Deck 18: Blood
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Blood
1
Fraction of blood comprised by erythrocytes.
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid
A
2
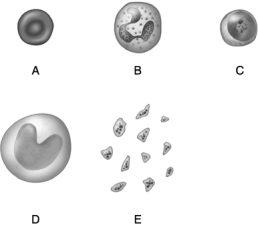 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the most abundant class of leukocyte.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
B
3
Cell mediator of inflammation.
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil
E
4
Most abundant formed element.
A) myeloid
B) monocyte
C) eosinophil
D) basophil
E) erythrocyte
A) myeloid
B) monocyte
C) eosinophil
D) basophil
E) erythrocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Along with leukocytes, these contribute less than 1% of whole blood.
A) albumin
B) erythrocytes
C) lymphocytes
D) reticulocytes
E) platelets
A) albumin
B) erythrocytes
C) lymphocytes
D) reticulocytes
E) platelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Parent cell that transforms into a macrophage.
A) lymphocyte
B) neutrophil
C) eosinophil
D) basophil
E) monocyte
A) lymphocyte
B) neutrophil
C) eosinophil
D) basophil
E) monocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
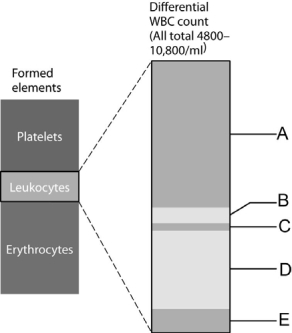 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the fraction of leukocytes that represents basophils.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the formed element of the blood that is packed with molecules of hemoglobin.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates formed elements of the blood that are important in blood clotting.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the formed element of the blood that produces antibodies.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Cell fragments, also called thrombocytes, involved in clotting.
A) globulins
B) fibrinogen
C) albumin
D) basophils
E) platelets
A) globulins
B) fibrinogen
C) albumin
D) basophils
E) platelets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Seen in abundance during parasitic infection.
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the fraction of leukocytes that represents lymphocytes.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the fraction of leukocytes that represents eosinophils.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the fraction of leukocytes that represents neutrophils.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Leukocyte primarily responsible for destroying bacteria.
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the fraction that of leukocytes that represents monocytes.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the formed element of the blood that develops into phagocytic cells called macrophages.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Blood protein that contributes osmotic pressure, keeping water from leaking out of the vessels.
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Plasma minus clotting factors.
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid
A) hematocrit
B) buffy coat
C) serum
D) albumin
E) myeloid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the cell line that forms erythrocytes in red bone marrow, all of the following occur except that
A) lysosome-like granules accumulate.
B) the cytoplasm goes from basophilic (blue-staining) to eosinophilic (pink-staining).
C) the nucleus is lost.
D) hemoglobin accumulates in the cells.
A) lysosome-like granules accumulate.
B) the cytoplasm goes from basophilic (blue-staining) to eosinophilic (pink-staining).
C) the nucleus is lost.
D) hemoglobin accumulates in the cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Disorders of red blood cells can be detected by obtaining counts of these immature structures.
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The most abundant white blood cell type is the
A) eosinophil.
B) monocyte.
C) neutrophil.
D) lymphocyte.
A) eosinophil.
B) monocyte.
C) neutrophil.
D) lymphocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which white blood cells contain granules of histamine?
A) eosinophils
B) neutrophils
C) basophils
D) lymphocytes
A) eosinophils
B) neutrophils
C) basophils
D) lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Young erythrocyte.
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What type of white blood cell increases dramatically during parasitic infections or allergic reactions?
A) monocyte
B) basophil
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
A) monocyte
B) basophil
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following organs does not form blood cells in the fetus?
A) lung
B) spleen
C) yolk sac
D) liver
A) lung
B) spleen
C) yolk sac
D) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cell containing a large, dark purple-staining spherical nucleus that almost completely fills the cell volume.
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte
A) myeloid
B) eosinophil
C) reticulocyte
D) lymphoid
E) lymphocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The unusual shape of the erythrocyte can be explained by which of the following?
A) It increases surface area for respiratory exchange across the plasma membrane.
B) It reflects the fact that erythrocytes are degenerating.
C) It is the best shape for a cell that must pass through narrow capillaries.
D) It allows each cell to hold a maximum amount of hemoglobin.
A) It increases surface area for respiratory exchange across the plasma membrane.
B) It reflects the fact that erythrocytes are degenerating.
C) It is the best shape for a cell that must pass through narrow capillaries.
D) It allows each cell to hold a maximum amount of hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the difference between a thrombus and an embolus?
A) One occurs in the bloodstream, whereas the other occurs outside the bloodstream.
B) A thrombus must travel to become an embolus.
C) One is a blood clot, whereas the other is a parasitic worm.
D) One occurs in arteries, the other in veins.
A) One occurs in the bloodstream, whereas the other occurs outside the bloodstream.
B) A thrombus must travel to become an embolus.
C) One is a blood clot, whereas the other is a parasitic worm.
D) One occurs in arteries, the other in veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Produces antibodies.
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil
A) erythrocyte
B) lymphocyte
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
E) basophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The functions of platelets include all of the following except
A) formation of a temporary patch in the walls of damaged blood vessels.
B) release of chemical signals that trigger the immune response.
C) secretion of chemicals that call more platelets to the site of injury.
D) release of molecules that initiate clotting.
A) formation of a temporary patch in the walls of damaged blood vessels.
B) release of chemical signals that trigger the immune response.
C) secretion of chemicals that call more platelets to the site of injury.
D) release of molecules that initiate clotting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which cells fight infection by producing antibodies?
A) B lymphocytes
B) plasma cells
C) T lymphocytes
D) eosinophils
A) B lymphocytes
B) plasma cells
C) T lymphocytes
D) eosinophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following cells lack mitochondria?
A) basophils
B) erythrocytes
C) platelets
D) neutrophils
A) basophils
B) erythrocytes
C) platelets
D) neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the anatomical difference between T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes?
A) B cells have a darker-staining nucleus.
B) T cells are larger.
C) B cells are larger.
D) They are structurally identical.
A) B cells have a darker-staining nucleus.
B) T cells are larger.
C) B cells are larger.
D) They are structurally identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Hematocrit measures the percentage of blood volume that consists of
A) plasma.
B) neutrophils.
C) platelets.
D) erythrocytes.
A) plasma.
B) neutrophils.
C) platelets.
D) erythrocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Stem cell from which eosinophils and basophils develop.
A) erythrocyte
B) basophil
C) monocyte
D) eosinophil
E) myeloid
A) erythrocyte
B) basophil
C) monocyte
D) eosinophil
E) myeloid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The most common formed elements in the blood are
A) leukocytes.
B) macrophages.
C) erythrocytes.
D) platelets.
A) leukocytes.
B) macrophages.
C) erythrocytes.
D) platelets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
is a condition in which the bloodʹs capacity for carrying oxygen is diminished.
A) Leukemia
B) Thrombocytopenia
C) Polycythemia
D) Anemia
A) Leukemia
B) Thrombocytopenia
C) Polycythemia
D) Anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not phagocytic?
A) lymphocyte
B) basophil
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil
A) lymphocyte
B) basophil
C) eosinophil
D) neutrophil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following groups of cells are most structurally related?
A) monocytes, platelets, and macrophages
B) eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils
C) basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes
D) lymphocytes, erythrocytes, and basophils
A) monocytes, platelets, and macrophages
B) eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils
C) basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes
D) lymphocytes, erythrocytes, and basophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements concerning the various leukocytes is false?
A) All are active in connective tissues but not in blood.
B) All have distorted, lobed nuclei.
C) All perform diapedesis.
D) All fight disease.
A) All are active in connective tissues but not in blood.
B) All have distorted, lobed nuclei.
C) All perform diapedesis.
D) All fight disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Megakaryocytes
A) give rise to platelets.
B) are phagocytic.
C) are small compared to erythrocytes.
D) circulate freely in the blood.
A) give rise to platelets.
B) are phagocytic.
C) are small compared to erythrocytes.
D) circulate freely in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Leukocytes, ordered from most to least abundant, are the
A) basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils.
B) basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and neutrophils.
C) neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes.
D) neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
A) basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils.
B) basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and neutrophils.
C) neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes.
D) neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The least abundant white blood cell type is the
A) eosinophil.
B) basophil.
C) monocyte.
D) lymphocyte.
A) eosinophil.
B) basophil.
C) monocyte.
D) lymphocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which type of connective tissue occurs in the bone marrow cavity?
A) loose areolar
B) dense irregular
C) reticular
D) cartilage
A) loose areolar
B) dense irregular
C) reticular
D) cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Diapedesis is
A) amoeboid motion.
B) the process by which eosinophils attack worms.
C) the exit of leukocytes from capillaries.
D) the ingestion of bacteria by macrophages.
A) amoeboid motion.
B) the process by which eosinophils attack worms.
C) the exit of leukocytes from capillaries.
D) the ingestion of bacteria by macrophages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
T cells function to
A) respond primarily to bacteria and bacterial toxins in body fluids.
B) phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes.
C) produce antibodies.
D) destroy body cells infected with viruses.
A) respond primarily to bacteria and bacterial toxins in body fluids.
B) phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes.
C) produce antibodies.
D) destroy body cells infected with viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following cells develop into macrophages?
A) monocytes
B) lymphocytes
C) basophils
D) neutrophils
A) monocytes
B) lymphocytes
C) basophils
D) neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If examination of the blood reveals a large number of immature leukocytes, the individual is probably suffering from
A) sickle cell disease.
B) thrombocytopenia.
C) anemia.
D) leukemia.
A) sickle cell disease.
B) thrombocytopenia.
C) anemia.
D) leukemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Yellow bone marrow gets its color from
A) the early stages of red blood cells being made there.
B) fat cells.
C) low densities of red blood cells.
D) the bone trabeculae in the center of this colorless marrow.
A) the early stages of red blood cells being made there.
B) fat cells.
C) low densities of red blood cells.
D) the bone trabeculae in the center of this colorless marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When centrifuged, blood separates into the following sequence of layers, from lightest to heaviest:
A) buffy coat, hematocrit, plasma.
B) plasma, buffy coat, hematocrit.
C) buffy coat, plasma, hematocrit.
D) hematocrit, plasma, buffy coat.
A) buffy coat, hematocrit, plasma.
B) plasma, buffy coat, hematocrit.
C) buffy coat, plasma, hematocrit.
D) hematocrit, plasma, buffy coat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An average female has approximately of blood.
A) 1 liter
B) 8 liters
C) 4 liters
D) 0.5 liter
A) 1 liter
B) 8 liters
C) 4 liters
D) 0.5 liter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The bloodʹs globulins include
A) antibodies.
B) hemoglobin.
C) albumin.
D) fibrinogen.
A) antibodies.
B) hemoglobin.
C) albumin.
D) fibrinogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The precursors of neutrophils, listed in their proper order from the least to the most differentiated cells, are:
A) myeloblast, metamyelocyte, and band cell.
B) metamyelocyte, neutrophil, and band cell.
C) band cell, myeloblast, and myelocyte.
D) metamyelocyte, myeloblast, and neutrophil.
A) myeloblast, metamyelocyte, and band cell.
B) metamyelocyte, neutrophil, and band cell.
C) band cell, myeloblast, and myelocyte.
D) metamyelocyte, myeloblast, and neutrophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The blood cell whose nucleus often resembles a telephone receiver is the
A) erythrocyte.
B) lymphocyte.
C) eosinophil.
D) basophil.
A) erythrocyte.
B) lymphocyte.
C) eosinophil.
D) basophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The replacement of red bone marrow with yellow bone marrow in the limbs occurs
A) by 2 years of age.
B) in fetal life.
C) before 8 years of age.
D) between 8 and 18 years of age.
A) by 2 years of age.
B) in fetal life.
C) before 8 years of age.
D) between 8 and 18 years of age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Reticulocytes are precursors to mature
A) neutrophils.
B) lymphocytes.
C) basophils.
D) erythrocytes.
A) neutrophils.
B) lymphocytes.
C) basophils.
D) erythrocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
B cells fight infections by
A) engulfing foreign pathogens.
B) killing off body cells.
C) producing antibodies.
D) acting as killer cells.
A) engulfing foreign pathogens.
B) killing off body cells.
C) producing antibodies.
D) acting as killer cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In adults, blood cells are manufactured in the marrow of all of the following bones except the
A) pelvis.
B) clavicle.
C) sternum.
D) forearm bones (radius and ulna).
A) pelvis.
B) clavicle.
C) sternum.
D) forearm bones (radius and ulna).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
is a condition in which there is an abnormal excess of erythrocytes in the blood.
A) Thrombocytopenia
B) Anemia
C) Polycythemia
D) Leukemia
A) Thrombocytopenia
B) Anemia
C) Polycythemia
D) Leukemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The formed element that is flattened, circular, lacks a nucleus, lacks mitochondria or ribosomes, and is red because of the presence of hemoglobin is
A) an erythrocyte.
B) a basophil.
C) a lymphocyte.
D) an eosinophil.
A) an erythrocyte.
B) a basophil.
C) a lymphocyte.
D) an eosinophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Elevated numbers of reticulocytes may indicate
A) a degenerative bone marrow disease.
B) a parasitic infection.
C) sickle cell disease.
D) a person is adapting to life at high elevations.
A) a degenerative bone marrow disease.
B) a parasitic infection.
C) sickle cell disease.
D) a person is adapting to life at high elevations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following precursors of erythrocytes are in their proper order, from least to most differentiated?
A) proerythroblast, normocyte, reticulocyte
B) reticulocyte, normocyte, erythroblast
C) normocyte, proerythroblast, erythrocyte
D) erythroblast, reticulocyte, normocyte
A) proerythroblast, normocyte, reticulocyte
B) reticulocyte, normocyte, erythroblast
C) normocyte, proerythroblast, erythrocyte
D) erythroblast, reticulocyte, normocyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Hemopoiesis is
A) different from hematopoiesis.
B) blood cell production.
C) a disease of erythrocytes.
D) a stain for blood smears.
A) different from hematopoiesis.
B) blood cell production.
C) a disease of erythrocytes.
D) a stain for blood smears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Giant cells located just outside of marrow sinusoids are called
A) reticulocytes.
B) myeloblasts.
C) monoblasts.
D) megakaryocytes.
A) reticulocytes.
B) myeloblasts.
C) monoblasts.
D) megakaryocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The percentage of erythrocytes in a normal volume of blood is about
A) 90%.
B) 10%.
C) 45%.
D) 30%.
A) 90%.
B) 10%.
C) 45%.
D) 30%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is the correct ranking of formed elements of blood by longevity (life span), from longest-lived to shortest-lived?
A) erythrocytes, platelets, neutrophils
B) neutrophils, basophils, erythrocytes
C) basophils, erythrocytes, eosinophils
D) monocytes, neutrophils, erythrocytes
A) erythrocytes, platelets, neutrophils
B) neutrophils, basophils, erythrocytes
C) basophils, erythrocytes, eosinophils
D) monocytes, neutrophils, erythrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which cells are the most responsible for the rejection of a transplanted organ, such as a heart?
A) T cells
B) macrophages
C) B cells
D) eosinophils
A) T cells
B) macrophages
C) B cells
D) eosinophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An eosinophil can be distinguished from a basophil because the eosinophil
A) has pink (versus dark purple) granules.
B) is smaller.
C) has a lobed (versus nonlobed) nucleus.
D) contains cytoplasmic granules.
A) has pink (versus dark purple) granules.
B) is smaller.
C) has a lobed (versus nonlobed) nucleus.
D) contains cytoplasmic granules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The defining characteristic of a reticulocyte in the blood is
A) dark-staining nucleus.
B) numerous endocytic vesicles.
C) collagen (reticular) fibers.
D) dark staining masses that represent degrading ribosomes.
A) dark-staining nucleus.
B) numerous endocytic vesicles.
C) collagen (reticular) fibers.
D) dark staining masses that represent degrading ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the body, erythrocytes are red because of the oxidized iron they contain. In stained blood smears, erythrocytes are
A) pink from eosin.
B) light blue from methylene blue.
C) also red from iron.
D) purple from hematoxylin stain.
A) pink from eosin.
B) light blue from methylene blue.
C) also red from iron.
D) purple from hematoxylin stain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following do not remain in red bone marrow after hematopoiesis?
A) fat cells
B) myeloid stem cells
C) lymphoid stem cells
D) reticulocytes
A) fat cells
B) myeloid stem cells
C) lymphoid stem cells
D) reticulocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
is a condition in which there is an abnormally low concentration of platelets in the blood.
A) Thrombocytopenia
B) Polycythemia
C) Leukemia
D) Anemia
A) Thrombocytopenia
B) Polycythemia
C) Leukemia
D) Anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
All of the following cell types are derived from the same precursor cell that generates neutrophils except the
A) myeloblast.
B) blood stem cell.
C) myelocyte.
D) plasma cell.
A) myeloblast.
B) blood stem cell.
C) myelocyte.
D) plasma cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Together, leukocytes and platelets constitute roughly which percentage of whole blood volume?
A) 1%
B) 45%
C) 10%
D) 55%
A) 1%
B) 45%
C) 10%
D) 55%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is not a phase of erythropoiesis?
A) production of ribosomes
B) production of vacuoles
C) synthesis of hemoglobin
D) ejection of the erythrocyteʹs nucleus
A) production of ribosomes
B) production of vacuoles
C) synthesis of hemoglobin
D) ejection of the erythrocyteʹs nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is not a committed cell in a blood cell line?
A) myeloblast
B) megakaryoblast
C) hemapoietic stem cell
D) proerythroblast
A) myeloblast
B) megakaryoblast
C) hemapoietic stem cell
D) proerythroblast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A plasma protein involved in blood clotting is
A) a platelet.
B) albumin.
C) fibrin (and fibrinogen).
D) globulin.
A) a platelet.
B) albumin.
C) fibrin (and fibrinogen).
D) globulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Graft-versus-host disease occurs in many marrow transplant patients because of the activity of
A) neutrophils.
B) lymphocytes.
C) platelets.
D) macrophages.
A) neutrophils.
B) lymphocytes.
C) platelets.
D) macrophages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



