Deck 24: Floating Exchange Rates and Internal Balance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Floating Exchange Rates and Internal Balance
1
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a high degree of capital mobility, in the short run an expansionary fiscal policy will most likely create pressure on:
A)the domestic currency to appreciate.
B)the domestic currency to depreciate.
C)monetary authorities to revalue the domestic currency.
D)monetary authorities to devalue the domestic currency.
A)the domestic currency to appreciate.
B)the domestic currency to depreciate.
C)monetary authorities to revalue the domestic currency.
D)monetary authorities to devalue the domestic currency.
A
2
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a low degree of capital mobility, an expansionary fiscal policy will most likely create pressure on:
A)monetary authorities to revalue the domestic currency.
B)the domestic currency to depreciate.
C)the domestic currency to appreciate.
D)monetary authorities to devalue the domestic currency.
A)monetary authorities to revalue the domestic currency.
B)the domestic currency to depreciate.
C)the domestic currency to appreciate.
D)monetary authorities to devalue the domestic currency.
B
3
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a high degree of capital mobility, a change in the exchange rate value of domestic currency following contractionary fiscal policy is most likely to:
A)improve the current account.
B)decrease the country's holdings of official reserve assets.
C)cause a surplus in the financial account.
D)induce inflow of foreign capital.
A)improve the current account.
B)decrease the country's holdings of official reserve assets.
C)cause a surplus in the financial account.
D)induce inflow of foreign capital.
A
4
Under a floating exchange rate regime, an expansion in the money supply will:
A)induce financial capital to leave the country.
B)attract financial capital into the country.
C)have no effect on financial account balance.
D)cause a surplus in the official settlement balance.
A)induce financial capital to leave the country.
B)attract financial capital into the country.
C)have no effect on financial account balance.
D)cause a surplus in the official settlement balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under a floating exchange rate regime:
A)only fiscal policy must be used to reconcile the goals of internal and external balance.
B)the changes in the exchange rate will take care of external balance leaving macroeconomic policy to take care of internal balance.
C)deficits and surpluses in the official settlements balance will be the primary concern of policy makers.
D)monetary policy must be used to manage the exchange rate.
A)only fiscal policy must be used to reconcile the goals of internal and external balance.
B)the changes in the exchange rate will take care of external balance leaving macroeconomic policy to take care of internal balance.
C)deficits and surpluses in the official settlements balance will be the primary concern of policy makers.
D)monetary policy must be used to manage the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Floating exchange rates ensure:
A)full employment in the trading countries.
B)domestic price stability.
C)equilibrium in the overall balance of payments.
D)a surplus in the trade balance.
A)full employment in the trading countries.
B)domestic price stability.
C)equilibrium in the overall balance of payments.
D)a surplus in the trade balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Other fundamental things equal, an increase in the exchange rate value of the domestic currency will cause the current account to:
A)fluctuate initially.
B)equal the official settlements balance.
C)move toward a long-run surplus.
D)move toward a deficit.
A)fluctuate initially.
B)equal the official settlements balance.
C)move toward a long-run surplus.
D)move toward a deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
With perfect capital mobility uncovered interest parity always holds because:
A)almost unlimited flows of capital can occur if there is any deviation from the parity.
B)lower domestic interest rates trigger hedging to avoid exchange rate risks.
C)capital flows out at a much faster rate than it flows in if the interest rate changes.
D)the no-arbitrage condition cannot be satisfied without using forward contract.
A)almost unlimited flows of capital can occur if there is any deviation from the parity.
B)lower domestic interest rates trigger hedging to avoid exchange rate risks.
C)capital flows out at a much faster rate than it flows in if the interest rate changes.
D)the no-arbitrage condition cannot be satisfied without using forward contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An expansion of the money supply by the country's central bank:
A)decreases the willingness of banks to lend money.
B)reduces the price level.
C)increases the level of international capital inflows.
D)causes domestic interest rates to fall.
A)decreases the willingness of banks to lend money.
B)reduces the price level.
C)increases the level of international capital inflows.
D)causes domestic interest rates to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For central bank liquidity swaps, which of the following is NOT true?
A)Central bank liquidity swaps were intended to provide dollar funding to non-U.S.financial institutions during the global financial and economic crisis.
B)In a central bank liquidity swap, the Fed provides dollars to a foreign central bank.
C)Central-bank liquidity swaps failed to effectively address the dollar problems in foreign banking systems during the global financial and economic crisis, so the swap programs were ended in February 2010.
D)Non-U.S.central banks used the dollars they received through central bank liquidity swaps to lend to financial institutions in their countries.
A)Central bank liquidity swaps were intended to provide dollar funding to non-U.S.financial institutions during the global financial and economic crisis.
B)In a central bank liquidity swap, the Fed provides dollars to a foreign central bank.
C)Central-bank liquidity swaps failed to effectively address the dollar problems in foreign banking systems during the global financial and economic crisis, so the swap programs were ended in February 2010.
D)Non-U.S.central banks used the dollars they received through central bank liquidity swaps to lend to financial institutions in their countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a high degree of capital mobility, international crowding out of expansionary fiscal policy occurs when:
A)the foreign money supply increases.
B)foreign interest rates increase.
C)the country's currency appreciates.
D)domestic interest rates increase.
A)the foreign money supply increases.
B)foreign interest rates increase.
C)the country's currency appreciates.
D)domestic interest rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Other fundamental things equal, an increase in the exchange rate value of the domestic currency will make the domestic goods:
A)to be demanded more internationally.
B)less competitive in the international markets.
C)more expensive in the domestic market.
D)more expensive to produce.
A)to be demanded more internationally.
B)less competitive in the international markets.
C)more expensive in the domestic market.
D)more expensive to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
With floating exchange rates, the effects of international trade shocks on internal balance are _____ by the effects of the resulting change in the _____.
A)not mitigated; LM curve.
B)not mitigated; exchange rate.
C)mitigated; LM curve.
D)mitigated; exchange rate.
A)not mitigated; LM curve.
B)not mitigated; exchange rate.
C)mitigated; LM curve.
D)mitigated; exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Monetary expansion, with perfect capital mobility, is effective in improving international price competitiveness of a country in:
A)the short-run with floating exchange rates.
B)the long-run with floating exchange rates.
C)the short-run with fixed exchange rates.
D)the long-run with fixed exchange rates.
A)the short-run with floating exchange rates.
B)the long-run with floating exchange rates.
C)the short-run with fixed exchange rates.
D)the long-run with fixed exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a low degree of capital mobility, a change in the exchange rate value of domestic currency following expansionary fiscal policy will tend to:
A)deteriorate the current account.
B)decrease the country's holdings of official reserve assets.
C)give a trade-based stimulus to domestic production.
D)cause a surplus in the financial account.
A)deteriorate the current account.
B)decrease the country's holdings of official reserve assets.
C)give a trade-based stimulus to domestic production.
D)cause a surplus in the financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Other fundamental things equal, a decrease in the exchange rate value of domestic currency will cause the current account to:
A)fluctuate initially.
B)equal the official settlements balance.
C)move toward a surplus.
D)move toward a long-run deficit.
A)fluctuate initially.
B)equal the official settlements balance.
C)move toward a surplus.
D)move toward a long-run deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Under a floating exchange rate regime, following an expansion in the money supply, monetary authorities will:
A)buy foreign currency in the foreign exchange market.
B)buy domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
C)not intervene in the foreign exchange market.
D)be forced to reverse the monetary expansion.
A)buy foreign currency in the foreign exchange market.
B)buy domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
C)not intervene in the foreign exchange market.
D)be forced to reverse the monetary expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Under a floating exchange rate regime with a low degree of capital mobility, if the domestic government uses an expansionary fiscal policy:
A)the domestic interest rate increases.
B)foreign capital inflows decrease domestic product.
C)the financial account balance deteriorates.
D)the official settlements balance tends to go into surplus.
A)the domestic interest rate increases.
B)foreign capital inflows decrease domestic product.
C)the financial account balance deteriorates.
D)the official settlements balance tends to go into surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Other fundamental things equal, a decrease in the exchange rate value of the domestic currency will make domestic goods:
A)to be demanded more internationally.
B)less competitive in the international markets.
C)less expensive in the domestic market.
D)less expensive to produce.
A)to be demanded more internationally.
B)less competitive in the international markets.
C)less expensive in the domestic market.
D)less expensive to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Under a floating exchange rate regime, the domestic currency will normally depreciate if the money supply:
A)contracts.
B)expands.
C)does not change with the change in the exchange rates.
D)is managed to keep the country's inflation rate steady.
A)contracts.
B)expands.
C)does not change with the change in the exchange rates.
D)is managed to keep the country's inflation rate steady.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Under a floating exchange rate regime, with a contraction in the money supply, which of the following is likely to happen in the short-run?
A)Increase in the country's holdings of official international reserves
B)Deficit in the financial account
C)Inflow of foreign capital
D)Rise in the domestic price level
A)Increase in the country's holdings of official international reserves
B)Deficit in the financial account
C)Inflow of foreign capital
D)Rise in the domestic price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT a reason why we see little international policy coordination?
A)The policy goals of different countries are often incompatible.
B)The benefits of international policy coordination are likely to be small in most situations.
C)Governments often have difficulty in delivering on their commitments as part of any international policy coordination.
D)The interventions by the different governments according to the policy coordination are usually effective in the very long-run.
A)The policy goals of different countries are often incompatible.
B)The benefits of international policy coordination are likely to be small in most situations.
C)Governments often have difficulty in delivering on their commitments as part of any international policy coordination.
D)The interventions by the different governments according to the policy coordination are usually effective in the very long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
With floating exchange rates, expansionary fiscal policy is more effective in increasing output when the:
A)FE curve is flatter than the LM curve.
B)FE curve is steeper than the LM curve.
C)FE curve is horizontal and the LM curve is vertical.
D)FE curve coincides with the LM curve.
A)FE curve is flatter than the LM curve.
B)FE curve is steeper than the LM curve.
C)FE curve is horizontal and the LM curve is vertical.
D)FE curve coincides with the LM curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At which of the following did the United States agree to implement policies to reduce U.S. inflation and reduce oil imports?
A)Bretton Woods
B)Plaza Accords
C)Bonn Summit
D)Louvre Accord
A)Bretton Woods
B)Plaza Accords
C)Bonn Summit
D)Louvre Accord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For a country with a floating exchange rate and, initially, an overall payments balance of zero, if the country implements expansionary monetary policy, the LM curve will shift to the _____ which will lead to the country's currency to __________.
A)left; appreciate
B)left; depreciate
C)right; depreciate
D)right; appreciate
A)left; appreciate
B)left; depreciate
C)right; depreciate
D)right; appreciate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under a floating exchange rate regime, in the very short run (before the exchange rate adjusts), expansionary fiscal policy will lead to:
A)improvement in both current account and financial account.
B)improvement in current account but deterioration in financial account.
C)deterioration in current account but improvement in financial account.
D)deterioration in both current account and financial account.
A)improvement in both current account and financial account.
B)improvement in current account but deterioration in financial account.
C)deterioration in current account but improvement in financial account.
D)deterioration in both current account and financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Monetary policy is a powerful economic tool for a country with fixed exchange rates and high capital mobility.
B)Under floating exchange rates, external capital-flow shocks can have effects on internal balance by altering the exchange rate and the country's international competitiveness.
C)Fiscal policy for a country with floating exchange rates is more powerful with a high degree of capital mobility than with a low degree of capital mobility.
D)An expansionary monetary policy tends to increase the exchange rate value of the domestic currency in the short run.
A)Monetary policy is a powerful economic tool for a country with fixed exchange rates and high capital mobility.
B)Under floating exchange rates, external capital-flow shocks can have effects on internal balance by altering the exchange rate and the country's international competitiveness.
C)Fiscal policy for a country with floating exchange rates is more powerful with a high degree of capital mobility than with a low degree of capital mobility.
D)An expansionary monetary policy tends to increase the exchange rate value of the domestic currency in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The figure given below depicts the IS-LM-FE model with floating exchange rates. 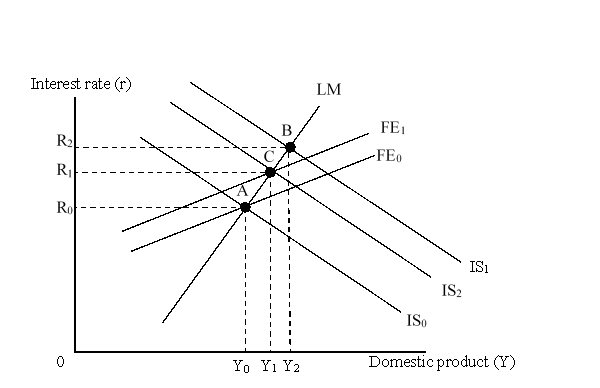 The shift of the IS curve from IS1 to IS2 was caused by:
The shift of the IS curve from IS1 to IS2 was caused by:
A)a contractionary monetary policy.
B)official intervention in the foreign exchange market.
C)an improvement in current account position.
D)a worsening of international price competitiveness.
 The shift of the IS curve from IS1 to IS2 was caused by:
The shift of the IS curve from IS1 to IS2 was caused by:A)a contractionary monetary policy.
B)official intervention in the foreign exchange market.
C)an improvement in current account position.
D)a worsening of international price competitiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Everything else remaining unchanged, the effect of domestic spending shocks on a country with a floating exchange rate differs depending on:
A)whether sterilized intervention is used or not.
B)the mobility of capital across countries.
C)the current trade balance situation of the country.
D)the interest rate differential between the country and its trading partners.
A)whether sterilized intervention is used or not.
B)the mobility of capital across countries.
C)the current trade balance situation of the country.
D)the interest rate differential between the country and its trading partners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If there is a shift of international trade away from a country's products, we can expect that the FE and IS curves will shift to the _____, the overall payments balance will move toward _____, and the domestic currency will _____.
A)right; surplus; appreciate
B)right; deficit; appreciate
C)left; surplus; depreciate
D)left; deficit; depreciate
A)right; surplus; appreciate
B)right; deficit; appreciate
C)left; surplus; depreciate
D)left; deficit; depreciate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Under a floating exchange rate regime, following an expansion in the money supply, the change in the value of domestic currency is most likely to:
A)increase demand for imports.
B)increase demand for exports.
C)lower the real product.
D)initiate foreign capital inflow.
A)increase demand for imports.
B)increase demand for exports.
C)lower the real product.
D)initiate foreign capital inflow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The figure given below depicts the IS-LM-FE model with floating exchange rates. 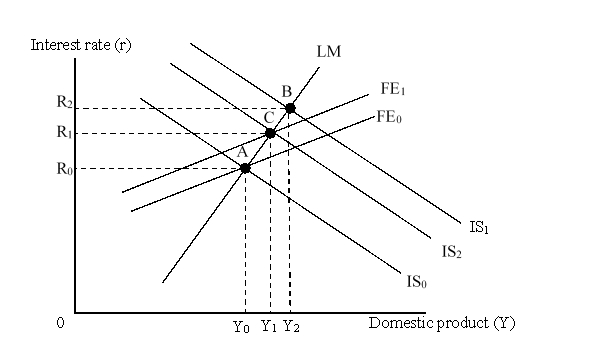 The move from point A to point B is caused by:
The move from point A to point B is caused by:
A)expansionary monetary policy.
B)expansionary fiscal policy.
C)contractionary monetary policy.
D)contractionary fiscal policy.
 The move from point A to point B is caused by:
The move from point A to point B is caused by:A)expansionary monetary policy.
B)expansionary fiscal policy.
C)contractionary monetary policy.
D)contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a possible benefit of international macroeconomic policy coordination?
A)International macroeconomic policy coordination gives countries the political cover to abolish import tariffs and export taxes.
B)International macroeconomic policy coordination gives countries the opportunity to consider spillover effects on other countries that arise from interdependence.
C)International macroeconomic policy coordination builds a forum where developing countries can come up with a common political agenda.
D)International macroeconomic policy coordination helps stronger countries to impose their prescribed economic policies on weaker countries.
A)International macroeconomic policy coordination gives countries the political cover to abolish import tariffs and export taxes.
B)International macroeconomic policy coordination gives countries the opportunity to consider spillover effects on other countries that arise from interdependence.
C)International macroeconomic policy coordination builds a forum where developing countries can come up with a common political agenda.
D)International macroeconomic policy coordination helps stronger countries to impose their prescribed economic policies on weaker countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At which of the following did the major countries of the world agree to intervene in the foreign exchange markets to lower the value of the U.S. dollar?
A)Bretton Woods
B)Plaza Agreement
C)Bonn Summit
D)Louvre Accord
A)Bretton Woods
B)Plaza Agreement
C)Bonn Summit
D)Louvre Accord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The figure given below depicts the IS-LM-FE model with floating exchange rates. 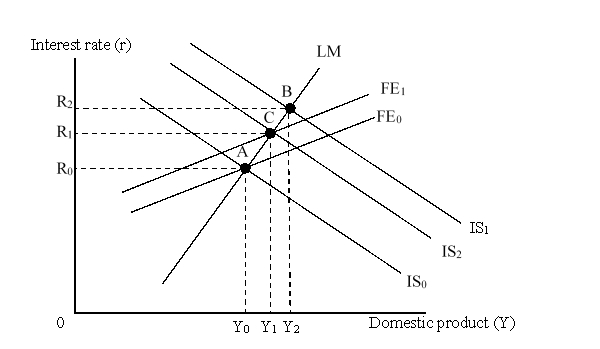 The domestic currency:
The domestic currency:
A)is under the pressure to appreciate.
B)is under the pressure to depreciate.
C)can remain relatively stable.
D)is at its possible highest value in the foreign exchange market vis-à-vis other currencies.
 The domestic currency:
The domestic currency:A)is under the pressure to appreciate.
B)is under the pressure to depreciate.
C)can remain relatively stable.
D)is at its possible highest value in the foreign exchange market vis-à-vis other currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Under which of the following scenarios is active domestic monetary policy least likely to be effective?
A)Flexible exchange rates; zero capital mobility
B)Fixed exchange rates; perfect capital mobility
C)Flexible exchange rates; perfect capital mobility
D)All three scenarios are equal
A)Flexible exchange rates; zero capital mobility
B)Fixed exchange rates; perfect capital mobility
C)Flexible exchange rates; perfect capital mobility
D)All three scenarios are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The figure given below depicts the IS-LM-FE model with floating exchange rates. 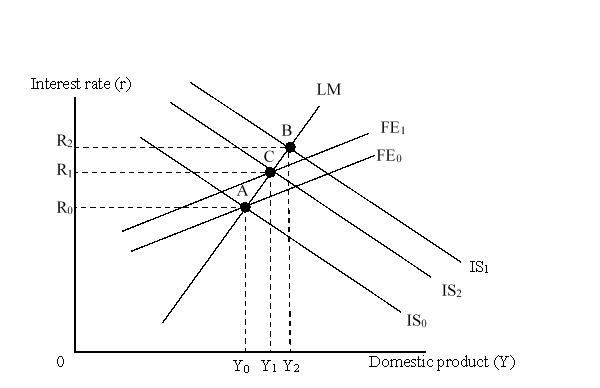 The shift of the FE curve from FE0 to FE1 was caused by:
The shift of the FE curve from FE0 to FE1 was caused by:
A)a contractionary monetary policy.
B)official intervention in the foreign exchange market.
C)an improvement in current account position.
D)an appreciation of the country's currency.
 The shift of the FE curve from FE0 to FE1 was caused by:
The shift of the FE curve from FE0 to FE1 was caused by:A)a contractionary monetary policy.
B)official intervention in the foreign exchange market.
C)an improvement in current account position.
D)an appreciation of the country's currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under _____ exchange rates, monetary policy is powerful in its effects on internal balance. This conclusion holds _____.
A)fixed; only with perfect capital mobility
B)floating; only with low capital mobility
C)fixed; with all degrees of capital mobility.
D)floating; with all degrees of capital mobility.
A)fixed; only with perfect capital mobility
B)floating; only with low capital mobility
C)fixed; with all degrees of capital mobility.
D)floating; with all degrees of capital mobility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following does NOT occur when a country with floating exchange rates increases the money supply?
A)Interest rates fall causing capital outflows in the short run.
B)Interest rates initially increases causing real spending, production, and income to fall.
C)The current account will initially tend to worsen as a result of the decrease in interest rates.
D)Aggregate demand will increase which will lead to an increase in the price level.
A)Interest rates fall causing capital outflows in the short run.
B)Interest rates initially increases causing real spending, production, and income to fall.
C)The current account will initially tend to worsen as a result of the decrease in interest rates.
D)Aggregate demand will increase which will lead to an increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following are accurate findings of recent studies about the effectiveness of intervention activities?
A)Intervention is often effective for two weeks or less in reversing the direction of the trend of the exchange rate or reducing the speed of the trend.
B)The effectiveness of the intervention usually continues past the initial two-week period and can be observed in the trend for months to come.
C)Smaller interventions are usually more successful than larger interventions.
D)The interventions are usually more effective when exercised by individual monetary authorities rather than by two or more authorities intervening jointly.
A)Intervention is often effective for two weeks or less in reversing the direction of the trend of the exchange rate or reducing the speed of the trend.
B)The effectiveness of the intervention usually continues past the initial two-week period and can be observed in the trend for months to come.
C)Smaller interventions are usually more successful than larger interventions.
D)The interventions are usually more effective when exercised by individual monetary authorities rather than by two or more authorities intervening jointly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
International macroeconomic policy coordination would give countries the opportunity to avoid beggar-thy-neighbor policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is most likely to happen if the Thai baht depreciates against the euro?
A)The money supply in Thailand will increase.
B)Thailand will have a trade deficit with the euro-area.
C)Thai demand for European goods will increase.
D)The number of European tourists visiting Thailand will increase.
A)The money supply in Thailand will increase.
B)Thailand will have a trade deficit with the euro-area.
C)Thai demand for European goods will increase.
D)The number of European tourists visiting Thailand will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Expansionary fiscal policy leads to higher domestic interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose the government of the United States has instituted an expansionary fiscal policy to boost aggregate output. The United States has a floating exchange rate regime and there is a high degree of capital mobility.
a.If the exchange rate value of the dollar remains steady, what are the effects of the expansionary fiscal policy on the U.S.national product and income? What is the effect on the U.S.unemployment rate? Explain.
b.Following the fiscal expansion, what is the likely pressure on the exchange rate value of the dollar? Explain.
c.What are the implications of the change in the exchange rate value of the pound for U.S.national product and unemployment? Does the exchange rate change tend to reinforce or counteract the expansionary thrust of U.S.fiscal policy? Explain.
a.If the exchange rate value of the dollar remains steady, what are the effects of the expansionary fiscal policy on the U.S.national product and income? What is the effect on the U.S.unemployment rate? Explain.
b.Following the fiscal expansion, what is the likely pressure on the exchange rate value of the dollar? Explain.
c.What are the implications of the change in the exchange rate value of the pound for U.S.national product and unemployment? Does the exchange rate change tend to reinforce or counteract the expansionary thrust of U.S.fiscal policy? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
International trade shocks are more disruptive with fixed exchange rates than with floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Contractionary fiscal policy with floating exchange rates and very low capital mobility leads to currency depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Monetary policy is only effective in a country with floating exchange rates when capital is highly mobile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain the possible reasons for and benefits of international macroeconomic policy coordination. What are two different reasons why we actually see little international macroeconomic policy coordination?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Using a flow chart, illustrate the effects of a decrease in government spending (G) in a country with floating exchange rates and highly mobile international capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
With floating exchange rates, the negative effects of international trade shocks on internal balance are worsened by the effects of the resulting change in the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose the U.K. has instituted an expansionary monetary policy to fight unemployment in the economy. The U.K. has a floating exchange rate.
a.If the exchange rate value of the pound remains steady, what are the effects of easy money on British national product and income? What is the effect on the British unemployment rate? Explain.
b.Following the monetary expansion, what is the likely pressure on the exchange rate value of the pound? Explain.
c.What are the implications of the change in the exchange rate value of the pound for British national product and unemployment? Does the exchange rate change tend to reinforce or counteract the expansionary thrust of the British monetary policy? Explain.
a.If the exchange rate value of the pound remains steady, what are the effects of easy money on British national product and income? What is the effect on the British unemployment rate? Explain.
b.Following the monetary expansion, what is the likely pressure on the exchange rate value of the pound? Explain.
c.What are the implications of the change in the exchange rate value of the pound for British national product and unemployment? Does the exchange rate change tend to reinforce or counteract the expansionary thrust of the British monetary policy? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the Plaza Agreement, the United States agreed to reduce its fiscal deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
International crowding out is the tendency of expansionary fiscal policy to appreciate the country's currency and worsen the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Using a flow chart, illustrate the effects of contracting the money supply in a country with floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Monetary policy is more effective with fixed exchange rates than with floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Coordinated intervention, in which more than one central bank intervenes to influence an exchange rate, is usually more effective than an intervention carried out by one country of the same total size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
One way that quantitative easing can work is through depreciation of the country's currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Larger interventions to stabilize a currency are usually more effective than smaller interventions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Major shocks occasionally strike a country's economy. List the types of shock that may occur and discuss the effects of these exogenous changes on a country that has a floating exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
For a country suffering from "liquidity trap", its government is unable to use standard monetary policy to boost borrowing and spending to move the economy toward its potential real product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



