Deck 17: Activity Resource Usage Model and Tactical Decision Making
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Activity Resource Usage Model and Tactical Decision Making
1
A keep-or-drop decision uses irrelevant cost analysis to determine whether to continue or discontinue a segment or line of business.
False
2
Choosing to make or buy may reduce the cost of producing the main product and increase the quality.
True
3
Changes in cost of an activity can occur if the demand for the resource exceeds the supply or if the demand for the resource drops.
True
4
Flexible resources are acquired way ahead of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The last of the six steps of the tactical decision model is to choose the quickest way to solve the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A sunk cost is irrelevant because it has no influence over future decisions, so it is depreciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The activity resource usage model focuses on sorting out the behavior of various activity costs and assess their relevancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A tariff is a tax on exports levied by the federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tactical cost analysis uses cost data to identify the choice that will bring the organization the most benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Relevant costs and revenues are present costs and revenues that differ across alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For flexible resources, if the demand for an activity changes across alternatives, then resource spending will remain the same and costs are relevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Tactical decision making consists of choosing among alternatives with an immediate or limited end in view.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Committed resources are acquired in advance of usage, through implicit contracting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Sound tactical decision making is limited to achieve small objectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The first of the six steps of the tactical decision model is to recognize and define the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A special-order decision focuses on whether a specially priced order should be accepted or rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Foreign trade zones are set up by the U.S. government to facilitate warehousing and/or manufacturing for companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Tactical decision making includes decisions to make or buy a component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An irrelevant cost is one that is the same for more than one alternative and has no bearing on future decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Outsourcing refers to the move of a business function to another company, either in or out of the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Past cost __________ represents an allocation of a cost already incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT a step in the tactical decision-making process?
A)Compare full costs and benefits for alternatives.
B)Identify feasible alternatives.
C)Select the best alternative.
D)Recognize and define the problem.
A)Compare full costs and benefits for alternatives.
B)Identify feasible alternatives.
C)Select the best alternative.
D)Recognize and define the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Sound tactical decision making
A)only concerns the short run.
B)consists of large scale actions that serve a broad purpose.
C)consists of supporting the strategic objectives of the firm.
D)only concerns the long run.
A)only concerns the short run.
B)consists of large scale actions that serve a broad purpose.
C)consists of supporting the strategic objectives of the firm.
D)only concerns the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An important qualitative factor to consider regarding a special order is the
A)variable costs associated with the special order.
B)avoidable fixed costs associated with the special order.
C)effect the sale of special-order units will have on existing customers.
D)incremental revenue from the special order.
A)variable costs associated with the special order.
B)avoidable fixed costs associated with the special order.
C)effect the sale of special-order units will have on existing customers.
D)incremental revenue from the special order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A decision to accept or reject a specially priced order is an example of a __________ decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A doctor choosing between buying laboratory tests externally or performing the tests in house is an example of a __________ decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Qualitative factors that should be considered when evaluating a make-or-buy decision are
A)the quality of the outside supplier's product.
B)whether the outside supplier can provide the needed quantities.
C)whether the outside supplier can provide the product when it is needed.
D)all of the above.
A)the quality of the outside supplier's product.
B)whether the outside supplier can provide the needed quantities.
C)whether the outside supplier can provide the product when it is needed.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A __________ model is a set of procedures that, if followed, will lead to a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is true of tactical decisions?
A)Tactical decisions are often large-scale actions that serve a smaller purpose.
B)Tactical decisions do not have an immediate or limited end in view.
C)Tactical decisions should support alternatives that result in long-term competitive advantage.
D)Tactical decisions are long run in nature and will have short-run consequences.
A)Tactical decisions are often large-scale actions that serve a smaller purpose.
B)Tactical decisions do not have an immediate or limited end in view.
C)Tactical decisions should support alternatives that result in long-term competitive advantage.
D)Tactical decisions are long run in nature and will have short-run consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Areas that are physically on U.S. soil but considered to be outside U.S. commerce are called __________ zones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Decisions consisting of selecting among alternatives with immediate ends in views are called __________ decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The cost of acquiring activity capacity is called __________ spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The choosing among alternatives with an immediate or limited end in view consists of:
A)Tactical decision making
B)Long-run decision making
C)Universal decision making
D)all of the above
A)Tactical decision making
B)Long-run decision making
C)Universal decision making
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The use of relevant cost data to identify the alternative that provides the greatest benefit to the organization describes
A)target cost analysis.
B)functional cost analysis.
C)activity cost analysis.
D)tactical cost analysis.
A)target cost analysis.
B)functional cost analysis.
C)activity cost analysis.
D)tactical cost analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The steps in the tactical decision making process are:
I.Comparing relevant costs and relating to strategic goals
II.Identifying feasible alternatives
III.Identifying costs and benefits and eliminating irrelevant costs
IV.Selecting best alternative
V.Defining the problem
What is the proper sequence of steps
A)I, II, V, III, IV
B)II, I, V, III, IV
C)V, II, III, I, IV
D)V, III, II, IV, I
I.Comparing relevant costs and relating to strategic goals
II.Identifying feasible alternatives
III.Identifying costs and benefits and eliminating irrelevant costs
IV.Selecting best alternative
V.Defining the problem
What is the proper sequence of steps
A)I, II, V, III, IV
B)II, I, V, III, IV
C)V, II, III, I, IV
D)V, III, II, IV, I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Leasing or buying a building are examples of __________resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true of relevant costs?
A)Relevant costs are future costs that differ across alternatives.
B)Relevant costs are sunk costs that alter future decisions.
C)Relevant costs have no effect on decision making.
D)Relevant costs are past costs that do not differ from one alternative to another.
A)Relevant costs are future costs that differ across alternatives.
B)Relevant costs are sunk costs that alter future decisions.
C)Relevant costs have no effect on decision making.
D)Relevant costs are past costs that do not differ from one alternative to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a keep-or-drop decision, the __________ income or loss determines whether a segment is kept or dropped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Future costs which differ across alternatives are called __________ costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Tactical decision making relies
A)only on relevant cost information.
B)only on qualitative factors.
C)on relevant costs as well as other qualitative factors.
D)on neither relevant costs nor qualitative decisions.
A)only on relevant cost information.
B)only on qualitative factors.
C)on relevant costs as well as other qualitative factors.
D)on neither relevant costs nor qualitative decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In order for costs or benefits to be relevant, what must be true?
A)All decisions must relate to future.
B)Identifying relevant costs and benefits is an easy process.
C)Relevancy will relate both to the future and the past.
D)all of the above are true statements.
A)All decisions must relate to future.
B)Identifying relevant costs and benefits is an easy process.
C)Relevancy will relate both to the future and the past.
D)all of the above are true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following costs is relevant to a make-or-buy decision of a particular part of a product?
A)The direct labor costs used to manufacture the part
B)The fixed annual rent paid for the office building
C)The salary of the sales manager who sells the product
D)The depreciation on the plant used to manufacture the part
A)The direct labor costs used to manufacture the part
B)The fixed annual rent paid for the office building
C)The salary of the sales manager who sells the product
D)The depreciation on the plant used to manufacture the part

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following costs is NOT relevant to a decision to sell a product at split-off or process the product further and then sell the product?
A)joint costs allocated to the product
B)the selling price of the product at split-off
C)the additional processing costs after split-off
D)the selling price of the product after further processing
A)joint costs allocated to the product
B)the selling price of the product at split-off
C)the additional processing costs after split-off
D)the selling price of the product after further processing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For flexible resources, which of the following statements is true?
A)A change in resource spending will only occur if the demand for a resource drops permanently and exceeds demand enough so the activity capacity will be reduced.
B)Often, resources are acquired in advance for multiple periods and are therefore irrelevant.
C)Decisions often affect multi-period capabilities.
D)If the demand for an activity changes across alternatives, then resource spending will change and the cost of the activity will be relevant to the decision.
A)A change in resource spending will only occur if the demand for a resource drops permanently and exceeds demand enough so the activity capacity will be reduced.
B)Often, resources are acquired in advance for multiple periods and are therefore irrelevant.
C)Decisions often affect multi-period capabilities.
D)If the demand for an activity changes across alternatives, then resource spending will change and the cost of the activity will be relevant to the decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One of Maersk cargo ships hit an iceberg and sank. In deciding whether or not to salvage the ship, its book value is a(n)
A)relevant cost.
B)discretionary cost.
C)opportunity cost.
D)sunk cost.
A)relevant cost.
B)discretionary cost.
C)opportunity cost.
D)sunk cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT a way that companies might reduce tariffs?
A)Alter materials to increase the domestic content.
B)Restrict the amount of imported materials.
C)Increase the amount of imported materials.
D)Utilize foreign trade zones.
A)Alter materials to increase the domestic content.
B)Restrict the amount of imported materials.
C)Increase the amount of imported materials.
D)Utilize foreign trade zones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The cost of acquiring activity capacity is(are)
A)Joint costs
B)Variable costing
C)Absorption costing
D)Resource spending
A)Joint costs
B)Variable costing
C)Absorption costing
D)Resource spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following costs is NOT relevant to a special-order decision?
A)the direct labor costs to manufacture the special-order units
B)the variable manufacturing overhead incurred to manufacture the special-order units
C)the portion of the cost of leasing the factory that is allocated to the special order
D)all of the above costs are relevant
A)the direct labor costs to manufacture the special-order units
B)the variable manufacturing overhead incurred to manufacture the special-order units
C)the portion of the cost of leasing the factory that is allocated to the special order
D)all of the above costs are relevant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sunk costs are
A)future costs that have no benefit.
B)relevant costs that have only short-run benefits.
C)target costs.
D)always irrelevant.
A)future costs that have no benefit.
B)relevant costs that have only short-run benefits.
C)target costs.
D)always irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is TRUE when making a decision between two alternatives?
A)Variable costs may not be relevant when the decision alternatives have the same activity levels.
B)Variable costs are not relevant when the decision alternatives have different activity levels.
C)Sunk costs are always relevant.
D)Fixed costs are never relevant.
A)Variable costs may not be relevant when the decision alternatives have the same activity levels.
B)Variable costs are not relevant when the decision alternatives have different activity levels.
C)Sunk costs are always relevant.
D)Fixed costs are never relevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which item is NOT an example of a sunk cost?
A)materials needed for production
B)purchase cost of machinery
C)depreciation
D)all are sunk costs
A)materials needed for production
B)purchase cost of machinery
C)depreciation
D)all are sunk costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The future costs that differ across alternatives are called
A)Sunk costs
B)Irrelevant costs
C)Relevant costs
D)Past costs
A)Sunk costs
B)Irrelevant costs
C)Relevant costs
D)Past costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following factor is irrelevant regarding a special order?
A)The additional revenue from the special order
B)The unused capacity of the plant that is used for the special order
C)The labor costs for the special order
D)The fixed overhead that can be avoided if the special order is not taken up
A)The additional revenue from the special order
B)The unused capacity of the plant that is used for the special order
C)The labor costs for the special order
D)The fixed overhead that can be avoided if the special order is not taken up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Buying multiperiod activity capacity is often done by paying cash up front and is always:
A)relevant because it is a variable cost.
B)relevant because it could reduce future costs.
C)irrelevant because it is a sunk cost.
D)relevant because it generates future revenues or benefits.
A)relevant because it is a variable cost.
B)relevant because it could reduce future costs.
C)irrelevant because it is a sunk cost.
D)relevant because it generates future revenues or benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A purchasing agent has two potential firms from which to buy materials for production. If both firms charge the same price, the material cost is a(n)
A)irrelevant cost.
B)relevant cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)opportunity cost.
A)irrelevant cost.
B)relevant cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The U.S. government has set up foreign trade zones (FTZ) that
A)are located on U.S. soil but are considered to be outside of U.S. commerce for tariff purposes.
B)are located in foreign countries and designed to export to the United States.
C)are located in foreign countries and are designed to import from the United States.
D)are located in the United States and are considered part of the United States for tariff purposes.
A)are located on U.S. soil but are considered to be outside of U.S. commerce for tariff purposes.
B)are located in foreign countries and designed to export to the United States.
C)are located in foreign countries and are designed to import from the United States.
D)are located in the United States and are considered part of the United States for tariff purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Maldovar Company is considering purchasing a new machine to replace a machine purchased one year ago that is not achieving the expected results. The following information is available: Which of these items is IRRELEVANT?
A)Expected maintenance costs of new machine
B)Expected maintenance costs of existing machine
C)Purchase cost of existing machine
D)Expected resale value of existing machine
A)Expected maintenance costs of new machine
B)Expected maintenance costs of existing machine
C)Purchase cost of existing machine
D)Expected resale value of existing machine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Santa Lucia Industries employs 500 workers in the factory. These workers produced 85,000 units in the preceding year. Due to a special order, the units produced in the current year increased to 95,000 units. However, Santa Lucia produced these units without adding workers. How is that possible?
A)The labor cost associated with the additional units sold will be a relevant cost.
B)The employees were a flexible resource in this situation.
C)The plant had some unused activity capacity.
D)none of the above
A)The labor cost associated with the additional units sold will be a relevant cost.
B)The employees were a flexible resource in this situation.
C)The plant had some unused activity capacity.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Future costs that differ across alternatives are referred to as:
A)sunk costs.
B)relevant costs.
C)marginal costs.
D)period costs.
A)sunk costs.
B)relevant costs.
C)marginal costs.
D)period costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following costs is relevant to a make-or-buy decision?
A)original cost of the production equipment
B)annual depreciation of the equipment
C)the amount that would be received if the production equipment were sold
D)the cost of direct materials purchased last month and used to manufacture the component
A)original cost of the production equipment
B)annual depreciation of the equipment
C)the amount that would be received if the production equipment were sold
D)the cost of direct materials purchased last month and used to manufacture the component

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Scarlet Company produces electronic components for electronic systems. The company sells 10,000 components per year for $15. The capacity is 12,500 units per year. Manufacturing and other costs are as follows:
Ocher Company has offered a one-year contract to supply the components at a cost of $8.50 per unit. If Scarlet Company accepts the offer, it will be able to rent unused space to an outside firm for $9,000 per year. All other information remains the same. What is the effect on profits if Scarlet Company buys the components from Ocher Company?
A)A decrease of $14,000
B)An increase of $14,000
C)An increase of $104,000
D)A decrease of $44,000
Ocher Company has offered a one-year contract to supply the components at a cost of $8.50 per unit. If Scarlet Company accepts the offer, it will be able to rent unused space to an outside firm for $9,000 per year. All other information remains the same. What is the effect on profits if Scarlet Company buys the components from Ocher Company?
A)A decrease of $14,000
B)An increase of $14,000
C)An increase of $104,000
D)A decrease of $44,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following items would be classified as committed resources (long-term)?
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)lease on machinery
D)both b and c
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)lease on machinery
D)both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The operations of Smithsonian Corporation are divided into the Manhattan Division and the Bronx Division. Projections for the next year are as follows: 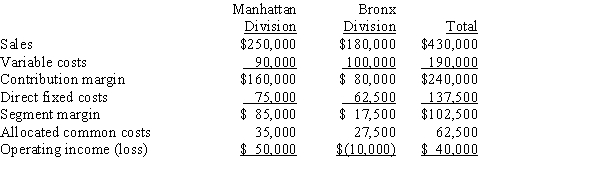 Operating income for Smithsonian Corporation as a whole if the Bronx Division were dropped would be
Operating income for Smithsonian Corporation as a whole if the Bronx Division were dropped would be
A)$40,000.
B)$22,500.
C)$50,000.
D)$60,000.
 Operating income for Smithsonian Corporation as a whole if the Bronx Division were dropped would be
Operating income for Smithsonian Corporation as a whole if the Bronx Division were dropped would beA)$40,000.
B)$22,500.
C)$50,000.
D)$60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The following data pertains to the Montrose Company's three products: When Montrose converted over to ABC it discovered the following: The product margin for product M using ABC would be
A)$9,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$13,840.
D)$27,000.
A)$9,000.
B)$19,000.
C)$13,840.
D)$27,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Concierge Industries manufactures 40,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $12.75.
Concierge Industries can rent its unused manufacturing facilities for $45,000 if it purchases the component from the outside supplier.
What is the effect on income if Concierge purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$195,000 increase
B)$165,000 decrease
C)$225,000 decrease
D)$135,000 increase
Concierge Industries can rent its unused manufacturing facilities for $45,000 if it purchases the component from the outside supplier.
What is the effect on income if Concierge purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$195,000 increase
B)$165,000 decrease
C)$225,000 decrease
D)$135,000 increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The operations of Erin Corporation are divided into the Coral Division and the Cyan Division. Projections for the next year are as follows: 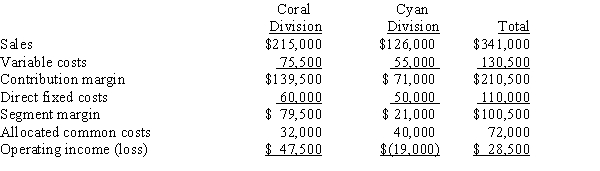 Operating income for Erin Corporation as a whole if the Cyan Division were dropped would be:
Operating income for Erin Corporation as a whole if the Cyan Division were dropped would be:
A)$7,500.
B)$47,500.
C)$(2,500).
D)$(42,500).
 Operating income for Erin Corporation as a whole if the Cyan Division were dropped would be:
Operating income for Erin Corporation as a whole if the Cyan Division were dropped would be:A)$7,500.
B)$47,500.
C)$(2,500).
D)$(42,500).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following items would be classified as committed resources (short-term)?
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)fuel to generate electricity internally
D)lease on machinery
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)fuel to generate electricity internally
D)lease on machinery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following items would be classified as flexible resources?
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)fuel to generate electricity internally
D)lease on machinery
A)salaried employees
B)depreciation on building
C)fuel to generate electricity internally
D)lease on machinery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The following information pertains to Lilac Company's three products: Assume that product C is discontinued and the space is used to produce B. Product B's production is increased to 4,000 units per month, but the selling price of all units of B is reduced to $5 per unit. Monthly profits will:
A)decrease by $1,000.
B)decrease by $520.
C)increase by $500.
D)increase by $980.
A)decrease by $1,000.
B)decrease by $520.
C)increase by $500.
D)increase by $980.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cerise Corporation manufacturers a part for its production cycle. The costs per unit for 5,000 units of this part are as follows: Jade Company has offered to sell Cerise Corporation 5,000 units of the part for $56 per unit. If Cerise Corporation accepts Jade Company's offer, total fixed costs will be reduced to $30,000. Which of the following is correct decision and correct increase in profit?
A)Buy, $50,000
B)Buy, $20,000
C)Make, $10,000
D)Buy, $10,000
A)Buy, $50,000
B)Buy, $20,000
C)Make, $10,000
D)Buy, $10,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Carmine Company uses 4,000 units of a product each year. The cost of manufacturing one unit at this volume is as follows: An outside supplier has offered to sell Carmine Company unlimited quantities at a unit cost of $30.00. If Carmine Company accepts this offer, it can eliminate 50 percent of the fixed costs assigned to the product. Furthermore, the space devoted to the manufacture of the product would be rented to another company for $18,000 per year. If Carmine Company accepts the offer of the outside supplier, annual profits will:
A)increase by $26,000.
B)increase by $16,000.
C)increase by $20,000.
D)decrease by $20,000.
A)increase by $26,000.
B)increase by $16,000.
C)increase by $20,000.
D)decrease by $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Hobart Company produces speakers for PA systems. The speakers are sold to retail music stores for $30. Manufacturing and other costs are as follows: The variable distribution costs are for transportation to the retail music stores. The current production and sales volume is 20,000 per year. Capacity is 25,000 units per year.
A Memphis manufacturing firm has offered a one-year contract to supply speaker parts at a cost of $6.00 per unit. If Hobart Company accepts the offer, it will be able to reduce variable costs by 30 percent and rent unused space to an outside firm for $18,000 per year. All other information remains the same as the original data. What is the effect on profits if Hobart Company buys from the Memphis firm?
A)decrease of $19,000
B)increase of $19,000
C)increase of $6,000
D)increase of $13,000
A Memphis manufacturing firm has offered a one-year contract to supply speaker parts at a cost of $6.00 per unit. If Hobart Company accepts the offer, it will be able to reduce variable costs by 30 percent and rent unused space to an outside firm for $18,000 per year. All other information remains the same as the original data. What is the effect on profits if Hobart Company buys from the Memphis firm?
A)decrease of $19,000
B)increase of $19,000
C)increase of $6,000
D)increase of $13,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The following data pertains to the Montrose Company's three products:
Common fixed costs
Inspecting products
Materials handling
Customer service
Plant depreciation
General administration When Montrose converted over to ABC it discovered the following: The operating income for Montrose would be
The operating income for Montrose would be
A)$8,500.
B)$9,000.
C)$19,000.
D)$27,000.
Common fixed costs
Inspecting products
Materials handling
Customer service
Plant depreciation
General administration When Montrose converted over to ABC it discovered the following:
 The operating income for Montrose would be
The operating income for Montrose would beA)$8,500.
B)$9,000.
C)$19,000.
D)$27,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Ecru Company manufactures 10,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $20.
What is the effect on income if Ecru Company purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)A $25,000 increase
B)A $25,000 decrease
C)A $85,000 decrease
D)A $85,000 increase
What is the effect on income if Ecru Company purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)A $25,000 increase
B)A $25,000 decrease
C)A $85,000 decrease
D)A $85,000 increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Yankton Industries manufactures 20,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $23.50.
Yankton Industries can rent its unused manufacturing facilities for $45,000 if it purchases the component from the outside supplier.
What is the effect on income if Yankton purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$25,000 increase
B)$45,000 increase
C)$75,000 decrease
D)$105,000 increase
Yankton Industries can rent its unused manufacturing facilities for $45,000 if it purchases the component from the outside supplier.
What is the effect on income if Yankton purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$25,000 increase
B)$45,000 increase
C)$75,000 decrease
D)$105,000 increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Yankton Industries manufactures 20,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: If the component is not produced by Yankton, inspection of products and provision of power costs will only be 10 percent of the production costs; moving materials costs and setting up equipment costs will only be 50 percent of the production costs; and supervision costs will amount to only 40 percent of the production amount. An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $23.50.
What is the effect on income if Yankton Industries purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$25,000 increase
B)$45,000 increase
C)$80,000 decrease
D)$80,000 increase
What is the effect on income if Yankton Industries purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$25,000 increase
B)$45,000 increase
C)$80,000 decrease
D)$80,000 increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the activity resource model, flexible resources are
A)resources acquired in advance of usage.
B)resources acquired as used and needed.
C)usually acquired in lumpy amounts.
D)are normally fixed or mixed costs.
A)resources acquired in advance of usage.
B)resources acquired as used and needed.
C)usually acquired in lumpy amounts.
D)are normally fixed or mixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Concierge Industries manufactures 40,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $12.75.
What is the effect on income if Concierge Industries purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$30,000 increase
B)$30,000 decrease
C)$270,000 increase
D)$270,000 decrease
What is the effect on income if Concierge Industries purchases the component from the outside supplier?
A)$30,000 increase
B)$30,000 decrease
C)$270,000 increase
D)$270,000 decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Hobart Company produces speakers for PA systems. The speakers are sold to retail music stores for $30. Manufacturing and other costs are as follows: The variable distribution costs are for transportation to the retail music stores. The current production and sales volume is 20,000 per year. Capacity is 25,000 units per year.
The speakers are currently unpackaged. Packaging them individually would increase costs by $1.20 per unit. However, the units could then be sold for $33.00. All other information remains the same as the original data. What is the effect on profits if Hobart Company packages the speakers?
A)no change
B)decrease of $24,000
C)decrease of $36,000
D)increase of $36,000
The speakers are currently unpackaged. Packaging them individually would increase costs by $1.20 per unit. However, the units could then be sold for $33.00. All other information remains the same as the original data. What is the effect on profits if Hobart Company packages the speakers?
A)no change
B)decrease of $24,000
C)decrease of $36,000
D)increase of $36,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The following information pertains to Dallas Churning Company's three products:
Assume that product F is discontinued and the space used to produce product F is rented for $600 per month. Monthly profits will
A)increase by $360.
B)increase by $840.
C)increase by $600.
D)decrease by $5,400.
Assume that product F is discontinued and the space used to produce product F is rented for $600 per month. Monthly profits will
A)increase by $360.
B)increase by $840.
C)increase by $600.
D)decrease by $5,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



