Deck 12: Trade Blocs and Trade Blocks
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Trade Blocs and Trade Blocks
1
Which of the following is true of a common market?
A)The member countries export similar products to the non-member countries.
B)The member countries do not import any good from the non-member countries.
C)The member countries have identical monetary and fiscal policies.
D)There is free movement of capital and labor among the member countries.
A)The member countries export similar products to the non-member countries.
B)The member countries do not import any good from the non-member countries.
C)The member countries have identical monetary and fiscal policies.
D)There is free movement of capital and labor among the member countries.
D
2
Which of the following is true of an economic union?
A)Free movement of resources, but restricted movement of goods among the member countries
B)The members have a common set of tariffs among themselves but the external tariff rates are determined independently
C)Free movement of goods, but restricted movement of resources across the member countries
D)Harmonization of all economic policies in the member countries
A)Free movement of resources, but restricted movement of goods among the member countries
B)The members have a common set of tariffs among themselves but the external tariff rates are determined independently
C)Free movement of goods, but restricted movement of resources across the member countries
D)Harmonization of all economic policies in the member countries
D
3
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 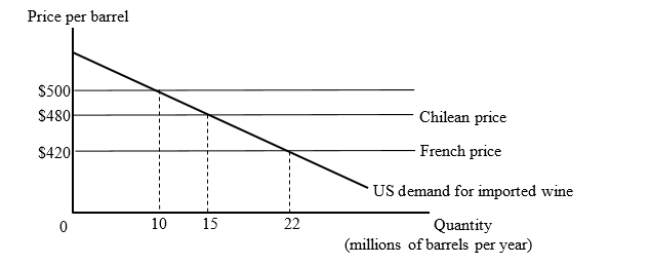 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How much will the U.S. government tariff revenue change (as a result of joining the free trade area)?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How much will the U.S. government tariff revenue change (as a result of joining the free trade area)?
A)Increase by $50 million
B)Decrease by $250 million
C)Increase by $600 million
D)Decrease by $800 million
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How much will the U.S. government tariff revenue change (as a result of joining the free trade area)?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How much will the U.S. government tariff revenue change (as a result of joining the free trade area)?A)Increase by $50 million
B)Decrease by $250 million
C)Increase by $600 million
D)Decrease by $800 million
D
4
Which of the following allows member countries to import from other member countries freely, but imposes trade barriers against imports from outside countries?
A)A trade embargo
B)A trade bloc
C)A cultural union
D)A trade union
A)A trade embargo
B)A trade bloc
C)A cultural union
D)A trade union

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 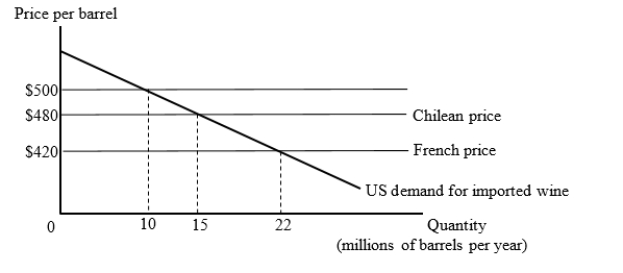 Under free trade, how many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
Under free trade, how many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
A)15 million barrels from Chile
B)22 million barrels from France
C)10 million barrels from France
D)22 million barrels from Chile
 Under free trade, how many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
Under free trade, how many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?A)15 million barrels from Chile
B)22 million barrels from France
C)10 million barrels from France
D)22 million barrels from Chile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is on a path toward full economic unity?
A)The NAFTA
B)The EU
C)The MERCOSUR
D)The CAFTA
A)The NAFTA
B)The EU
C)The MERCOSUR
D)The CAFTA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following features does a customs union have?
A)Free trade among those members which have similar economic policies
B)Common set of external tariffs
C)Free movement of factors of production
D)Harmonization of all economic policies
A)Free trade among those members which have similar economic policies
B)Common set of external tariffs
C)Free movement of factors of production
D)Harmonization of all economic policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 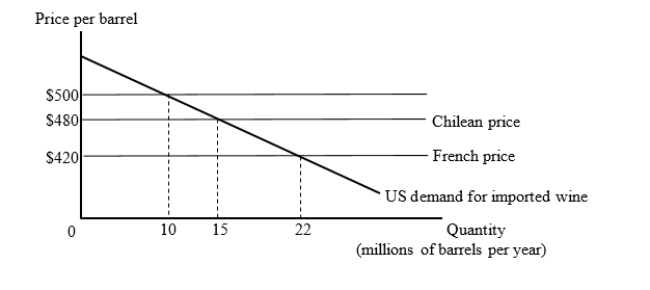 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. Calculate the loss suffered by the U.S. arising from the shift of trade from low-cost exporters to higher-cost bloc-partner exporter.
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. Calculate the loss suffered by the U.S. arising from the shift of trade from low-cost exporters to higher-cost bloc-partner exporter.
A)$50 million
B)$250 million
C)$600 million
D)$800 million
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. Calculate the loss suffered by the U.S. arising from the shift of trade from low-cost exporters to higher-cost bloc-partner exporter.
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. Calculate the loss suffered by the U.S. arising from the shift of trade from low-cost exporters to higher-cost bloc-partner exporter.A)$50 million
B)$250 million
C)$600 million
D)$800 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 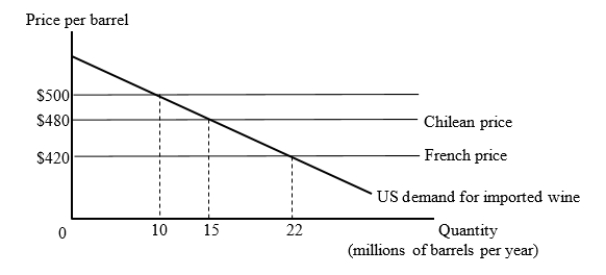 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. At what price per barrel will the imported wines be purchased by the U.S. consumers?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. At what price per barrel will the imported wines be purchased by the U.S. consumers?
A)$420
B)$480
C)$500
D)$560
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. At what price per barrel will the imported wines be purchased by the U.S. consumers?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. At what price per barrel will the imported wines be purchased by the U.S. consumers?A)$420
B)$480
C)$500
D)$560

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following states that any trade concession given to any foreign country must be given to all other countries having the same status?
A)The principle of retaliation
B)The structural adjustment program
C)The most favored nation principle
D)The purchasing power parity theory
A)The principle of retaliation
B)The structural adjustment program
C)The most favored nation principle
D)The purchasing power parity theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR) is actually a _____.
A)free trade area
B)customs union
C)economic union
D)common market
A)free trade area
B)customs union
C)economic union
D)common market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The NAFTA is an example of a(n):
A)free-trade area.
B)customs union.
C)common market.
D)economic union.
A)free-trade area.
B)customs union.
C)common market.
D)economic union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 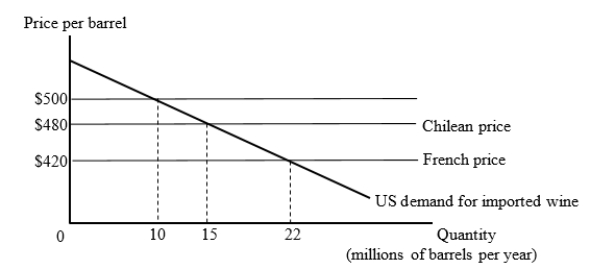 Suppose that the United States imposes a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. How many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
Suppose that the United States imposes a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. How many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
A)15 million barrels from Chile
B)22 million barrels from France
C)10 million barrels from France
D)10 million barrels from Chile
 Suppose that the United States imposes a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. How many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?
Suppose that the United States imposes a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. How many barrels of wine will the United States import and who will they import from?A)15 million barrels from Chile
B)22 million barrels from France
C)10 million barrels from France
D)10 million barrels from Chile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following refers to trade diversion?
A)The volume of trade that is redirected from low-cost exporters to higher cost domestic firms when the domestic government imposes import restrictions
B)The volume of trade that is redirected from low-cost exporters to higher-cost trade bloc member countries
C)The amount of the imported goods that is substituted with domestically produced goods
D)The change in the trade pattern such that the good which was formerly imported is now exported as the government subsidizes its production
A)The volume of trade that is redirected from low-cost exporters to higher cost domestic firms when the domestic government imposes import restrictions
B)The volume of trade that is redirected from low-cost exporters to higher-cost trade bloc member countries
C)The amount of the imported goods that is substituted with domestically produced goods
D)The change in the trade pattern such that the good which was formerly imported is now exported as the government subsidizes its production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following refers to trade creation?
A)The net increase in exports when the currency of a country depreciates with respect to a foreign currency
B)The net increase in imports when foreign firms lower the prices of their exports
C)The net volume of new trade that results from the formation of a trade bloc
D)The net change in the volume of trade when a country raises its barriers on its imports
A)The net increase in exports when the currency of a country depreciates with respect to a foreign currency
B)The net increase in imports when foreign firms lower the prices of their exports
C)The net volume of new trade that results from the formation of a trade bloc
D)The net change in the volume of trade when a country raises its barriers on its imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Formation of trade blocs can be considered beneficial because it:
A)encourages purchases from higher-cost producers.
B)causes international friction when certain countries are let in the bloc and others are left out.
C)diverts world trade from low-cost producers to high-cost producers by encouraging too much trade within blocs.
D)encourages increased total trade by each member country.
A)encourages purchases from higher-cost producers.
B)causes international friction when certain countries are let in the bloc and others are left out.
C)diverts world trade from low-cost producers to high-cost producers by encouraging too much trade within blocs.
D)encourages increased total trade by each member country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following features does a free trade area necessarily have?
A)Absence of any trade barriers among the member nations
B)Equal tariffs rates
C)Free movement of factors of production across the member nations
D)Harmonization of all economic policies
A)Absence of any trade barriers among the member nations
B)Equal tariffs rates
C)Free movement of factors of production across the member nations
D)Harmonization of all economic policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 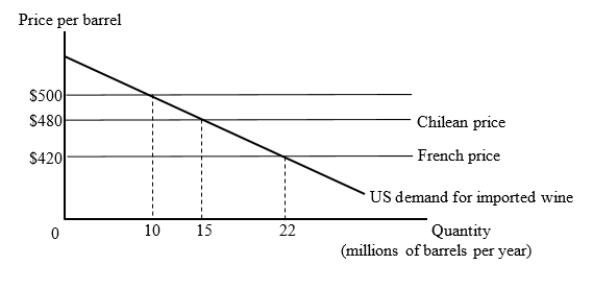 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How many barrels of wine will the United States import after joining the free trade area?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How many barrels of wine will the United States import after joining the free trade area?
A)15 million barrels
B)22 million barrels
C)10 million barrels
D)zero barrels
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How many barrels of wine will the United States import after joining the free trade area?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. How many barrels of wine will the United States import after joining the free trade area?A)15 million barrels
B)22 million barrels
C)10 million barrels
D)zero barrels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 
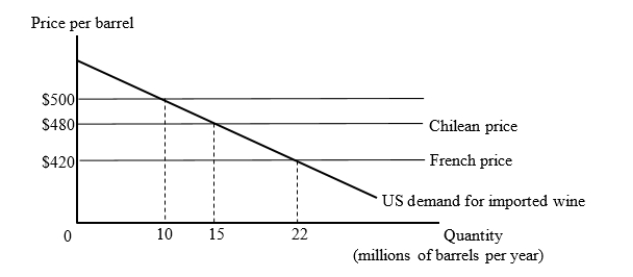



 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. Calculate the gain arising from an increase in net volume of trade after the U.S. joins the free trade area.
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. Calculate the gain arising from an increase in net volume of trade after the U.S. joins the free trade area.
A)$50 million
B)$350 million
C)$550 million
D)$800 billion





 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. Calculate the gain arising from an increase in net volume of trade after the U.S. joins the free trade area.
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. Calculate the gain arising from an increase in net volume of trade after the U.S. joins the free trade area.A)$50 million
B)$350 million
C)$550 million
D)$800 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 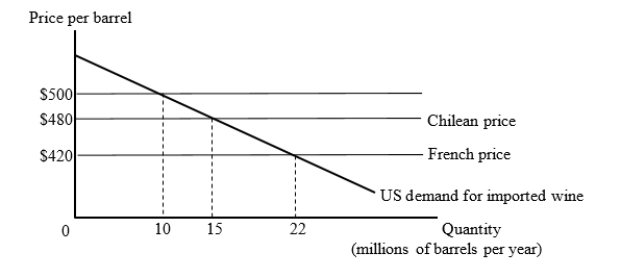 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. What will be the change in the consumer surplus after the U.S. enters into a free trade agreement with Chile?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. What will be the change in the consumer surplus after the U.S. enters into a free trade agreement with Chile?
A)+$50 million
B)+$250 million
C)-$50 million
D)-$970 million
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. What will be the change in the consumer surplus after the U.S. enters into a free trade agreement with Chile?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the U.S. joins a free trade area with Chile. What will be the change in the consumer surplus after the U.S. enters into a free trade agreement with Chile?A)+$50 million
B)+$250 million
C)-$50 million
D)-$970 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following correctly identifies the impact of the formation of NAFTA on Mexico?
A)Mexico's import of financial services and high-tech equipment from the U.S.has declined.
B)After Mexico joined NAFTA, the average wage rates for the unskilled workers have declined.
C)Mexican exports of fruits and vegetables to the United States declined substantially.
D)NAFTA allows Mexico to better exploit its comparative advantage based on low-skilled workers in such products as apparels, food crops, etc.
A)Mexico's import of financial services and high-tech equipment from the U.S.has declined.
B)After Mexico joined NAFTA, the average wage rates for the unskilled workers have declined.
C)Mexican exports of fruits and vegetables to the United States declined substantially.
D)NAFTA allows Mexico to better exploit its comparative advantage based on low-skilled workers in such products as apparels, food crops, etc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As of 2011, which of the following Balkan states was closest to qualifying for EU membership?
A)Serbia
B)Bosnia
C)Croatia
D)Albania
A)Serbia
B)Bosnia
C)Croatia
D)Albania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
H. Ross Perot's famous claim in 1992 that NAFTA would cause a "great sucking sound" referred to:
A)a huge increase in foreign direct investment in the U.S.
B)an instant shift of jobs from the U.S.to the Mexico.
C)a rapid increase in the U.S.exports to Canada.
D)a rapid increase in the wage inequality in Mexico.
A)a huge increase in foreign direct investment in the U.S.
B)an instant shift of jobs from the U.S.to the Mexico.
C)a rapid increase in the U.S.exports to Canada.
D)a rapid increase in the wage inequality in Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true of trade embargoes?
A)A trade embargo refers to a uniform tariff being imposed on all imported products by a country.
B)Embargoes are discriminatory restrictions or bans on economic exchange.
C)Unlike other trade restrictions, a trade embargo does not harm the imposing country.
D)Trade embargoes refer to import bans on tangible goods, and not services.
A)A trade embargo refers to a uniform tariff being imposed on all imported products by a country.
B)Embargoes are discriminatory restrictions or bans on economic exchange.
C)Unlike other trade restrictions, a trade embargo does not harm the imposing country.
D)Trade embargoes refer to import bans on tangible goods, and not services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The figure given below shows the U.S. market for imported wine. For simplicity, we consider export supply curves to be flat. Chilean wine is available for $480 per barrel and French wine is available for $420 per barrel. 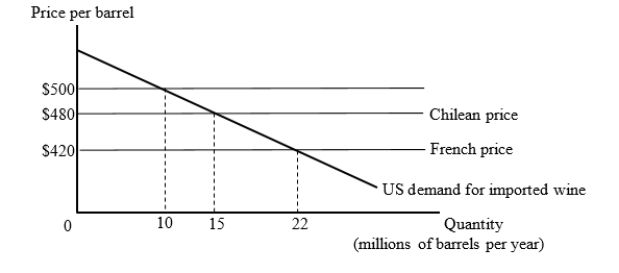 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. What is the net effect on the U.S. well-being of joining the trade bloc?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. What is the net effect on the U.S. well-being of joining the trade bloc?
A)The national welfare increases by $50 million.
B)The national welfare decreases by $550 million.
C)The national welfare decreases by $800 million.
D)The national welfare increases by $250 billion.
 Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. What is the net effect on the U.S. well-being of joining the trade bloc?
Suppose the United States has a tariff of $80 per barrel on imported wine. Then, the United States joins a trade bloc with Chile. What is the net effect on the U.S. well-being of joining the trade bloc?A)The national welfare increases by $50 million.
B)The national welfare decreases by $550 million.
C)The national welfare decreases by $800 million.
D)The national welfare increases by $250 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The gains from trade creation is likely to be larger for a country if:
A)its import demand curve is relatively elastic.
B)it mainly imports primary products.
C)the country's government sufficiently subsidizes the production of its exportable goods.
D)the supply of the imported good by the foreigners is relatively inelastic.
A)its import demand curve is relatively elastic.
B)it mainly imports primary products.
C)the country's government sufficiently subsidizes the production of its exportable goods.
D)the supply of the imported good by the foreigners is relatively inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An economic failure of an embargo is said to have occurred if:
A)the embargo inflicts little damage on the target country but possibly a greater damage on the imposing country.
B)the target country suffers a greater welfare loss than does the imposing country.
C)the price of the good exported by the imposing country to the target country rises substantially in the target country when the embargo is imposed.
D)the prices of the embargoed goods do not decline in the imposing country.
A)the embargo inflicts little damage on the target country but possibly a greater damage on the imposing country.
B)the target country suffers a greater welfare loss than does the imposing country.
C)the price of the good exported by the imposing country to the target country rises substantially in the target country when the embargo is imposed.
D)the prices of the embargoed goods do not decline in the imposing country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following identifies an important reason why empirical studies find that joining the EC in 1973 may have imposed a substantial net cost on Britain?
A)Trade creation for British manufactured goods
B)Removal of trade barriers on imports from Australia and New Zealand
C)Trade diversion on agricultural products
D)Withdrawal of subsidies received by the British farmers
A)Trade creation for British manufactured goods
B)Removal of trade barriers on imports from Australia and New Zealand
C)Trade diversion on agricultural products
D)Withdrawal of subsidies received by the British farmers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Embargoes are likely to be effective when:
A)the supply curve of the embargoing country is highly inelastic.
B)the demand for imports by the target country is relatively elastic.
C)a small county imposes an embargo on a large country.
D)the sanctions are sudden and comprehensive when first imposed.
A)the supply curve of the embargoing country is highly inelastic.
B)the demand for imports by the target country is relatively elastic.
C)a small county imposes an embargo on a large country.
D)the sanctions are sudden and comprehensive when first imposed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The figures given below illustrate a situation of a trade embargo. In Figure (a) Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and supply curves of the embargoing countries. The import price is P0 and the target country imports the amount Q0 before the embargo is imposed. 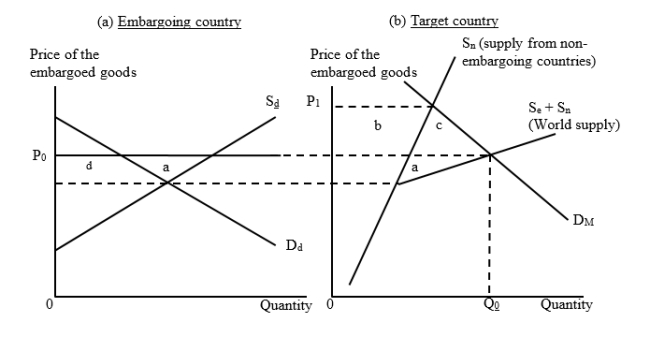 The embargo initiator(s) lose area _____ while the target country loses _____.
The embargo initiator(s) lose area _____ while the target country loses _____.
A)(b + c); (a + c)
B)(a + d); (b + c)
C)a; b
D)a; (b + c)
 The embargo initiator(s) lose area _____ while the target country loses _____.
The embargo initiator(s) lose area _____ while the target country loses _____.A)(b + c); (a + c)
B)(a + d); (b + c)
C)a; b
D)a; (b + c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which countries joined the European Union in 2007?
A)The Czech Republic and Slovakia
B)Portugal and Spain
C)Bulgaria and Romania
D)Macedonia and Montenegro
A)The Czech Republic and Slovakia
B)Portugal and Spain
C)Bulgaria and Romania
D)Macedonia and Montenegro

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
_____ determine(s) which products have been produced within a free-trade area and which products have been produced outside the area and therefore are subject to trade barriers.
A)Trade diversion
B)Trade creation
C)Rules of origin
D)The most favored nation principle
A)Trade diversion
B)Trade creation
C)Rules of origin
D)The most favored nation principle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The net loss from trade diversion for a country is likely to be smaller if:
A)the county's import demand is more elastic.
B)the country's tariff rate on the product is higher.
C)the good can be produced at relatively lower cost in the bloc-partners than in the outside world.
D)the bloc partner's export price is closer to the tariff-inclusive price for imports from countries outside the bloc.
A)the county's import demand is more elastic.
B)the country's tariff rate on the product is higher.
C)the good can be produced at relatively lower cost in the bloc-partners than in the outside world.
D)the bloc partner's export price is closer to the tariff-inclusive price for imports from countries outside the bloc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A political failure of a trade embargo is most likely to occur if:
A)the target country is a dictatorship and the dictatorship is jeopardized by retreating from the policy that provoked the embargo.
B)the target country is a colony of the imposing country and the embargo adversely affects the imposing country.
C)the country that imposes the embargo has an unstable government.
D)the imposing country is a relatively smaller country than the target country in terms of trade volume.
A)the target country is a dictatorship and the dictatorship is jeopardized by retreating from the policy that provoked the embargo.
B)the target country is a colony of the imposing country and the embargo adversely affects the imposing country.
C)the country that imposes the embargo has an unstable government.
D)the imposing country is a relatively smaller country than the target country in terms of trade volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following was an observable effect of NAFTA?
A)NAFTA led to a substantial decrease in the volume of trade among the three member countries.
B)Low-cost firms in Canadian manufacturing industries were replaced by the high-cost firms.
C)Imports of clothing and textiles into the member countries were diverted away from low-cost suppliers in Asia.
D)There was massive shift of jobs toward Mexico.
A)NAFTA led to a substantial decrease in the volume of trade among the three member countries.
B)Low-cost firms in Canadian manufacturing industries were replaced by the high-cost firms.
C)Imports of clothing and textiles into the member countries were diverted away from low-cost suppliers in Asia.
D)There was massive shift of jobs toward Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements about a trade bloc is accurate?
A)The gains from a trade bloc are shared equally by each member.
B)Increased competition within a trade bloc can result in higher commodity prices in the domestic markets of the member countries.
C)A trade bloc may lower firms' costs by allowing them to exploit economies of scale.
D)A trade bloc can increase the opportunities for domestic business investments but usually repels foreign direct investments into the member countries.
A)The gains from a trade bloc are shared equally by each member.
B)Increased competition within a trade bloc can result in higher commodity prices in the domestic markets of the member countries.
C)A trade bloc may lower firms' costs by allowing them to exploit economies of scale.
D)A trade bloc can increase the opportunities for domestic business investments but usually repels foreign direct investments into the member countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The figures given below illustrate a situation of a trade embargo. In Figure (a) Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and supply curves of the embargoing countries. The import price is P0 and the target country imports the amount Q0 before the embargo is imposed. 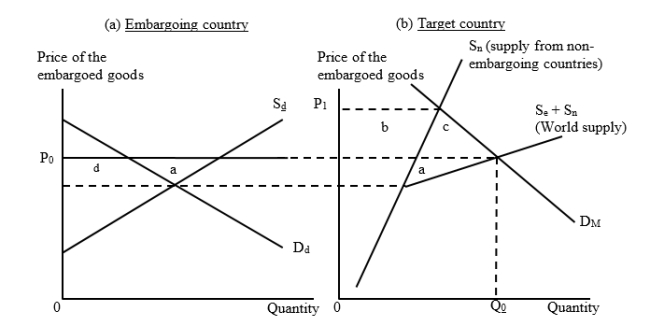 As a result of this embargo, the exporting countries not participating in the embargo gain area _____.
As a result of this embargo, the exporting countries not participating in the embargo gain area _____.
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)(b + c)
 As a result of this embargo, the exporting countries not participating in the embargo gain area _____.
As a result of this embargo, the exporting countries not participating in the embargo gain area _____.A)a
B)b
C)c
D)(b + c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A trade embargo harms:
A)only the target country.
B)only the country that initiates the embargo.
C)both the target country and the country initiating the embargo.
D)the target country and the nonembargoing countries.
A)only the target country.
B)only the country that initiates the embargo.
C)both the target country and the country initiating the embargo.
D)the target country and the nonembargoing countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The figures given below illustrate a situation of a trade embargo. In Figure (a) Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and supply curves of the embargoing countries. The import price is P0 and the target country imports the amount Q0 before the embargo is imposed. 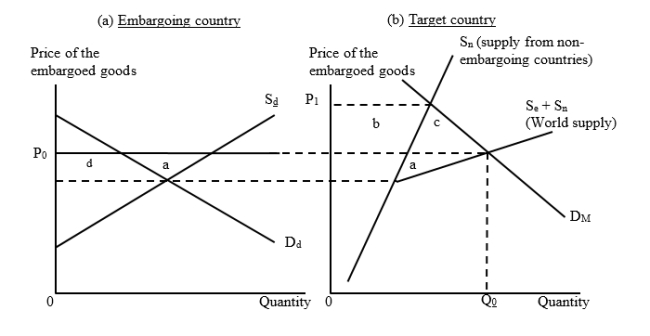 As a result of this embargo, the world as a whole loses area _____.
As a result of this embargo, the world as a whole loses area _____.
A)a
B)(a + b + c + d)
C)(a + c)
D)(b + c)
 As a result of this embargo, the world as a whole loses area _____.
As a result of this embargo, the world as a whole loses area _____.A)a
B)(a + b + c + d)
C)(a + c)
D)(b + c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is NOT among the features that are phased in gradually during the integration of new members in the European Union?
A)The subsidies that the farmers of the new members receive started at only one-fourth of the standard levels for the common agricultural policy.
B)The new members were not full members of the common market for labor.
C)The citizens of the new members were not generally free to work in most other EU countries until seven years after the country joined the EU.
D)The new members were allowed to impose a nominal tariff on the imports from the other members to stabilize themselves for the first seven years.
A)The subsidies that the farmers of the new members receive started at only one-fourth of the standard levels for the common agricultural policy.
B)The new members were not full members of the common market for labor.
C)The citizens of the new members were not generally free to work in most other EU countries until seven years after the country joined the EU.
D)The new members were allowed to impose a nominal tariff on the imports from the other members to stabilize themselves for the first seven years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a customs union, members remove all trade barriers among themselves and adopt a common set of external barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A trade bloc allows member countries to import from other member countries freely, but imposes trade barriers against imports from countries outside the bloc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The WTO does not permit any deviation from the MFN principle, even for the developing countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What experiences have developing countries had with trade blocs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The formation of a trade bloc necessarily improves well-being worldwide because it is a step toward free trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose Chile joins a trade bloc formed by Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Before joining the trade bloc, the Chilean government has a tariff of 30 percent on imported meat, and Chile's imports of 40,000 tons of meat came exclusively from the United States. The U.S. sold meat at a price of $2,000 per ton in the international market. After joining the trade bloc, Chile switched to importing meat from the other member countries at a price of $2,100 per ton. Its import increased to 50,000 tons. Calculate the amount of trade creation and trade diversion as a result of this change. For this product, did Chile gain economic well-being from joining the trade bloc? If so, then how much? If not, then by how much would Chilean imports of meat have to increase for Chile to benefit from joining the trade bloc?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
It has been observed that trade within MERCOSUR trade has increased most rapidly in protected capital-intensive products like automobiles, machinery and electronic goods in which the member countries enjoy global comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
"Countries usually experience substantial economic gains from joining trade blocs." Do you agree or disagree with this statement? Why? In your answer, include discussion of the roles of trade creation and trade diversion. Also include discussion of other gains that can arise in a country that chooses to join a trade bloc?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Gains from joining a trade bloc will be higher if the import demands of the member countries are relatively elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a few countries join a trade bloc, it not only expands the market for their firms but also creates a larger market for the countries outside the bloc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that the constant marginal cost of producing an automobile is $11,000 in Canada, $8,000 in the United States, and $12,000 in Japan.
a.Under free trade, would Canada produce its own cars or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?
b.If the Canadian government imposes a 100% tariff on all auto imports, would it produce its own automobiles or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?
c.Canada has a tariff of 100% on imported autos.Then Canada decides to join a customs union with the United States (with a uniform external tariff of 100%).After the customs union is formed, what will the domestic price of automobiles be in Canada?
d.If Canada decides to join this customs union with the United States, will there be trade creation, trade diversion, or both? Explain.
a.Under free trade, would Canada produce its own cars or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?
b.If the Canadian government imposes a 100% tariff on all auto imports, would it produce its own automobiles or import them? If it imports, which country will it import from?
c.Canada has a tariff of 100% on imported autos.Then Canada decides to join a customs union with the United States (with a uniform external tariff of 100%).After the customs union is formed, what will the domestic price of automobiles be in Canada?
d.If Canada decides to join this customs union with the United States, will there be trade creation, trade diversion, or both? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
After the formation of the NAFTA, Mexico became a more attractive country for business investments of foreign firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
NAFTA has not only eliminated all tariffs and nontariff barriers to trade within the member countries but also allows free human migration across the countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Members of a free trade area not only remove barriers among themselves but also engage in free trade with the non-member countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is an economic embargo? While the embargo is in effect, does it benefit or hurt the embargoing countries? The country on which the embargo is being imposed? What conditions lend themselves toward a successful embargo?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The gains from joining a trade bloc are tied to trade diversion and the losses are tied to trade creation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Single European Act that came into effect in 1992 removed restrictions on people working in other member countries but retained restrictions on the flows of financial investments across the member countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain the basic requirements a country needs to fulfill to become a member of the European Union and the process of integration of new members.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If the target country of an embargo has a very inelastic demand for imports, the embargo is more likely to be successful in an economic sense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Turkey joined the EU in 2008 after implementing the necessary political and economic policy changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



