Deck 20: Statistical Process Control
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Statistical Process Control
1
The 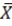 chart charts the averages of small subsamples through time.
chart charts the averages of small subsamples through time.
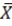 chart charts the averages of small subsamples through time.
chart charts the averages of small subsamples through time.True
2
Out-of control indicators may include a number of conditions. What is not one of these?
A) at least 8 upward (or downward) consecutive changes
B) at least 8 consecutive points above (or below) the centerline
C) at least 1 point beyond two standard deviations from the centerline
D) at least 4 of 5 consecutive points beyond one standard deviation from the centerline
A) at least 8 upward (or downward) consecutive changes
B) at least 8 consecutive points above (or below) the centerline
C) at least 1 point beyond two standard deviations from the centerline
D) at least 4 of 5 consecutive points beyond one standard deviation from the centerline
at least 1 point beyond two standard deviations from the centerline
3
Morgan has calculated the upper and lower limit for control limits in an 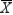 chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she determines what happens to these limits if n decreases. Suppose Morgan is now using a smaller sample size, but she has forgotten to adjust the upper and lower limits to reflect the smaller sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she determines what happens to these limits if n decreases. Suppose Morgan is now using a smaller sample size, but she has forgotten to adjust the upper and lower limits to reflect the smaller sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
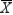 chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she determines what happens to these limits if n decreases. Suppose Morgan is now using a smaller sample size, but she has forgotten to adjust the upper and lower limits to reflect the smaller sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she determines what happens to these limits if n decreases. Suppose Morgan is now using a smaller sample size, but she has forgotten to adjust the upper and lower limits to reflect the smaller sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?The limits are narrower with larger samples, so she is likely to observe more observations that lie outside these limits. She might decide she is observing out-of-control behavior.
4
The two basic types of control charts are control charts for factors and control charts for treatments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mohammed is monitoring the diameter of bolts being produced on one of his assigned production lines. During this process, he notices one, single measurement that jumped above the upper control limit. He immediately adjusts the alignment on several machines to address the problem. Mohammed has likely committed a(n):
A) type II error
B) average run length error
C) type I error
D) type I and type II error
A) type II error
B) average run length error
C) type I error
D) type I and type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Jean is examining variation on a control chart. One of the machines was misaligned and is operated by an inexperienced worker. The variation caused by these factors is caused by ____.
A) assignable causes
B) in statistical control causes
C) common causes
D) in control causes
A) assignable causes
B) in statistical control causes
C) common causes
D) in control causes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A p chart plots the proportions of items that are conforming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Michael has incorporated a vigorous cross-training program within his department. This is an example of which of Deming's 14 points?
A) Improve Every Process.
B) Institute Training.
C) Drive Out Fear.
D) Encourage Education.
A) Improve Every Process.
B) Institute Training.
C) Drive Out Fear.
D) Encourage Education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Taveen, the production manager at Wire Express, has noticed that one of his machines seems to stall out briefly toward the end of a run. He is wondering whether this stalling is affecting the width of the wire product. He creates several control charts and notices about four consecutive points above the centerline and one point beyond two standard deviations from the centerline. How should Taveen react?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Common cause variation is the inherent variation in an in-control process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Morgan has calculated the upper and lower limit for control limits in an 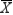 chart, and determines the out-of-control behavior she observed might be due to the fact that she was using an extremely small sample. Therefore, she quadruples her sample size, and the sample is now much larger than even her original sample. Unfortunately, she forgets to adjust the upper and lower limits again to reflect the much larger sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
chart, and determines the out-of-control behavior she observed might be due to the fact that she was using an extremely small sample. Therefore, she quadruples her sample size, and the sample is now much larger than even her original sample. Unfortunately, she forgets to adjust the upper and lower limits again to reflect the much larger sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
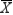 chart, and determines the out-of-control behavior she observed might be due to the fact that she was using an extremely small sample. Therefore, she quadruples her sample size, and the sample is now much larger than even her original sample. Unfortunately, she forgets to adjust the upper and lower limits again to reflect the much larger sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
chart, and determines the out-of-control behavior she observed might be due to the fact that she was using an extremely small sample. Therefore, she quadruples her sample size, and the sample is now much larger than even her original sample. Unfortunately, she forgets to adjust the upper and lower limits again to reflect the much larger sample size. What is likely to occur as she manually plots observations on the chart?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The average run length (ARL) indicates the mean length of time between:
A) false alarms in an in-control process
B) false alarms in an out-of-control process
C) out-of-control indications in an out-of-control process
D) type II errors in an in-control process
A) false alarms in an in-control process
B) false alarms in an out-of-control process
C) out-of-control indications in an out-of-control process
D) type II errors in an in-control process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
"Tampering" can actually make a system worse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Taveen, the production manager at Wire Express, has noticed that one of his machines seems to stall out briefly toward the end of a run. He is wondering whether this stalling is affecting the width of the wire product. He creates several control charts and notices about 11 consecutive points above the centerline and three points beyond two standard deviations from the centerline. How should Taveen react?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following are attributes charts?
A) p chart,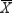 chart, and u chart
chart, and u chart
B) p chart, X chart, and u chart
C) p chart, c chart, and u chart
D) p chart, c chart, and R chart
A) p chart,
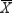 chart, and u chart
chart, and u chartB) p chart, X chart, and u chart
C) p chart, c chart, and u chart
D) p chart, c chart, and R chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Jada has decided to implement weekly meetings between departments to discuss issues that occur cross-department. She also has implemented a worker morale program aimed at building teamwork. These are both events that even the most upper management will attend. Which of Deming's 14 Points is Jada addressing?
A) Have Constancy of Purpose.
B) Embrace the New Philosophy.
C) Institute Leadership of People.
D) Break Down Barriers.
A) Have Constancy of Purpose.
B) Embrace the New Philosophy.
C) Institute Leadership of People.
D) Break Down Barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Morgan has calculated the upper and lower limit for control limits in an 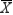 chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she is wondering what happens to these limits if n decreases. Explain what happens to the limits and why.
chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she is wondering what happens to these limits if n decreases. Explain what happens to the limits and why.
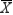 chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she is wondering what happens to these limits if n decreases. Explain what happens to the limits and why.
chart. She doesn't have the software available to create these charts automatically, so she is wondering what happens to these limits if n decreases. Explain what happens to the limits and why.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not one of Deming's 14 Points?
A) Use Lowest-Tender Contracts.
B) Have Constancy of Purpose.
C) Institute Leadership of People.
D) Break Down Barriers.
A) Use Lowest-Tender Contracts.
B) Have Constancy of Purpose.
C) Institute Leadership of People.
D) Break Down Barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The control limits for an R chart are set at:
A) one mean distance from the average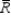
B) -1 and +1
C) approximately three standard deviations from the average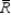
D) 0 and +1
A) one mean distance from the average
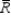
B) -1 and +1
C) approximately three standard deviations from the average
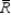
D) 0 and +1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Mohammed is monitoring the diameter of bolts that are being produced on one of his assigned production lines. During this process, he notices nine, consecutive measurements that jumped above the upper control limit. He immediately examines the machine, finds it to be misaligned, and makes a small adjustment. Mohammed has likely committed:
A) a type II error
B) both a type I and type II error
C) a type I error
D) neither a type I nor a type II error
A) a type II error
B) both a type I and type II error
C) a type I error
D) neither a type I nor a type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



