Deck 13: Comparative Forms of Doing Business
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Comparative Forms of Doing Business
1
Each of the following can pass profits and losses through to the owners: general partnership, limited partnership, S corporation, and limited liability company.
True
2
A limited liability company (LLC) cannot elect under the check-the-box rules to be taxed as an S corporation.
True
3
A limited partnership can indirectly avoid unlimited liability of the general partner if the general partner is a corporation.
True
4
The corporation has a greater potential for raising capital than does the partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All of the shareholders of an S corporation have limited liability with respect to their ownership interests in the corporation, whereas only limited partners in a limited partnership have such limited liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a C corporation has earnings and profits at least equal to the amount of a distribution, the tax consequences to the shareholders are the same, regardless of whether the distribution is classified as a dividend or as a stock redemption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Daniel, who is single, estimates that the profits of his business for the current tax year will be $100,000. Since the highest tax rate (34%) applicable to corporate taxable income of $100,000 is greater than the highest tax rate (28%) applicable to individual taxable income of $100,000, the Federal income tax liability will be less if Daniel conducts his business as a sole proprietorship rather than as a C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A C corporation offers greater flexibility in terms of the types of owners and capital structure than an S corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A corporation may alternate between S corporation and C corporation status each year, depending on which results in more tax savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a business entity has a majority of corporate characteristics, it is taxed as a corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Techniques are available that may permit a C corporation to avoid double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Lime, Inc., has taxable income of $334,000. If Lime is a C corporation, its tax liability must be either $113,510 [($50,000 × 15%) + ($25,000 × 25%) + ($25,000 × 34%) + ($234,000 × 39%)] or $116,900.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A limited partner in a limited partnership has limited liability whereas a general partner in a limited partnership has unlimited liability unless the limited partners agree that the general partner will have limited liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The § 465 at-risk provision and the § 469 passive activity loss provision have decreased the tax attractiveness of investments in real estate for partnerships and for limited liability companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In its first year of operations (2014), Lavender, Inc. (a C corporation) has gross receipts of $8 million and net income of $2 million. Lavender is not subject to the AMT for 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
S corporation status always avoids double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For Federal income tax purposes, a business entity with two or more owners may be conducted as a partnership, C corporation, S corporation, or limited liability company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A sole proprietorship files Schedule C of Form 1040, a partnership files Form 1065, a C corporation files Form 1120, and an S corporation files Form 1120S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A limited liability company (LLC) is a hybrid business form that combines the corporate characteristic of limited liability for the owners with the tax characteristics of a partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
C corporations and their shareholders are subject to double taxation. S corporations and their shareholders typically are subject to single taxation. Therefore, for any given amount of corporate taxable income, the combined tax liability of a C corporation and its shareholders will exceed that of an S corporation and its shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Transferring funds to shareholders, that are deductible by the C corporation, can reduce or eliminate double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The accumulated earnings tax rate in 2014 is greater than the highest tax rate for a C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Actual dividends paid to shareholders result in double taxation. Likewise, deemed dividends (e.g., free use of corporate assets by a shareholder) result in double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An S corporation election for Federal income tax purposes also is effective for all states' income tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Roger owns 40% of the stock of Gold, Inc. (adjusted basis of $800,000). Silver redeems 60% of Roger's shares for $900,000. If the stock redemption qualifies for return of capital treatment, Roger's recognized gain is $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the IRS reclassifies debt as equity under § 385, the repayment of the debt by the corporation to the shareholder automatically is treated as a dividend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Molly transfers land with an adjusted basis of $28,000 and a fair market value of $65,000 to the Sand Partnership for a 30% ownership interest. The land is encumbered by a mortgage of $18,000 which the partnership assumes. Her basis for her ownership interest is $10,000 ($28,000 - $18,000).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Only C corporations are subject to the accumulated earnings tax (i.e., S corporations are not).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In its first year of operations, a corporation projects losses of $400,000. Since losses are involved, the corporation definitely should elect S corporation status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Of the corporate types of entities, all are subject to double taxation on current earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A corporation can avoid the accumulated earnings tax by demonstrating that it has plans to distribute earnings at a later date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ACE adjustment associated with the C corporation AMT can be either positive or negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
C corporations and S corporations can generate an AMT adjustment known as Adjusted Current Earnings (ACE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The AMT statutory rate for C corporations and for S corporation shareholders on the AMT base is 20%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If lease rental payments to a noncorporate shareholder-lessor are classified as unreasonable, the taxable income of a C corporation increases and the gross income of the shareholder increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An effective way for all C corporations to avoid double taxation is not to make dividend distributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The AMT tax rate for a C corporation is greater than the regular tax rate for C corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Some fringe benefits always provide a double benefit-a deduction for the employer and an exclusion for the employee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An S corporation is not subject to the AMT, but its shareholders are in that the S corporation's AMT adjustments and preferences are passed through to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The tax treatment of S corporation shareholders with respect to fringe benefits is not the same as the tax treatment for C corporation shareholders but is the same as the fringe benefit treatment for partners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If an S corporation distributes appreciated property as a dividend, it must recognize gain as to the appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Section 1244 ordinary loss treatment is available to shareholders in a C corporation but not to those in an S corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The profits of a business owned by Taylor (60%) and Maggie (40%) for the current tax year are $100,000. If the business is a C corporation or an S corporation, there is no effect on Taylor's basis in her stock. If the business is a partnership or an LLC, Taylor's basis in her partnership interest or basis in her stock is increased by $60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A benefit of an S corporation when compared with a C corporation is that it is subject to Federal income tax only in limited circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
After a § 721 contribution by a partner to a partnership, the partner's basis for his or her ownership interest is the same as the basis of the assets contributed (no liabilities are involved).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
John wants to buy a business whose assets have appreciated in value. If the business is operated as a C corporation, it does not matter to John whether he purchases the assets or the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If an individual contributes an appreciated personal use asset to a C corporation in a transaction which qualifies for nonrecognition treatment under § 351, the corporation's basis in the asset is the same as was the shareholder's adjusted basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
To the extent of built-in gain or built-in loss at the time of contribution, partnerships may choose to allocate or not allocate this built-in gain or loss to the contributing partner on the sale of the contributed property by the partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Melinda's basis for her partnership interest is $250,000. If she receives a cash distribution of $290,000, her recognized gain is $40,000 and her basis for her partnership interest is reduced to $0. Melinda is still a partner after the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Wally contributes land (adjusted basis of $30,000; fair market value of $100,000) to an S corporation in a transaction which qualifies under § 351. The corporation subsequently sells the land for $120,000, recognizing a gain of $90,000 ($120,000 - $30,000). If Wally owns 30% of the stock, $76,000 [$70,000 + 30%($20,000)] of the $90,000 recognized gain is allocated to Wally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A shareholder's basis in the stock of an S corporation is increased by corporate profits and decreased by losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The § 469 passive activity loss rules apply to S corporations but not to C corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Techniques that can be used to minimize the current period tax liability include:
A) Recognizing the interaction between the regular income tax liability and the alternative minimum tax liability.
B) Utilization of special allocations.
C) Favorable treatment of certain fringe benefits.
D) Minimizing double taxation.
E) All of the above.
A) Recognizing the interaction between the regular income tax liability and the alternative minimum tax liability.
B) Utilization of special allocations.
C) Favorable treatment of certain fringe benefits.
D) Minimizing double taxation.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Mercedes owns a 30% interest in Magenta Partnership (basis of $52,000) which she sells to Calvin for $65,000. Mercedes' recognized gain of $13,000 will be classified as capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Amber, Inc., has taxable income of $212,000. In addition, Amber accumulates the following information which may affect its AMT.
∙
Depreciation on buildings placed in service in the early 1990s was $52,000. ADS would have been $41,000.
∙
The president of Amber exercised stock options on Amber stock. She paid $30,000 for the stock, which had a fair market value at exercise date of $49,000. At the end of the year, the stock was worth $54,000.
∙
Amber deducted percentage depletion of $65,000. The adjusted basis of the natural resource at the beginning of the year was $39,000.
∙
Amber contributed CSX stock worth $20,000 to the Red Cross. Amber purchased the stock four months ago for $19,000.
What is Amber's AMTI?
A) $212,000.
B) $233,000.
C) $238,000.
D) $249,000.
E) None of the above
∙
Depreciation on buildings placed in service in the early 1990s was $52,000. ADS would have been $41,000.
∙
The president of Amber exercised stock options on Amber stock. She paid $30,000 for the stock, which had a fair market value at exercise date of $49,000. At the end of the year, the stock was worth $54,000.
∙
Amber deducted percentage depletion of $65,000. The adjusted basis of the natural resource at the beginning of the year was $39,000.
∙
Amber contributed CSX stock worth $20,000 to the Red Cross. Amber purchased the stock four months ago for $19,000.
What is Amber's AMTI?
A) $212,000.
B) $233,000.
C) $238,000.
D) $249,000.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) is owed by both high income individuals and corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The special allocation opportunities that are available to partnerships are available to S corporations only if affected shareholders elect to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Amos contributes land with an adjusted basis of $150,000 and a fair market value of $200,000 to White, Inc., an S corporation, in exchange for 50% of the stock of White, Inc. Carol contributes cash of $200,000 for the other 50% of the stock. If White later sells the land for $225,000, $62,500 [$50,000 + 50%($25,000)] is allocated to Amos and $12,500 ($25,000 × 50%) is allocated to Carol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Arthur is the sole shareholder of Purple, Inc. Purple's taxable income before the payment of Arthur's salary is $300,000. Based on this information, Arthur has the corporation pay him a salary of $200,000 and a bonus of $100,000. A reasonable salary and bonus would be $175,000. Which of the following is correct?
A) The taxable income of Purple, Inc., is $0 ($300,000 - $300,000 salary and bonus).
B) The taxable income of Purple, Inc., is $100,000 ($300,000 - $200,000).
C) Arthur has salary and bonus income of $300,000.
D) Arthur has salary and bonus income of $175,000 and dividend income of $125,000.
E) None of the above.
A) The taxable income of Purple, Inc., is $0 ($300,000 - $300,000 salary and bonus).
B) The taxable income of Purple, Inc., is $100,000 ($300,000 - $200,000).
C) Arthur has salary and bonus income of $300,000.
D) Arthur has salary and bonus income of $175,000 and dividend income of $125,000.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Arnold purchases a building for $750,000 which is going to be used by his wholly-owned corporation. Which of the following statements are correct?
A) If Arnold contributes the building to the corporation, there will be no recognition under § 351 and a carryover basis of $750,000.
B) If Arnold leases the building to the corporation, lease-rental payments of $30,000 per year to Arnold will result in a $30,000 deduction for the corporation.
C) If Arnold leases the building to the corporation, lease-rental payments of $30,000 per year to Arnold will result in $30,000 of gross income for Arnold.
D) Leasing the building to the corporation will contribute to the tax avoidance objective of minimizing double taxation.
E) All of the above are correct.
A) If Arnold contributes the building to the corporation, there will be no recognition under § 351 and a carryover basis of $750,000.
B) If Arnold leases the building to the corporation, lease-rental payments of $30,000 per year to Arnold will result in a $30,000 deduction for the corporation.
C) If Arnold leases the building to the corporation, lease-rental payments of $30,000 per year to Arnold will result in $30,000 of gross income for Arnold.
D) Leasing the building to the corporation will contribute to the tax avoidance objective of minimizing double taxation.
E) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Barb and Chuck each own one-half of the stock of Wren, Inc., a C corporation. Each shareholder has a stock basis of $175,000. Wren has accumulated E & P of $300,000. Wren's taxable income for the current year is $100,000, and it distributes $75,000 to each shareholder. Barb's stock basis at the end of the year is:
A) $0.
B) $100,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $175,000.
E) None of the above.
A) $0.
B) $100,000.
C) $150,000.
D) $175,000.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Beige, Inc., has 3,000 shares of stock authorized and 1,000 shares outstanding. The shares are owned by Sam (700 shares) and Lois (300 shares). Sam's adjusted basis for his stock is $100,000 and Lois' adjusted basis for her stock is $90,000. Beige's earnings and profits are $500,000. Beige redeems 200 of Lois' shares for $150,000. Determine the amount of Lois' recognized gain (1) if she is Sam's mother and (2) if they are unrelated.
A) $0 and $0.
B) $150,000 and $60,000.
C) $150,000 and $90,000.
D) $50,000 and $150,000.
E) None of the above.
A) $0 and $0.
B) $150,000 and $60,000.
C) $150,000 and $90,000.
D) $50,000 and $150,000.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the following attributes with the different forms. A particular attribute may apply to more than one entity form
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
Sole proprietorship
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
Sole proprietorship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Bart contributes $100,000 to the Fish Partnership for a 40% interest. During the first year of operations, Fish has a profit of $20,000. At the end of the first year, Fish has outstanding loans from the following banks.
First Bank (recourse)
$10,000
Second Bank (nonrecourse)
30,000
What is Bart's at-risk basis in Fish at the end of the first year?
A) $100,000
B) $108,000
C) $112,000
D) $124,000
E) None of the above
First Bank (recourse)
$10,000
Second Bank (nonrecourse)
30,000
What is Bart's at-risk basis in Fish at the end of the first year?
A) $100,000
B) $108,000
C) $112,000
D) $124,000
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match the following attributes with the different forms. A particular attribute may apply to more than one entity form
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
S corporation
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
S corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Alice contributes equipment (fair market value of $82,000; adjusted basis of $20,000), subject to a $14,000 liability, to form Orange Partnership, a general partnership. Mary contributes $68,000 cash. Alice and Mary share equally in partnership profits and losses. What is Alice's and Mary's basis for their partnership interests?
A) $6,000 to Alice, $68,000 to Mary.
B) $6,000 to Alice, $75,000 to Mary.
C) $13,000 to Alice, $75,000 to Mary.
D) $20,000 to Alice, $68,000 to Mary.
E) None of the above.
A) $6,000 to Alice, $68,000 to Mary.
B) $6,000 to Alice, $75,000 to Mary.
C) $13,000 to Alice, $75,000 to Mary.
D) $20,000 to Alice, $68,000 to Mary.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Khalid contributes land (fair market value of $700,000; adjusted basis of $200,000) and Dan contributes $700,000 cash to form Teal Partnership. Khalid and Dan each own a 50% interest. One year later, Teal sells the land for $800,000. How much gain is recognized by each partner?
A) $600,000 to Khalid, $0 to Dan.
B) $550,000 to Khalid, $50,000 to Dan.
C) $300,000 to Khalid, $300,000 to Dan.
D) $50,000 to Khalid, $50,000 to Dan.
E) None of the above.
A) $600,000 to Khalid, $0 to Dan.
B) $550,000 to Khalid, $50,000 to Dan.
C) $300,000 to Khalid, $300,000 to Dan.
D) $50,000 to Khalid, $50,000 to Dan.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Bev and Cabel each own one-half of the stock of Finch, Inc., an S corporation with no accumulated E & P. Bev's basis in the Finch stock is $225,000. Finch's taxable income for the current year is $100,000, and it distributes $180,000 to each shareholder. Bev's stock basis at the end of the year is:
A) $0.
B) $45,000.
C) $95,000.
D) $100,000.
E) None of the above.
A) $0.
B) $45,000.
C) $95,000.
D) $100,000.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Kristine owns all of the stock of a C corporation which owns the following assets: 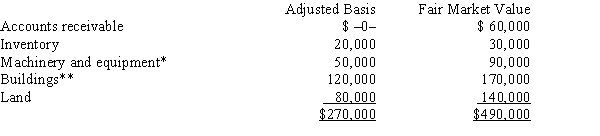 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Her adjusted basis for her stock is $270,000. Calculate Kristine's recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary if she sells her stock for $500,000.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.
 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Her adjusted basis for her stock is $270,000. Calculate Kristine's recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary if she sells her stock for $500,000.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Albert's sole proprietorship owns the following assets: 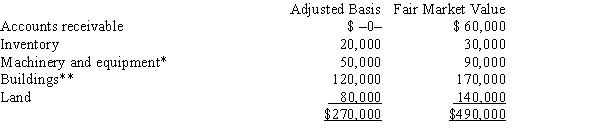 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Albert sells his sole proprietorship for $500,000. Calculate Albert's recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.
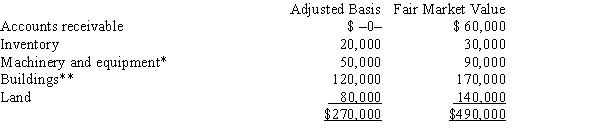 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Albert sells his sole proprietorship for $500,000. Calculate Albert's recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Mr. and Ms. Smith's partnership owns the following assets: 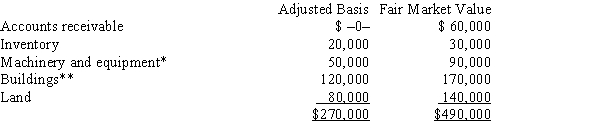 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Mr) and Ms. Smith each have a basis for their partnership interest of $135,000. Calculate their combined recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary if they sell their partnership interests for $500,000.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.
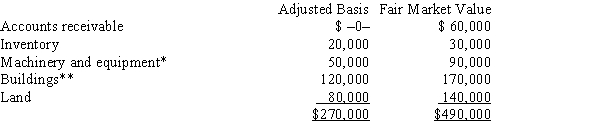 * Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.
* Potential § 1245 recapture of $45,000.** Straight-line depreciation was used.
Mr) and Ms. Smith each have a basis for their partnership interest of $135,000. Calculate their combined recognized gain or loss and classify it as capital or ordinary if they sell their partnership interests for $500,000.
A) $230,000 ordinary income.
B) $230,000 capital gain.
C) $115,000 ordinary income and $115,000 capital gain.
D) $110,000 ordinary income and $120,000 capital gain.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Fred and Ella are going to establish a business. They expect the business to be very successful in the long-run, but project losses of approximately $100,000 for each of the first five years. Due to potential environmental concerns, limited liability is a requisite for the owners. Which form of business entity should they select?
A) General partnership.
B) Limited partnership.
C) C corporation.
D) S corporation.
E) Any of the above should satisfy Fred and Ella.
A) General partnership.
B) Limited partnership.
C) C corporation.
D) S corporation.
E) Any of the above should satisfy Fred and Ella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the following attributes with the different forms. A particular attribute may apply to more than one entity form
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
General partnership
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
General partnership

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Malcomb and Sandra (shareholders) each loan Crow Corporation $50,000 at the market rate of 6% interest. Which of the following statements are false?
A) Crow may deduct the interest expense, and the interest income is taxable to Malcomb and Sandra.
B) When the note principal is repaid, neither Malcomb nor Sandra recognizes gross income from the repayment.
C) If the IRS were successful in reclassifying the notes as equity, the interest payments would not be deductible by Crow, and Malcomb and Sandra would still recognize income.
D) If the IRS were successful in reclassifying the notes as equity, repayment of the note principal to Malcomb and Sandra would not qualify for return of capital treatment and would most likely result in dividend income treatment for Malcomb and Sandra.
E) All of the above are true.
A) Crow may deduct the interest expense, and the interest income is taxable to Malcomb and Sandra.
B) When the note principal is repaid, neither Malcomb nor Sandra recognizes gross income from the repayment.
C) If the IRS were successful in reclassifying the notes as equity, the interest payments would not be deductible by Crow, and Malcomb and Sandra would still recognize income.
D) If the IRS were successful in reclassifying the notes as equity, repayment of the note principal to Malcomb and Sandra would not qualify for return of capital treatment and would most likely result in dividend income treatment for Malcomb and Sandra.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the following statements:
a.Transaction in this form enables double taxation to be avoided.b.Gain or loss is calculated separately for each asset and is subject to single taxation.c.Subject to double taxation.d.The sale is treated as the sale of a capital asset under § 741 subject to ordinary income potential under § 751.e.Not subject to double taxation on the sale of corporate stock.
Sale of the individual assets of an unincorporated sole proprietorship by the owner.
a.Transaction in this form enables double taxation to be avoided.b.Gain or loss is calculated separately for each asset and is subject to single taxation.c.Subject to double taxation.d.The sale is treated as the sale of a capital asset under § 741 subject to ordinary income potential under § 751.e.Not subject to double taxation on the sale of corporate stock.
Sale of the individual assets of an unincorporated sole proprietorship by the owner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Bev and Cabel each have 50% ownership in Finch Partnership. Bev's partnership interest has a basis of $225,000. Finch's taxable income for the current year is $100,000, and it distributes $180,000 to each partner. Bev's partnership interest basis at the end of the year is:
A) $0.
B) $45,000.
C) $95,000.
D) $100,000.
E) None of the above.
A) $0.
B) $45,000.
C) $95,000.
D) $100,000.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match the following attributes with the different forms. A particular attribute may apply to more than one entity form
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
C corporation
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
C corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match the following attributes with the different forms. A particular attribute may apply to more than one entity form
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
Limited partnership
a.Ability of all owners to have limited liability.b.Ability to pass tax attributes through to the owners.c.Right of all owners to participate in the management of the business.d.Number of owners is limited.e.Ability to have multiple owners.
Limited partnership

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Match the following statements:
a.Transaction in this form enables double taxation to be avoided.b.Gain or loss is calculated separately for each asset and is subject to single taxation.c.Subject to double taxation.d.The sale is treated as the sale of a capital asset under § 741 subject to ordinary income potential under § 751.e.Not subject to double taxation on the sale of corporate stock.
Sale of the corporate assets by the C corporation.
a.Transaction in this form enables double taxation to be avoided.b.Gain or loss is calculated separately for each asset and is subject to single taxation.c.Subject to double taxation.d.The sale is treated as the sale of a capital asset under § 741 subject to ordinary income potential under § 751.e.Not subject to double taxation on the sale of corporate stock.
Sale of the corporate assets by the C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following are "reasonable needs" that will help a corporation in avoiding the accumulated earnings tax?
A) The corporation is opening locations in neighboring cities.
B) Funds are used to make a loan to a major shareholder.
C) The corporation uses funds for the redemption of the stock of a disgruntled shareholder.
D) Not making distributions helps to minimize the combined shareholder/corporation tax liabilities.
E) All of the above.
A) The corporation is opening locations in neighboring cities.
B) Funds are used to make a loan to a major shareholder.
C) The corporation uses funds for the redemption of the stock of a disgruntled shareholder.
D) Not making distributions helps to minimize the combined shareholder/corporation tax liabilities.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



