplasmas
C) cyanobacteria
D) deeply branching bacteria
E) proteobacteria
A) thermophiles
B) mycoplasmas
C) cyanobacteria
D) deeply branching bacteria
E) proteobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Many cyanobacteria carry out both oxygenic photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation, but oxygen inhibits nitrogen fixation. How do these cyanobacteria manage both processes?
A) They trap the oxygen in special cells called heterocysts.
B) They produce cells called akinetes for photosynthesis.
C) The processes are seasonal; photosynthesis occurs in summer and nitrogen fixation takes place in winter.
D) Nitrogen fixation is sequestered in special cells called heterocysts.
E) They have special membranous structures like chloroplasts to separate the processes within the cell.
A) They trap the oxygen in special cells called heterocysts.
B) They produce cells called akinetes for photosynthesis.
C) The processes are seasonal; photosynthesis occurs in summer and nitrogen fixation takes place in winter.
D) Nitrogen fixation is sequestered in special cells called heterocysts.
E) They have special membranous structures like chloroplasts to separate the processes within the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Bacteria described as ʺLow G + Cʺ
A) include filamentous Actinomycetes.
B) are Gram-negative Cyanobacteria.
C) have unmethylated GC DNA.
D) have DNA composed of more than 50% AT pairs.
E) Gram stain pink and are cocci.
A) include filamentous Actinomycetes.
B) are Gram-negative Cyanobacteria.
C) have unmethylated GC DNA.
D) have DNA composed of more than 50% AT pairs.
E) Gram stain pink and are cocci.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Phototrophic bacteria that use chlorophyll a are in the phylum
A) Chlorobi.
B) Actinobacteria.
C) Cyanobacteria.
D) Chloroflexi.
E) Proteobacteria.
A) Chlorobi.
B) Actinobacteria.
C) Cyanobacteria.
D) Chloroflexi.
E) Proteobacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Bergeyʹs Manual of Systematic Bacteriology contains
A) genetic sequences of prokaryotes.
B) recipes for bacterial growth media.
C) classification schemes for prokaryotes.
D) treatments for bacterial diseases.
E) rules for naming new bacterial species.
A) genetic sequences of prokaryotes.
B) recipes for bacterial growth media.
C) classification schemes for prokaryotes.
D) treatments for bacterial diseases.
E) rules for naming new bacterial species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Pleomorphic Gram-negative members of the Firmicutes that colonize mammalian respiratory mucous membranes are the
A) mycobacteria.
B) clostridia.
C) Rickettsias.
D) Actinobacteria.
E) mycoplasmas.
A) mycobacteria.
B) clostridia.
C) Rickettsias.
D) Actinobacteria.
E) mycoplasmas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Gram negative facultative anaerobes that metabolize carbohydrates via glycolysis are members of the
A) epsilonproteobacteria.
B) alphaproteobacteria.
C) gammaproteobacteria.
D) deltaproteobacteria.
E) betaproteobacteria.
A) epsilonproteobacteria.
B) alphaproteobacteria.
C) gammaproteobacteria.
D) deltaproteobacteria.
E) betaproteobacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A Gram stain of a tissue sample from a patient shows Gram-negative spheres that can barely be resolved on the best light microscope. A transmission electron micrograph reveals the spheres have a double membrane but no cell wall. The intracellular parasites are likely to be a
A) Listeria.
B) Mycoplasma.
C) Coxiella.
D) Chlamydia.
E) Rickettsia.
A) Listeria.
B) Mycoplasma.
C) Coxiella.
D) Chlamydia.
E) Rickettsia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A flexible, spiral-shaped bacterium is called a
A) sarcina.
B) vibrio.
C) spirochete.
D) spirillum.
E) coccobacillus.
A) sarcina.
B) vibrio.
C) spirochete.
D) spirillum.
E) coccobacillus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What feature of mycobacteria is responsible for the unusually slow growth of these bacteria?
A) Their low tolerance for oxygen retards their growth.
B) They cannot fully metabolize carbohydrates and must rely on fermentation.
C) They lack a cell wall and are extremely fragile.
D) The mycolic acid in their cell walls requires signification metabolic investment.
E) They have limited numbers of ribosomes so protein production is slow.
A) Their low tolerance for oxygen retards their growth.
B) They cannot fully metabolize carbohydrates and must rely on fermentation.
C) They lack a cell wall and are extremely fragile.
D) The mycolic acid in their cell walls requires signification metabolic investment.
E) They have limited numbers of ribosomes so protein production is slow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Gram-negative diplococci are pathogenic members of the betaproteobacteria that infect mammalian mucous membranes.
A) Streptococcus
B) Neisseria
C) Coxiella
D) Listeria
E) Haemophilus
A) Streptococcus
B) Neisseria
C) Coxiella
D) Listeria
E) Haemophilus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A microbiologist observes what appears to be a pink -staining long rod within the periplasmic space of a Gram-negative bacillus. What is this structure likely to be?
A) Rickettsia
B) Bdellovibrio
C) Chlamydia
D) a heterocyst
E) an endospore
A) Rickettsia
B) Bdellovibrio
C) Chlamydia
D) a heterocyst
E) an endospore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A soil sample dilution spread on a plate containing carbohydrate-based medium yields a wide variety of colonies. One colony has no other bacterial colonies growing near it. Further investigation reveals the bacteria in the colony are Gram -positive and filamentous. The bacteria in the colony may be a member of the genus
A) Streptomyces.
B) Bacillus.
C) Pseudomonas.
D) Enterococcus.
E) Acetobacter.
A) Streptomyces.
B) Bacillus.
C) Pseudomonas.
D) Enterococcus.
E) Acetobacter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Prokaryotes of the genus Pyrodictium are
A) thermophiles.
B) halophiles.
C) endospore formers.
D) intracellular parasites.
E) members of the deeply branching bacteria.
A) thermophiles.
B) halophiles.
C) endospore formers.
D) intracellular parasites.
E) members of the deeply branching bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Unusual cellular extensions called prosthecae are associated with which of the following groups of proteobacteria?
A) delta
B) epsilon
C) gamma
D) alpha
E) beta
A) delta
B) epsilon
C) gamma
D) alpha
E) beta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A large number of Gram-negative human pathogens are members of the
A) epsilonproteobacteria.
B) gammaproteobacteria.
C) deltaproteobacteria.
D) alphaproteobacteria.
E) betaproteobacteria.
A) epsilonproteobacteria.
B) gammaproteobacteria.
C) deltaproteobacteria.
D) alphaproteobacteria.
E) betaproteobacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following bacterial genera plays an important role in environmental nitrogen cycles?
A) Nitrobacter
B) Azospirillum
C) Rhizobium
D) both Nitrobacter and Rhizobium
E) Nitrobacter, Rhizobium, and Azospirillum
A) Nitrobacter
B) Azospirillum
C) Rhizobium
D) both Nitrobacter and Rhizobium
E) Nitrobacter, Rhizobium, and Azospirillum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following bacteria oxidize ammonia (NH3) to produce nitrate (NO3)?
A) Rhizobium
B) Cyanobacter
C) Azospirillum
D) Nocardia
E) Nitrobacter
A) Rhizobium
B) Cyanobacter
C) Azospirillum
D) Nocardia
E) Nitrobacter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The ʺgiantʺ bacterium Epulopiscium reproduces by means of
A) viviparity.
B) snapping division.
C) sexual reproduction.
D) budding.
E) binary fission.
A) viviparity.
B) snapping division.
C) sexual reproduction.
D) budding.
E) binary fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Gram-positive coccus grows in irregular clusters, and is frequently found in the human nasal cavity. When it invades other parts of the body it can cause serious disease.
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Helicobacter pylori
C) Bacillus thuringiensis
D) Escherichia coli
E) Staphylococcus aureus
A) Clostridium perfringens
B) Helicobacter pylori
C) Bacillus thuringiensis
D) Escherichia coli
E) Staphylococcus aureus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Classification of bacteria into different phyla is based on comparisons involving which of the following?
A) cell wall composition
B) protein sequences
C) DNA sequences
D) both DNA and protein sequences
E) DNA and protein sequences, as well as cell wall composition
A) cell wall composition
B) protein sequences
C) DNA sequences
D) both DNA and protein sequences
E) DNA and protein sequences, as well as cell wall composition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The anaerobic Clostridium species are troublesome pathogens in part because of their capacity for
A) oxygen production.
B) biofilm production.
C) endospore production.
D) rapid reproduction.
E) high salt tolerance.
A) oxygen production.
B) biofilm production.
C) endospore production.
D) rapid reproduction.
E) high salt tolerance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The production of large masses of bacteria and organic materials (flocs) that settle out of solution make useful in sewage treatment.
A) Thiobacillus
B) Nitrosomonas
C) Neisseria
D) Zoogloea
E) Burkholderia
A) Thiobacillus
B) Nitrosomonas
C) Neisseria
D) Zoogloea
E) Burkholderia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Aerobic free-living Gram-negative bacilli in the phylum Proteobacteria that are capable of metabolizing a wide range of organic compounds are members of the genus
A) Rickettsia.
B) Pseudomonas.
C) Cytophagia.
D) Salmonella.
E) Vibrio.
A) Rickettsia.
B) Pseudomonas.
C) Cytophagia.
D) Salmonella.
E) Vibrio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A field biologist finds what might be a new species of prokaryote in sewage sludge. It is an obligate anaerobe that metabolizes organic acids and requires hydrogen gas. It lacks a peptidoglycan cell wall. The new find may be a
A) clostridium.
B) mycoplasma.
C) bacteroides.
D) methanogen.
E) cyanobacterium.
A) clostridium.
B) mycoplasma.
C) bacteroides.
D) methanogen.
E) cyanobacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Halophiles grow equally well in the presence or absence of high salt concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The process by which a bacterial cell produces an endospore is called (endosporing/sporulation/vegetation).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
All taxonomists are in agreement about the taxonomic scheme set forth in Bergeyʹs Manual of Systematic Bacteriology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A species of the genus Streptococcus is the leading cause of
A) contaminated milk and meat.
B) urinary tract infections.
C) food poisoning from rice.
D) tuberculosis.
E) ʺflesh-eatingʺ bacterial infections.
A) contaminated milk and meat.
B) urinary tract infections.
C) food poisoning from rice.
D) tuberculosis.
E) ʺflesh-eatingʺ bacterial infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Members of the genus Chlamydia are
A) classified with the deeply branching bacteria.
B) Gram-positive bacteria.
C) intracellular parasites.
D) endospore-formers.
E) thermophiles.
A) classified with the deeply branching bacteria.
B) Gram-positive bacteria.
C) intracellular parasites.
D) endospore-formers.
E) thermophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Members of the Streptomyces are environmentally important because they can degrade a wide range of compounds including lignin from trees, chitin and keratin from animals, and latex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 This bacterial shape is called (bacillus/vibrio/rod).
This bacterial shape is called (bacillus/vibrio/rod).
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Mycoplasmas are named for the large quantities of mycolic acid in their cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The most common form of reproduction among prokaryotes is (snapping/budding/binary) fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The rod-shaped (rickettsias/chlamydias/brucella) are intracellular parasitic members of the alphaproteobacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Some strains of Staphylococcus aureus can invade the body and cause diseases such as pneumonia and bacteremia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Most of the methane produced by methanogens is oxidized by other types of bacteria before it affects the Earthʹs climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Gram-negative nitrogen-fixing bacteria found in association with plant roots are
A) betaproteobacteria.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) gammaproteobacteria.
D) alphaproteobacteria.
E) deeply branching bacteria.
A) betaproteobacteria.
B) cyanobacteria.
C) gammaproteobacteria.
D) alphaproteobacteria.
E) deeply branching bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cocci can be spherical as well as kidney-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When an endospore germinates, it gives rise to two daughter cells called vegetative cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The majority of archaea are extremophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Myxobacteria exhibit traits, such as cooperation and differentiation, not normally observed in prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is caused by Gram-negative tiny bacilli that are intracellular parasites. They are in the genus
A) Enterococcus.
B) Bordetella.
C) Coxiella.
D) Acetobacter.
E) Rickettsia.
A) Enterococcus.
B) Bordetella.
C) Coxiella.
D) Acetobacter.
E) Rickettsia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The genus Mycobacterium includes species responsible for
A) food poisoning from contaminated dairy products.
B) urinary tract infections.
C) tuberculosis.
D) gastric ulcers.
E) food poisoning from rice.
A) food poisoning from contaminated dairy products.
B) urinary tract infections.
C) tuberculosis.
D) gastric ulcers.
E) food poisoning from rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Some members of the alphaproteobacteria produce a structure called a (prosthecae/pilus/filament) to produce extra surface area for nutrient absorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Compare and contrast methanogens and methane oxidizers, including their roles in the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The genus of pathogenic cocci responsible for a wide range of human disease and whose members grow in chains is (Staphylococcus/Streptococcus/Enterococcus).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Will is a graduate student working in a microbiology lab. He is given the task of characterizing a newly discovered nitrogen fixing bacterium. What type of tests or observations will help him determine whether it is a member of the Cyanobacteria, alphaproteobacteria or gammaproteobacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The G + C content is a(n) (RNA/structural/genetic) determination used in classifying the different taxa of Gram-positive bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Burkholderia is a common (true/opportunistic) pathogen of patients with cystic fibrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
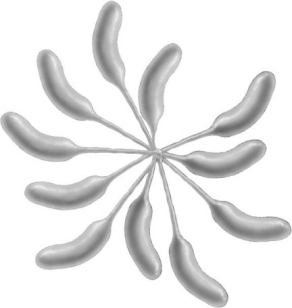 The arrangement shown in the figure is characteristic of (Actinomycetes/Caulobacter/Myxobacteria/Planctomyces) cells. (Use genus or taxon name.)
The arrangement shown in the figure is characteristic of (Actinomycetes/Caulobacter/Myxobacteria/Planctomyces) cells. (Use genus or taxon name.)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe the similarities and differences observed among phototrophic bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The (bacilli/Lactobacilli/bacteroids) are a group of Gram-negative bacteria that include obligate anaerobes normally found in the intestinal tracts of animals and humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Plant tumors caused by Agrobacterium infections are called (galls/heterocysts).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The reduction of nitrogen gas to ammonia is called nitrogen (fixation/cycling).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Explain the significance of endospores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Nitrogen is frequently a limiting nutrient even though the atmosphere of the planet consists mostly of nitrogen. Discuss the prokaryotes described in this chapter which have roles in the availability and cycling of nitrogen in the biosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The members of the (alphaproteobacteria/gammaproteobacteria/actinomycetes) may alternate between a flagellated motile stage and a nonmotile stage attached by means of a prosthecae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The infective stage of chlamydia is called the (elementary/initial) body.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The (streptobacilli/actinomycetes/mycoplasmas) are a group of Gram-positive bacteria that form branching filaments resembling those of fungi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



