Deck 3: Finding Relationships Among Variables
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Finding Relationships Among Variables
1
If the sample is a good representation of the population, what percentage of the students in the population should we expect to spend the weekend studying and do poorly on the final exam?
15 out of 150, or 10%
2
We must specify appropriate bins for side-by-side histograms in order to make fair comparisons of distributions by category.
True
3
What percentage of the students in the sample spent the weekend studying and did well in the final exam?
60 out of 150, or 40%
4
Side-by-side box plots allow you to quickly see how two or more categories of a numerical variable compare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Comparing a numerical variable across two or more subpopulations is known as a comparison problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which Excel® function allows you to count using more than one criterion?
A) COUNTIF
B) COUNTIFS
C) SUMPRODUCT
D) VLOOKUP
E) HLOOKUP
A) COUNTIF
B) COUNTIFS
C) SUMPRODUCT
D) VLOOKUP
E) HLOOKUP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Of those in the sample who went partying the weekend before the final exam, what percentage of them did poorly in the exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A sample of 150 students at a state university was taken after the final business statistics exam to ask them whether they went partying the weekend before the final or spent the weekend studying, and whether they did well or poorly on the final. The following table contains the result. 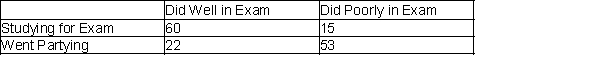
Of those in the sample who did well on the final exam, what percentage of them went partying the weekend before the exam?

Of those in the sample who did well on the final exam, what percentage of them went partying the weekend before the exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What percentage of the students in the sample went partying the weekend before the final exam and did well in the exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A sample of 150 students at a state university was taken after the final business statistics exam to ask them whether they went partying the weekend before the final or spent the weekend studying, and whether they did well or poorly on the final. The following table contains the result. 
Of those in the sample who went partying the weekend before the final exam, what percentage of them did well in the exam?

Of those in the sample who went partying the weekend before the final exam, what percentage of them did well in the exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the sample is a good representation of the population, what percentage of those who spent the weekend studying should we expect to do poorly on the final exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Examples of comparison problems include:
A) salary broken down by male and female subpopulations
B) cost of living broken down by region of a country
C) recovery rate for a disease broken down by patients who have taken a drug and patients who have taken a placebo
D) starting salary of recent graduates broken down by academic major
E) all of these choices
A) salary broken down by male and female subpopulations
B) cost of living broken down by region of a country
C) recovery rate for a disease broken down by patients who have taken a drug and patients who have taken a placebo
D) starting salary of recent graduates broken down by academic major
E) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most common data format is:
A) long
B) short
C) stacked
D) unstacked
A) long
B) short
C) stacked
D) unstacked

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A useful way of comparing the distribution of a numerical variable across categories of some categorical variable is with:
A) a side-by-side box plot
B) a side-by-side pivot table
C) a side-by-side plot or side-by-side pivot table
D) neither a side-by-side box plot nor side-by-side pivot table
A) a side-by-side box plot
B) a side-by-side pivot table
C) a side-by-side plot or side-by-side pivot table
D) neither a side-by-side box plot nor side-by-side pivot table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the sample is a good representation of the population, what percentage of those who did poorly on the final exam should we expect to have spent the weekend studying?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Tables used to display counts of a categorical variable are called:
A) crosstabs
B) contingency tables
C) either crosstabs or contingency tables
D) neither crosstabs nor contingency tables
A) crosstabs
B) contingency tables
C) either crosstabs or contingency tables
D) neither crosstabs nor contingency tables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What percentage of the students in the sample went partying the weekend before the final exam and did poorly on the exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An example of a joint category of two variables is the count of all non-drinkers who are also nonsmokers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To examine relationships between two categorical variables, we can use:
A) counts and corresponding charts of the counts
B) scatter plots
C) histograms
D) none of these choices
A) counts and corresponding charts of the counts
B) scatter plots
C) histograms
D) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Of those in the sample who did well in the final exam, what percentage of them spent the weekend before the exam studying?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
We cannot attempt to interpret correlations numerically, with the one possible exception of indicating whether they are positive or negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Strongly related variables may have a correlation close to zero if the relationship is nonlinear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Correlation can be affected by the measurement scales applied to X and Y variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The correlation between two variables is unitless and always between -1 and +1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following are considered numerical summary measures?
A) mean and variance
B) variance and correlation
C) correlation and covariance
D) covariance and variance
E) first quartile and third quartile
A) mean and variance
B) variance and correlation
C) correlation and covariance
D) covariance and variance
E) first quartile and third quartile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Displaying all correlations between 0.6 and 0.999 on a scatterplot as green and all correlations between -1.0 and -0.6 as red is known as:
A) rank-order formatting
B) categorical formatting
C) conditional formatting
D) numerical formatting
A) rank-order formatting
B) categorical formatting
C) conditional formatting
D) numerical formatting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The limitation of covariance as a descriptive measure of association is that it
A) only captures positive relationships
B) does not capture the units of the variables
C) is very sensitive to the units of the variables
D) is invalid if one of the variables is categorical
E) none of these options
A) only captures positive relationships
B) does not capture the units of the variables
C) is very sensitive to the units of the variables
D) is invalid if one of the variables is categorical
E) none of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the standard deviations of X and Y are 15.5 and 10.8, respectively, and the covariance of X and Y is 128.8, then the correlation coefficient is approximately 0.77.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Correlation is a single-number summary of a scatterplot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A line or curve superimposed on a scatterplot to quantify an apparent relationship is known as a(n):
A) average
B) trend line
C) data point
D) positive variable
E) slope
A) average
B) trend line
C) data point
D) positive variable
E) slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Scatterplots are also referred to as:
A) crosstabs
B) contingency charts
C) X-Y charts
D) all of these choices
E) none of these choices
A) crosstabs
B) contingency charts
C) X-Y charts
D) all of these choices
E) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
We can infer that there is a strong relationship between two numerical variables when:
A) the points on a scatterplot cluster tightly around an upward sloping straight line
B) the points on a scatterplot cluster tightly around a downward sloping straight line
C) both of these choices
D) neither of these choices
A) the points on a scatterplot cluster tightly around an upward sloping straight line
B) the points on a scatterplot cluster tightly around a downward sloping straight line
C) both of these choices
D) neither of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
We study relationships among numerical variables using:
A) correlation
B) covariance
C) scatterplot charts
D) all of these choices
E) none of these choices
A) correlation
B) covariance
C) scatterplot charts
D) all of these choices
E) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which correlation coefficient suggests the strongest relationship?
A) +1
B) -0.1
C) 0
D) +0.5
A) +1
B) -0.1
C) 0
D) +0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the correlation of variables is close to 0, then we expect to see:
A) an upward sloping cluster of points on the scatterplot
B) a downward sloping cluster of points on the scatterplot
C) a cluster of points around a trendline on the scatterplot
D) a cluster of points with no apparent relationship on the scatterplot
E) no explanation of how the scatterplot looks based on the correlation
A) an upward sloping cluster of points on the scatterplot
B) a downward sloping cluster of points on the scatterplot
C) a cluster of points around a trendline on the scatterplot
D) a cluster of points with no apparent relationship on the scatterplot
E) no explanation of how the scatterplot looks based on the correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Correlation is useful only for:
A) assessing the weakness of a linear relationship
B) conveying the same information in a simpler format than a scatterplot
C) measuring the strength of a linear relationship
D) automatically calculating covariances
E) measuring the strength of a nonlinear relationship
A) assessing the weakness of a linear relationship
B) conveying the same information in a simpler format than a scatterplot
C) measuring the strength of a linear relationship
D) automatically calculating covariances
E) measuring the strength of a nonlinear relationship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Correlation and covariance measure:
A) the strength of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
B) the direction of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
C) the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
D) the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two categorical variables
E) none of these choices
A) the strength of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
B) the direction of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
C) the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two numerical variables
D) the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two categorical variables
E) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One characteristic of "paired variables" is that:
A) one variable is a negative value and the other is a positive value
B) both variables are positive values
C) each variable has the same number of observations
D) each variable has a different number of observations
A) one variable is a negative value and the other is a positive value
B) both variables are positive values
C) each variable has the same number of observations
D) each variable has a different number of observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The cutoff for defining a large correlation is 0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To form a scatterplot of X versus Y, X and Y must be paired variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An economic development researcher wants to understand the relationship between the average monthly expenditure on utilities for households in a particular middle-class neighborhood and each of the following household variables: family size, approximate location of the household within the neighborhood, and indication of whether those surveyed owned or rented their home, gross annual income of the first household wage earner, gross annual income of the second household wage earner (if applicable), size of the monthly home mortgage or rent payment, and the total indebtedness (excluding the value of a home mortgage) of the household.
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations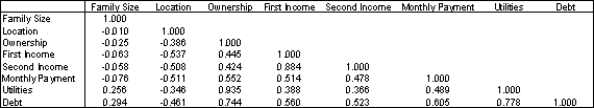
Which of the variables have a positive linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations

Which of the variables have a positive linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What other data would you need to be more confident that increased income inequality leads to lower unemployment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An economic development researcher wants to understand the relationship between the average monthly expenditure on utilities for households in a particular middle-class neighborhood and each of the following household variables: family size, approximate location of the household within the neighborhood, and indication of whether those surveyed owned or rented their home, gross annual income of the first household wage earner, gross annual income of the second household wage earner (if applicable), size of the monthly home mortgage or rent payment, and the total indebtedness (excluding the value of a home mortgage) of the household.
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations
Which of the variables have essentially no linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations

Which of the variables have essentially no linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Below you will find current annual salary data and related information for 30 employees at Gamma Technologies, Inc. These data include each selected employees gender (1 for female; 0 for male), age, number of years of relevant work experience prior to employment at Gamma, number of years of employment at Gamma, the number of years of post-secondary education, and annual salary. The tables of correlations and covariances are presented below.
Table of Correlations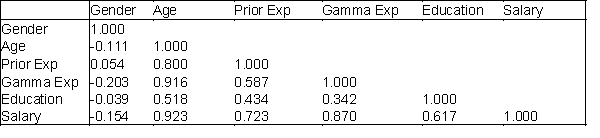 Table of Covariances (variances on the diagonal)
Table of Covariances (variances on the diagonal) 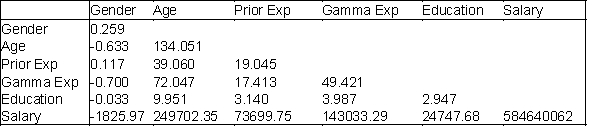
Which two variables have the strongest linear relationship with annual salary?
Table of Correlations
 Table of Covariances (variances on the diagonal)
Table of Covariances (variances on the diagonal) 
Which two variables have the strongest linear relationship with annual salary?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For which of the two variables, number of years of prior work experience or number of years of post-secondary education, is the relationship with salary stronger? Justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose that the table shown below contains information technology (IT) investment as a percentage of total investment for eight countries during a recent decade. It also contains the average annual percentage change in employment during this decade. Explain how these data shed light on the question of whether IT investment creates or costs jobs. (Hint: Use the data to construct a scatterplot.) 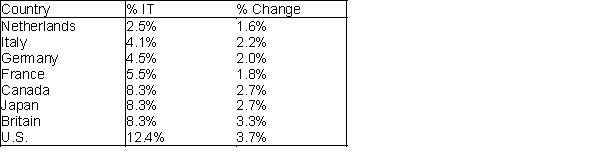


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Economists believe that historically, countries with more income inequality have had lower unemployment rates. For example, an economist in 1996 developed the table below containing the following information for 10 countries during the 1980-1995 time period:
· The change from 1980 to 1995 in ratio of the average wage of the top 10% of all wage earners to the median wage
· The change from 1980 to 1995 in unemployment rate.
Income inequality vs. Unemployment rate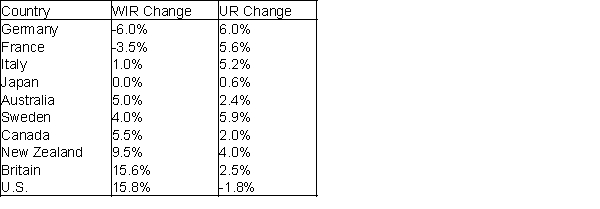
Explain why the ratio of the average wage of the top 10% of all wage earners to the median measures income inequality.
· The change from 1980 to 1995 in ratio of the average wage of the top 10% of all wage earners to the median wage
· The change from 1980 to 1995 in unemployment rate.
Income inequality vs. Unemployment rate

Explain why the ratio of the average wage of the top 10% of all wage earners to the median measures income inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What does a scatterplot illustrate?
A) whether there is any relationship between two variables
B) what type of relationship there is between two variables
C) both of these choices
D) neither of these choices
A) whether there is any relationship between two variables
B) what type of relationship there is between two variables
C) both of these choices
D) neither of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Data has been collected on store size in square feet and profit per square foot, yielding the following observations: 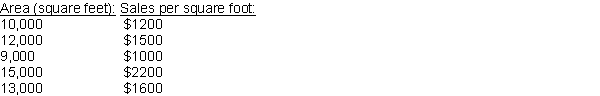 How is the value of the correlation affected in each of the following cases?
How is the value of the correlation affected in each of the following cases?
a) Each X value is multiplied by 4.
b) Each X value is switched with the corresponding Y value.
c) Each X value is increased by 2.
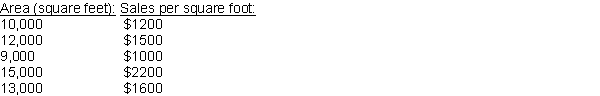 How is the value of the correlation affected in each of the following cases?
How is the value of the correlation affected in each of the following cases?a) Each X value is multiplied by 4.
b) Each X value is switched with the corresponding Y value.
c) Each X value is increased by 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
It is possible that the data points close to a curve have a correlation close to 0, because correlation is relevant only for measuring linear relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the coefficient of correlation r = 0 .80, the standard deviations of X and Y are 20 and 25, respectively, then Cov(X, Y) must be 400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Do these data help to confirm or contradict the hypothesis that increased wage inequality is associated with lower unemployment levels? [Hint: construct a scatterplot.]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following scatterplot compares the selling price and the appraised value. 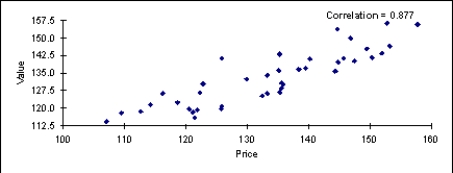 Is there a linear relationship between these two variables? If so, how would you characterize the relationship?
Is there a linear relationship between these two variables? If so, how would you characterize the relationship?
 Is there a linear relationship between these two variables? If so, how would you characterize the relationship?
Is there a linear relationship between these two variables? If so, how would you characterize the relationship?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
There are two scatterplots shown below. The first chart shows the relationship between the size of the home and the selling price. The second chart examines the relationship between the number of bedrooms in the home and its selling price. Which of these two variables (the size of the home or the number of bedrooms) seems to have the stronger relationship with the home's selling price? Justify your answer. 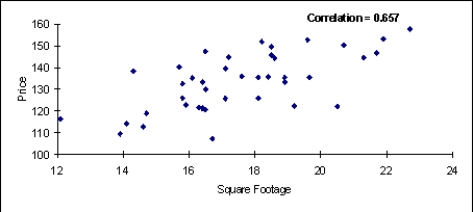
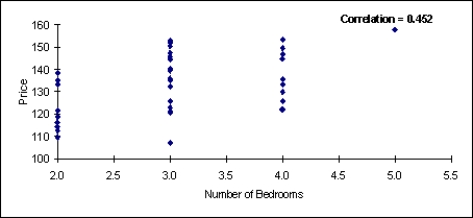



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the standard deviation of X is 15, the covariance of X and Y is 94.5, and the correlation is 0.90, then the variance of Y is 7.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose that the percentage of a country's population without health insurance coverage based on samples from all its regions for both 2016 and 2017 produced the following table of correlations.
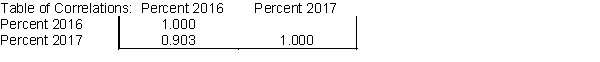
What does the table for the two given sets of percentages tell you in this case?
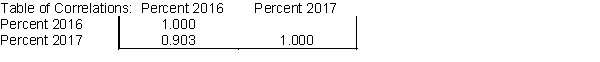
What does the table for the two given sets of percentages tell you in this case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How would you characterize the relationship between gender and annual salary?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The scatterplot is a graphical technique used to indicate the relationship between two numerical variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The advantage that correlation has over covariance is that the former has a set lower and upper limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An economic development researcher wants to understand the relationship between the average monthly expenditure on utilities for households in a particular middle-class neighborhood and each of the following household variables: family size, approximate location of the household within the neighborhood, and indication of whether those surveyed owned or rented their home, gross annual income of the first household wage earner, gross annual income of the second household wage earner (if applicable), size of the monthly home mortgage or rent payment, and the total indebtedness (excluding the value of a home mortgage) of the household.
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations
Which of the variables have a negative linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?
The correlation for each pairing of variables are shown in the table below:
Table of correlations

Which of the variables have a negative linear relationship with the household's average monthly expenditure on utilities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A recent survey collected data from 1000 randomly selected Internet users. The characteristics of the users include their gender, age, education, marital status, and annual income. Using Excel®, the following pivot tables are produced.
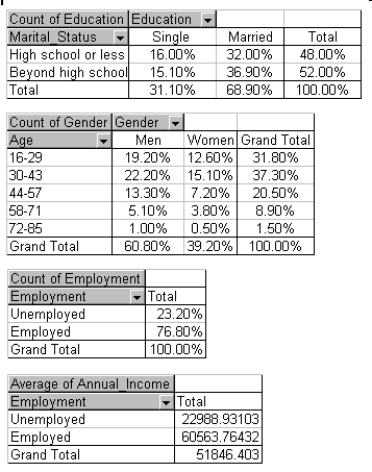
Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are men under the age of 30.

Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are men under the age of 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A sample of 30 schools produced the pivot table shown below for the average percentage of students graduating from high school. Use this table to determine how the type of school (public or Catholic) that students attend affects their chance of graduating from high school. 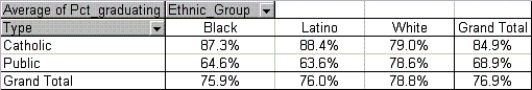


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A recent survey collected data from 1000 randomly selected Internet users. The characteristics of the users include their gender, age, education, marital status, and annual income. Using Excel®, the following pivot tables are produced.

Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are currently employed.

Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are currently employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that a health magazine reports that a man's weight at birth has a significant impact on the chance that the man will suffer a heart attack during his life. A statistician analyzes a data set from a sample of 798 men, and produces the pivot table and histogram shown below. Determine how birth weight influences the chances that a man will have a heart attack. 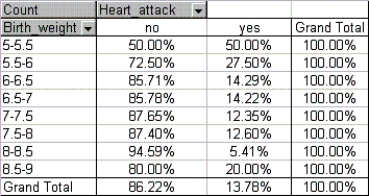
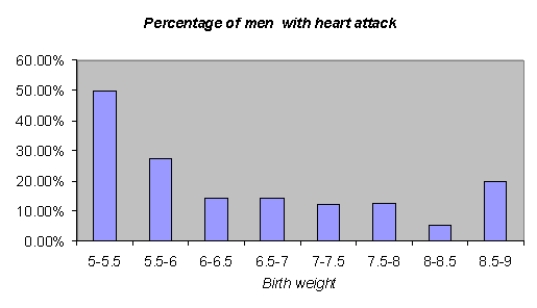



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Relationships between two variables are less evident when counts are expressed as percentages of row totals or column totals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A data set from a sample of 399 Michigan families was collected. The data include family size (large or small), number of cars owned by family (1, 2, 3, or 4), and whether family owns a foreign car. Excel® produced the pivot table shown below. 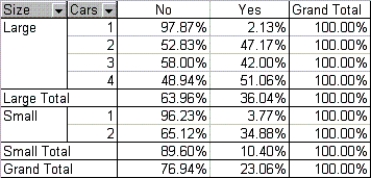 Use this pivot table to determine how family size and number of cars owned influence the likelihood that a family owns a foreign car.
Use this pivot table to determine how family size and number of cars owned influence the likelihood that a family owns a foreign car.
 Use this pivot table to determine how family size and number of cars owned influence the likelihood that a family owns a foreign car.
Use this pivot table to determine how family size and number of cars owned influence the likelihood that a family owns a foreign car.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A recent survey collected data from 1000 randomly selected Internet users. The characteristics of the users include their gender, age, education, marital status, and annual income. Using Excel®, the following pivot tables are produced.

Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are single with no formal education beyond high school.

Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are single with no formal education beyond high school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The students at a small community college in Iowa apply to study either English or Business. Some administrators at the college are concerned that women are being discriminated against in being allowed admittance, particularly in the business program. Below, you will find two pivot tables that show the percentage of students admitted by gender to the English program and the Business school. The data has also been presented graphically. What do the data and graphs indicate? 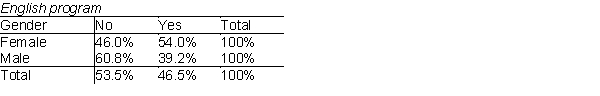
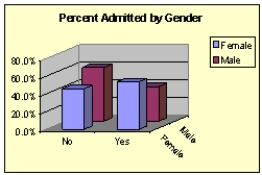 Business school
Business school 
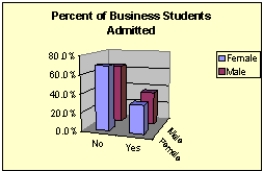

 Business school
Business school 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Changing the location of fields in a pivot table is known as:
A) slicing
B) dicing
C) sorting
D) pivoting
A) slicing
B) dicing
C) sorting
D) pivoting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The four areas of a pivot table are:
A) Crosstabs, Fields, Rows, and Columns
B) Data, Count, Contingency, and Percentage
C) Filters, Rows, Columns, and Values
D) Sort, Rows, Columns, and Count
A) Crosstabs, Fields, Rows, and Columns
B) Data, Count, Contingency, and Percentage
C) Filters, Rows, Columns, and Values
D) Sort, Rows, Columns, and Count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Filters field of a pivot table contains the data that you want summarized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the average annual salary of the employed Internet users in this sample?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Statisticians often refer to the pivot tables that display counts as contingency tables or crosstabs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A trend line on a scatterplot is a line or a curve that "fits" the scatter as well as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are married with formal education beyond high school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Correlation and covariance can be used to examine relationships between numerical variables as well as for categorical variables that have been coded numerically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Approximate the percentage of these Internet users who are married.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The tool that provides useful information about a data set by breaking it down into categories is the:
A) histogram
B) scatterplot
C) pivot table
D) spreadsheet
A) histogram
B) scatterplot
C) pivot table
D) spreadsheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The tables of counts that result from pivot tables are often called:
A) samples
B) sub-tables
C) specimens
D) crosstabs
A) samples
B) sub-tables
C) specimens
D) crosstabs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Counts for categorical variable are often expressed as percentages of the total.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



