Deck 17: The Islamic World Powers, 1300-1800
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: The Islamic World Powers, 1300-1800
1
Where was the center of Timur's empire?
A) Samarkand
B) Baghdad
C) Kabul
D) Isfahan
A) Samarkand
B) Baghdad
C) Kabul
D) Isfahan
Samarkand
2
How did Mehmet repopulate Istanbul?
A) By forcing Byzantines from other cities to move there or become slaves
B) By granting tax remissions and free houses to people willing to move there
C) By encouraging migrations by offering jobs in the government
D) By offering bonuses to Turkish families with multiple children
A) By forcing Byzantines from other cities to move there or become slaves
B) By granting tax remissions and free houses to people willing to move there
C) By encouraging migrations by offering jobs in the government
D) By offering bonuses to Turkish families with multiple children
By granting tax remissions and free houses to people willing to move there
3
After the death of Timur, his empire was held together by which of the following?
A) Financial gain
B) Islamic faith
C) The Mongol language
D) Timur's dynasty
A) Financial gain
B) Islamic faith
C) The Mongol language
D) Timur's dynasty
Islamic faith
4
Suleiman and Francis I of France formed an alliance to prevent the expansion in Europe of what ruling family?
A) The Stuarts
B) The Habsburgs
C) The Romanovs
D) The Mongols
A) The Stuarts
B) The Habsburgs
C) The Romanovs
D) The Mongols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Who were the janissaries?
A) Muslim scholars in Turkey
B) Elite Ottoman slave soldiers
C) Children born to royal slave concubines
D) The Ottoman bureaucratic corps
A) Muslim scholars in Turkey
B) Elite Ottoman slave soldiers
C) Children born to royal slave concubines
D) The Ottoman bureaucratic corps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following was a distinctive feature of the Ottoman sultans from about 1500 onward?
A) They were allowed unlimited wives.
B) Most did not appoint their sons as heirs.
C) They were all elected from the janissaries.
D) They did not marry and only perpetuated the ruling line through concubines.
A) They were allowed unlimited wives.
B) Most did not appoint their sons as heirs.
C) They were all elected from the janissaries.
D) They did not marry and only perpetuated the ruling line through concubines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What was unusual about the Ottoman ruling class?
A) They were required to be descendants of Turkish families from Anatolia.
B) They were required to perform lifelong military service to the sultan.
C) They did not own their own land.
D) They passed on their wealth through a system of hereditary rights.
A) They were required to be descendants of Turkish families from Anatolia.
B) They were required to perform lifelong military service to the sultan.
C) They did not own their own land.
D) They passed on their wealth through a system of hereditary rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What was the Ottoman devshirme?
A) A system for the enslavement of Christian youths
B) The various levels within the imperial bureaucracy
C) The Ottoman model of a theocratic state
D) A legal code that rectified Islamic and secular law
A) A system for the enslavement of Christian youths
B) The various levels within the imperial bureaucracy
C) The Ottoman model of a theocratic state
D) A legal code that rectified Islamic and secular law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What does the term shah mean?
A) King
B) Leader
C) Divine one
D) High priest
A) King
B) Leader
C) Divine one
D) High priest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What was the religious basis of the Safavid Dynasty?
A) Sunni Islam
B) Shi'ite Islam
C) Hinduism
D) Orthodox Christianity
A) Sunni Islam
B) Shi'ite Islam
C) Hinduism
D) Orthodox Christianity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How did the Safavid shahs gain the loyalty of the Qizilbash?
A) The shahs gave them vast grazing lands, often on the frontier.
B) The shahs alone controlled tax revenue.
C) The shahs were their relatives.
D) The shahs owned them as slaves.
A) The shahs gave them vast grazing lands, often on the frontier.
B) The shahs alone controlled tax revenue.
C) The shahs were their relatives.
D) The shahs owned them as slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to Map 17.4, "The Muslim World, ca. 1700," which of the following empires were once a part of Timur's empire? 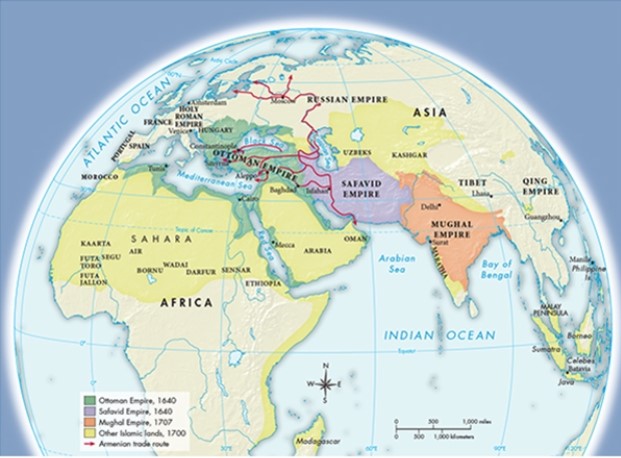
A) Ottoman and Safavid
B) Mughal and Russian
C) Holy Roman and Ottoman
D) Safavid and Russian

A) Ottoman and Safavid
B) Mughal and Russian
C) Holy Roman and Ottoman
D) Safavid and Russian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As illustrated in Map 17.4,"The Muslim World, ca. 1700," Armenian traders traversed a path through the Russian Empire similar to that used by which of the following? 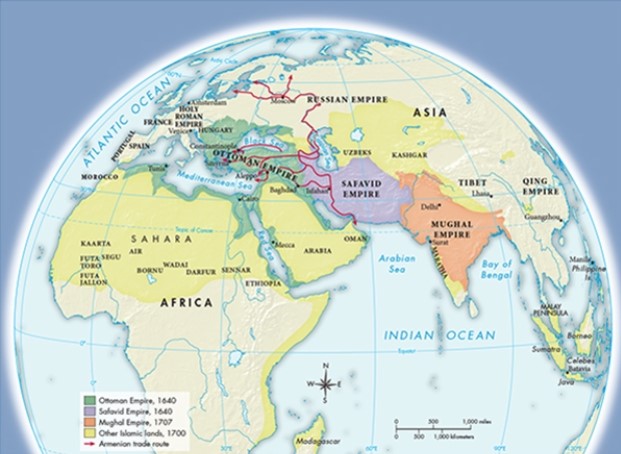
A) The Magyars
B) The Vikings
C) The Huns
D) The Muslims

A) The Magyars
B) The Vikings
C) The Huns
D) The Muslims

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What important group did Selim bring under Ottoman control?
A) Most Arab people
B) All of Europe's Orthodox Christians
C) All of the former Mongol territory
D) All Silk Road merchants
A) Most Arab people
B) All of Europe's Orthodox Christians
C) All of the former Mongol territory
D) All Silk Road merchants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Where did the Turks originate?
A) Anatolia
B) Mongolia
C) Persia
D) Siberia
A) Anatolia
B) Mongolia
C) Persia
D) Siberia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In 1453, the Ottomans conquered what capital city?
A) Kavala
B) Thrace
C) Constantinople
D) Achi Baba
A) Kavala
B) Thrace
C) Constantinople
D) Achi Baba

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which leader extended Ottoman dominion to its widest geographical extent?
A) Suleiman
B) Osman
C) Mehmet
D) Selim
A) Suleiman
B) Osman
C) Mehmet
D) Selim

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What was Lütfi Paşa's contribution to Ottoman society?
A) He reconciled Sunni and Shi'a beliefs.
B) He introduced gunpowder weapons.
C) He authored an Ottoman national epic.
D) He created a reformed law code.
A) He reconciled Sunni and Shi'a beliefs.
B) He introduced gunpowder weapons.
C) He authored an Ottoman national epic.
D) He created a reformed law code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What did being an imperial slave in the Ottoman Empire mean for those individuals?
A) They always had a feeling of uncertainty about their social status.
B) They were never allowed to marry or have children.
C) They possessed great social prestige, as well as the chance to acquire power and wealth.
D) They were given the privilege of practicing Christianity at court.
A) They always had a feeling of uncertainty about their social status.
B) They were never allowed to marry or have children.
C) They possessed great social prestige, as well as the chance to acquire power and wealth.
D) They were given the privilege of practicing Christianity at court.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the Balkans, the Ottomans saw themselves as protectors of which of the following?
A) The Orthodox Church and Orthodox Christians
B) The Holy Roman Empire
C) Serbian culture
D) Bosnian monasteries
A) The Orthodox Church and Orthodox Christians
B) The Holy Roman Empire
C) Serbian culture
D) Bosnian monasteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How did Aurangzeb anger many of his subjects?
A) He failed to conquer Bengal.
B) His Islamic zealotry troubled his non-Muslim subjects.
C) He insisted on speaking Persian all the time.
D) He spent vast sums of money on concubines.
A) He failed to conquer Bengal.
B) His Islamic zealotry troubled his non-Muslim subjects.
C) He insisted on speaking Persian all the time.
D) He spent vast sums of money on concubines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Sikh movement, which began in the sixteenth century, was influenced by what other religious movement?
A) Sufi Islam
B) Shi'a fanaticism
C) Coptic Christianity
D) Kabbalah mysticism
A) Sufi Islam
B) Shi'a fanaticism
C) Coptic Christianity
D) Kabbalah mysticism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Where did Shah Jahan found a new Indian capital city in 1639?
A) Fatehpur Sikri
B) Delhi
C) Calcutta
D) Agra
A) Fatehpur Sikri
B) Delhi
C) Calcutta
D) Agra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Where was the Sikh movement most successful?
A) Afghanistan
B) Anatolia
C) Sri Lanka
D) Northwest India
A) Afghanistan
B) Anatolia
C) Sri Lanka
D) Northwest India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What inspired Akbar to build the city of Fatehpur Sikri?
A) His victory at Bengal
B) The birth of his son Jahangir
C) His marriage to a Hindu
D) His competition with Suleiman's building projects
A) His victory at Bengal
B) The birth of his son Jahangir
C) His marriage to a Hindu
D) His competition with Suleiman's building projects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following was an important feature of the governing of the Mughal Empire under Akbar?
A) Akbar relied exclusively on the military for control.
B) All business was conducted in Turkish as the state language.
C) Akbar discouraged religious or ethnic factions at court.
D) Slaves filled most administrative positions.
A) Akbar relied exclusively on the military for control.
B) All business was conducted in Turkish as the state language.
C) Akbar discouraged religious or ethnic factions at court.
D) Slaves filled most administrative positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What was an important feature of Akbar's religious policy?
A) It featured an acceptance of various religious beliefs.
B) It was strongly anti-Semitic.
C) It provided for a prominent role for Buddhists in the state.
D) It called for the forced conversion of Hindus to Shi'ite Islam.
A) It featured an acceptance of various religious beliefs.
B) It was strongly anti-Semitic.
C) It provided for a prominent role for Buddhists in the state.
D) It called for the forced conversion of Hindus to Shi'ite Islam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Book of the Sea was a collection of what?
A) Poems
B) Maps
C) Military treatises
D) Laws
A) Poems
B) Maps
C) Military treatises
D) Laws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Based on the evidence in Map 17.3, "India, 1707-1805," what did the British East India Company share in common with others who traded in spices, slaves, precious metals, and material goods? 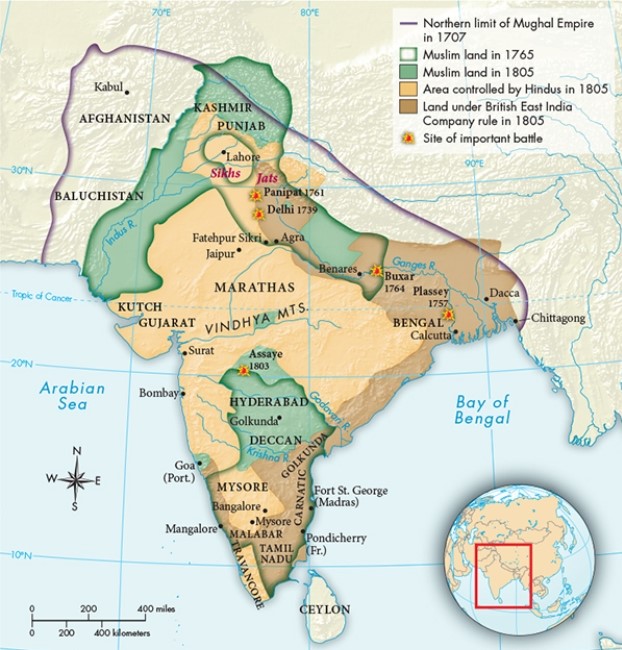
A) They dominated overland trade routes into northern India.
B) They maintained a strong alliance with Muslims at key strategic points.
C) They all managed to avoid major armed conflict.
D) They all relied heavily upon the strength of their maritime fleets.

A) They dominated overland trade routes into northern India.
B) They maintained a strong alliance with Muslims at key strategic points.
C) They all managed to avoid major armed conflict.
D) They all relied heavily upon the strength of their maritime fleets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In 1454, European rabbi Isaac Sarfati encouraged Jews to migrate to what state, because of its official policy of toleration?
A) The Holy Roman Empire
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) The Byzantine Empire
D) Mughal India
A) The Holy Roman Empire
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) The Byzantine Empire
D) Mughal India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To where have Arabs traced the first use of coffee?
A) To coffee houses in Istanbul
B) To Sufi religious rituals in Yemen
C) To Yemeni plantations to increase the productivity of African slaves
D) To pilgrims who drank it on their journey to Mecca
A) To coffee houses in Istanbul
B) To Sufi religious rituals in Yemen
C) To Yemeni plantations to increase the productivity of African slaves
D) To pilgrims who drank it on their journey to Mecca

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Shah Jahan built the Taj Mahal as a monument to whom?
A) His new son Jahangir
B) Himself and his rule
C) His favorite wife, who died in childbirth
D) His faith and Muhammad
A) His new son Jahangir
B) Himself and his rule
C) His favorite wife, who died in childbirth
D) His faith and Muhammad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why were women and children often employed in the manufacture of Persian rugs?
A) Shari'a law banned adult men from such demeaning work.
B) The smaller hands of women and children were better at tying tiny knots.
C) They were thought to have a superior aesthetic sense.
D) Most men were conscripted into the Abbasid military.
A) Shari'a law banned adult men from such demeaning work.
B) The smaller hands of women and children were better at tying tiny knots.
C) They were thought to have a superior aesthetic sense.
D) Most men were conscripted into the Abbasid military.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What practice did Shah Abbas of the Safavids adopt from the Ottomans?
A) He promoted Shi'ism and persecuted the Sunni ulama.
B) He refused marriage and had only slave concubines.
C) He built an army of slaves.
D) He allowed nobles to own their land.
A) He promoted Shi'ism and persecuted the Sunni ulama.
B) He refused marriage and had only slave concubines.
C) He built an army of slaves.
D) He allowed nobles to own their land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of these did Akbar use to help govern his vast empire?
A) A system of imperial governors called satraps
B) A representative legislature
C) Four co-equal ministers
D) A rotating set of advisers selected by lottery
A) A system of imperial governors called satraps
B) A representative legislature
C) Four co-equal ministers
D) A rotating set of advisers selected by lottery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to Map 17.1, "The Ottoman Empire at Its Height, 1566," the far eastern portion of the Ottoman Empire occupied territory that was once part of which ancient civilization? 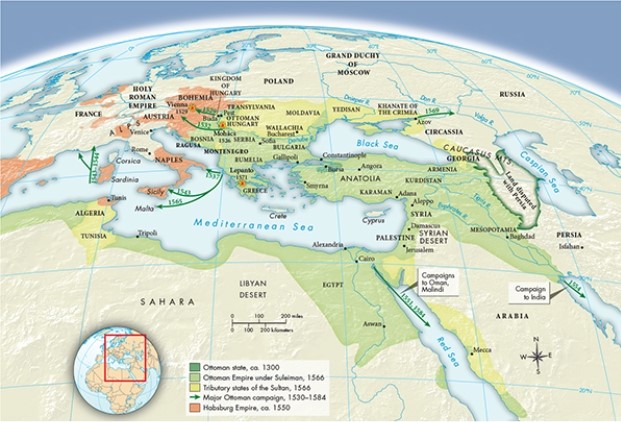
A) Egypt
B) Mauryan
C) Mesopotamia
D) Etruscan

A) Egypt
B) Mauryan
C) Mesopotamia
D) Etruscan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What did Aurangzeb do in his attempts to enforce a more Islamic culture?
A) He outlawed Hinduism and Buddhism.
B) He gave a bonus to anyone who converted to Islam.
C) He converted the Taj Mahal into a mosque.
D) He forbade sati and abolished all taxes not authorized by Islamic law.
A) He outlawed Hinduism and Buddhism.
B) He gave a bonus to anyone who converted to Islam.
C) He converted the Taj Mahal into a mosque.
D) He forbade sati and abolished all taxes not authorized by Islamic law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The interactions between the subjects of this illustration reflect which of the following?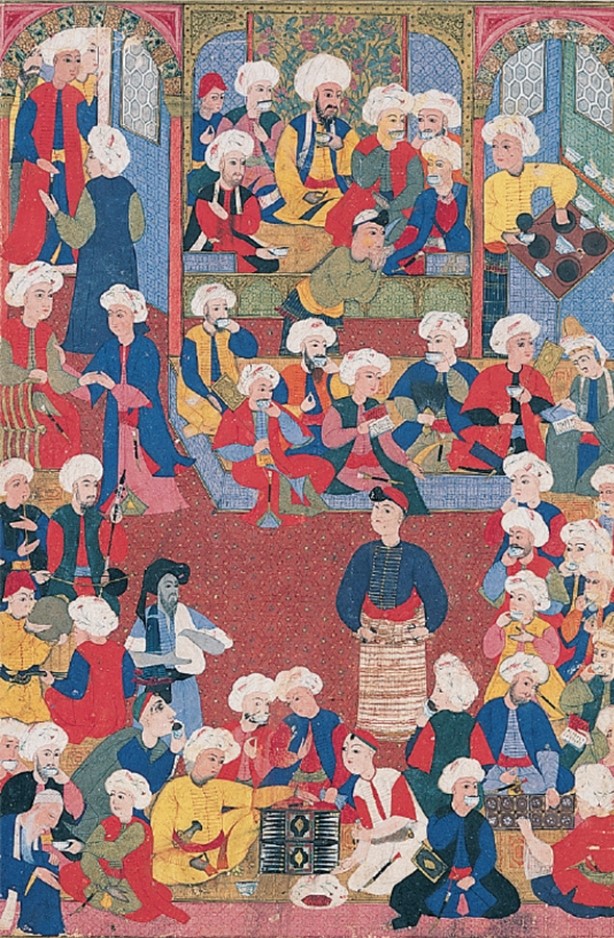 
A) The belief that coffeehouses encouraged male sociability
B) The belief that coffee was intoxicating
C) The belief that coffee drinking could lead to sedition
D) The belief that coffee drinking fostered greater concentration on God

A) The belief that coffeehouses encouraged male sociability
B) The belief that coffee was intoxicating
C) The belief that coffee drinking could lead to sedition
D) The belief that coffee drinking fostered greater concentration on God

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which was the largest and wealthiest of the three Islamic empires of the early modern world?
A) Ottoman Empire
B) Mughal Empire
C) Safavid Empire
D) Persian Empire
A) Ottoman Empire
B) Mughal Empire
C) Safavid Empire
D) Persian Empire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What happened to the Mughal ruler Humayun after he lost most of the Mughal territory in Afghanistan?
A) He was exiled to Persia.
B) He was captured by the Safavid army.
C) He hid in caves in northern India until his army prevailed.
D) He immediately went to Afghanistan to reclaim it and was killed in battle.
A) He was exiled to Persia.
B) He was captured by the Safavid army.
C) He hid in caves in northern India until his army prevailed.
D) He immediately went to Afghanistan to reclaim it and was killed in battle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What were the causes of the wars between the Ottomans and Safavids in the sixteenth century?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 1739, the Mughal army was defeated in battle by Nadir Shah, who was from where?
A) The Ottoman Empire
B) Afghanistan
C) Marathas
D) Persia
A) The Ottoman Empire
B) Afghanistan
C) Marathas
D) Persia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Akbar's reign has been characterized as the "Golden Age of India." Why? Why did the Mughal Empire ultimately collapse?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Explain the significance, both short and long term, of the code of laws created under Suleiman I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How did the Ottomans view the coffeehouses that became popular in the sixteenth century?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What did Shah Abbas force the merchant community of Julfa to do after he conquered Armenia?
A) Become Muslims
B) Move to Isfahan
C) Sell silk only to him
D) Trade cotton as well
A) Become Muslims
B) Move to Isfahan
C) Sell silk only to him
D) Trade cotton as well

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How was the British East India Company able to enter the Indian spice trade?
A) It achieved a naval victory over the Portuguese.
B) It built an alliance with the Dutch East India Company.
C) It established a fort at Bombay that overran the country.
D) It received a grant from Emperor Jahangir.
A) It achieved a naval victory over the Portuguese.
B) It built an alliance with the Dutch East India Company.
C) It established a fort at Bombay that overran the country.
D) It received a grant from Emperor Jahangir.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How extensive was the Indian cloth trade in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries? Who profited from the trade and how?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How did Armenian merchants build and maintain their trade networks?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why was Akbar more tolerant of other religions than other Islamic leaders? How did he express his tolerance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What was India's chief export to Europe?
A) Rice
B) Silver jewelry
C) Wheat
D) Cotton cloth
A) Rice
B) Silver jewelry
C) Wheat
D) Cotton cloth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
After the reign of Suleiman, the Ottoman inheritance system changed so that the sons of the sultan were
A) sent to the provinces for training.
B) fostered in the Mughal court.
C) educated in madrasas in Mecca.
D) raised in the harems.
A) sent to the provinces for training.
B) fostered in the Mughal court.
C) educated in madrasas in Mecca.
D) raised in the harems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Treaty of Paris in 1763 gave control of India to whom?
A) The French
B) The Mughals
C) The Portuguese
D) The British
A) The French
B) The Mughals
C) The Portuguese
D) The British

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Describe, in general terms, the expansion of the Ottoman Empire up to 1683. In what ways did this expansion transform the Ottoman state into a world power?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Who controlled the spice trade in the Indian Ocean throughout the sixteenth century?
A) Portugal
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) The Mughal Empire
D) China
A) Portugal
B) The Ottoman Empire
C) The Mughal Empire
D) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Discuss the symbolic importance of gardens in Islamic art, architecture, and literature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What was the actual purpose of the Dutch East India Company?
A) To colonize the Indian subcontinent
B) To take over the spice trade from Portugal
C) To convert the Indians to Christianity
D) To open the Indian market to Dutch exports such as wine and oil
A) To colonize the Indian subcontinent
B) To take over the spice trade from Portugal
C) To convert the Indians to Christianity
D) To open the Indian market to Dutch exports such as wine and oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How did Hastings, Cornwallis, and Wellesley extend British rule in India?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What was the main reason for the fall of the Safavid Empire?
A) Insufficient trade with foreigners
B) A lack of religious unity
C) A weak military
D) The aggressive Mughals
A) Insufficient trade with foreigners
B) A lack of religious unity
C) A weak military
D) The aggressive Mughals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For the British East India Company, who were the sepoys?
A) British sailors
B) Armenian merchants
C) Native Indian troops
D) Sufi mystics
A) British sailors
B) Armenian merchants
C) Native Indian troops
D) Sufi mystics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The text refers to Ottoman Turkey, Safavid Persia, and Mughal India as world powers. How accurate is this assertion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions :
Qizilbash
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
Qizilbash
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
devshirme
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
devshirme
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions :
viziers
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
viziers
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
sultan
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
sultan
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions :
Ottomans
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
Ottomans
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions :
concubine
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
concubine
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
ulama
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
ulama
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How did Suleiman, Abbas, and Akbar use monumental buildings to establish and display the wealth and power of their empires?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions :
sepoys
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
sepoys
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
Mughal
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
Mughal
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Compare the careers and accomplishments of Sultan Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire and Shah Akbar of the Mughal Empire. Which ruler seems to have been more successful?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer questions :
shah
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
shah
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What were the common weaknesses in the three Islamic empires that contributed to their demise?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Describe the European takeover of India. What were causative factors in this process? To what extent can we argue that the Europeans were acting imperialistically?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions :
janissaries
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
janissaries
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer questions :
Safavid
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.
Safavid
A)Ruling house of the Turkish empire that lasted from 1299 to 1922.
B)An Arabic word originally used by the Ottomans to describe a supreme political and military ruler.
C)Chief assistants to caliphs.
D)A process whereby the sultan's agents swept the provinces for Christian youths to be trained as soldiers or civil servants.
E)Turkish for "recruits"; they formed the elite army corps.
F)A woman who is a recognized spouse but of lower status than a wife.
G)Persian word for "king."
H)The dynasty that ruled all of Persia and other regions from 1501 to 1722; its state religion was Shi'ism.
I)Nomadic Turkish Sufis who supplied the early Safavid state with military troops in exchange for grazing rights.
J)Religious scholars who interpret the Qur'an and the Sunna, the deeds and sayings of Muhammad.
K)A term used to refer to the Muslim empire of India, which was the largest, wealthiest, and most populous of the Islamic empires of the early modern world.
L)The native Indian troops who were trained as infantrymen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



