Deck 16: Analysis of Variance and
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Analysis of Variance and
1
Which statement about MANOVA is not true?
A) Multivariate analysis of variance is appropriate when there are two or more dependent variables that are correlated.
B) In MANOVA, the null hypothesis is that the vectors of means on multiple dependent variables are equal across groups.
C) MANOVA is most appropriate if there are multiple dependent variables that are uncorrelated or orthogonal.
D) MANOVA examines group differences across multiple dependent variables simultaneously.
A) Multivariate analysis of variance is appropriate when there are two or more dependent variables that are correlated.
B) In MANOVA, the null hypothesis is that the vectors of means on multiple dependent variables are equal across groups.
C) MANOVA is most appropriate if there are multiple dependent variables that are uncorrelated or orthogonal.
D) MANOVA examines group differences across multiple dependent variables simultaneously.
C
2
Suppose that four groups, each consisting of 100 randomly selected individuals, were exposed to four different commercials about Tide detergent. After seeing the commercial, each individual provided ratings on preference for Tide, preference for Proctor and Gamble (the company making Tide), and preference for the commercial itself. Because these three preference variables are correlated, should be conducted to determine which commercial is the most effective (produced the highest preferences across the three variables).
A) regression
B) n- way ANOVA
C) one- way ANOVA
D) MANOVA
A) regression
B) n- way ANOVA
C) one- way ANOVA
D) MANOVA
D
3
The strength of the effects of X (independent variable or factor) on Y (dependent variable) is measured by .
A) SSwithin B) SSy C) SSx D) eta2 (42)
A) SSwithin B) SSy C) SSx D) eta2 (42)
D
4
In one- way ANOVA, separation of the variation observed in the dependent variable into the variation due to the independent variables plus the variation due to error is called _ .
A) one- way analysis of variance
B) analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)
C) decomposition of the total variation
D) n- way analysis of variance
A) one- way analysis of variance
B) analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)
C) decomposition of the total variation
D) n- way analysis of variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement is correct concerning one- way ANOVA?
A) Only one categorical variable is involved.
B) A treatment is the same as a particular combination of factor levels.
C) The set of independent variables consists of both categorical and metric variables.
D) Both A and B are correct.
A) Only one categorical variable is involved.
B) A treatment is the same as a particular combination of factor levels.
C) The set of independent variables consists of both categorical and metric variables.
D) Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
is an ANOVA technique for examining the difference in the central tendencies of more than two groups when the dependent variable is measured on an ordinal scale.
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Repeated measures analysis of variance may be thought of as an extension of the to the case of more than two related samples.
A) z test
B) paired samples t test
C) F test
D) t test
A) z test
B) paired samples t test
C) F test
D) t test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the statistical techniques below does not involve a metric independent variable (Figure 16.1 in the text)?
A) ANOVA
B) t test
C) regression
D) Both A and B are correct.
A) ANOVA
B) t test
C) regression
D) Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A major advantage of is that it enables the researcher to examine interactions between the factors.
A) t tests
B) n- way ANOVA
C) one- way ANOVA
D) F tests
A) t tests
B) n- way ANOVA
C) one- way ANOVA
D) F tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
are contrasts that enable the researcher to construct generalized confidence intervals that can be used to make pairwise comparisons of all treatment means.
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which F test is used to test the significance of the overall effect? 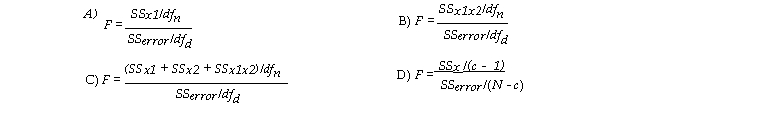
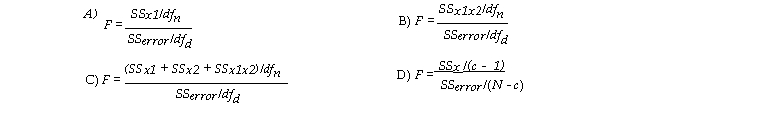

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you are estimating y2, you are at which step in the procedure for conducting one- way analysis of variance?
A) decompose the total variation
B) interpret the results
C) measure the effects
D) test the significance
A) decompose the total variation
B) interpret the results
C) measure the effects
D) test the significance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement is correct concerning the decomposition of the total variation?
A) By comparing the Y variance estimates based on between- group and within group variation, we can test the null hypothesis.
B) If the population mean is the same in all the groups, then the variation in the sample means and the sizes of the sample groups can be used to estimate the variance of Y.
C) Because it is not known that all the groups have the same mean, we cannot calculate the variance of all the observations together.
D) All statements are correct.
A) By comparing the Y variance estimates based on between- group and within group variation, we can test the null hypothesis.
B) If the population mean is the same in all the groups, then the variation in the sample means and the sizes of the sample groups can be used to estimate the variance of Y.
C) Because it is not known that all the groups have the same mean, we cannot calculate the variance of all the observations together.
D) All statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In one- way ANOVA, the null hypothesis may be tested by _ .
A) F statistic
B) eta2 C) chi- square
D) the t statistic
A) F statistic
B) eta2 C) chi- square
D) the t statistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
are used to examine differences among two or more means of the treatment groups.
A) Contrasts
B) Nonmetric ANOVA
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)
A) Contrasts
B) Nonmetric ANOVA
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
is a measure of variation in Y that is explained by the independent variable X.
A) SSy B) SSwithin C) SSx D) eta2 (y2)
A) SSy B) SSwithin C) SSx D) eta2 (y2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which step are you on in the procedure for conducting one- way analysis of variance if you are decomposing SSy into two components using the equation SSy = SSbetween + SSwithin?
A) decompose the total variation
B) interpret the results
C) measure the effects
D) test the significance
A) decompose the total variation
B) interpret the results
C) measure the effects
D) test the significance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The effects of X on Y is measured by .
A) SSy B) SSwithin C) SSerror D) SSx
A) SSy B) SSwithin C) SSerror D) SSx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In determining how different price levels will affect a household's cereal consumption, it may be essential to take household size into account. This is best analyzed by .
A) ANCOVA
B) one- way ANOVA
C) regression
D) n- way ANOVA
A) ANCOVA
B) one- way ANOVA
C) regression
D) n- way ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A test finding that some differences exist between some of the treatment groups is a test of the .
A) significance of the main effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the interaction effect
D) significance of the overall effect
A) significance of the main effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the interaction effect
D) significance of the overall effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How consumers' intentions to buy a brand vary with different levels of price and different levels of distribution is best analyzed via .
A) regression
B) ANCOVA
C) n- way ANOVA
D) one- way ANOVA
A) regression
B) ANCOVA
C) n- way ANOVA
D) one- way ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An advanced analysis of variance procedure in which the effects of one or more metric- scaled extraneous variables are removed from the dependent variable before conducting the ANOVA is called .

A) decomposition of the total variation
B) one- way analysis of variance
C) n- way analysis of variance
D) analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)

A) decomposition of the total variation
B) one- way analysis of variance
C) n- way analysis of variance
D) analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Categorical independent variables are . The independent variables must all be categorical (nonmetric) to use .
A) parameters; regression
B) items; ANOVA
C) covariates; ANOVA
D) factors; ANOVA
A) parameters; regression
B) items; ANOVA
C) covariates; ANOVA
D) factors; ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A covariate is a independent variable used in . 
A) metric; ANOVA
B) categorical; ANCOVA
C) categorical; ANOVA
D) metric; ANCOVA

A) metric; ANOVA
B) categorical; ANCOVA
C) categorical; ANOVA
D) metric; ANCOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The refers to the fact that ordinarily the assumption in analysis of variance that the categories of the independent variable are fixed.
A) fixed- effects model
B) mixed- effects model
C) standard- effects model
D) random- effects model
A) fixed- effects model
B) mixed- effects model
C) standard- effects model
D) random- effects model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A test of the significance of the interaction between two or more independent variables is a test of the .
A) significance of the interaction effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the overall effect
D) significance of the main effect
A) significance of the interaction effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the overall effect
D) significance of the main effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A test of the significance of the main effect for each individual factor is a test of the .
A) significance of the overall effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the interaction effect
D) significance of the main effect
A) significance of the overall effect
B) multiple y2
C) significance of the interaction effect
D) significance of the main effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In ANOVA the relative contribution of a factor X is calculated as . 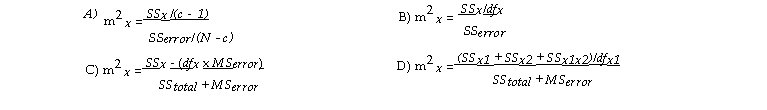
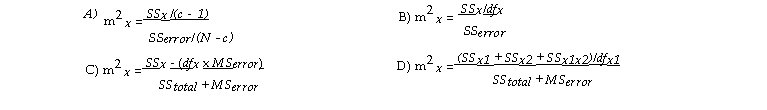

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At what point does m2 begin to represent a larger experimental effect?
A) )25
B) )15
C) )10
D) )06
A) )25
B) )15
C) )10
D) )06

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The strength of the joint effect of two (or more) factors or the overall effect is known as .
A) significance of the overall effect
B) significance of the interaction effect
C) multiple y2 D) significance of the main effect
A) significance of the overall effect
B) significance of the interaction effect
C) multiple y2 D) significance of the main effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Also referred to as SSerror, is the variation in Y due to the variation within each of the categories of X. This variation is not accounted for by X.
A) SSwithin B) SSbetween C) SSx D) SSy
A) SSwithin B) SSbetween C) SSx D) SSy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The null hypothesis for ANOVA typically is that all .
A) means are unequal
B) proportions are equal
C) means are equal
D) proportions are unequal
A) means are unequal
B) proportions are equal
C) means are equal
D) proportions are unequal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
are determined before conducting the analysis, based on the researcher's theoretical framework.
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The total variation in Y, denoted by SSy, can be decomposed into which two components?
A) SSy = SSx - SSerror B) SSy = SSx + SSerror
C) SSy = SSbetween + SSwithin D) B and C are correct.
A) SSy = SSx - SSerror B) SSy = SSx + SSerror
C) SSy = SSbetween + SSwithin D) B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement is not true concerning interactions resulting from ANOVA?
A) Disordinal interactions of a crossover type represent the weakest interactions.
B) In disordinal interactions of a crossover type, the relative effect of the levels of one factor changes with the levels of the other.
C) Because it involves a change in rank order, disordinal interaction is stronger than ordinal interaction.
D) In ordinal interaction, the rank order of the effects related to one factor does not change across the levels of the second factor.
A) Disordinal interactions of a crossover type represent the weakest interactions.
B) In disordinal interactions of a crossover type, the relative effect of the levels of one factor changes with the levels of the other.
C) Because it involves a change in rank order, disordinal interaction is stronger than ordinal interaction.
D) In ordinal interaction, the rank order of the effects related to one factor does not change across the levels of the second factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How consumers' "intentions to buy the brand" varies with different price levels is best analyzed via .
A) regression
B) one- way ANOVA
C) t tests
D) ANCOVA
A) regression
B) one- way ANOVA
C) t tests
D) ANCOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Analysis of covariance includes at least one _ independent variable and at least one independent variable.
A) parametric; interval
B) categorical; interval
C) metric; interval
D) ordinal; categorical
A) parametric; interval
B) categorical; interval
C) metric; interval
D) ordinal; categorical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When using SPSS Windows, for nonmetric analysis of variance, including the k- sample median test and Kruskal- Wallis one way analysis of variance, the program _ _ should be used.
A) univariate
B) compare means
C) nonparametric tests
D) general linear model
A) univariate
B) compare means
C) nonparametric tests
D) general linear model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
is an ANOVA technique used when respondents are exposed to more than one treatment condition and repeated measurements are obtained.
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
are contrasts made after the analysis.
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts
A) Single comparison contrasts
B) Multiple comparison contrasts
C) A priori contrasts
D) A posteriori contrasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The total variation in y is _ .
A) SSwithin B) SSbetween C) SSy D) SSx
A) SSwithin B) SSbetween C) SSy D) SSx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Interactions occur when the effects of one factor on the dependent variable depend on the level (category) of the other factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When using SPSS Windows one- way ANOVA can be efficiently performed using the program.
A) NONPARAMETRIC TESTS
B) GENERAL LINEAR MODEL
C) COMPARE MEANS
D) UNIVARIATE
A) NONPARAMETRIC TESTS
B) GENERAL LINEAR MODEL
C) COMPARE MEANS
D) UNIVARIATE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A statistical technique for examining the differences among means for two or more populations is called .
A) cross- tabulation
B) independent samples t test
C) chi- square
D) analysis of variance (ANOVA)
A) cross- tabulation
B) independent samples t test
C) chi- square
D) analysis of variance (ANOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Analysis of variance and analysis of covariance are tests of differences between two means or median.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The value of y2 varies between 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement is correct if the null hypothesis for a one- way ANOVA is rejected?
A) The effect of the independent variable is significant.
B) The independent variable does not have a significant effect on the dependent variable.
C) The mean value of the dependent variable will be the same for different categories of the independent variable.
D) Both B and C are correct.
A) The effect of the independent variable is significant.
B) The independent variable does not have a significant effect on the dependent variable.
C) The mean value of the dependent variable will be the same for different categories of the independent variable.
D) Both B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An interaction effect occurs when the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable is different for different categories or levels of another independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The estimated value of m2 can be negative, in which case the estimated value of m2 is set equal to one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Omega squared, m2, indicates what proportion of the variation in the dependent variable is related to a particular independent variable or factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the , the categories or treatments are considered to be random samples from a universe of treatments. Inferences are made to other categories not examined in the analysis.
A) fixed- effects model
B) mixed- effects model
C) random- effects model
D) standard- effects model
A) fixed- effects model
B) mixed- effects model
C) random- effects model
D) standard- effects model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Modest departures from the assumptions in analysis of variance do not seriously affect the validity of the analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The most commonly used measure in ANOVA indicating the relative importance of factors is omega squared, (m2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
is an ANOVA technique using two or more metric dependent variables.
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)
A) Nonmetric ANOVA
B) Contrasts
C) Repeated measures ANOVA
D) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The most common use of the covariate is to remove extraneous variation from the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Analysis of variance is so named because it examines the variability or variation in the sample (dependent variable) and, based on the variability, determines whether there is reason to believe that the population means differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In examining the differences among means, one- way analysis of variance involves the decomposition of the total variation observed in the independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Important issues involved in the interpretation of ANOVA results include all of the following except .
A) determining the appropriateness of the test
B) interactions
C) relative importance of factors
D) multiple comparisons
A) determining the appropriateness of the test
B) interactions
C) relative importance of factors
D) multiple comparisons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Nonmetric analysis of variance examines the difference in the central tendencies of more than two groups when the dependent variable is measured on a nominal scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
ANOVA and ANCOVA include one independent variable and t tests include more than one independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The null hypothesis for ANOVA is that all means are not equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Kruskal- Wallis one- way analysis of variance also examines the difference in medians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In analysis of variance, it is assumed that all the groups have the same variation in the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A particular combination of factor levels, or categories, is called a treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In one- way analysis of variance, under the null hypothesis, SSx and SSerror come from different sources of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
SSwithin is the variation in Y related to the variation within each category of X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A marketing survey conducted by EgeBank in Istanbul, Turkey used analysis of variance techniques to help identify affective and perceptual factors that differentiate alternative tourist destinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When using n- way ANOVA the significance of the overall effect may be tested by a t test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The last step in the procedure for conducting one- way analysis of variance is to test the significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
SSbetween is also denoted as SSy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
y2 assumes a value of 0 when all the category means are equal, indicating that X has no effect of X
on Y.
on Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
SSbetween is the portion of the sum of squares in Y related to the independent variable or factor X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Multivariate analysis of variance is appropriate when there are two or more dependent variables that are correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Contrasts are used in ANOVA to determine which of the means are statistically different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Kruskal- Wallis one- way analysis of variance and the k- sample median test have the same null hypothesis -"medians of the k populations are equal."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
ANOVA and ANCOVA can include more than one independent variable and at least one of the independent variables must be categorical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Analysis of covariance is most useful when the covariate is not linearly related to the dependent variable and is not related to the factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Ordinal interaction involves a change in the rank order of the effects of one factor across the levels of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
SSwithin is referred to as SSerror.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The n- way ANOVA assumes that the design was orthogonal, or balanced (the number of cases in each cell was the same).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



