Deck 19: The Heart
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: The Heart
1
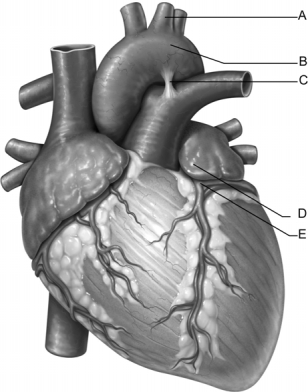 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the aortic arch.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
2
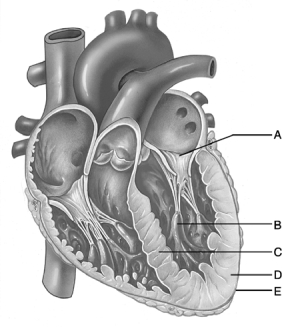 Figure 19.2
Figure 19.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the location of the subendocardial conducting network.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
3
 Figure 19.2
Figure 19.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates anchor points for chordae tendineae, composed of cells from the myocardium.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
4
Threadlike structures of the endocardium that prevent prolapse of the atrioventricular valves.
A) fossa ovalis
B) pectinate muscles
C) trabeculae carneae
D) ligamentum arteriosum
E) chordae tendineae
A) fossa ovalis
B) pectinate muscles
C) trabeculae carneae
D) ligamentum arteriosum
E) chordae tendineae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the left common carotid artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The heart chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
A) left atrium
B) left ventricle
C) right auricle
D) right atrium
E) right ventricle
A) left atrium
B) left ventricle
C) right auricle
D) right atrium
E) right ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The accumulation of pericardial fluid due to inflammation or the accumulation of blood in the pericardial cavity can lead to
A) pericarditis.
B) cardiac tamponade.
C) pleuritis.
D) mitral valve prolapse.
E) fasciae adherens.
A) pericarditis.
B) cardiac tamponade.
C) pleuritis.
D) mitral valve prolapse.
E) fasciae adherens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Contraction of these structures tightens the chordae tendineae, preventing valve prolapse.
A) atrioventricular bundle
B) papillary muscles
C) pectinate muscles
D) crista terminalis
E) trabeculae carneae
A) atrioventricular bundle
B) papillary muscles
C) pectinate muscles
D) crista terminalis
E) trabeculae carneae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Figure 19.2
Figure 19.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the location of the bundle branches.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Heart valve with two cusps.
A) mitral valve
B) atrioventricular bundle
C) aortic semilunar valve
D) pulmonary semilunar valve
E) fossa ovalis
A) mitral valve
B) atrioventricular bundle
C) aortic semilunar valve
D) pulmonary semilunar valve
E) fossa ovalis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The heart chamber that receives blood from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus.
A) right ventricle
B) left atrium
C) left auricle
D) left ventricle
E) right atrium
A) right ventricle
B) left atrium
C) left auricle
D) left ventricle
E) right atrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the left coronary artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The internal C-shaped crest of the right atrium which indicates the openings for the Superior vena cava and Inferior vena cava is
A) fossa ovalis.
B) pectinate muscles.
C) crista terminalis.
D) trabeculae carneae.
E) ligamentum arteriosum.
A) fossa ovalis.
B) pectinate muscles.
C) crista terminalis.
D) trabeculae carneae.
E) ligamentum arteriosum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 19.2
Figure 19.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the left atrioventricular valve.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The region between the right and left pleural cavities is the
A) pericardial cavity.
B) mediastinum.
C) peritoneal cavity.
D) vertebral cavity.
E) pulmonary cavity.
A) pericardial cavity.
B) mediastinum.
C) peritoneal cavity.
D) vertebral cavity.
E) pulmonary cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the left auricle.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Cells of the conducting system located between the AV node and bundle branches.
A) trabeculae carneae
B) papillary muscles
C) crista terminalis
D) atrioventricular bundle
E) pectinate muscles
A) trabeculae carneae
B) papillary muscles
C) crista terminalis
D) atrioventricular bundle
E) pectinate muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the ligamentum arteriosum.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 19.2
Figure 19.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the tissue layer of the heart known as the epicardium.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The valve responsible for preventing backflow of blood from the lungs into the heart.
A) tricuspid valve
B) pectinate muscles
C) aortic semilunar valve
D) bicuspid valve
E) pulmonary semilunar valve
A) tricuspid valve
B) pectinate muscles
C) aortic semilunar valve
D) bicuspid valve
E) pulmonary semilunar valve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Parasympathetic impulses to the SA node are transmitted on this cranial nerve.
A) Vagus nerve
B) Hypoglossal nerve
C) Accessory nerve-spinal part
D) Glossopharyngeal nerve
E) Trigeminal nerve
A) Vagus nerve
B) Hypoglossal nerve
C) Accessory nerve-spinal part
D) Glossopharyngeal nerve
E) Trigeminal nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Coronary artery that supplies the left atrium.
A) circumflex artery
B) posterior descending artery
C) left anterior descending artery
D) pulmonary artery
E) marginal artery
A) circumflex artery
B) posterior descending artery
C) left anterior descending artery
D) pulmonary artery
E) marginal artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A drop of blood returning to the heart from the head region would enter the heart through which vessel?
A) the coronary sinus
B) the inferior vena cava
C) the superior vena cava
D) a pulmonary vein
A) the coronary sinus
B) the inferior vena cava
C) the superior vena cava
D) a pulmonary vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following vessels does not carry oxygen-poor blood to the heart?
A) the inferior vena cava
B) the superior vena cava
C) the coronary sinus
D) the pulmonary vein
A) the inferior vena cava
B) the superior vena cava
C) the coronary sinus
D) the pulmonary vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The right ventricle pumps blood into which vessel?
A) the pulmonary vein
B) the aorta
C) the superior vena cava
D) the pulmonary trunk
A) the pulmonary vein
B) the aorta
C) the superior vena cava
D) the pulmonary trunk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A condition in which the ventricles are unable to pump blood efficiently because of rapid, random contraction of cardiac muscle fibers is called
A) atrial fibrillation.
B) congestive heart failure.
C) pulmonary arterial hypertension.
D) ventricular fibrillation.
A) atrial fibrillation.
B) congestive heart failure.
C) pulmonary arterial hypertension.
D) ventricular fibrillation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Enlargement of the heart with progressive decline in pumping efficiency.
A) congestive heart failure
B) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C) heart block
D) cardiac tamponade
E) myocardial infarction
A) congestive heart failure
B) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
C) heart block
D) cardiac tamponade
E) myocardial infarction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The cusps of the valves of the heart are covered by
A) modified pericardium.
B) epicardium.
C) myocardium.
D) endocardium.
A) modified pericardium.
B) epicardium.
C) myocardium.
D) endocardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The pericardial cavity lies between
A) the serous pericardium and the epicardium.
B) the fibrous pericardium and the diaphragm.
C) the fibrous pericardium and the parietal pericardium.
D) the parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium.
A) the serous pericardium and the epicardium.
B) the fibrous pericardium and the diaphragm.
C) the fibrous pericardium and the parietal pericardium.
D) the parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following structures is not found in the left ventricle?
A) the trabeculae carneae
B) the mitral valve
C) the pectinate muscles
D) the papillary muscles
A) the trabeculae carneae
B) the mitral valve
C) the pectinate muscles
D) the papillary muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Death of heart musculature due to lack of oxygen.
A) myocardial infarction
B) cardiac tamponade
C) heart block
D) ventricular fibrillation
E) valve insufficiency
A) myocardial infarction
B) cardiac tamponade
C) heart block
D) ventricular fibrillation
E) valve insufficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Large cardiac cells of the conducting system embedded in the ventricular walls between the endocardium and myocardium.
A) sinoatrial node
B) atrioventricular node
C) subendocardial conducting network (Purkinje fibers)
D) atrioventricular bundle
E) atrioventricular branches
A) sinoatrial node
B) atrioventricular node
C) subendocardial conducting network (Purkinje fibers)
D) atrioventricular bundle
E) atrioventricular branches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The superior corner of the right atrium of the heart is located at the
A) costal cartilage of the sixth rib, a fingerʹs width lateral to the sternum.
B) fifth intercostal space along a line extending inferiorly from the midpoint of the clavicle.
C) costal cartilage of the third rib where it attaches to the sternum.
D) midpoint of the jugular notch.
A) costal cartilage of the sixth rib, a fingerʹs width lateral to the sternum.
B) fifth intercostal space along a line extending inferiorly from the midpoint of the clavicle.
C) costal cartilage of the third rib where it attaches to the sternum.
D) midpoint of the jugular notch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The inner endothelial layer that lines the heart is the
A) epicardium.
B) endocardium.
C) pericardium.
D) myocardium.
A) epicardium.
B) endocardium.
C) pericardium.
D) myocardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The auricles are
A) earlike flaps on the surface of the atria.
B) modifications of the pectinate muscles on the inner surface of the atria.
C) earlike flaps on the surface of the ventricles.
D) projections of the endothelium into the ventricles.
A) earlike flaps on the surface of the atria.
B) modifications of the pectinate muscles on the inner surface of the atria.
C) earlike flaps on the surface of the ventricles.
D) projections of the endothelium into the ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What structures anchor the chordae tendineae?
A) papillary muscles
B) trabeculae carneae
C) semilunar valves
D) pectinate muscles
A) papillary muscles
B) trabeculae carneae
C) semilunar valves
D) pectinate muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How did the sinoatrial (SA) node most likely get its name?
A) It is damaged by sinus infections (head colds).
B) It develops from the sinus venosus and lies in an atrium.
C) It is on the side of the atrium.
D) It lies at the opening of the coronary sinus.
A) It is damaged by sinus infections (head colds).
B) It develops from the sinus venosus and lies in an atrium.
C) It is on the side of the atrium.
D) It lies at the opening of the coronary sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Semilunar valves are located
A) between the great veins and the atria.
B) between the atria and the ventricles.
C) only between the left ventricle and the aorta.
D) between the ventricles and the great arteries.
A) between the great veins and the atria.
B) between the atria and the ventricles.
C) only between the left ventricle and the aorta.
D) between the ventricles and the great arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which structure develops from the embryological chamber called the bulbus cordis?
A) the left ventricle
B) the sinoatrial node
C) the right ventricle
D) the left atrium
A) the left ventricle
B) the sinoatrial node
C) the right ventricle
D) the left atrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A penetrating stab wound to the heart wall that causes blood to leak into the pericardial cavity would result in
A) endocarditis.
B) cardiac tamponade.
C) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
D) myocardial infarction.
A) endocarditis.
B) cardiac tamponade.
C) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
D) myocardial infarction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The heart chamber with the thickest wall is the
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The artery that nourishes the walls of the left atrium is the
A) circumflex.
B) anterior interventricular.
C) right coronary.
D) posterior interventricular.
A) circumflex.
B) anterior interventricular.
C) right coronary.
D) posterior interventricular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The small cardiac vein is present on the
A) right ventricle.
B) left ventricle.
C) left atrium.
D) right atrium.
A) right ventricle.
B) left ventricle.
C) left atrium.
D) right atrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
During ventricular systole, blood is
A) forced from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
B) not flowing into or out of the heart.
C) forced from the atria into the ventricles.
D) flowing from the systemic and pulmonary circuits into both the atria and ventricles.
A) forced from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
B) not flowing into or out of the heart.
C) forced from the atria into the ventricles.
D) flowing from the systemic and pulmonary circuits into both the atria and ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The crista terminalis can be used to locate all of the following structures except the
A) opening of the superior vena cava.
B) opening of the inferior vena cava.
C) opening of the pulmonary veins.
D) opening of the coronary sinus.
A) opening of the superior vena cava.
B) opening of the inferior vena cava.
C) opening of the pulmonary veins.
D) opening of the coronary sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Oxygen-poor blood returns to the heart and enters the
A) left atrium.
B) right atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) left ventricle.
A) left atrium.
B) right atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) left ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which structure develops from the embryological chamber called the sinus venosus?
A) the right ventricle
B) the left atrium
C) the pulmonary trunk
D) sinoatrial (SA) node
A) the right ventricle
B) the left atrium
C) the pulmonary trunk
D) sinoatrial (SA) node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Blood within the pulmonary veins returns to the
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The epicardium is the same as the
A) visceral layer of serous pericardium.
B) endocardium.
C) pericardium.
D) fibrous pericardium.
A) visceral layer of serous pericardium.
B) endocardium.
C) pericardium.
D) fibrous pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The desmosome-like structures that attach adjacent cardiac muscle cells are called
A) gap junctions.
B) intercalated disks.
C) T tubules.
D) fasciae adherens.
A) gap junctions.
B) intercalated disks.
C) T tubules.
D) fasciae adherens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Blood is carried to capillaries in the myocardium by way of the
A) coronary arteries.
B) coronary sinus.
C) fossa ovalis.
D) coronary veins.
A) coronary arteries.
B) coronary sinus.
C) fossa ovalis.
D) coronary veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The term for pain caused by deficient blood delivery to the heart wall is
A) angina pectoris.
B) myocardial infarct.
C) ischemia.
D) pericarditis.
A) angina pectoris.
B) myocardial infarct.
C) ischemia.
D) pericarditis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A specific coronary vessel that lies in the coronary sulcus is the
A) posterior interventricular artery.
B) right coronary artery.
C) right marginal artery.
D) small cardiac vein.
A) posterior interventricular artery.
B) right coronary artery.
C) right marginal artery.
D) small cardiac vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A specific coronary vessel that lies in the anterior interventricular sulcus is the
A) coronary sinus.
B) middle cardiac vein.
C) anterior interventricular artery/Left anterior descending artery (LAD).
D) circumflex artery.
A) coronary sinus.
B) middle cardiac vein.
C) anterior interventricular artery/Left anterior descending artery (LAD).
D) circumflex artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which vessel returns most of the venous blood from the heart to the right atrium?
A) the posterior interventricular vein
B) the anterior cardiac vein
C) the coronary sinus
D) the great cardiac vein
A) the posterior interventricular vein
B) the anterior cardiac vein
C) the coronary sinus
D) the great cardiac vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Stenosis of the mitral valve may cause blood to back up into the
A) coronary circulation.
B) right ventricle.
C) pulmonary circulation.
D) venae cavae.
A) coronary circulation.
B) right ventricle.
C) pulmonary circulation.
D) venae cavae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the effect of the parasympathetic fibers carried by the vagus nerve?
A) The heartbeat is not influenced by the vagus nerve.
B) They slow the heartbeat.
C) They speed up the heartbeat.
D) They increase the force of cardiac contractions.
A) The heartbeat is not influenced by the vagus nerve.
B) They slow the heartbeat.
C) They speed up the heartbeat.
D) They increase the force of cardiac contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The heart chamber that pumps oxygenated blood around the systemic circuit is the
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.
A) left ventricle.
B) left atrium.
C) right ventricle.
D) right atrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following veins does not deliver blood directly to the right atrium?
A) coronary sinus
B) superior vena cava
C) the great cardiac veins
D) inferior vena cava
A) coronary sinus
B) superior vena cava
C) the great cardiac veins
D) inferior vena cava

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At which corner point of the heart does one listen for the sound of the closing aortic semilunar valve?
A) inferior right
B) inferior left
C) superior left
D) superior right
A) inferior right
B) inferior left
C) superior left
D) superior right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Destruction of which structure will result in electrical signals traveling to only one ventricle?
A) sinoatrial node
B) internodal pathway
C) bundle branch
D) atrioventricular bundle
A) sinoatrial node
B) internodal pathway
C) bundle branch
D) atrioventricular bundle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Of the three layers of the heart wall, the layer that contains the cardiac muscle is the
A) endocardium.
B) myocardium.
C) epicardium.
D) visceral layer of serous pericardium.
A) endocardium.
B) myocardium.
C) epicardium.
D) visceral layer of serous pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
To listen for the aortic semilunar valve on the chest wall, one would place the stethoscope in the
A) second intercostal space to the right of the sternum.
B) fifth intercostal space inferior to the left nipple.
C) second intercostal space to the left of the sternum.
D) fifth right intercostal space.
A) second intercostal space to the right of the sternum.
B) fifth intercostal space inferior to the left nipple.
C) second intercostal space to the left of the sternum.
D) fifth right intercostal space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Clinically, the posterior interventricular artery is referred to as the
A) left artery ascending.
B) posterior descending artery.
C) left artery descending.
D) posterior ascending artery.
A) left artery ascending.
B) posterior descending artery.
C) left artery descending.
D) posterior ascending artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
There is a foramen ovale in the skull and another one in the heart. The foramen ovale in the heart gives rise to the
A) openings between the ventricles.
B) openings between the atria and ventricles.
C) aortic semilunar valve.
D) fossa ovalis.
A) openings between the ventricles.
B) openings between the atria and ventricles.
C) aortic semilunar valve.
D) fossa ovalis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Cells of the subendocardial conducting network
A) are pacemaker cells located in the SA node that initiate each heartbeat.
B) are sensory cells that monitor the stretch of the myocardium to prevent overexpansion by high blood pressure.
C) are larger and have fewer myofilaments than other cardiac cells.
D) are nonconducting cells that electrically insulate the bundle branches of the interventricular septum.
A) are pacemaker cells located in the SA node that initiate each heartbeat.
B) are sensory cells that monitor the stretch of the myocardium to prevent overexpansion by high blood pressure.
C) are larger and have fewer myofilaments than other cardiac cells.
D) are nonconducting cells that electrically insulate the bundle branches of the interventricular septum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The ʺheartstringsʺ are
A) trabeculae carneae.
B) chordae tendineae.
C) cusps of the atrioventricular valves.
D) papillary muscles.
A) trabeculae carneae.
B) chordae tendineae.
C) cusps of the atrioventricular valves.
D) papillary muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is not an age-related change in the heart?
A) fibrosis of cardiac muscle
B) decline in cardiac reserve
C) atherosclerosis
D) thinning of the valve cusps
A) fibrosis of cardiac muscle
B) decline in cardiac reserve
C) atherosclerosis
D) thinning of the valve cusps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the beating heart makes a ʺlub-dupʺ sound, the ʺdupʺ sound is caused by
A) the apex of the heart hitting the anterior chest wall.
B) vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut.
C) a stenotic atrioventricular valve.
D) the large force of the contracting ventricles.
A) the apex of the heart hitting the anterior chest wall.
B) vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut.
C) a stenotic atrioventricular valve.
D) the large force of the contracting ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Of the following heart chambers, which is most affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
A) right atrium
B) right ventricle
C) left atrium
D) left ventricle
A) right atrium
B) right ventricle
C) left atrium
D) left ventricle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Pericarditis can lead to all of the following except
A) a myocardial infarction.
B) excess fluid in the pericardial cavity.
C) pericardial friction rub.
D) adhesions.
A) a myocardial infarction.
B) excess fluid in the pericardial cavity.
C) pericardial friction rub.
D) adhesions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right ventricular wall so that it can
A) expand the thoracic cage during diastole.
B) pump blood with greater pressure.
C) pump blood through a smaller valve.
D) accommodate a greater volume of blood.
A) expand the thoracic cage during diastole.
B) pump blood with greater pressure.
C) pump blood through a smaller valve.
D) accommodate a greater volume of blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The semilunar valves are closed when
A) atria are contracting.
B) the ventricles are relaxing.
C) the atrioventricular valves are closed.
D) the ventricles are contracting.
A) atria are contracting.
B) the ventricles are relaxing.
C) the atrioventricular valves are closed.
D) the ventricles are contracting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
During left ventricular systole, blood exits the heart to enter the
A) pulmonary trunk.
B) venae cavae.
C) pulmonary vein.
D) aorta.
A) pulmonary trunk.
B) venae cavae.
C) pulmonary vein.
D) aorta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The atrioventricular node is located in the
A) interventricular septum, near the heart base.
B) inferior part of the interatrial septum.
C) walls of the ventricles, with the other Purkinje fibers.
D) right atrium, just inferior to the opening of the superior vena cava.
A) interventricular septum, near the heart base.
B) inferior part of the interatrial septum.
C) walls of the ventricles, with the other Purkinje fibers.
D) right atrium, just inferior to the opening of the superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Insertion of a stent to treat coronary artery disease (CAD)
A) is accomplished by laparoscopic incision at the jugular notch.
B) involves grafting a portion of the saphenous vein that contains the stent into the occluded artery.
C) occurs through a catheter inserted in the femoral artery.
D) requires open heart surgery.
A) is accomplished by laparoscopic incision at the jugular notch.
B) involves grafting a portion of the saphenous vein that contains the stent into the occluded artery.
C) occurs through a catheter inserted in the femoral artery.
D) requires open heart surgery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the pericardial sac, the lies directly deep to the fibrous pericardium.
A) parietal layer of the serous pericardium
B) visceral layer of serous pericardium
C) epicardium
D) pericardial cavity
A) parietal layer of the serous pericardium
B) visceral layer of serous pericardium
C) epicardium
D) pericardial cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements about fetal heart development is false?
A) The heart develops from mesodermal mesenchyme.
B) The four heart chambers first develop during the third trimester.
C) The two atria are connected by a foramen ovale until birth.
D) The heart begins as a pair of tubes in the midline of the thorax.
A) The heart develops from mesodermal mesenchyme.
B) The four heart chambers first develop during the third trimester.
C) The two atria are connected by a foramen ovale until birth.
D) The heart begins as a pair of tubes in the midline of the thorax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The tricuspid valve is closed
A) when the ventricle is in systole.
B) while the atrium is contracting.
C) while the ventricle is in diastole.
D) by movement of blood from atrium to ventricle.
A) when the ventricle is in systole.
B) while the atrium is contracting.
C) while the ventricle is in diastole.
D) by movement of blood from atrium to ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The base of the aorta derives from which of these ʺoriginalʺ heart chambers in the embryo?
A) ventricle
B) bulbus cordis
C) sinus venosus
D) atrium
A) ventricle
B) bulbus cordis
C) sinus venosus
D) atrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



