Deck 20: The Cardiovascular System: Blood
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: The Cardiovascular System: Blood
1
A ʺcoming togetherʺ of alternate pathways of blood vessels.
A) vascular anastomosis
B) thoroughfare channel
C) metarterioles
D) converging veins
E) vasa vasorum
A) vascular anastomosis
B) thoroughfare channel
C) metarterioles
D) converging veins
E) vasa vasorum
A
2
Layer of blood vessels innervated by sympathetic vasomotor fibers.
A) vasa vasorum
B) tunica intima
C) tunica externa
D) tunica media
E) subendothelial layer
A) vasa vasorum
B) tunica intima
C) tunica externa
D) tunica media
E) subendothelial layer
D
3
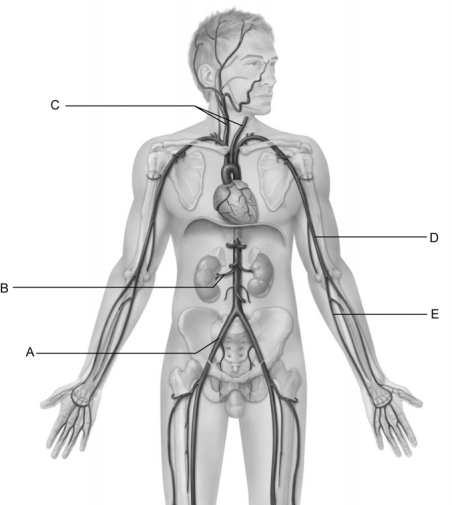 Figure 20.2
Figure 20.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the common carotid arteries.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
4
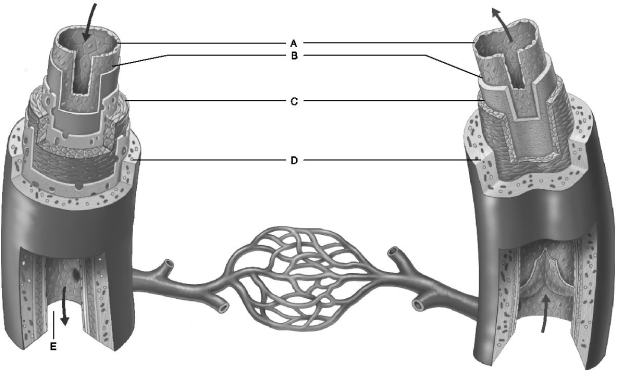 Figure 20.1
Figure 20.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the blood vessel layer that is comprised of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 20.2
Figure 20.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the ulnar artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Figure 20.1
Figure 20.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that is indicating the lumen.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 Figure 20.2
Figure 20.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the brachial artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Structure that regulates blood flow into true capillaries.
A) fenestrations
B) metarteriole
C) thoroughfare channel
D) sinusoids
E) precapillary sphincter
A) fenestrations
B) metarteriole
C) thoroughfare channel
D) sinusoids
E) precapillary sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Figure 20.3
Figure 20.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the longest vein in the body.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Figure 20.1
Figure 20.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the subendothelial layer associated with larger blood vessels.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Figure 20.3
Figure 20.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the internal jugular vein.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 20.2
Figure 20.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the common iliac artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Wide leaky capillaries found in bone marrow and spleen.
A) continuous capillaries
B) metarterioles
C) sinusoids
D) fenestrated capillaries
E) none of the above
A) continuous capillaries
B) metarterioles
C) sinusoids
D) fenestrated capillaries
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 20.3
Figure 20.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the vessel that is easy to find in most people and is used to obtain blood.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Capillaries consist of only this layer.
A) tunica externa
B) tunica media
C) subendothelial layer
D) tunica intima
E) vasa vasorum
A) tunica externa
B) tunica media
C) subendothelial layer
D) tunica intima
E) vasa vasorum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Figure 20.1
Figure 20.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates a connective tissue layer consisting of longitudinal collagen fibers.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 20.3
Figure 20.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the vessel that arises from the union of the left and right brachiocephalic veins.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Figure 20.1
Figure 20.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the layer common to all blood vessels regardless of their size.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 20.3
Figure 20.3Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the cephalic vein.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Figure 20.2
Figure 20.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the renal artery.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which vessel is missing in the following statement? ʺTracing venous blood from the inferior left side of the posterior abdominal wall to the heart, we find that blood enters the posterior intercostal veins, the hemiazygos vein, the superior vena cava, and the right atrium.ʺ
A) the inferior vena cava
B) the azygos vein
C) the right brachiocephalic vein
D) the hepatic portal vein
A) the inferior vena cava
B) the azygos vein
C) the right brachiocephalic vein
D) the hepatic portal vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Microvasculature that provides nourishment to the outer walls of the aorta.
A) tunica externa
B) tunica media
C) subendothelial layer
D) vasa vasorum
E) tunica intima
A) tunica externa
B) tunica media
C) subendothelial layer
D) vasa vasorum
E) tunica intima

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The hepatic portal system has two distinct capillary beds separated by a portal vein. What are the functions of these two capillary beds?
A) The first picks up toxins from the liver, and the second delivers them to the digestive tube for detoxification.
B) The first nourishes the digestive tube, and the second picks up nutrients from the digestive tube.
C) The first picks up digested nutrients, and the second delivers these nutrients to liver cells.
D) The first provides oxygen to the liver, and the second picks up nutrients from the liver.
A) The first picks up toxins from the liver, and the second delivers them to the digestive tube for detoxification.
B) The first nourishes the digestive tube, and the second picks up nutrients from the digestive tube.
C) The first picks up digested nutrients, and the second delivers these nutrients to liver cells.
D) The first provides oxygen to the liver, and the second picks up nutrients from the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the following, the only unpaired dural sinus is the
A) transverse sinus.
B) carotid sinus.
C) superior sagittal sinus.
D) cavernous sinus.
A) transverse sinus.
B) carotid sinus.
C) superior sagittal sinus.
D) cavernous sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Vessels of the small intestines, renal glomerulus, and synovial membranes that allow passage of fluid and solutes through ʺwindowsʺ in the endothelium.
A) metarterioles
B) sinusoids
C) fenestrated capillaries
D) continuous capillaries
E) none of the above
A) metarterioles
B) sinusoids
C) fenestrated capillaries
D) continuous capillaries
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The pulse of the facial artery is palpated
A) anterior to the auricle of the ear near the temple.
B) anterior to the masseter muscle at the inferior margin of the mandible.
C) in the anterior triangle of the neck.
D) anterior to the sternocleidomastoid.
A) anterior to the auricle of the ear near the temple.
B) anterior to the masseter muscle at the inferior margin of the mandible.
C) in the anterior triangle of the neck.
D) anterior to the sternocleidomastoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What artery enters the skull through the foramen spinosum and supplies the inner surface of the parietal bone, dura mater, and parts of the temporal bone?
A) middle cerebral artery
B) basilar artery
C) middle meningeal artery
D) internal carotid artery
A) middle cerebral artery
B) basilar artery
C) middle meningeal artery
D) internal carotid artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An aneurysm is
A) a rupture in an artery.
B) a stroke.
C) a sac-like widening or outpocketing of an artery.
D) a buildup of fatty deposits on an arterial wall.
A) a rupture in an artery.
B) a stroke.
C) a sac-like widening or outpocketing of an artery.
D) a buildup of fatty deposits on an arterial wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Most small molecules pass through a capillary wall through which route?
A) via pinocytotic vesicles
B) through intercellular clefts
C) through tight junctions
D) via direct diffusion through the endothelium
A) via pinocytotic vesicles
B) through intercellular clefts
C) through tight junctions
D) via direct diffusion through the endothelium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Present in most capillaries, these structures are absent in those of the blood-brain barrier.
A) basement membrane
B) endothelial cells
C) tight junctions
D) pericytes
E) intercellular clefts
A) basement membrane
B) endothelial cells
C) tight junctions
D) pericytes
E) intercellular clefts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Blood pressure is highest in the
A) arterioles.
B) elastic arteries.
C) veins.
D) capillaries.
A) arterioles.
B) elastic arteries.
C) veins.
D) capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Two large (wide) arteries that have relatively superficial locations and are often wounded are the
A) brachial artery and posterior intercostal arteries.
B) right and left coronary arteries.
C) aorta and the popliteal artery.
D) common carotid artery and the femoral artery (in the superior thigh).
A) brachial artery and posterior intercostal arteries.
B) right and left coronary arteries.
C) aorta and the popliteal artery.
D) common carotid artery and the femoral artery (in the superior thigh).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which layer of blood vessels contains smooth muscle tissue?
A) tunica adventitia
B) tunica media
C) tunica intima
D) tunica externa
A) tunica adventitia
B) tunica media
C) tunica intima
D) tunica externa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Collective name for the structures that drain the cranium.
A) inferior vena cava
B) internal jugular vein
C) cavernous sinuses
D) vascular anastomosis
E) dural sinuses
A) inferior vena cava
B) internal jugular vein
C) cavernous sinuses
D) vascular anastomosis
E) dural sinuses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The dorsalis pedis artery is located by
A) placing the fingers behind the knee.
B) finding the head of the fibula and palpating inferior to its neck.
C) placing a finger behind the medial malleolus.
D) palpating between the first and second metatarsal.
A) placing the fingers behind the knee.
B) finding the head of the fibula and palpating inferior to its neck.
C) placing a finger behind the medial malleolus.
D) palpating between the first and second metatarsal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a capillary bed, relaxation of the precapillary sphincters causes more blood to flow
A) through the metarterioles.
B) through the true capillaries.
C) into the arterioles.
D) into the thoroughfare channels.
A) through the metarterioles.
B) through the true capillaries.
C) into the arterioles.
D) into the thoroughfare channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Precapillary sphincters allow blood to leave this structure and enter true capillaries.
A) metarterioles
B) fenestrated capillaries
C) sinusoids
D) continuous capillaries
E) none of the above
A) metarterioles
B) fenestrated capillaries
C) sinusoids
D) continuous capillaries
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A blood vessel that ranges from 0.3 mm to about 1 cm in diameter and has a large tunica media relative to the size of the lumen is
A) a muscular artery.
B) a capillary.
C) an elastic artery.
D) an arteriole.
A) a muscular artery.
B) a capillary.
C) an elastic artery.
D) an arteriole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Functionally, there are no valves in arteries (as opposed to in veins) because
A) the blood pressure in arteries is high enough that there is no backflow of blood.
B) valves direct blood only toward the heart and arterial blood passes away from the heart.
C) arteries get more atherosclerosis, so valves would cause lethal blood clotting.
D) valves would tear apart from the high arterial pressure.
A) the blood pressure in arteries is high enough that there is no backflow of blood.
B) valves direct blood only toward the heart and arterial blood passes away from the heart.
C) arteries get more atherosclerosis, so valves would cause lethal blood clotting.
D) valves would tear apart from the high arterial pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a physician cannot feel a pulse in the popliteal fossa, the artery is most likely narrowed by atherosclerosis.
A) femoral
B) dorsalis pedis
C) greater saphenous
D) fibular
A) femoral
B) dorsalis pedis
C) greater saphenous
D) fibular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The foramen ovale in the heart normally closes
A) shortly after birth.
B) in the 7-month fetus.
C) in the 2-month fetus.
D) never.
A) shortly after birth.
B) in the 7-month fetus.
C) in the 2-month fetus.
D) never.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What prevents the backflow of blood in veins?
A) valves
B) increased blood pressure
C) thick smooth muscle and elastic layers
D) the narrowed lumen
A) valves
B) increased blood pressure
C) thick smooth muscle and elastic layers
D) the narrowed lumen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements about arteries is false?
A) Arteries have a smaller lumen than veins of similar size.
B) Arterial walls are thicker than venous walls.
C) Arteries carry oxygenated blood to the heart.
D) Arteries have more elastin than veins.
A) Arteries have a smaller lumen than veins of similar size.
B) Arterial walls are thicker than venous walls.
C) Arteries carry oxygenated blood to the heart.
D) Arteries have more elastin than veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements about arterioles is false?
A) They have the largest content of smooth muscle in their tunica media.
B) They regulate the flow of blood to capillary beds through contraction and relaxation of the tunica media.
C) They redirect blood flow in a sympathetic response to skeletal muscle.
D) They can lead into metarterioles.
A) They have the largest content of smooth muscle in their tunica media.
B) They regulate the flow of blood to capillary beds through contraction and relaxation of the tunica media.
C) They redirect blood flow in a sympathetic response to skeletal muscle.
D) They can lead into metarterioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which branch (or branches) of the abdominal aorta supplies the stomach?
A) suprarenal arteries
B) inferior phrenic arteries
C) celiac trunk
D) superior mesenteric artery
A) suprarenal arteries
B) inferior phrenic arteries
C) celiac trunk
D) superior mesenteric artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The diameter of a typical capillary is similar to that of
A) a fat cell.
B) a venule.
C) an erythrocyte.
D) a sinusoid.
A) a fat cell.
B) a venule.
C) an erythrocyte.
D) a sinusoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What vessel in the fetus connects the pulmonary trunk to the aortic arch so that most of the blood bypasses the immature lungs?
A) ductus arteriosus
B) umbilical vein
C) foramen ovale
D) ductus venosus
A) ductus arteriosus
B) umbilical vein
C) foramen ovale
D) ductus venosus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is most likely to become a varicose vein?
A) the femoral vein
B) the popliteal vein
C) the fibular (peroneal) vein
D) the saphenous vein
A) the femoral vein
B) the popliteal vein
C) the fibular (peroneal) vein
D) the saphenous vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The cerebral arterial circle forms a loop around which structures?
A) the internal and external carotid arteries
B) the cerebellum
C) the pituitary gland and the optic chiasma
D) the great vessels at the base of the heart
A) the internal and external carotid arteries
B) the cerebellum
C) the pituitary gland and the optic chiasma
D) the great vessels at the base of the heart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The delivers arterial blood to the rotator cuff muscles and thyroid gland.
A) vertebral artery
B) axillary artery
C) costocervical trunk
D) thyrocervical trunk
A) vertebral artery
B) axillary artery
C) costocervical trunk
D) thyrocervical trunk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Systemic venous blood that is oxygen-poor but contains the lowest concentration of nitrogenous wastes occurs in the
A) hepatic portal vein.
B) renal veins.
C) pulmonary veins.
D) umbilical veins of the fetus.
A) hepatic portal vein.
B) renal veins.
C) pulmonary veins.
D) umbilical veins of the fetus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The largest molecules that pass through the walls of typical capillaries are thought to use which route?
A) direct diffusion through the endothelium
B) intercellular clefts
C) pinocytotic vesicles
D) tight junctions
A) direct diffusion through the endothelium
B) intercellular clefts
C) pinocytotic vesicles
D) tight junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which vessel is most commonly used to bypass a damaged coronary artery in coronary bypass surgery?
A) great saphenous vein
B) internal carotid artery
C) azygos vein
D) femoral artery
A) great saphenous vein
B) internal carotid artery
C) azygos vein
D) femoral artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The internal carotid artery branches to form the
A) middle meningeal and middle cerebral arteries.
B) posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries.
C) facial, maxillary, and superficial temporal arteries.
D) anterior cerebral, middle cerebral, and ophthalmic arteries.
A) middle meningeal and middle cerebral arteries.
B) posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries.
C) facial, maxillary, and superficial temporal arteries.
D) anterior cerebral, middle cerebral, and ophthalmic arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The correct proximal to distal sequence of the three vessels branching from the aortic arch is
A) brachiocephalic, left subclavian, left common carotid.
B) brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian.
C) left common carotid, left subclavian, brachiocephalic.
D) left subclavian, left common carotid, brachiocephalic.
A) brachiocephalic, left subclavian, left common carotid.
B) brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian.
C) left common carotid, left subclavian, brachiocephalic.
D) left subclavian, left common carotid, brachiocephalic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Most systemic venous blood is both oxygen-poor and nutrient-poor. However, systemic venous blood that is not oxygen-poor and is nutrient-rich occurs in
A) the hepatic portal vein.
B) the renal vein.
C) superficial veins of the limbs.
D) the pulmonary veins.
A) the hepatic portal vein.
B) the renal vein.
C) superficial veins of the limbs.
D) the pulmonary veins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The abdominal aorta divides at its distal end into which arteries?
A) the femoral arteries
B) the common iliac arteries
C) the external iliac arteries
D) the internal iliac arteries
A) the femoral arteries
B) the common iliac arteries
C) the external iliac arteries
D) the internal iliac arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Fenestrated capillaries
A) have pores in their walls.
B) permit the movement of very few molecules.
C) are located in the central nervous system.
D) occur in most of the organs of the body.
A) have pores in their walls.
B) permit the movement of very few molecules.
C) are located in the central nervous system.
D) occur in most of the organs of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The major cause of atherosclerosis is due to the
A) destruction of elastic fibers in artery walls.
B) destruction of valves in veins.
C) formation of atheromas.
D) lack of formation of anastomosis between vessels.
A) destruction of elastic fibers in artery walls.
B) destruction of valves in veins.
C) formation of atheromas.
D) lack of formation of anastomosis between vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A common theme to the development of atherosclerosis is
A) a failure of the venous valves resulting in engorged and twisted vessels.
B) an inflammatory response to a damaged endothelium.
C) an accumulation of glycoproteins in the basement membrane of capillaries.
D) a ballooning out of the vessel walls.
A) a failure of the venous valves resulting in engorged and twisted vessels.
B) an inflammatory response to a damaged endothelium.
C) an accumulation of glycoproteins in the basement membrane of capillaries.
D) a ballooning out of the vessel walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All arteries carry oxygen-rich blood, whereas veins carry oxygen-poor blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which body tissues lack capillaries?
A) tendons and ligaments
B) the myocardium and epicardium of the heart
C) bones
D) the lens and the cornea
A) tendons and ligaments
B) the myocardium and epicardium of the heart
C) bones
D) the lens and the cornea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A preferred site to insert intravenous catheters is into the
A) great saphenous vein.
B) superficial palmar venous arch of the hand.
C) dorsal venous network of the hand.
D) brachial vein.
A) great saphenous vein.
B) superficial palmar venous arch of the hand.
C) dorsal venous network of the hand.
D) brachial vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which arteries connect the basilar artery and the internal carotid artery forming the posterior aspect of the cerebral arterial circle?
A) ulnar artery that encircles the elbow joint
B) anterior communicating arteries
C) genicular arteries that encircle the knee
D) posterior communicating arteries
A) ulnar artery that encircles the elbow joint
B) anterior communicating arteries
C) genicular arteries that encircle the knee
D) posterior communicating arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which vessel is missing from the following statement? ʺTracing blood that drains from the large intestine, we find that blood drains from the distal colon is collected in the inferior mesenteric vein, merges with the splenic vein then directed to the hepatic portal vein, the liver sinusoids, and the inferior vena cava.ʺ
A) umbilical vein
B) celiac vein
C) azygos vein
D) hepatic vein
A) umbilical vein
B) celiac vein
C) azygos vein
D) hepatic vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
By definition, veins are
A) vessels that always carry nutrient-poor blood.
B) vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood.
C) the only vessels that lead from capillaries.
D) vessels that carry blood toward the heart.
A) vessels that always carry nutrient-poor blood.
B) vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood.
C) the only vessels that lead from capillaries.
D) vessels that carry blood toward the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Systemic blood pressure is regulated by adjusting the diameter of arterioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Phlebitis is
A) ballooning of an artery.
B) cancer of the tunica intima.
C) a condition characterized by excessively leaky capillaries.
D) inflammation of a vein.
A) ballooning of an artery.
B) cancer of the tunica intima.
C) a condition characterized by excessively leaky capillaries.
D) inflammation of a vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The main arteries of the sole of the foot-the medial and lateral plantar arteries-arise behind the ankle from which artery?
A) fibular
B) posterior tibial
C) dorsalis pedis
D) saphenous
A) fibular
B) posterior tibial
C) dorsalis pedis
D) saphenous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The right suprarenal and gonadal veins drain into the inferior vena cava, whereas the left suprarenal and gonadal veins drain into the
A) left renal vein.
B) other side of the inferior vena cava.
C) hepatic portal system.
D) superior vena cava.
A) left renal vein.
B) other side of the inferior vena cava.
C) hepatic portal system.
D) superior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the adult, the hepatic portal system carries nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract to the liver. In the fetus, nutrients are absorbed at the placenta, and the vessel that carries these nutrients to the liver is the
A) placental vein.
B) hepatic portal vein.
C) internal iliac vein.
D) umbilical vein.
A) placental vein.
B) hepatic portal vein.
C) internal iliac vein.
D) umbilical vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The extensor muscles of the forearm are supplied by which artery?
A) deep palmar arch
B) posterior interosseous
C) radial
D) ulnar
A) deep palmar arch
B) posterior interosseous
C) radial
D) ulnar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which artery arises from the inferior part of the abdominal aorta and supplies the distal half of the large intestine?
A) median sacral artery
B) gonadal artery
C) superior phrenic artery
D) inferior mesenteric artery
A) median sacral artery
B) gonadal artery
C) superior phrenic artery
D) inferior mesenteric artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
All types of blood vessels contain a tunica intima.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The circulatory route that runs from the digestive tract to the liver is called
A) cerebral circulation.
B) hepatic portal circulation.
C) pulmonary circulation.
D) coronary circulation.
A) cerebral circulation.
B) hepatic portal circulation.
C) pulmonary circulation.
D) coronary circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Blood passing through the fetal ductus arteriosus bypasses the
A) right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, and lungs.
B) right atrium and ventricle.
C) pulmonary trunk and lungs.
D) lungs, left atrium, and ventricle.
A) right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, and lungs.
B) right atrium and ventricle.
C) pulmonary trunk and lungs.
D) lungs, left atrium, and ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is not a branch of the celiac trunk?
A) left gastric artery
B) splenic artery
C) sigmoidal artery
D) common hepatic artery
A) left gastric artery
B) splenic artery
C) sigmoidal artery
D) common hepatic artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The lumbar veins drain the inferior posterior abdominal wall and direct oxygen-poor blood into the
A) superior vena cava.
B) internal iliac vein.
C) inferior vena cava.
D) external iliac vein.
A) superior vena cava.
B) internal iliac vein.
C) inferior vena cava.
D) external iliac vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A dural sinus that contains a major artery and some cranial nerves within it is the
A) cavernous.
B) transverse.
C) inferior sagittal.
D) superior sagittal.
A) cavernous.
B) transverse.
C) inferior sagittal.
D) superior sagittal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The right gonadal vein drains into the
A) lumbar vein.
B) inferior vena cava.
C) internal iliac vein.
D) renal vein.
A) lumbar vein.
B) inferior vena cava.
C) internal iliac vein.
D) renal vein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



