Deck 5: Elasticity and Its Applications
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/282
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Elasticity and Its Applications
1
Which one of the following products would tend to have inelastic demand?
A) luxury sedans
B) candy
C) crude oil
D) Black Angus T-bone steak
A) luxury sedans
B) candy
C) crude oil
D) Black Angus T-bone steak
C
2
Which good below might be expected to have the most inelastic demand curve?
A) salt
B) women's blouses from Walmart
C) potato chips
D) Tylenol
A) salt
B) women's blouses from Walmart
C) potato chips
D) Tylenol
A
3
Figure: Demand Elasticities 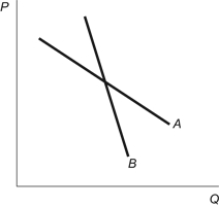 Refer to the figure. It shows two different demand curves. Based on the graph, which statement is TRUE?
Refer to the figure. It shows two different demand curves. Based on the graph, which statement is TRUE?
A) Elasticity of demand equals the slope of the curve so demand curve A is more elastic.
B) Elasticity of demand equals the slope of the curve so demand curve B is more elastic.
C) Since these two linear demand curves run through a common point we can say that at any given quantity, demand curve A is more elastic than curve B.
D) We cannot infer anything about elasticity from this diagram because slope does not equal elasticity.
 Refer to the figure. It shows two different demand curves. Based on the graph, which statement is TRUE?
Refer to the figure. It shows two different demand curves. Based on the graph, which statement is TRUE?A) Elasticity of demand equals the slope of the curve so demand curve A is more elastic.
B) Elasticity of demand equals the slope of the curve so demand curve B is more elastic.
C) Since these two linear demand curves run through a common point we can say that at any given quantity, demand curve A is more elastic than curve B.
D) We cannot infer anything about elasticity from this diagram because slope does not equal elasticity.
C
4
The demand for oil is inelastic because there are:
A) many complements for oil in its major use.
B) few complements for oil in its major use.
C) many substitutes for oil in its major use.
D) few substitutes for oil in its major use.
A) many complements for oil in its major use.
B) few complements for oil in its major use.
C) many substitutes for oil in its major use.
D) few substitutes for oil in its major use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The demand curve for Froot Loops breakfast cereal is very elastic because:
A) most breakfast cereals are considered a luxury good.
B) there are many good substitutes for Froot Loops.
C) the demand curve is negatively sloped.
D) it is one of the most advertised cereals in the world.
A) most breakfast cereals are considered a luxury good.
B) there are many good substitutes for Froot Loops.
C) the demand curve is negatively sloped.
D) it is one of the most advertised cereals in the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The price of wheat increases, but few people cut back on their consumption of bread because:
A) the price of bread is a small portion of the budget, and thus the demand for bread is inelastic.
B) the price of bread is a large portion of the budget, and thus the demand for bread is elastic.
C) change in the price of wheat does not affect the price of bread.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) the price of bread is a small portion of the budget, and thus the demand for bread is inelastic.
B) the price of bread is a large portion of the budget, and thus the demand for bread is elastic.
C) change in the price of wheat does not affect the price of bread.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The demand curve for oil is inelastic, meaning that the quantity of oil demanded:
A) rises by a lot even when the price of oil increases by only a little.
B) rises by only a little even when the price of oil increases by a lot.
C) falls by a lot even when the price of oil increases by only a little.
D) falls by only a little even when the price of oil increases by a lot.
A) rises by a lot even when the price of oil increases by only a little.
B) rises by only a little even when the price of oil increases by a lot.
C) falls by a lot even when the price of oil increases by only a little.
D) falls by only a little even when the price of oil increases by a lot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following factors causes a demand curve to become more elastic over time?
A) New substitutes for the product are discovered.
B) New and important uses for the product are discovered.
C) More producers begin to produce the product.
D) More consumers acquire a desire for the product.
A) New substitutes for the product are discovered.
B) New and important uses for the product are discovered.
C) More producers begin to produce the product.
D) More consumers acquire a desire for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The demand curve for physician office visits is quite inelastic; therefore:
A) a large increase in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by very little.
B) a large decrease in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by a lot.
C) a small increase in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by a lot.
D) a small decrease in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by very little.
A) a large increase in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by very little.
B) a large decrease in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by a lot.
C) a small increase in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by a lot.
D) a small decrease in price causes quantity demanded to decrease by very little.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All of the following conditions would cause the demand curve for a good to be more elastic EXCEPT:
A) a longer time horizon.
B) the good is considered a luxury good.
C) the price of the good falls.
D) the good has many substitutes.
A) a longer time horizon.
B) the good is considered a luxury good.
C) the price of the good falls.
D) the good has many substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Table: Elasticity Characteristics The table lists the characteristics of three goods. Good ________ is the most inelastic, and Good ________ is the most elastic.
A) X; Y
B) Z; Y
C) X; Z
D) Y; X
A) X; Y
B) Z; Y
C) X; Z
D) Y; X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why is the demand curve for oil rather inelastic?
A) There are few widely available good substitutes for oil.
B) To increase the production of oil requires a significant outlay of exploration and drilling costs.
C) The world supply of oil is low relative to demand.
D) The demand curve for oil is always perfectly inelastic.
A) There are few widely available good substitutes for oil.
B) To increase the production of oil requires a significant outlay of exploration and drilling costs.
C) The world supply of oil is low relative to demand.
D) The demand curve for oil is always perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a reason why the demand curve for an item would be more elastic?
A) The item is a necessity.
B) People's incomes are very high relative to the cost of the item.
C) The item has many very good substitutes.
D) The cost of the item forms a very small part of consumers' budgets.
A) The item is a necessity.
B) People's incomes are very high relative to the cost of the item.
C) The item has many very good substitutes.
D) The cost of the item forms a very small part of consumers' budgets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure: Price Elasticity of Demand 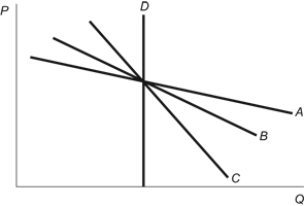 Refer to the figure. Which of the four demand curves has the greatest responsiveness to price changes?
Refer to the figure. Which of the four demand curves has the greatest responsiveness to price changes?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
 Refer to the figure. Which of the four demand curves has the greatest responsiveness to price changes?
Refer to the figure. Which of the four demand curves has the greatest responsiveness to price changes?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure: Elasticity and Quantity Demanded 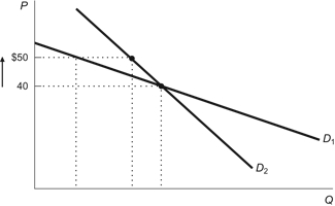 Refer to the figure. An increase in price from $40 to $50 would cause the change in quantity demanded for D1 to be:
Refer to the figure. An increase in price from $40 to $50 would cause the change in quantity demanded for D1 to be:
A) greater than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D1 is more elastic than D2.
B) greater than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D2 is more elastic than D1.
C) less than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D1 is more inelastic than D2.
D) less than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D2 is more inelastic than D1.
 Refer to the figure. An increase in price from $40 to $50 would cause the change in quantity demanded for D1 to be:
Refer to the figure. An increase in price from $40 to $50 would cause the change in quantity demanded for D1 to be:A) greater than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D1 is more elastic than D2.
B) greater than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D2 is more elastic than D1.
C) less than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D1 is more inelastic than D2.
D) less than the change in quantity demanded for D2 so D2 is more inelastic than D1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The elasticity of demand:
A) equals the inverse of price to quantity demanded.
B) measures how far the demand curve shifts from a change in price.
C) tells us how responsive consumer purchases are to price changes.
D) estimates the relationship between quantity demanded and production costs.
A) equals the inverse of price to quantity demanded.
B) measures how far the demand curve shifts from a change in price.
C) tells us how responsive consumer purchases are to price changes.
D) estimates the relationship between quantity demanded and production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would NOT make elasticity of demand for a good more elastic?
A) more substitutes
B) luxuries
C) large part of budget
D) less time
A) more substitutes
B) luxuries
C) large part of budget
D) less time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The price elasticity of demand is:
A) the responsiveness of price to changes in the quantity demanded of the product.
B) the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in the price of the product.
C) the change in the firm's total revenue when prices change.
D) exactly the same as the slope of the demand curve.
A) the responsiveness of price to changes in the quantity demanded of the product.
B) the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in the price of the product.
C) the change in the firm's total revenue when prices change.
D) exactly the same as the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The elasticity of demand measures:
A) the height of the demand curve.
B) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C) how sensitive the price is to a change in demand.
D) the extent to which demand shifts in response to supply changes.
A) the height of the demand curve.
B) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C) how sensitive the price is to a change in demand.
D) the extent to which demand shifts in response to supply changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The elasticity of demand measures how sensitive the:
A) price is to a change in quantity demanded.
B) quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C) price is to a change in the quantity supplied.
D) demand is to a change in the number of suppliers.
A) price is to a change in quantity demanded.
B) quantity demanded is to a change in price.
C) price is to a change in the quantity supplied.
D) demand is to a change in the number of suppliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The price of cigars is $10, with a quantity demanded of 1,000 per day. If the price increases to $12, the quantity demanded declines to 800 per day. What is the absolute value of elasticity of demand?
A) 1.00
B) 0.82
C) 1.22
D) 12.2
A) 1.00
B) 0.82
C) 1.22
D) 12.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A 4 percent increase in the price of beer will cause a 1 percent decline in the quantity of beer demanded. The demand for beer is:
A) elastic.
B) unitary elastic.
C) inelastic.
D) elastic at 4 (in absolute value).
A) elastic.
B) unitary elastic.
C) inelastic.
D) elastic at 4 (in absolute value).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an increase in the price of oil by 10 percent would cause the quantity demanded for oil to fall by 5 percent, the elasticity of demand for oil in absolute terms is:
A)10.
B)5.
C)2.
D) 0.5.
A)10.
B)5.
C)2.
D) 0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the price of Good X rises from $4 to $5, and the quantity demanded of it falls from 200 units to 180 units, the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is:
A) 2.1.
B) 0.47.
C) 1.4.
D) 0.4.
A) 2.1.
B) 0.47.
C) 1.4.
D) 0.4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If demand is elastic, a price ________ causes ________ in total revenue.
A) decrease; a decrease
B) increase; an increase
C) decrease; an increase
D) increase; no change.
A) decrease; a decrease
B) increase; an increase
C) decrease; an increase
D) increase; no change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the price of gasoline in this country were expected to rise due to a permanent increase in the tax on gasoline, which of the following would you expect to happen?
A) The demand for gasoline would become more elastic.
B) The demand for gasoline would decrease as a result of the higher price.
C) Producers will have less of an incentive to supply gasoline as a result of the higher taxes.
D) The elasticity of demand will not change since gasoline is a necessary good.
A) The demand for gasoline would become more elastic.
B) The demand for gasoline would decrease as a result of the higher price.
C) Producers will have less of an incentive to supply gasoline as a result of the higher taxes.
D) The elasticity of demand will not change since gasoline is a necessary good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If Major League Baseball ticket prices rise by 15 percent, the number of tickets sold falls by 5 percent. The elasticity of demand is:
A) -3.
B) -1/3.
C) -7.5.
D) -0.75.
A) -3.
B) -1/3.
C) -7.5.
D) -0.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The demand curve is inelastic if the absolute value of the elasticity is:
A) greater than 1.
B) greater than 0.
C) less than 1.
D) equal to 1.
A) greater than 1.
B) greater than 0.
C) less than 1.
D) equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the price of ice cream changes by 30 percent and the quantity demanded changes by 75 percent, what is the absolute value of demand elasticity?
A) 2.5, so demand is inelastic
B) 0.4, so demand is inelastic
C) 0.4, so demand is elastic
D) 2.5, so demand is elastic
A) 2.5, so demand is inelastic
B) 0.4, so demand is inelastic
C) 0.4, so demand is elastic
D) 2.5, so demand is elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Marge tutors English students. If she raises rates, her revenues increase. Brad tutors biology students. If he lowers rates, his revenues increase. Which of the following is TRUE?
A) Marge's demand is elastic, and Brad's demand is inelastic.
B) Marge's demand is inelastic, and Brad's demand is elastic.
C) Marge's demand is elastic, and Brad's demand is elastic.
D) Marge's demand is inelastic, and Brad's demand is inelastic.
A) Marge's demand is elastic, and Brad's demand is inelastic.
B) Marge's demand is inelastic, and Brad's demand is elastic.
C) Marge's demand is elastic, and Brad's demand is elastic.
D) Marge's demand is inelastic, and Brad's demand is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assume that the supply curve for a good is fixed at 100 units. Now suppose that the demand curve for the good increases such that the equilibrium price rises from $20 to $30. How does total revenue for the sale of this product change?
A) Total revenue rises by $1,000.
B) Total revenue does not change.
C) Total revenue rises by $3,000.
D) Total revenue rises by $10.
A) Total revenue rises by $1,000.
B) Total revenue does not change.
C) Total revenue rises by $3,000.
D) Total revenue rises by $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Total revenue is:
A) price × quantity.
B) quantity/price.
C) the elasticity of demand X price.
D) price + quantity.
A) price × quantity.
B) quantity/price.
C) the elasticity of demand X price.
D) price + quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure: Elasticity and Revenue 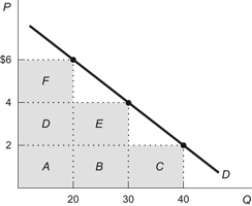 Refer to the figure. When the price of the product rises from $4 to $6, the total revenue changes by the area(s) represented by:
Refer to the figure. When the price of the product rises from $4 to $6, the total revenue changes by the area(s) represented by:
A) F.
B) F - E.
B).
C) F - (E +
D) F + D + A.
 Refer to the figure. When the price of the product rises from $4 to $6, the total revenue changes by the area(s) represented by:
Refer to the figure. When the price of the product rises from $4 to $6, the total revenue changes by the area(s) represented by:A) F.
B) F - E.
B).
C) F - (E +
D) F + D + A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the price elasticity of demand is 0.5, then when the price of Good X rises by 20 percent:
A) the quantity demanded of it rises by 40 percent.
B) the quantity demanded of it rises by 10 percent.
C) the quantity demanded of it falls by 10 percent.
D) the quantity demanded of it falls by 40 percent.
A) the quantity demanded of it rises by 40 percent.
B) the quantity demanded of it rises by 10 percent.
C) the quantity demanded of it falls by 10 percent.
D) the quantity demanded of it falls by 40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If demand is inelastic, a price ________ causes ________ in total revenue.
A) decrease; a decrease
B) decrease; an increase
C) increase; a decrease
D) increase; no change.
A) decrease; a decrease
B) decrease; an increase
C) increase; a decrease
D) increase; no change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When the demand curve for a good is unit elastic, raising the price of the good by 25 percent will change the revenue of the firm by:
A) 125 percent.
B) 100 percent.
C) 25 percent.
D) 0 percent.
A) 125 percent.
B) 100 percent.
C) 25 percent.
D) 0 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure: Elasticity and Total Revenue 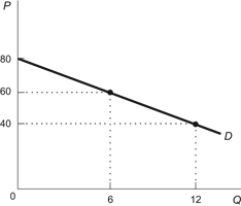 Refer to the figure. If price falls from $60 to $40, total revenue goes ________, so demand is ________.
Refer to the figure. If price falls from $60 to $40, total revenue goes ________, so demand is ________.
A) down by $100; inelastic
B) down by $480; elastic
C) up by $360; inelastic
D) up by $120; elastic
 Refer to the figure. If price falls from $60 to $40, total revenue goes ________, so demand is ________.
Refer to the figure. If price falls from $60 to $40, total revenue goes ________, so demand is ________.A) down by $100; inelastic
B) down by $480; elastic
C) up by $360; inelastic
D) up by $120; elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the price of Good Y falls from $10 to $8, and the quantity demanded of it rises from 1,000 units to 1,200 units, the price elasticity of demand expressed in absolute value is:
A) 1.00.
B) 0.20.
C) 0.82.
D) 1.22.
A) 1.00.
B) 0.20.
C) 0.82.
D) 1.22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The elasticity of demand for a good is -0.75. A 4 percent increase in price will cause a:
A) 3 percent decrease in quantity demanded.
B) 5.33 percent increase in quantity demanded.
C) 5.33 percent decrease in quantity demanded.
D) 0.19 percent decrease in quantity demanded.
A) 3 percent decrease in quantity demanded.
B) 5.33 percent increase in quantity demanded.
C) 5.33 percent decrease in quantity demanded.
D) 0.19 percent decrease in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the price elasticity of demand is 2 in absolute value, then when the price of Good X rises by 25 percent:
A) the quantity demanded of it rises by 50 percent.
B) the quantity demanded of it falls by 50 percent.
C) the quantity demanded of it rises by 12.5 percent.
D) the quantity demanded of it falls by 12.5 percent.
A) the quantity demanded of it rises by 50 percent.
B) the quantity demanded of it falls by 50 percent.
C) the quantity demanded of it rises by 12.5 percent.
D) the quantity demanded of it falls by 12.5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure: Price Decrease and Elasticity 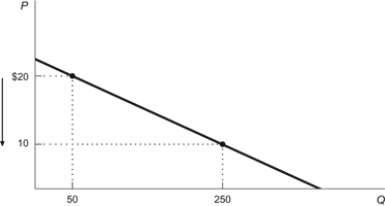 Refer to the figure. If price decreases from $20 to $10, total revenue will:
Refer to the figure. If price decreases from $20 to $10, total revenue will:
A) decrease by $1,500, so the demand curve is inelastic.
B) decrease by $2,500, so the demand curve is inelastic.
C) increase by $1,500, so the demand curve is elastic.
D) increase by $2,500, so the demand curve is elastic.
 Refer to the figure. If price decreases from $20 to $10, total revenue will:
Refer to the figure. If price decreases from $20 to $10, total revenue will:A) decrease by $1,500, so the demand curve is inelastic.
B) decrease by $2,500, so the demand curve is inelastic.
C) increase by $1,500, so the demand curve is elastic.
D) increase by $2,500, so the demand curve is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the demand for a good is estimated to be _____, then firms producing the good will experience an increase in total revenue if prices fall.
A) .05
B) .75
C) 1
D) 2.5
A) .05
B) .75
C) 1
D) 2.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If two linear demand (or supply) curves run through a common point, then at any given quantity, the curve that is steeper is more:
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) responsive.
D) resilient.
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) responsive.
D) resilient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If demand is inelastic then an increase in price would cause a _____ in the quantity demanded and a(n) _____ in total revenue:
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
To examine how responsive consumers are to price changes, economists measure:
A) the elasticity of demand.
B) mean household income.
C) median household income.
D) key economic indicators such as unemployment, inflation, and economic growth.
A) the elasticity of demand.
B) mean household income.
C) median household income.
D) key economic indicators such as unemployment, inflation, and economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What happens to total revenue when demand is unit elastic and the price changes?
A) Revenues increase when the price increases.
B) Revenues remain unchanged.
C) Revenues decrease when the price increases.
D) The change in revenues cannot be estimated.
A) Revenues increase when the price increases.
B) Revenues remain unchanged.
C) Revenues decrease when the price increases.
D) The change in revenues cannot be estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Over time, the demand for most goods becomes ______ elastic since we are able to ______.
A) more; develop more/better substitutes
B) less; develop more/better substitutes
C) more; produce more of the good or service
D) less; produce more of the good or service
A) more; develop more/better substitutes
B) less; develop more/better substitutes
C) more; produce more of the good or service
D) less; produce more of the good or service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The demand for most goods tends to become ______ over time.
A) downward sloping
B) more vertical
C) more elastic
D) less elastic
A) downward sloping
B) more vertical
C) more elastic
D) less elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The elasticity of demand measures:
A) whether consumers will buy more or less as the price increases.
B) how much less of a good or service consumers will buy when the price increases.
C) a supplier's estimate of market demand.
D) how consumers substitute across goods when the price of one good increases.
A) whether consumers will buy more or less as the price increases.
B) how much less of a good or service consumers will buy when the price increases.
C) a supplier's estimate of market demand.
D) how consumers substitute across goods when the price of one good increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following probably has the least elastic demand?
A) cable television
B) prescription medications
C) eggs
D) McDonald's hamburgers
A) cable television
B) prescription medications
C) eggs
D) McDonald's hamburgers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure: Price Increase and Elasticity 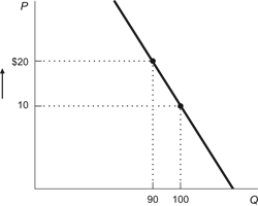 Refer to the figure. If price increases from $10 to $20, total revenue will:
Refer to the figure. If price increases from $10 to $20, total revenue will:
A) increase by $800 so the demand curve must be inelastic.
B) increase by $100 so the demand curve must be inelastic.
C) decrease by $800 so the demand curve must be elastic.
D) decrease by $100 so the demand curve must be elastic.
 Refer to the figure. If price increases from $10 to $20, total revenue will:
Refer to the figure. If price increases from $10 to $20, total revenue will:A) increase by $800 so the demand curve must be inelastic.
B) increase by $100 so the demand curve must be inelastic.
C) decrease by $800 so the demand curve must be elastic.
D) decrease by $100 so the demand curve must be elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The more quantity demanded responds to a change in the price of that good the _____ is for that good.
A) more elastic demand
B) less elastic demand
C) more elastic supply
D) less elastic supply
A) more elastic demand
B) less elastic demand
C) more elastic supply
D) less elastic supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The price of good X increases from $55 to $60, and quantity demanded decreases from 500 to 400. The price of good Y increases from $55 to $60, and quantity demanded decreases from 500 to 475. Given this information, the:
A) consumers who buy good X are less sensitive to price changes than consumers who buy good Y.
B) demand curve for good X is less elastic than the demand curve for good Y.
C) demand curve for good X is more elastic than the demand curve for good Y.
D) demand curves for good X and good Y violate the law of demand.
A) consumers who buy good X are less sensitive to price changes than consumers who buy good Y.
B) demand curve for good X is less elastic than the demand curve for good Y.
C) demand curve for good X is more elastic than the demand curve for good Y.
D) demand curves for good X and good Y violate the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The elasticity of demand measures:
A) how responsive price is to a change in the quantity demanded of a good or service.
B) how much value consumers place on each unit of the good or service.
C) the rate of change of demand in relation to supply.
D) how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in the price of a good or service.
A) how responsive price is to a change in the quantity demanded of a good or service.
B) how much value consumers place on each unit of the good or service.
C) the rate of change of demand in relation to supply.
D) how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in the price of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When comparing two linear demand curves at a common point, the flatter curve is:
A) more normal.
B) less responsive.
C) more elastic.
D) less elastic.
A) more normal.
B) less responsive.
C) more elastic.
D) less elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following probably has the most elastic demand?
A) gasoline
B) prescription medications
C) toilet paper
D) McDonald's hamburgers
A) gasoline
B) prescription medications
C) toilet paper
D) McDonald's hamburgers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Table: Demand Curves In the table, which demand curve is most price elastic over the range of prices considered?
A) demand curve A
B) demand curve B
C) demand curve C
D) demand curve D
A) demand curve A
B) demand curve B
C) demand curve C
D) demand curve D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The elasticity of demand measures:
A) how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
B) the percent change in quantity demanded.
C) the percent change in price.
D) the percent change in quantity supplied divided by the percent change in price.
A) how responsive quantity demanded is to a change in price.
B) the percent change in quantity demanded.
C) the percent change in price.
D) the percent change in quantity supplied divided by the percent change in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The fundamental determinant of the elasticity of demand for a good is:
A) the opportunity cost of producing the good.
B) the value that consumers place on one more unit of the good.
C) how easy it is to substitute the good for another.
D) the number of consumers in the market.
A) the opportunity cost of producing the good.
B) the value that consumers place on one more unit of the good.
C) how easy it is to substitute the good for another.
D) the number of consumers in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The manager of a company notices that the company's total revenue would increase if she raised the price of the company's product. Accordingly, the manager can assert that the demand for the company's product is:
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The demand for Michelin tires is ______ elastic than the demand for tires, and the demand for chocolate is ______ elastic than the demand for Godiva chocolate.
A) more; more
B) less; more
C) less; less
D) more; less
A) more; more
B) less; more
C) less; less
D) more; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A good with many substitutes will have a _____ curve that is relatively _____ elastic than a good with few substitutes.
A) supply; less
B) supply; more
C) demand; less
D) demand; more
A) supply; less
B) supply; more
C) demand; less
D) demand; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand for a good is 1.5, the good has a(n):
A) elastic demand.
B) inelastic demand.
C) unit elastic demand.
D) unit inelastic demand.
A) elastic demand.
B) inelastic demand.
C) unit elastic demand.
D) unit inelastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economists categorize price elasticity of demand greater than 1 as:
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) normal.
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If gasoline prices remain high long enough, people will arrange to do more telecommuting. This would be an example of why the elasticity of:
A) supply for gasoline is higher in the long run.
B) supply for gasoline is lower in the long run.
C) demand for gasoline is higher in the long run.
D) demand for gasoline is lower in the long run.
A) supply for gasoline is higher in the long run.
B) supply for gasoline is lower in the long run.
C) demand for gasoline is higher in the long run.
D) demand for gasoline is lower in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Are there more substitutes for Cheerios or for cereal in general? For which good is demand more elastic?
A) Cheerios; Cheerios
B) Cheerios; cereal
C) cereal; Cheerios
D) cereal; cereal
A) Cheerios; Cheerios
B) Cheerios; cereal
C) cereal; Cheerios
D) cereal; cereal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Necessities tend to have a(n) ______ demand than luxuries.
A) more elastic
B) more inelastic
C) equally elastic
D) equally inelastic
A) more elastic
B) more inelastic
C) equally elastic
D) equally inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The long-run demand for oil ______ the short-run demand for oil.
A) is more elastic than
B) is less elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) differs in elasticity in an indeterminate direction compared with
A) is more elastic than
B) is less elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) differs in elasticity in an indeterminate direction compared with

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Most people, when asked, cannot name the price of a canister of table salt at the grocery store within a factor of 25 percent. Which elasticity argument explains why?
A) Table salt has many substitutes; demand is highly elastic.
B) Expenditures on table salt make up a tiny fraction of the average person's budget; demand is highly inelastic.
C) Most people make their salt consumption decisions in the short run.
D) People are loyal to their specific brands of salt.
A) Table salt has many substitutes; demand is highly elastic.
B) Expenditures on table salt make up a tiny fraction of the average person's budget; demand is highly inelastic.
C) Most people make their salt consumption decisions in the short run.
D) People are loyal to their specific brands of salt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A good with an absolute value of the price elasticity of demand of 1.0 is classified as:
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly inelastic.
A) elastic.
B) inelastic.
C) unit elastic.
D) perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The availability of fewer substitutes for a good means its demand curve:
A) becomes less elastic.
B) becomes more elastic.
C) maintains the same elasticity.
D) changes elasticity in an indeterminate direction.
A) becomes less elastic.
B) becomes more elastic.
C) maintains the same elasticity.
D) changes elasticity in an indeterminate direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The fundamental determinant of the elasticity of demand is:
A) how quickly per-unit costs increase with an increase in production.
B) tastes and preferences.
C) population.
D) the number and closeness of substitutes.
A) how quickly per-unit costs increase with an increase in production.
B) tastes and preferences.
C) population.
D) the number and closeness of substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why might the demand for massages be more elastic than the demand for chiropractic adjustments?
A) Relative to massages, there are more substitutes for chiropractic adjustments.
B) People get massages in the short run and chiropractic adjustments in the long run.
C) Massages are much cheaper than chiropractic adjustments.
D) Massages tend to be luxuries and chiropractic adjustments tend to be necessities.
A) Relative to massages, there are more substitutes for chiropractic adjustments.
B) People get massages in the short run and chiropractic adjustments in the long run.
C) Massages are much cheaper than chiropractic adjustments.
D) Massages tend to be luxuries and chiropractic adjustments tend to be necessities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The most important determinant of the elasticity of demand is the:
A) number of consumers.
B) number of substitutes.
C) size of the population.
D) level of income in the economy.
A) number of consumers.
B) number of substitutes.
C) size of the population.
D) level of income in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Luxury goods tend to have more elastic demand curves.
B) Goods that are necessities tend to have more elastic demand curves.
C) The elasticity of demand for a particular brand of product equals the elasticity of demand for the product category.
D) Goods with more substitutes tend to have a lower elasticity of demand.
A) Luxury goods tend to have more elastic demand curves.
B) Goods that are necessities tend to have more elastic demand curves.
C) The elasticity of demand for a particular brand of product equals the elasticity of demand for the product category.
D) Goods with more substitutes tend to have a lower elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Demand for a specific brand ______ demand for the corresponding product category.
A) is more elastic than
B) is less elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) differs indeterminately from
A) is more elastic than
B) is less elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) differs indeterminately from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A good with an absolute value of the price elasticity of demand of 0.5 has:
A) an elastic demand.
B) an inelastic demand.
C) unit elastic demand.
D) perfectly inelastic demand.
A) an elastic demand.
B) an inelastic demand.
C) unit elastic demand.
D) perfectly inelastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A higher income tends to make demand for a given good ______ elastic.
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) indeterminately
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) indeterminately

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
There are ______ substitutes for oil, so the elasticity of demand for oil is ______ elastic.
A) few; very
B) few; not very
C) many; perfectly
D) many; very
A) few; very
B) few; not very
C) many; perfectly
D) many; very

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In 2005, Ireland began taxing residents on how much garbage they threw away in an effort to promote recycling. In response, residents began burning trash (which is environmentally more harmful and resulted in an increase in burn victims as people accidentally set themselves on fire). This story suggests that the elasticity of demand for trash collection was more ______ than lawmakers believed because ______ than previously thought.
A) elastic; the tax took up a larger part of residents' budgets
B) elastic; there were more substitutes for trash collection
C) inelastic; the tax took up a smaller part of residents' budgets
D) inelastic; there were fewer substitutes for trash collection
A) elastic; the tax took up a larger part of residents' budgets
B) elastic; there were more substitutes for trash collection
C) inelastic; the tax took up a smaller part of residents' budgets
D) inelastic; there were fewer substitutes for trash collection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 282 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



