Deck 13: Inference About Comparing Two Populations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/168
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Inference About Comparing Two Populations
1
The pooled proportion estimate is used when the null hypothesis states that the two population proportions differ by ____________________.
0
zero
zero
2
The difference in two sample proportions is a(n) ____________________ estimator of the difference in their respective population proportions.
unbiased
consistent
consistent
3
In constructing a confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions, we pool the population proportions when the populations are normally distributed.
False
4
The pooled proportion estimate is used when the null hypothesis states that the two population proportions differ by some non-zero number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In constructing a confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions, we ____________________ (always/sometimes/never) pool the population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The difference in two sample proportions is an unbiased consistent estimator of the difference in their respective population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The pooled proportion estimate is used when the proportion of successes from sample 1 equals the proportion of successes from sample 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For testing the difference between two population proportions, the pooled proportion estimate should be used to compute the value of the test statistic when the:
A)populations are normally distributed.
B)sample sizes are small.
C)null hypothesis states that the two population proportions are equal.
D)samples are independently drawn from the populations.
A)populations are normally distributed.
B)sample sizes are small.
C)null hypothesis states that the two population proportions are equal.
D)samples are independently drawn from the populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The variance of the difference in sample proportions equals the difference of their population variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Pooling is made possible by hypothesizing (under the null hypothesis) that p1 = p2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The expected value of the difference between two sample proportions is the difference between their corresponding population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The variance of the difference between two sample proportions equals the ____________________ of their population proportion variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a required condition for using the normal approximation to the binomial in testing the difference between two population proportions?
A)
B) , , , and
C) , , , and
D)Choice b is the true requirement, but choice c is the one you actually check.
A)
B) , , , and
C) , , , and
D)Choice b is the true requirement, but choice c is the one you actually check.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The pooled proportion estimate is used when:
A)the proportion of successes from sample 1 equals the proportion of successes from sample 2.
B)the total number of successes in both samples divided by the total of both sample sizes equals 1.
C)the null hypothesis states that the two population proportions differ by some non-zero number.
D)None of these choices.
A)the proportion of successes from sample 1 equals the proportion of successes from sample 2.
B)the total number of successes in both samples divided by the total of both sample sizes equals 1.
C)the null hypothesis states that the two population proportions differ by some non-zero number.
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Pooling is made possible by hypothesizing (under the null hypothesis) that p1 __________ p2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The pooled proportion estimate is found by taking the proportion of successes from sample 1 plus the proportion of successes from sample 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A required condition for using the normal approximation to the binomial in testing the difference between two population proportions is that n1p1 30 and n2p2 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In constructing a confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions, we:
A)pool the population proportions when the populations are normally distributed.
B)pool the population proportions when the population means are equal.
C)pool the population proportions when they are equal.
D)never pool the population proportions.
A)pool the population proportions when the populations are normally distributed.
B)pool the population proportions when the population means are equal.
C)pool the population proportions when they are equal.
D)never pool the population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For testing the difference between two population proportions, the pooled proportion estimate is found by taking:
A)the proportion of successes from sample 1 plus the proportion of successes from sample 2.
B)the total number of successes in both samples divided by the total of both sample sizes.
C)the difference between the proportion of successes in each sample.
D)None of these choices.
A)the proportion of successes from sample 1 plus the proportion of successes from sample 2.
B)the total number of successes in both samples divided by the total of both sample sizes.
C)the difference between the proportion of successes in each sample.
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In comparing two population means the statistic under consideration is .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
NARRBEGIN: Worker Safety
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} What is the p-value of the test? Explain how to use it for testing the hypotheses.
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} What is the p-value of the test? Explain how to use it for testing the hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
NARRBEGIN: Headache Medicine
Headache Medicine
A researcher wants to see if/how men and women differ in their reaction to a headache medicine with respect to drowsiness. In testing the hypotheses vs. , the following statistics were obtained: n1 = 400, x1 = 208, n2 = 250, and x2 = 115, where x1 and x2 represent the number of patients in the two samples (men vs. women) who reported to have drowsiness as a result of taking headache medicine.NARREND
-{Headache Medicine Narrative} Estimate with 90% confidence the difference between the two population proportions.
Headache Medicine
A researcher wants to see if/how men and women differ in their reaction to a headache medicine with respect to drowsiness. In testing the hypotheses vs. , the following statistics were obtained: n1 = 400, x1 = 208, n2 = 250, and x2 = 115, where x1 and x2 represent the number of patients in the two samples (men vs. women) who reported to have drowsiness as a result of taking headache medicine.NARREND
-{Headache Medicine Narrative} Estimate with 90% confidence the difference between the two population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When the data from two populations are ____________________ the parameter to be tested and estimated is the difference between the two population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
NARRBEGIN: Worker Safety
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} Can the statistician infer at the 5% significance level that efforts to promote safety have been successful?
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} Can the statistician infer at the 5% significance level that efforts to promote safety have been successful?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the sample sizes are large enough so the conditions are met, the difference between two sample proportions has an approximate ____________________ distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
NARRBEGIN: TV Sex
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
-{TV Sex Narrative} Estimate with 99% confidence the difference in the proportion of Canadians and Americans who believe that there is too much sex on television.
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
-{TV Sex Narrative} Estimate with 99% confidence the difference in the proportion of Canadians and Americans who believe that there is too much sex on television.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
NARRBEGIN: Senatorial Election
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
-{Senatorial Election Narrative} Explain how to use the interval estimate to test the hypotheses.
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
-{Senatorial Election Narrative} Explain how to use the interval estimate to test the hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
NARRBEGIN: Worker Safety
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.
Worker Safety
An OSHA agent wanted to determine if efforts to promote safety have been successful. By checking the records of 250 workers, he found that 30 of them suffered either minor or major injuries that year. A random sample of 400 workers last year revealed that 80 suffered some form of injury.NARREND
-{Worker Safety Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
NARRBEGIN: Mass Production Line
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below. NARREND
-{Mass Production Line Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below. NARREND
-{Mass Production Line Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
NARRBEGIN: Senatorial Election
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
{Senatorial Election Narrative} Can we infer at the 5% significance level that the proportions of male and female voters who intend to vote for the Democrat candidate differ?
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
{Senatorial Election Narrative} Can we infer at the 5% significance level that the proportions of male and female voters who intend to vote for the Democrat candidate differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
NARRBEGIN: TV Sex
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
A councilwoman regularly polls her constituency to gauge her level of support among voters. This month, 652 out of 1158 voters support her. Five months ago, 412 out of 982 voters supported her. With a 5% significance level, can she infer that support has increased by at least 10 percentage points?
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
A councilwoman regularly polls her constituency to gauge her level of support among voters. This month, 652 out of 1158 voters support her. Five months ago, 412 out of 982 voters supported her. With a 5% significance level, can she infer that support has increased by at least 10 percentage points?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
NARRBEGIN: Mass Production Line
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below. NARREND
-{Mass Production Line Narrative} What is the p-value of the test? Explain how to use it for testing the hypotheses.
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below. NARREND
-{Mass Production Line Narrative} What is the p-value of the test? Explain how to use it for testing the hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
NARRBEGIN: Headache Medicine
Headache Medicine
A researcher wants to see if/how men and women differ in their reaction to a headache medicine with respect to drowsiness. In testing the hypotheses vs. , the following statistics were obtained: n1 = 400, x1 = 208, n2 = 250, and x2 = 115, where x1 and x2 represent the number of patients in the two samples (men vs. women) who reported to have drowsiness as a result of taking headache medicine.NARREND
-{Headache Medicine Narrative} What conclusion can we draw at the 10% significance level?
Headache Medicine
A researcher wants to see if/how men and women differ in their reaction to a headache medicine with respect to drowsiness. In testing the hypotheses vs. , the following statistics were obtained: n1 = 400, x1 = 208, n2 = 250, and x2 = 115, where x1 and x2 represent the number of patients in the two samples (men vs. women) who reported to have drowsiness as a result of taking headache medicine.NARREND
-{Headache Medicine Narrative} What conclusion can we draw at the 10% significance level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
NARRBEGIN: Senatorial Election
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
-{Senatorial Election Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in the proportion of male and female voters who intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
-{Senatorial Election Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in the proportion of male and female voters who intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
NARRBEGIN: Mass Production Line
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below.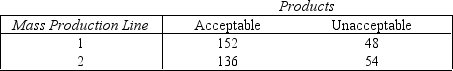 NARREND
NARREND
{Mass Production Line Narrative} Can the inspector infer at the 5% significance level that production line 1 is doing a better job than production line 2?
Mass Production Line
A quality control examiner keeps a tally sheet of the number of acceptable and unacceptable products that come off two different production lines. The completed sheet is shown below.
 NARREND
NARREND{Mass Production Line Narrative} Can the inspector infer at the 5% significance level that production line 1 is doing a better job than production line 2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
NARRBEGIN: Speed Limits Violation
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow. NARREND
-{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Do these data provide enough evidence to support the highway patrol's claim at the 5% significance level?
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow. NARREND
-{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Do these data provide enough evidence to support the highway patrol's claim at the 5% significance level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The expected value of the difference between two sample proportions is the ____________________ of/between their corresponding population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
NARRBEGIN: Senatorial Election
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
{Senatorial Election Narrative} What is the p-value of the test?
Senatorial Election
A political poll immediately prior to a senatorial election reveals that 145 out of 250 male voters and 105 out of 200 female voters intend to vote for the Democrat candidate.NARREND
{Senatorial Election Narrative} What is the p-value of the test?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
NARRBEGIN: TV Sex
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
{TV Sex Narrative} Briefly explain what the interval estimate tells you.
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
{TV Sex Narrative} Briefly explain what the interval estimate tells you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
NARRBEGIN: TV Sex
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
{TV Sex Narrative} Can we infer at the 99% significance level that the proportion of Canadians and Americans who believe that there is too much sex on television differ?
TV Sex
A survey of 1,500 Canadians reveals that 945 believe that there is too much sex on television. In a survey of 1,500 Americans, 810 believe that there is too much television sex.NARREND
{TV Sex Narrative} Can we infer at the 99% significance level that the proportion of Canadians and Americans who believe that there is too much sex on television differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The test statistic employed to test is is F-distributed with v1 = n1 - 1 and v2 = n2 -1 degrees of freedom if the two populations are F-distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The statistical distribution used for testing the difference between two population variances is the
A)Student t-distribution
B)standard normal distribution
C)F-distribution
D)None of these choices.
A)Student t-distribution
B)standard normal distribution
C)F-distribution
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In testing for the equality of two population variances, when the populations are normally distributed, the 5% level of significance has been used. To determine the rejection region, it will be necessary to refer to the F table corresponding to an upper-tail area of 0.05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The F-distribution is the sampling distribution of the ratio of:
A)two sample variances.
B)two normal population means.
C)two normal population variances.
D)None of these choices.
A)two sample variances.
B)two normal population means.
C)two normal population variances.
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
NARRBEGIN: Speed Limits Violation
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow. NARREND
-{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow. NARREND
-{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the difference in population proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When comparing two population variances, we use the ratio rather than the difference .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
We use a t-test to determine whether two population variances are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In testing for the equality of two population variances, when the populations are normally distributed, the 10% level of significance has been used. To determine the rejection region, it will be necessary to refer to the F table corresponding to an upper-tail area of:
A)0.90
B)0.20
C)0.10
D)0.05
A)0.90
B)0.20
C)0.10
D)0.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The ratio of two independent chi-squared variables divided by their degrees of freedom is:
A)normally distributed
B)Student t-distributed
C)chi-squared distributed
D)F-distributed
A)normally distributed
B)Student t-distributed
C)chi-squared distributed
D)F-distributed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The F-test used for testing the difference in 2 population variances is always a one-tailed test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All F-tests for the equality of two population variances are one-tailed tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The F-distribution can only have non-negative values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements is false for an F-distribution?
A)Variables that are F-distributed range from 0 to .
B)The exact shape of the distribution is determined by two numbers of degrees of freedom.
C)The degrees of freedom for the numerator can be larger than, smaller than, or equal to the degrees of freedom for the denominator.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)Variables that are F-distributed range from 0 to .
B)The exact shape of the distribution is determined by two numbers of degrees of freedom.
C)The degrees of freedom for the numerator can be larger than, smaller than, or equal to the degrees of freedom for the denominator.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When testing the equality of two population variances the number in the null hypothesis is 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The F-distribution is symmetric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
NARRBEGIN: Speed Limits Violation
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow.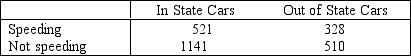 NARREND
NARREND
{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Briefly describe what the interval estimate tells you.
Speed Limits Violation
Do out-of-state motorists violate the speed limit more frequently than in-state motorists? This vital question was addressed by the highway patrol in a large eastern state. A random sample of the speeds of 2,500 randomly selected cars was categorized according to whether the car was registered in the state or in some other state and whether or not the car was violating the speed limit. The data follow.
 NARREND
NARREND{Speed Limits Violation Narrative} Briefly describe what the interval estimate tells you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The test for the equality of two population variances assumes that each of the two populations is normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When testing for the difference between two population variances with sample sizes of n1 = 8 and n2 = 10, the degrees of freedom are:
A)8 and 10
B)7 and 9
C)2 and 18
D)18 and 2
A)8 and 10
B)7 and 9
C)2 and 18
D)18 and 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When the necessary conditions are met, a two-tail test is being conducted at = 0.05 to test . The two sample variances are and , and the sample sizes are n1 = 25 and n2 = 25. The calculated value of the test statistic will be F = 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the percentile points of the F-distribution?
A)F0.05,10,20 = 1/F0.95,10,20
B)F0.05,10,20 = 1/F0.05,20,10
C)F0.95,10,20 = 1/F0.05,20,10
D)F0.95,10,20 = 1/F0.95,20,10
A)F0.05,10,20 = 1/F0.95,10,20
B)F0.05,10,20 = 1/F0.05,20,10
C)F0.95,10,20 = 1/F0.05,20,10
D)F0.95,10,20 = 1/F0.95,20,10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The sampling distribution of the ratio of two sample variances is said to be F-distributed provided that we have two ____________________ samples drawn from their respective populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When testing for the equality of two population variances the number in the null hypothesis is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
NARRBEGIN: Clinic Waiting Time
Clinic Waiting Time
In a random sample of 20 patients who visited a clinic at Medical Center 1, a researcher found that the variance of the waiting time (in minutes) was 128.0. In a random sample of 15 patients in the clinic of Medical Center 2, the researcher found the variance to be 178.8.NARREND
-{Clinic Waiting Time Narrative} Can we infer at the 5% level of significance that the population variances differ?
Clinic Waiting Time
In a random sample of 20 patients who visited a clinic at Medical Center 1, a researcher found that the variance of the waiting time (in minutes) was 128.0. In a random sample of 15 patients in the clinic of Medical Center 2, the researcher found the variance to be 178.8.NARREND
-{Clinic Waiting Time Narrative} Can we infer at the 5% level of significance that the population variances differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
NARRBEGIN: Profit Margin
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances.
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The test statistic for testing for the equality of two population variances has a(n) ____________________ distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
NARRBEGIN: Profit Margin
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Briefly describe what the interval estimate tells you.
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Briefly describe what the interval estimate tells you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To estimate the ratio of the population variances you use the ____________________ of the ____________________ variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
NARRBEGIN: Profit Margin
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Can she infer at the 5% significance level that the population variance of investment 1 exceeds that of investment 2?
Profit Margin
An investor is considering two types of investment. She is quite satisfied that the expected profit margin on Investment 1 is higher than the expected profit margin on Investment 2. However, she is quite concerned that the risk associated with Investment 1 is higher than that of Investment 2. To help make her decision, she randomly selects seven monthly profit margins on investment 1 and ten monthly profit margins on investment 2. She finds that the sample variances of Investments 1 and 2 are 225 and 118, respectively.NARREND
{Profit Margin Narrative} Can she infer at the 5% significance level that the population variance of investment 1 exceeds that of investment 2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The test statistic for testing for the equality of two population variances has an F-distribution with ____________________ and ____________________ degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Two independent samples are drawn from two normal populations, where the population variances are assumed to be equal. The sampling distribution of the ratio of the two sample variances is:
A)normal
B)Student-t
C)F
D)chi-squared
A)normal
B)Student-t
C)F
D)chi-squared

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
We compare two population variances by examining their ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Random samples from two normal populations produced the following statistics: 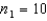 ,
, 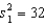 ,
,  , and
, and 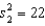 . Is there enough evidence at the 5% significance level to infer that the variance of Population 1 is larger than the variance of Population 2?
. Is there enough evidence at the 5% significance level to infer that the variance of Population 1 is larger than the variance of Population 2?
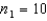 ,
, 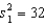 ,
,  , and
, and 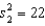 . Is there enough evidence at the 5% significance level to infer that the variance of Population 1 is larger than the variance of Population 2?
. Is there enough evidence at the 5% significance level to infer that the variance of Population 1 is larger than the variance of Population 2?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
NARRBEGIN: Fitness Program
Fitness Program
A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. The number of pound lost at the completion of the program data follow:
NARREND
-{Fitness Program Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances and interpret.
Fitness Program
A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. The number of pound lost at the completion of the program data follow:
NARREND
-{Fitness Program Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances and interpret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The sampling distribution of the ratio of two (independent) sample variances is said to be ____________________ distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the F-test statistic is large, that means the variance of Population 1 is ____________________ than/to the variance of Population 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
NARRBEGIN: Clinic Waiting Time
Clinic Waiting Time
In a random sample of 20 patients who visited a clinic at Medical Center 1, a researcher found that the variance of the waiting time (in minutes) was 128.0. In a random sample of 15 patients in the clinic of Medical Center 2, the researcher found the variance to be 178.8.NARREND
{Clinic Waiting Time Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances and interpret.
Clinic Waiting Time
In a random sample of 20 patients who visited a clinic at Medical Center 1, a researcher found that the variance of the waiting time (in minutes) was 128.0. In a random sample of 15 patients in the clinic of Medical Center 2, the researcher found the variance to be 178.8.NARREND
{Clinic Waiting Time Narrative} Estimate with 95% confidence the ratio of the two population variances and interpret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The test for the equality of two population variances is based on the:
A)difference between the two sample variances.
B)ratio of the two sample variances.
C)sum of the two sample variances.
D)product of the two sample variances.
A)difference between the two sample variances.
B)ratio of the two sample variances.
C)sum of the two sample variances.
D)product of the two sample variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
NARRBEGIN: Anioxidants
Antioxidants
A food processor wants to compare two antioxidants for their effects on retarding spoilage. Suppose 16 cuts of fresh meat are treated with antioxidant A and 16 are treated with antioxidant B, and the number of hours until spoilage begins is recorded for each of the 32 cuts of meat. The results are summarized in the table below
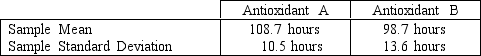 NARREND
NARREND
{Antioxidants Narrative} State the null and alternative hypotheses for determining if the population variances differ for Antioxidants A and B.
Antioxidants
A food processor wants to compare two antioxidants for their effects on retarding spoilage. Suppose 16 cuts of fresh meat are treated with antioxidant A and 16 are treated with antioxidant B, and the number of hours until spoilage begins is recorded for each of the 32 cuts of meat. The results are summarized in the table below
 NARREND
NARREND{Antioxidants Narrative} State the null and alternative hypotheses for determining if the population variances differ for Antioxidants A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
NARRBEGIN: Fitness Program
Fitness Program
A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. The number of pound lost at the completion of the program data follow:
 NARREND
NARREND
{Fitness Program Narrative} Can the statistician conclude at the 5% significance level that the required condition is not satisfied?
Fitness Program
A statistician wants to test for the equality of means in two independent samples drawn from normal populations of people enrolled in a fitness program. However, he will not perform the equal-variance t-test of the difference between the population means if the condition necessary for its use is not satisfied. The number of pound lost at the completion of the program data follow:
 NARREND
NARREND{Fitness Program Narrative} Can the statistician conclude at the 5% significance level that the required condition is not satisfied?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The sampling distribution of the ratio of two sample variances is said to be F-distributed provided that:
A)the samples are independent from any distributions.
B)the populations are normal with equal variances.
C)the samples are matched and their sizes are large.
D)the samples are independently drawn from two normal populations.
A)the samples are independent from any distributions.
B)the populations are normal with equal variances.
C)the samples are matched and their sizes are large.
D)the samples are independently drawn from two normal populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



