Deck 11: Pushing Exports
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Pushing Exports
1
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 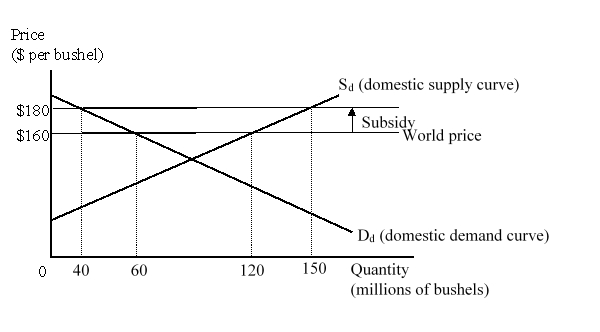 The net loss in national well-being as a result of the subsidy is:
The net loss in national well-being as a result of the subsidy is:
A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$500 million.
D)$2.2 billion.
 The net loss in national well-being as a result of the subsidy is:
The net loss in national well-being as a result of the subsidy is:A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$500 million.
D)$2.2 billion.
C
2
A firm maximizes profits by charging a lower price to foreign buyers if:
A)it has a greater monopoly power in the foreign market than it has in its home market.
B)the foreign demand for its good is more elastic than the domestic demand.
C)the buyers in the home country have access to cheaper imports from the rest of the world.
D)the size of the foreign market is much larger than the home market.
A)it has a greater monopoly power in the foreign market than it has in its home market.
B)the foreign demand for its good is more elastic than the domestic demand.
C)the buyers in the home country have access to cheaper imports from the rest of the world.
D)the size of the foreign market is much larger than the home market.
B
3
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 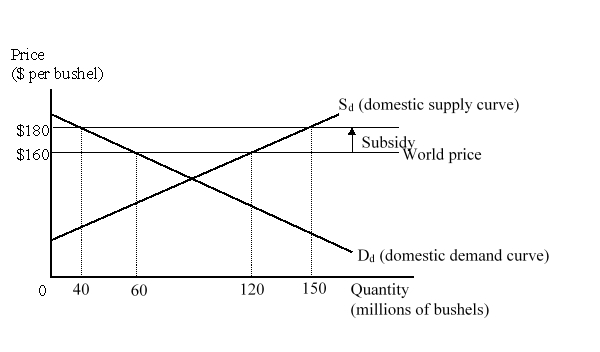 The consumption effect of the subsidy amounts to:
The consumption effect of the subsidy amounts to:
A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$1 billion.
D)$2.2 billion.
 The consumption effect of the subsidy amounts to:
The consumption effect of the subsidy amounts to:A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$1 billion.
D)$2.2 billion.
$200 million.
4
_____ occurs when a firm temporarily charges a low price in the foreign export market, with the purpose of driving its foreign competitors out of business.
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is said to occur when a firm lowers its price to limit the decline in the quantity sold during a period of recession?
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following refers to dumping?
A)Selling domestic goods in the international market at much lower prices.
B)Selling domestic goods of inferior quality in the international markets at higher prices.
C)Restricting the sale of domestic goods within the geographic boundary of the country.
D)Selling domestic goods at discounted prices to the local consumers and selling the same at much higher prices to the foreign consumers.
A)Selling domestic goods in the international market at much lower prices.
B)Selling domestic goods of inferior quality in the international markets at higher prices.
C)Restricting the sale of domestic goods within the geographic boundary of the country.
D)Selling domestic goods at discounted prices to the local consumers and selling the same at much higher prices to the foreign consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which country had no antidumping cases until the early 1990s, but became a top initiator of antidumping cases for the time period 2005-2009?
A)Canada
B)India
C)China
D)United States
A)Canada
B)India
C)China
D)United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An export subsidy imposed by a large country can be more damaging to national welfare than an export subsidy imposed by a small country because:
A)the production effect is necessarily larger for the large country.
B)the consumption effect is necessarily larger for the large country.
C)the terms of trade worsen for the large country but not for the small country.
D)the net national gains of the large country are overshadowed by the net welfare loss of the world.
A)the production effect is necessarily larger for the large country.
B)the consumption effect is necessarily larger for the large country.
C)the terms of trade worsen for the large country but not for the small country.
D)the net national gains of the large country are overshadowed by the net welfare loss of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 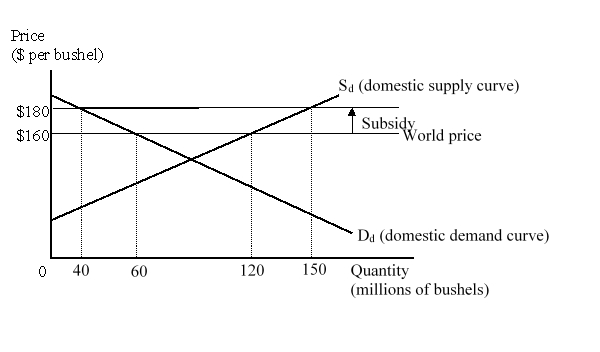 The production effect of the subsidy amounts to:
The production effect of the subsidy amounts to:
A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$1 billion.
D)$2.2 billion.
 The production effect of the subsidy amounts to:
The production effect of the subsidy amounts to:A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$1 billion.
D)$2.2 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is said to occur when a firm lowers its price in order to sell off excess inventories of a product?
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Persistent dumping can occur if a profit maximizing firm faces a _____ demand in the home market and sells its good in a _____ international market.
A)relatively elastic; less competitive
B)relatively inelastic; less competitive
C)relatively inelastic; highly competitive
D)relatively elastic; highly competitive
A)relatively elastic; less competitive
B)relatively inelastic; less competitive
C)relatively inelastic; highly competitive
D)relatively elastic; highly competitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In early 2011, nearly half of all antidumping duties in effect in the United States were on _____.
A)textiles
B)chemicals
C)steel products
D)food grains
A)textiles
B)chemicals
C)steel products
D)food grains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 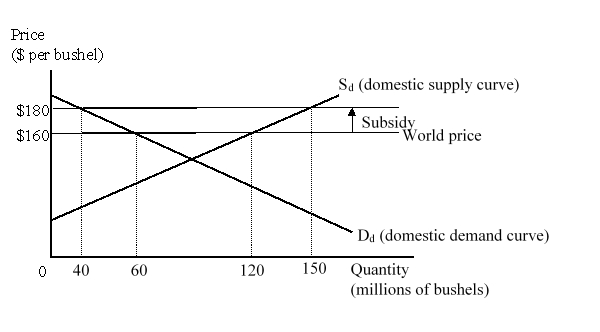 At a world price of $160 per bushel, the country produced _____ bushels of wheat and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
At a world price of $160 per bushel, the country produced _____ bushels of wheat and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
A)60; 60
B)120; 80
C)120; 60
D)150; 120
 At a world price of $160 per bushel, the country produced _____ bushels of wheat and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
At a world price of $160 per bushel, the country produced _____ bushels of wheat and exported _____ bushels of wheat.A)60; 60
B)120; 80
C)120; 60
D)150; 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Country X imports rice from the world market. Which of the following policy instruments, if adopted by its government, may result in a switch from rice being imported to being exported?
A)Agricultural price ceiling that includes the government selling any excess production to foreign buyers
B)Division of land holdings
C)Taxing import of agricultural inputs
D)Agricultural price support that includes the government selling any excess production to foreign buyers
A)Agricultural price ceiling that includes the government selling any excess production to foreign buyers
B)Division of land holdings
C)Taxing import of agricultural inputs
D)Agricultural price support that includes the government selling any excess production to foreign buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 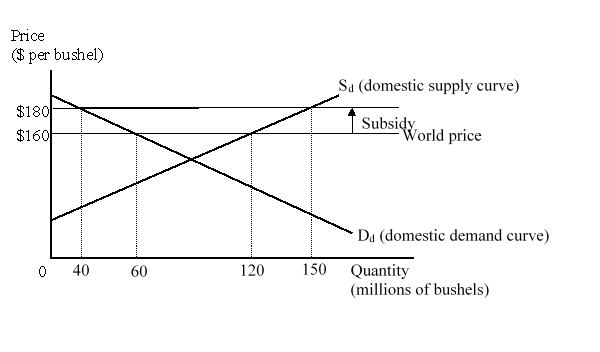 Following the imposition of a $20 per bushel export subsidy to the country's wheat exports, the country consumed _____ bushels of wheat, and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
Following the imposition of a $20 per bushel export subsidy to the country's wheat exports, the country consumed _____ bushels of wheat, and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
A)40; 110
B)60; 90
C)60; 60
D)40; 80
 Following the imposition of a $20 per bushel export subsidy to the country's wheat exports, the country consumed _____ bushels of wheat, and exported _____ bushels of wheat.
Following the imposition of a $20 per bushel export subsidy to the country's wheat exports, the country consumed _____ bushels of wheat, and exported _____ bushels of wheat.A)40; 110
B)60; 90
C)60; 60
D)40; 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is said to occur when a firm with market power uses price discrimination between markets to increase its total profit?
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping
A)Persistent dumping
B)Cyclical dumping
C)Predatory dumping
D)Seasonal dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements about an export subsidy on a particular product is accurate?
A)An export subsidy can switch the product from being exported to being imported.
B)An export subsidy reduces the amount available in the domestic market of the exporting country and increase the amount imported by the foreign country.
C)An export subsidy increases the price paid by foreign buyers, relative to the price that local consumers pay for the product.
D)An export subsidy increases the net national well-being of a large exporting country.
A)An export subsidy can switch the product from being exported to being imported.
B)An export subsidy reduces the amount available in the domestic market of the exporting country and increase the amount imported by the foreign country.
C)An export subsidy increases the price paid by foreign buyers, relative to the price that local consumers pay for the product.
D)An export subsidy increases the net national well-being of a large exporting country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT a way in which the safeguard policy is better than antidumping policies?
A)Firms and governments do not need to show that foreign exporters have done anything unfair.
B)There is pressure for import-competing firms to adjust their production in order to be more competitive with foreign exporters.
C)The interests of consumers can be disregarded since they do not play a role in determining whether to invoke a safeguard policy.
D)The protection provided to the import competing sector is explicitly temporary.
A)Firms and governments do not need to show that foreign exporters have done anything unfair.
B)There is pressure for import-competing firms to adjust their production in order to be more competitive with foreign exporters.
C)The interests of consumers can be disregarded since they do not play a role in determining whether to invoke a safeguard policy.
D)The protection provided to the import competing sector is explicitly temporary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about dumping is true?
A)Consumers and import-competing producers in the importing country are both hurt by dumping.
B)Logically, an import country should never allow seasonal and introductory-price dumping.
C)Dumping helps to improve the importing country's terms of trade.
D)Predatory dumping occurs quite frequently in modern markets.
A)Consumers and import-competing producers in the importing country are both hurt by dumping.
B)Logically, an import country should never allow seasonal and introductory-price dumping.
C)Dumping helps to improve the importing country's terms of trade.
D)Predatory dumping occurs quite frequently in modern markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The figure given below represents the domestic market for wheat in a small country. Imports of wheat are prohibited. 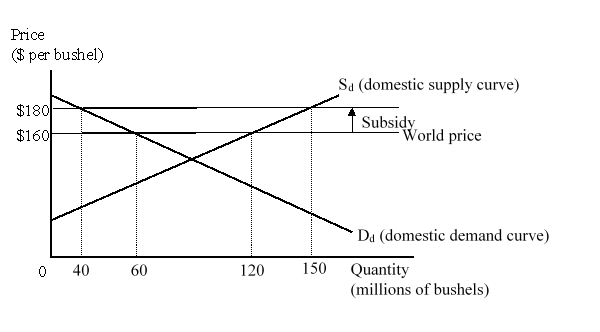 The cost to the government of paying the subsidy is:
The cost to the government of paying the subsidy is:
A)$1.2 billion.
B)$3 billion.
C)$600 million.
D)$2.2 billion.
 The cost to the government of paying the subsidy is:
The cost to the government of paying the subsidy is:A)$1.2 billion.
B)$3 billion.
C)$600 million.
D)$2.2 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The figure given below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton. 


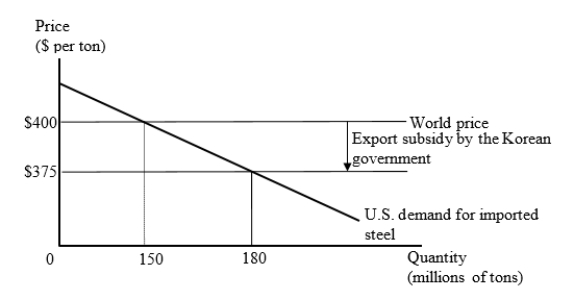 What is the cost of the export subsidy to the Korean government?
What is the cost of the export subsidy to the Korean government?
A)$375 million
B)$3.75 billion
C)$4.5 billion
D)$52.25 billion



 What is the cost of the export subsidy to the Korean government?
What is the cost of the export subsidy to the Korean government?A)$375 million
B)$3.75 billion
C)$4.5 billion
D)$52.25 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider firm X belongs to country A and firm Y belongs to country B. Suppose that it is technologically feasible for both firms to produce good Z. Also assume that if they do, then they will be the only suppliers of good Z in the world. Now, both the firms have to decide simultaneously whether to produce good Z or not. Figure (a) shows the payoffs of both firms if their respective governments do not provide them with export subsidies. Figure (b) shows the payoffs when the government of country B grants an export subsidy to firm Y, but the government of country A does not. From Figure (b), the country B's government's decision to subsidize firm Y: 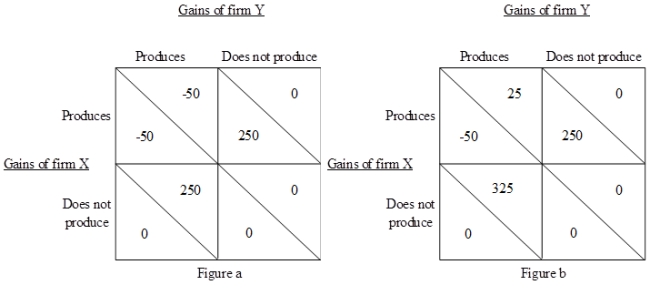
A)can be good for country B because firm X will decide not to produce.
B)will be good for country B only if government of country A decides to subsidize firm X.
C)can never lead to an optimal solution since firm X will surely produce.
D)will be suboptimal since it will lose its customers in country A.

A)can be good for country B because firm X will decide not to produce.
B)will be good for country B only if government of country A decides to subsidize firm X.
C)can never lead to an optimal solution since firm X will surely produce.
D)will be suboptimal since it will lose its customers in country A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following subsidies is prohibited under WTO rules?
A)Subsidies to research and development
B)Subsidies to assist disadvantaged regions within the exporting country
C)Subsidies to assist firms in meeting environmental regulations
D)Subsidies to encourage firms in a developed country to export more
A)Subsidies to research and development
B)Subsidies to assist disadvantaged regions within the exporting country
C)Subsidies to assist firms in meeting environmental regulations
D)Subsidies to encourage firms in a developed country to export more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An export subsidy can be good for a country if:
A)the subsidy allows the country's only exporting firm to capture the entire world market.
B)the subsidy decreases the export price so that the export quantity increases.
C)the subsidy is offset by a countervailing duty.
D)the international market for the export product is highly competitive.
A)the subsidy allows the country's only exporting firm to capture the entire world market.
B)the subsidy decreases the export price so that the export quantity increases.
C)the subsidy is offset by a countervailing duty.
D)the international market for the export product is highly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Aggressive competition in the foreign market through exports by a domestic firm due to a protected home market is known as:
A)cyclical dumping.
B)persistent dumping.
C)strategic dumping.
D)seasonal dumping.
A)cyclical dumping.
B)persistent dumping.
C)strategic dumping.
D)seasonal dumping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If markets are competitive, policies that restrict imports are usually harmful to the importing country while policies that encourage exports are usually beneficial to the exporting country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the United States, the tests used to evaluate injury from dumping not only consider the loss of well-being of the import-competing producers from dumping but also emphasize the benefits to consumers of the low-priced imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The figure given below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton. 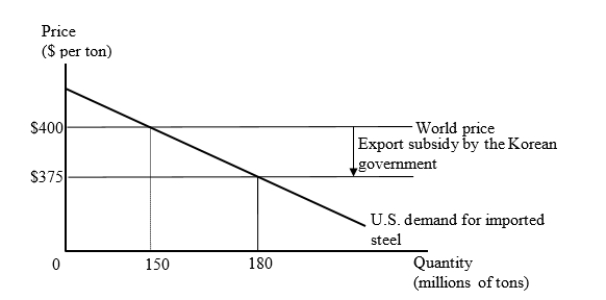



 Calculate the change in national welfare in the United States when the Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton?
Calculate the change in national welfare in the United States when the Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton?
A)+ $375 million
B)- $3.75 billion
C)+ $4.125 billion
D)-$4.5 billion




 Calculate the change in national welfare in the United States when the Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton?
Calculate the change in national welfare in the United States when the Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton?A)+ $375 million
B)- $3.75 billion
C)+ $4.125 billion
D)-$4.5 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The figure given below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton. 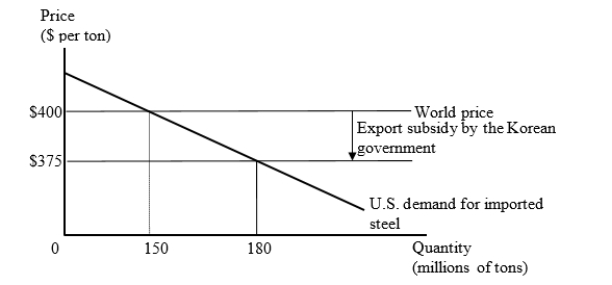
 Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?
Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?
A)The welfare of the world as a whole is reduced by $750 million.
B)The welfare loss of Korea exceeds the welfare gain of the U.S.
C)The producers in the U.S.lose whereas the producers in Korea gain.
D)The world price level and volume of trade becomes similar to the free-trade condition.

 Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?
Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?A)The welfare of the world as a whole is reduced by $750 million.
B)The welfare loss of Korea exceeds the welfare gain of the U.S.
C)The producers in the U.S.lose whereas the producers in Korea gain.
D)The world price level and volume of trade becomes similar to the free-trade condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assume that country A provides a subsidy on its exports to country B. Country B is about to impose a countervailing duty (of the same magnitude as the export subsidy) on the imports from country A. Which of the following statements is true in this context?
A)The exporters in country A gain surplus when the government of country B imposes a countervailing duty.
B)The import-competing producers in country B are worse off after the imposition of the countervailing duty by the government.
C)The overall national well-being of country B would be lower when the domestic government imposes a countervailing duty to offset the impact of the export subsidy.
D)The consumers in country B are better off after the government of country B imposes a countervailing duty.
A)The exporters in country A gain surplus when the government of country B imposes a countervailing duty.
B)The import-competing producers in country B are worse off after the imposition of the countervailing duty by the government.
C)The overall national well-being of country B would be lower when the domestic government imposes a countervailing duty to offset the impact of the export subsidy.
D)The consumers in country B are better off after the government of country B imposes a countervailing duty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Firms that are engaging in persistent dumping need to be able to prevent resale between the foreign and domestic markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
While the U. S. government investigates few claims of dumping, nearly all of the claims are upheld by the International Trade Commission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Firms that are participating in persistent dumping will sell less in the foreign market and charge a higher price than in the home market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The fight over export policy usually focuses on artificial export limits rather than artificial promotion of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The figure given below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton. 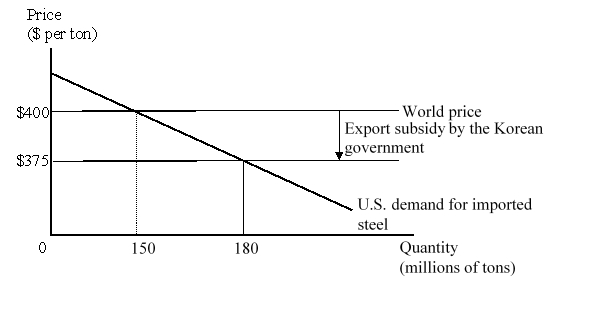 Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on its steel imports from Korea to offset the impact of the subsidy provided by the Korean government on its steel exports. Calculate the change in the national welfare of the U.S. due to the imposition of this duty.
Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on its steel imports from Korea to offset the impact of the subsidy provided by the Korean government on its steel exports. Calculate the change in the national welfare of the U.S. due to the imposition of this duty.
A)-$375 million
B)+$3.375 billion
C)+$3.75 billion
D)-$4.125 billion
 Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on its steel imports from Korea to offset the impact of the subsidy provided by the Korean government on its steel exports. Calculate the change in the national welfare of the U.S. due to the imposition of this duty.
Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on its steel imports from Korea to offset the impact of the subsidy provided by the Korean government on its steel exports. Calculate the change in the national welfare of the U.S. due to the imposition of this duty.A)-$375 million
B)+$3.375 billion
C)+$3.75 billion
D)-$4.125 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The figure given below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton. 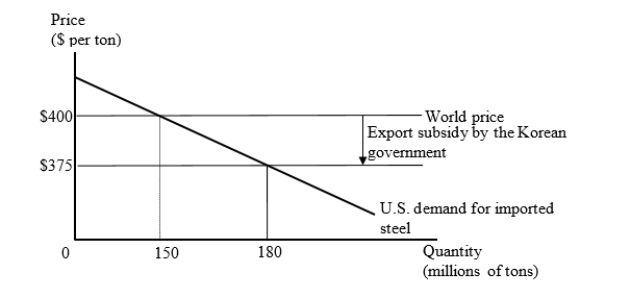 Suppose the United States imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. What is the amount of revenue collected by the U.S. government on account of this countervailing duty?
Suppose the United States imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. What is the amount of revenue collected by the U.S. government on account of this countervailing duty?
A)$750 million
B)$3.75 billion
C)$4.125 billion
D)$375 million
 Suppose the United States imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. What is the amount of revenue collected by the U.S. government on account of this countervailing duty?
Suppose the United States imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. What is the amount of revenue collected by the U.S. government on account of this countervailing duty?A)$750 million
B)$3.75 billion
C)$4.125 billion
D)$375 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In 1992, the bilateral agreement of the U.S. with the European Union regarding the subsidies for production of civil aircraft included that:
A)direct government support for new airplane development are limited to one-tenth of the total development costs.
B)indirect government support is limited to four percent of a firm's civil aircraft sales.
C)only production but no marketing subsidies could be provided to the firm.
D)subsidies could only be in the form of loans at a market rate of interest with a short repayment period.
A)direct government support for new airplane development are limited to one-tenth of the total development costs.
B)indirect government support is limited to four percent of a firm's civil aircraft sales.
C)only production but no marketing subsidies could be provided to the firm.
D)subsidies could only be in the form of loans at a market rate of interest with a short repayment period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Antidumping duties increase overall economic well-being in a country by protecting the domestic import-competing firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The impact on world welfare of an export subsidy and a countervailing duty (of the same size as the subsidy) is:
A)zero.
B)negative due to overproduction.
C)negative due to under-consumption.
D)negative due to deadweight loss.
A)zero.
B)negative due to overproduction.
C)negative due to under-consumption.
D)negative due to deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider firm X belongs to country A and firm Y belongs to country B. Suppose that it is technologically feasible for both firms to produce good Z. Also assume that if they do, then they will be the only suppliers of good Z in the world. Now, both the firms have to decide simultaneously whether to produce good Z or not. Figure (a) shows the payoffs of both firms if their respective governments do not provide them with export subsidies. Figure (b) shows the payoffs when the government of country B grants an export subsidy to firm Y, but the government of country A does not. From Figure (a), we can correctly infer that: 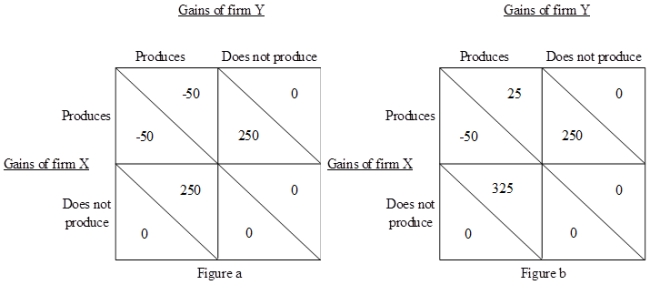
A)it is optimal for firm X not to produce if firm Y does not produce.
B)both firms can decide to produce since they can anticipate that the other firm will not produce.
C)it is optimal for firm Y not to produce no matter what firm X does.
D)both the firms will suffer losses if they produce simultaneously.

A)it is optimal for firm X not to produce if firm Y does not produce.
B)both firms can decide to produce since they can anticipate that the other firm will not produce.
C)it is optimal for firm Y not to produce no matter what firm X does.
D)both the firms will suffer losses if they produce simultaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
With free trade the United States imports about half of its steel consumption from Brazil. What would be the impact on the United States of an export subsidy on steel provided by the Brazilian government? Would it be beneficial for the U.S. if they impose an equal amount of countervailing duty on the import of steel? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain when strategic export subsidies could be good for a country. Consider firm X belongs to country A and firm Y belongs to country B. Use a duopolistic market structure where both firms are dominant players in the world market. Discuss the differences between the game in which no subsidies are given and the game in which only one firm receives a subsidy. Create a hypothetical matrix in this context to aid your explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How can you define dumping? If the importing country suspects dumping, what action can be taken?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand and supply functions of the food grains in country X are as follows:
QD = 150 - 0.6P
QS = -40 + 0.5P
where QD and QS are in millions of tons and P is the price per ton. The world price of grain is $200 per ton. The figure given below illustrates the demand and supply functions of food grains in country X.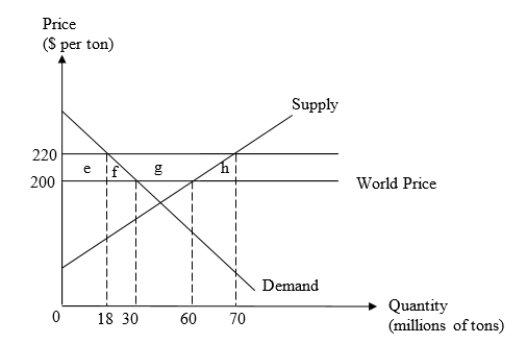
a.In a situation of free trade, how much food grains would be produced, consumed, and traded in country X?
b.As a response to alleged unfair foreign practices, the U.S.farmers successfully lobby for a $20 export subsidy per ton of the grains exported.Assuming that country A is a "small country" in the world grain markets, and that imports of food grains are banned, illustrate the impact of the export subsidy on domestic prices, consumption, production, and exports of grain by this country.Also indicate the welfare effects on producers and consumers.Calculate the cost of the subsidy to the government, and the overall change in welfare in country A.
QD = 150 - 0.6P
QS = -40 + 0.5P
where QD and QS are in millions of tons and P is the price per ton. The world price of grain is $200 per ton. The figure given below illustrates the demand and supply functions of food grains in country X.

a.In a situation of free trade, how much food grains would be produced, consumed, and traded in country X?
b.As a response to alleged unfair foreign practices, the U.S.farmers successfully lobby for a $20 export subsidy per ton of the grains exported.Assuming that country A is a "small country" in the world grain markets, and that imports of food grains are banned, illustrate the impact of the export subsidy on domestic prices, consumption, production, and exports of grain by this country.Also indicate the welfare effects on producers and consumers.Calculate the cost of the subsidy to the government, and the overall change in welfare in country A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
It is generally the case that imposing a countervailing duty in response to a foreign export subsidy provides less well-being for a country than had the country not imposed the countervailing duty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is predatory dumping? How likely is dumping to be predatory? Discuss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An export subsidy imposed in a large exporting country will cause the country's international terms of trade to improve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Proposals for reform of antidumping policy include restricting its use to cases where predatory dumping is plausible, accounting for consumer interests in the analysis of injury from dumping, and replacing antidumping policy with safeguard policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For developed countries, more price supports and subsidies are provided to agriculture worldwide than to any other sector of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A large enough production subsidy can turn an imported-product into an exportable product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A major reason why agricultural products are heavily subsidized in the European Union is because farmers have strong political lobbies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A price support on agricultural products is a minimum domestic price set by the government. The government outlaws transaction below the price support, but usually has no commitment to buy any amounts that farmers cannot sell at this price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



