Deck 25: The Reproductive System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: The Reproductive System
1
Fertilization of the ovum normally occurs in this region of the oviduct.
A) isthmus
B) intrauterine portion
C) ampulla
D) infundibulum
E) fimbriae
A) isthmus
B) intrauterine portion
C) ampulla
D) infundibulum
E) fimbriae
C
2
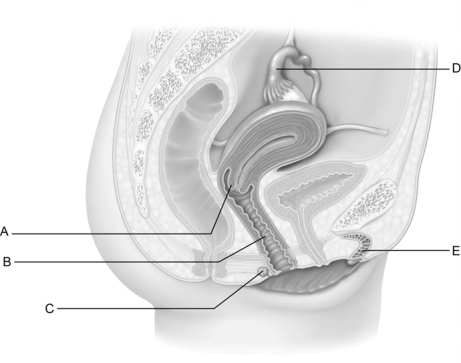 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the organ which is commonly referred to as the birth canal.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
3
 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the infundibulum.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
4
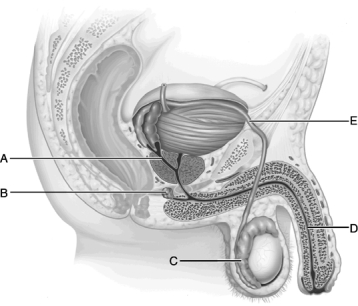 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the common passageway for semen and urine in men.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the female erectile tissue that is homologous to the penis.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the gland that secretes neutralizing mucus prior to ejaculation.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
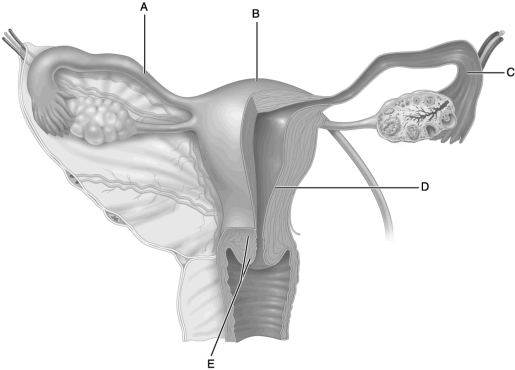 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the tissue layer that is shed during menstruation.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the organ where ectopic pregnancies commonly occur.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The fluid-filled cavity in a mature ovarian follicle is known as
A) theca folliculi.
B) corona radiate.
C) antrum.
D) zona pellucidum.
E) granulaosa cells.
A) theca folliculi.
B) corona radiate.
C) antrum.
D) zona pellucidum.
E) granulaosa cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the cervix.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the region of the uterus known as the fundus.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the ejaculatory duct.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the organ that directs sperm toward the seminal vesicles during ejaculation.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 25.1
Figure 25.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the site of sperm maturation and storage.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the ʺneckʺ of the uterus.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Figure 25.2
Figure 25.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates where fertilization normally occurs.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Tubular organ that is transected during a vasectomy.
A) ductus deferens
B) spermatic cord
C) epididymis
D) pampiniform plexus
E) rete testis
A) ductus deferens
B) spermatic cord
C) epididymis
D) pampiniform plexus
E) rete testis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
This layer of the uterus contracts during parturition to expel the baby.
A) stratum functionalis
B) endometrium
C) perimetrium
D) stratum basalis
E) myometrium
A) stratum functionalis
B) endometrium
C) perimetrium
D) stratum basalis
E) myometrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The opening of the oviduct is surrounded by these structures.
A) external os
B) fimbriae
C) isthmus
D) cardinal ligaments
E) internal os
A) external os
B) fimbriae
C) isthmus
D) cardinal ligaments
E) internal os

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Figure 25.3
Figure 25.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the gland that secretes lubricating mucus into the vaginal orifice.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In breast cancer, the cancer cells usually originate from the
A) fat cells in the breast.
B) lactiferous ductules.
C) cuboidal acinar cells.
D) endothelium of the lymph vessels in the breasts.
A) fat cells in the breast.
B) lactiferous ductules.
C) cuboidal acinar cells.
D) endothelium of the lymph vessels in the breasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The female homologue of the male scrotum is the
A) labia majora.
B) ovary.
C) bulb of the vestibule.
D) penile urethra.
A) labia majora.
B) ovary.
C) bulb of the vestibule.
D) penile urethra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A woman has developed a cancerous lump in each breast, and the skin of the breasts is dimpled. What structure(s) is (are) causing the dimpling?
A) pectoralis major muscle
B) smooth muscle cells around the ducts of the large glands in the breast
C) pectoralis minor muscle
D) suspensory ligaments of the breast
A) pectoralis major muscle
B) smooth muscle cells around the ducts of the large glands in the breast
C) pectoralis minor muscle
D) suspensory ligaments of the breast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A factor that propels an oocyte through the uterine tube is
A) secretions of the nonciliated cells.
B) amoeboid motion of the oocyte.
C) smooth muscle contraction (peristalsis).
D) pressure exerted by ovarian fluid.
A) secretions of the nonciliated cells.
B) amoeboid motion of the oocyte.
C) smooth muscle contraction (peristalsis).
D) pressure exerted by ovarian fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The seminal vesicles
A) store sperm.
B) secrete digestive enzymes when cancerous.
C) are glands that secrete most of the volume of the semen.
D) empty into the epididymis.
A) store sperm.
B) secrete digestive enzymes when cancerous.
C) are glands that secrete most of the volume of the semen.
D) empty into the epididymis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The usual site of embryo implantation is the
A) uterus.
B) peritoneal cavity.
C) uterine tube.
D) vagina.
A) uterus.
B) peritoneal cavity.
C) uterine tube.
D) vagina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Tubules that connect testicular lobules with the efferent ductules of the epididymis.
A) straight tubules
B) pampiniform plexus
C) seminiferous tubules
D) rete testis
E) ductus deferens
A) straight tubules
B) pampiniform plexus
C) seminiferous tubules
D) rete testis
E) ductus deferens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Type of cell in the testes that produces testosterone.
A) spermatogonium
B) interstitial
C) spermatid
D) sustentocytes
E) primary spermatocyte
A) spermatogonium
B) interstitial
C) spermatid
D) sustentocytes
E) primary spermatocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which testicular cells help deliver sperm to the epididymis by contracting rhythmically?
A) interstitial
B) type A spermatocytes
C) sustentocytes
D) myoid
A) interstitial
B) type A spermatocytes
C) sustentocytes
D) myoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The function of the pampiniform plexus of veins is to
A) form the outer wall of the spermatic cord.
B) help cool blood.
C) help prevent hernias.
D) form hydroceles.
A) form the outer wall of the spermatic cord.
B) help cool blood.
C) help prevent hernias.
D) form hydroceles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The correct sequence of sperm-transporting tubules that transport spermatozoa to the epididymis is the
A) seminiferous tubule to straight tubule to rete testis to efferent ductule.
B) seminiferous tubule to efferent ductule to straight tubule to rete testis.
C) seminiferous tubule to rete testis to efferent ductule to straight tubule.
D) seminiferous tubule to rete testis to straight tubule to efferent ductule.
A) seminiferous tubule to straight tubule to rete testis to efferent ductule.
B) seminiferous tubule to efferent ductule to straight tubule to rete testis.
C) seminiferous tubule to rete testis to efferent ductule to straight tubule.
D) seminiferous tubule to rete testis to straight tubule to efferent ductule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the primary sex organ in the male?
A) the epididymis
B) the penis
C) the testis
D) the prostate
A) the epididymis
B) the penis
C) the testis
D) the prostate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All of the following are adaptations for keeping the testes cool except the
A) pampiniform plexus of veins.
B) testicular artery.
C) cremaster and dartos.
D) descent of the testes into the scrotum before birth.
A) pampiniform plexus of veins.
B) testicular artery.
C) cremaster and dartos.
D) descent of the testes into the scrotum before birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A womanʹs sex cells (germ cells) originate embryologically
A) from the germinal epithelium of the ovary.
B) from yolk sac endoderm.
C) from the follicular cells of the follicles.
D) in the innermost part of the gonad.
A) from the germinal epithelium of the ovary.
B) from yolk sac endoderm.
C) from the follicular cells of the follicles.
D) in the innermost part of the gonad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Involuntary contraction of this smooth muscle layer wrinkles and thickens the walls of the scrotum to prevent heat loss.
A) dartos muscle
B) internal spermatic fascia
C) cremaster muscle
D) tunica vaginalis
E) tunica albuginea
A) dartos muscle
B) internal spermatic fascia
C) cremaster muscle
D) tunica vaginalis
E) tunica albuginea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Sperm become motile in the
A) epididymis.
B) ductus deferens.
C) prostate.
D) seminiferous tubules.
A) epididymis.
B) ductus deferens.
C) prostate.
D) seminiferous tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In cows, the nipples (teats) are in the groin region, not in the midthorax as in humans. What is the most logical reason for this difference between cows and people?
A) Cowsʹ mammary glands have entirely different embryonic origins from human ones.
B) Cows are more likely to develop inguinal hernias, and their mammary glands protect against that.
C) Cowsʹ mammary glands arise from a different part of the milk line.
D) Male cows do not produce milk.
A) Cowsʹ mammary glands have entirely different embryonic origins from human ones.
B) Cows are more likely to develop inguinal hernias, and their mammary glands protect against that.
C) Cowsʹ mammary glands arise from a different part of the milk line.
D) Male cows do not produce milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
At what point during fetal development is the decidua basalis/chorionic villi collectively referred to as the placenta?
A) the start of fourth month
B) the end of second month
C) the ninth month
D) the first month
A) the start of fourth month
B) the end of second month
C) the ninth month
D) the first month

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
This multinucleate embryonic structure invades the uterus, digesting cells and maternal blood vessels to make way for development of the placenta.
A) syncytiotrophoblast
B) decidua capsularis
C) decidua basalis
D) inner cell mass
E) morula
A) syncytiotrophoblast
B) decidua capsularis
C) decidua basalis
D) inner cell mass
E) morula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Fingerlike placental structures where oxygen and nutrients from the maternal blood supply diffuse into the embryonic blood.
A) amnion
B) extraembryonic membrane
C) allantois
D) chorionic villi
E) syncytiotrophoblast
A) amnion
B) extraembryonic membrane
C) allantois
D) chorionic villi
E) syncytiotrophoblast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Hypospadias
A) never occurs in females.
B) cannot be detected through an examination of the outside of a babyʹs body.
C) is characterized by the absence of a urethra.
D) has no effects until puberty, when males start producing sperm.
A) never occurs in females.
B) cannot be detected through an examination of the outside of a babyʹs body.
C) is characterized by the absence of a urethra.
D) has no effects until puberty, when males start producing sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The function of the cremaster muscle is to
A) squeeze semen from the urethra during ejaculation.
B) alter the position of the testes in the scrotal sac with increases in ambient temperature.
C) maintain erection in both sexes.
D) increase intra-abdominal pressure during childbirth.
A) squeeze semen from the urethra during ejaculation.
B) alter the position of the testes in the scrotal sac with increases in ambient temperature.
C) maintain erection in both sexes.
D) increase intra-abdominal pressure during childbirth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
By undergoing meiosis, each primary spermatocyte ultimately gives rise to how many sperm cells?
A) two
B) four
C) billions
D) eight
A) two
B) four
C) billions
D) eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The female uterine cycle begins
A) at the end of menstruation.
B) on the first day of menstruation.
C) every six weeks.
D) at ovulation.
A) at the end of menstruation.
B) on the first day of menstruation.
C) every six weeks.
D) at ovulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In females, the paramesonephric ducts give rise to
A) the uterine tubes and uterus.
B) the ovaries.
C) the vestibule in the vulva.
D) the corpora cavernosa (erectile bodies).
A) the uterine tubes and uterus.
B) the ovaries.
C) the vestibule in the vulva.
D) the corpora cavernosa (erectile bodies).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In addition to remaining granulosa cells, which of the following cell types make up the corpus luteum?
A) cells of the corona radiata
B) interstitial cells
C) oocyte
D) theca cells
A) cells of the corona radiata
B) interstitial cells
C) oocyte
D) theca cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following events occurs when the testes do not descend before birth?
A) Viable sperm will not be produced.
B) Inadequate blood supply will retard the development of the testes.
C) Sperm will have no route of exit from the body.
D) Male sex hormones will not circulate in the body.
A) Viable sperm will not be produced.
B) Inadequate blood supply will retard the development of the testes.
C) Sperm will have no route of exit from the body.
D) Male sex hormones will not circulate in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Of the following tubes, which is the only one that lies partly outside the testis?
A) efferent ductule
B) rete testis
C) tubulus rectus
D) seminiferous tubule
A) efferent ductule
B) rete testis
C) tubulus rectus
D) seminiferous tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
During the proliferative phase of the uterine cycle, these vessels grow and proliferate.
A) straight arteries
B) radial arteries
C) spiral arteries
D) arcuate arteries
A) straight arteries
B) radial arteries
C) spiral arteries
D) arcuate arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The most common site of ectopic pregnancy is the
A) uterus.
B) vagina.
C) peritoneal cavity.
D) uterine tube.
A) uterus.
B) vagina.
C) peritoneal cavity.
D) uterine tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Inguinal hernias
A) always enter the inguinal canal.
B) are signs of old age and almost never congenital.
C) always reach the scrotum.
D) occur with equal frequency in males and females.
A) always enter the inguinal canal.
B) are signs of old age and almost never congenital.
C) always reach the scrotum.
D) occur with equal frequency in males and females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following anchors the uterus into an anteverted position in the pelvis?
A) round ligament
B) suspensory ligament
C) broad ligament
D) ovarian ligament
A) round ligament
B) suspensory ligament
C) broad ligament
D) ovarian ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The epithelium lining the vagina is
A) stratified squamous.
B) pseudostratified columnar.
C) simple squamous.
D) simple columnar.
A) stratified squamous.
B) pseudostratified columnar.
C) simple squamous.
D) simple columnar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The milk-producing cells in the breast are
A) columnar epithelial cells in lobules.
B) simple cuboidal epithelial cells in alveoli.
C) adipose cells (because milk contains 4% fat).
D) endocrine cells.
A) columnar epithelial cells in lobules.
B) simple cuboidal epithelial cells in alveoli.
C) adipose cells (because milk contains 4% fat).
D) endocrine cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The zona pellucida
A) is the portion of the placenta in which maternal blood contacts fetal tissues.
B) is a protective shell around the oocyte that sperm must penetrate for fertilization to occur.
C) is the remnant of the vesicular follicle that becomes the corpus luteum.
D) is the region of the uterine tube where fertilization occurs.
A) is the portion of the placenta in which maternal blood contacts fetal tissues.
B) is a protective shell around the oocyte that sperm must penetrate for fertilization to occur.
C) is the remnant of the vesicular follicle that becomes the corpus luteum.
D) is the region of the uterine tube where fertilization occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The ovarian cortex consists of
A) the largest blood vessels of the ovary.
B) follicles and connective tissue.
C) the hilus of the ovary.
D) the mesovarium.
A) the largest blood vessels of the ovary.
B) follicles and connective tissue.
C) the hilus of the ovary.
D) the mesovarium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The prepuce of the clitoris is formed by
A) the hymen of the vagina.
B) the fourchette.
C) the mons pubis.
D) the labia minora.
A) the hymen of the vagina.
B) the fourchette.
C) the mons pubis.
D) the labia minora.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the early fetus, all of the following are parts of the chorionic villi except the
A) decidua.
B) syncytiotrophoblast.
C) extraembryonic mesoderm.
D) cytotrophoblast.
A) decidua.
B) syncytiotrophoblast.
C) extraembryonic mesoderm.
D) cytotrophoblast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following organs does not contribute secretion(s) during the male sexual response?
A) corpus cavernosum
B) bulbourethral glands
C) prostate
D) seminal vesicles
A) corpus cavernosum
B) bulbourethral glands
C) prostate
D) seminal vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The largest macroscopic region of the uterus is its
A) cervix.
B) body.
C) fornix.
D) fundus.
A) cervix.
B) body.
C) fornix.
D) fundus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The placenta consists of which two structures?
A) cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast
B) chorionic villi and amnion
C) decidua basalis and decidua capsularis
D) chorionic villi and decidua basalis
A) cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast
B) chorionic villi and amnion
C) decidua basalis and decidua capsularis
D) chorionic villi and decidua basalis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An episiotomy during childbirth is performed to
A) save the babyʹs life.
B) eliminate the pain to the mother.
C) minimize tearing of the central tendon and muscles of the pelvic floor.
D) prevent the anal canal from being crushed.
A) save the babyʹs life.
B) eliminate the pain to the mother.
C) minimize tearing of the central tendon and muscles of the pelvic floor.
D) prevent the anal canal from being crushed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The structural basis of the blood-testis barrier is
A) the basal lamina around the seminiferous tubules.
B) the thick basal lamina around the capillaries that supply the seminiferous tubules.
C) the endothelial cells of the continuous (nonfenestrated) capillaries that supply the seminiferous tubules.
D) the tight junctions between sustentocytes.
A) the basal lamina around the seminiferous tubules.
B) the thick basal lamina around the capillaries that supply the seminiferous tubules.
C) the endothelial cells of the continuous (nonfenestrated) capillaries that supply the seminiferous tubules.
D) the tight junctions between sustentocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The deep inguinal ring is formed by
A) cremaster muscle.
B) fascia layer deep to the transversus abdominis muscle.
C) extension of the external oblique muscle.
D) extension of the internal oblique muscle.
A) cremaster muscle.
B) fascia layer deep to the transversus abdominis muscle.
C) extension of the external oblique muscle.
D) extension of the internal oblique muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements about pelvic inflammatory disease is incorrect?
A) It inhibits ovulation.
B) It can lead to sterility.
C) It is usually caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea.
D) It includes salpingitis.
A) It inhibits ovulation.
B) It can lead to sterility.
C) It is usually caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea.
D) It includes salpingitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Erection is caused by
A) erectile bodies filling with blood.
B) a jointed bone in the penis that unfolds.
C) impulses from the sympathetic nervous system.
D) the penis filling up with semen that is about to be ejaculated.
A) erectile bodies filling with blood.
B) a jointed bone in the penis that unfolds.
C) impulses from the sympathetic nervous system.
D) the penis filling up with semen that is about to be ejaculated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The embryonic urethral folds develop into the female
A) labia minora.
B) bulb of the vestibule.
C) urethra.
D) labia majora.
A) labia minora.
B) bulb of the vestibule.
C) urethra.
D) labia majora.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following pairs of structures is not derived from the same embryonic tissues?
A) penis, clitoris
B) ductus deferens, uterine tube
C) spongy urethra, labia minora
D) testes, ovaries
A) penis, clitoris
B) ductus deferens, uterine tube
C) spongy urethra, labia minora
D) testes, ovaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Sperm are moved into the epididymis from the testis by
A) gravity.
B) testicular fluid moved by cilia and smooth muscle cells.
C) swimming under their own power.
D) suction.
A) gravity.
B) testicular fluid moved by cilia and smooth muscle cells.
C) swimming under their own power.
D) suction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A difference between a primary follicle and a primordial follicle is that
A) the oocyte is larger in the primordial follicle.
B) the primary follicle is an earlier stage than the primordial follicle.
C) one has an antrum and the other does not.
D) the primordial follicle has only a single layer of flat follicular cells, whereas the primary follicle is comprised of cuboidal follicle cells.
A) the oocyte is larger in the primordial follicle.
B) the primary follicle is an earlier stage than the primordial follicle.
C) one has an antrum and the other does not.
D) the primordial follicle has only a single layer of flat follicular cells, whereas the primary follicle is comprised of cuboidal follicle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The acrosomal reaction occurs
A) during spermiogenesis.
B) just before fertilization.
C) during placentation.
D) during meiosis of the sperm.
A) during spermiogenesis.
B) just before fertilization.
C) during placentation.
D) during meiosis of the sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The cells that secrete estrogens in females are
A) germinal epithelium of the ovary.
B) oocytes.
C) cells in the pituitary gland.
D) granulosa cells.
A) germinal epithelium of the ovary.
B) oocytes.
C) cells in the pituitary gland.
D) granulosa cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
All of the following are functions of the sustentocytes in the seminiferous tubules except
A) secretion of testosterone.
B) secretion of testicular fluid.
C) secretion of androgen-binding protein.
D) phagocytosis of excess cytoplasm from spermatids during spermiogenesis.
A) secretion of testosterone.
B) secretion of testicular fluid.
C) secretion of androgen-binding protein.
D) phagocytosis of excess cytoplasm from spermatids during spermiogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which structure develops into the umbilical cord?
A) placenta
B) decidua capsularis
C) body stalk
D) chorionic villi
A) placenta
B) decidua capsularis
C) body stalk
D) chorionic villi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A hydrocele
A) is a series of varicosities of the pampiniform plexus.
B) occurs in females only.
C) is excess serous fluid in the scrotum.
D) is a sac filled with intestines that have pushed through the abdominal wall.
A) is a series of varicosities of the pampiniform plexus.
B) occurs in females only.
C) is excess serous fluid in the scrotum.
D) is a sac filled with intestines that have pushed through the abdominal wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which structure is not derived from the embryonic paramesonephric ducts?
A) uterine tube
B) cervix
C) upper vagina
D) clitoris
A) uterine tube
B) cervix
C) upper vagina
D) clitoris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the late stages of pregnancy, the placental barrier of the chorionic villi consists only of which two layers?
A) cytotrophoblast and extraembryonic mesoderm
B) decidua capsularis and decidua basalis
C) syncytiotrophoblast and capillary endothelium
D) syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast
A) cytotrophoblast and extraembryonic mesoderm
B) decidua capsularis and decidua basalis
C) syncytiotrophoblast and capillary endothelium
D) syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
All of the following are located within the spermatic cord except the
A) ductus deferens.
B) testicular artery.
C) pampiniform plexus.
D) superficial inguinal ring.
A) ductus deferens.
B) testicular artery.
C) pampiniform plexus.
D) superficial inguinal ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The typical (diploid) cells of the body have 46 chromosomes; how many chromosomes does each gamete have?
A) 23
B) 184
C) 46
D) 46 pairs
A) 23
B) 184
C) 46
D) 46 pairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which female structure is homologous to the corpus spongiosum of the penis?
A) crura
B) labia minora
C) bulb of the vestibule
D) clitoris
A) crura
B) labia minora
C) bulb of the vestibule
D) clitoris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



