Deck 9: Nontariff Barriers to Imports
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Nontariff Barriers to Imports
1
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. The quota on MP3 players will cause domestic producers to: 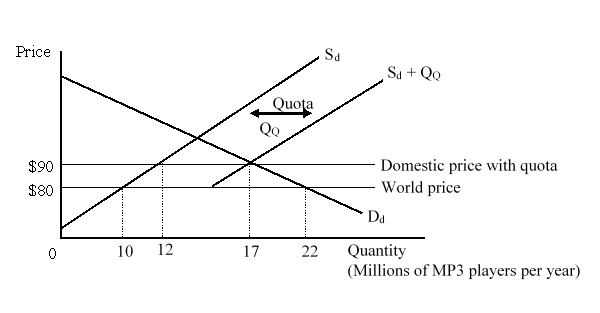
A)gain $150 million.
B)lose $100 million.
C)gain $110 million.
D)lose $120 million.

A)gain $150 million.
B)lose $100 million.
C)gain $110 million.
D)lose $120 million.
C
2
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. If the import licenses are allocated based on fixed favoritism, how much will be gained by the importers with the quota licenses?
A)$40 million
B)$70 million
C)$200 million
D)$240 million
A)$40 million
B)$70 million
C)$200 million
D)$240 million
A
3
In the case of a small country, the effects of a quota and a tariff are (almost) identical if:
A)the government allocates licenses for free to importers using a rule or process that involves (almost) no resource cost.
B)the government auctions off import licenses to the highest bidder.
C)the government allocates licenses to importers through application and selection procedures that require the use of substantial resources.
D)the government allocates import licenses directly to the public using a free lottery system.
A)the government allocates licenses for free to importers using a rule or process that involves (almost) no resource cost.
B)the government auctions off import licenses to the highest bidder.
C)the government allocates licenses to importers through application and selection procedures that require the use of substantial resources.
D)the government allocates import licenses directly to the public using a free lottery system.
B
4
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. If the government auctions the import licenses, the quota on MP3 players will result in a(n) _____ in the national well-being by_____. 
A)decrease; $35 million
B)decrease; $85 million
C)increase; $70 million
D)increase; $195 million

A)decrease; $35 million
B)decrease; $85 million
C)increase; $70 million
D)increase; $195 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. Referring to the figure, if instead of using a quota to limit imports they were limited by a voluntary export restraint (VER), the loss to the nation would be: 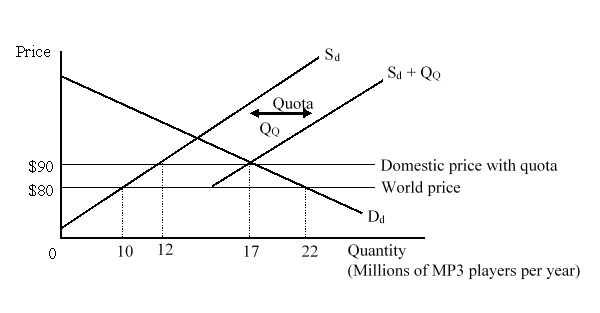
A)$35 million.
B)$50 million.
C)$85 million.
D)$195 million.

A)$35 million.
B)$50 million.
C)$85 million.
D)$195 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. The quota on MP3 players will cause domestic consumers to: 
A)lose $25 million.
B)gain $25 million.
C)lose $170 million.
D)lose $195 million.

A)lose $25 million.
B)gain $25 million.
C)lose $170 million.
D)lose $195 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. How many MP3 players can be imported from abroad after the quota is imposed? 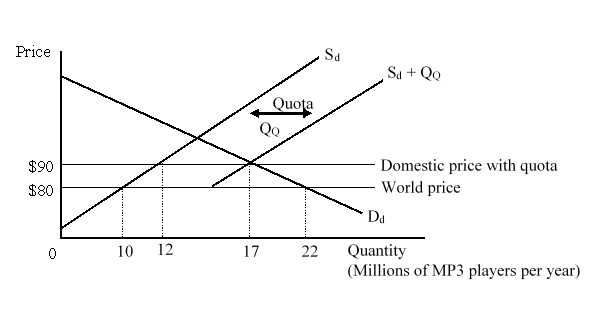
A)2 million.
B)5 million
C)12 million
D)17 million

A)2 million.
B)5 million
C)12 million
D)17 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. If the government auctions the import licenses, the national well-being will _____ by _____.
A)increase; $40 million
B)decrease; $12 million
C)increase; $65 million
D)decrease; $5 million
A)increase; $40 million
B)decrease; $12 million
C)increase; $65 million
D)decrease; $5 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. The quota on T-shirts causes domestic producers to:
A)gain $5 million.
B)lose $5 million.
C)gain $25 million.
D)gain $30 million.
A)gain $5 million.
B)lose $5 million.
C)gain $25 million.
D)gain $30 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT true of nontariff barriers to imports?
A)Nontariff barriers can limit imports with greater certainty than tariffs.
B)Unlike tariffs, the nontariff barriers do not increase the price of the imported goods in the domestic markets.
C)Some nontariff barriers create uncertainty about the conditions under which imports will be permitted.
D)Like tariffs, nontariff barriers also result in a net welfare loss in a small country.
A)Nontariff barriers can limit imports with greater certainty than tariffs.
B)Unlike tariffs, the nontariff barriers do not increase the price of the imported goods in the domestic markets.
C)Some nontariff barriers create uncertainty about the conditions under which imports will be permitted.
D)Like tariffs, nontariff barriers also result in a net welfare loss in a small country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Restricting imports into a small country by the government:
A)protects domestic producers from foreign competition.
B)increases consumer welfare in the country.
C)increases the general welfare of the importing nation.
D)increases well-being of the global economy.
A)protects domestic producers from foreign competition.
B)increases consumer welfare in the country.
C)increases the general welfare of the importing nation.
D)increases well-being of the global economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. If the government auctions the quota licenses, calculate the revenue collected by the government.
A)$40 million
B)$70 million
C)$200 million
D)$240 million
A)$40 million
B)$70 million
C)$200 million
D)$240 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is true of a quota:
A)Imposition of a quota causes domestic prices to fall below world prices.
B)Imposition of a quota by a country causes the world price of the good imported by this country to rise.
C)A quota is a quantitative restriction on imports.
D)A quota is always more efficient than a tariff.
A)Imposition of a quota causes domestic prices to fall below world prices.
B)Imposition of a quota by a country causes the world price of the good imported by this country to rise.
C)A quota is a quantitative restriction on imports.
D)A quota is always more efficient than a tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. The quota on T-shirts causes domestic consumers to:
A)gain $7 million.
B)lose $7 million.
C)lose $70 million.
D)lose $77 million.
A)gain $7 million.
B)lose $7 million.
C)lose $70 million.
D)lose $77 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Under which of the following situations will a tariff imposed by a country fail to reduce imports by as much as expected?
A)The current tariff rate is less than the prohibitive tariff rate.
B)The foreign export quantity supplied of the good imported by this country is more responsive to changes in the world price than was expected.
C)The domestic supply of the import-competing products is more price-elastic than was expected.
D)The domestic quantity demanded of the imported product is less responsive to price changes than was expected.
A)The current tariff rate is less than the prohibitive tariff rate.
B)The foreign export quantity supplied of the good imported by this country is more responsive to changes in the world price than was expected.
C)The domestic supply of the import-competing products is more price-elastic than was expected.
D)The domestic quantity demanded of the imported product is less responsive to price changes than was expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A small country imports T-shirts. With free trade at a world price of $10, domestic production is 10 million T-shirts and domestic consumption is 42 million T-shirts. The country's government now decides to impose a quota to limit T-shirt imports to 20 million per year. With the import quota in place, the domestic price rises to $12 per T-shirt and domestic production rises to 15 million T-shirts per year. How much would the importing nation lose if the government used VER instead of import quota?
A)$12 million
B)$20 million
C)$52 million
D)$24 million
A)$12 million
B)$20 million
C)$52 million
D)$24 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. According to the figure, if import licenses are allocated based on a resource-using procedure, the loss to the economy will be: 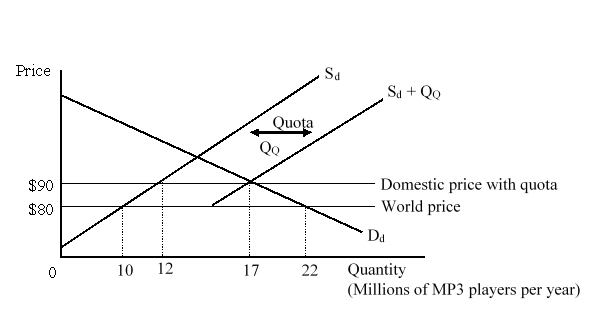
A)$35 million.
B)less than $10 million.
C)greater than $35 million.
D)$25 million.

A)$35 million.
B)less than $10 million.
C)greater than $35 million.
D)$25 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One of the reasons that protectionists and government officials may favor using a quota instead of a tariff is:
A)quotas generate more revenue for the government than tariffs.
B)quotas ensure that the quantities of imports are strictly limited.
C)quotas create less market distortions than tariffs.
D)quotas give less power to politicians than tariffs.
A)quotas generate more revenue for the government than tariffs.
B)quotas ensure that the quantities of imports are strictly limited.
C)quotas create less market distortions than tariffs.
D)quotas give less power to politicians than tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a means of allocating import licenses by assigning the licenses without competition, applications, or negotiation?
A)Fixed favoritism
B)Resource-using application procedures
C)Import-license auctions
D)Domestic content requirements
A)Fixed favoritism
B)Resource-using application procedures
C)Import-license auctions
D)Domestic content requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The figure given below shows the market for MP3 players in a small country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and domestic supply curves of the MP3 players before the imposition of the quota. (Sd + QQ) is the total available domestic supply curve after the quota has been imposed. According to the figure, how much revenue can the government expect to receive if the import licenses are auctioned? 
A)$20 million
B)$50 million
C)$120 million
D)$170 million

A)$20 million
B)$50 million
C)$120 million
D)$170 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following mandates that an import distributor must buy a certain percentage of the product locally?
A)An import quota
B)A mixing requirement
C)A voluntary export restraint
D)A domestic content requirement
A)An import quota
B)A mixing requirement
C)A voluntary export restraint
D)A domestic content requirement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT true of the Uruguay Round of the multilateral trade negotiations?
A)The Uruguay Round initiated the process of liberalizing trade in services.
B)The Uruguay Round agreements began the process of liberalizing trade in agricultural products.
C)The Uruguay Round included agreement requiring member countries to provide minimum levels of ownership protection for intellectual property.
D)The Uruguay Round narrowed down the set of NTB codes as set up by the Kennedy Round and the Tokyo Round.
A)The Uruguay Round initiated the process of liberalizing trade in services.
B)The Uruguay Round agreements began the process of liberalizing trade in agricultural products.
C)The Uruguay Round included agreement requiring member countries to provide minimum levels of ownership protection for intellectual property.
D)The Uruguay Round narrowed down the set of NTB codes as set up by the Kennedy Round and the Tokyo Round.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The figure given below shows the market for moped imports in the country. DM and SX are the domestic demand for imports and export supply curves respectively. 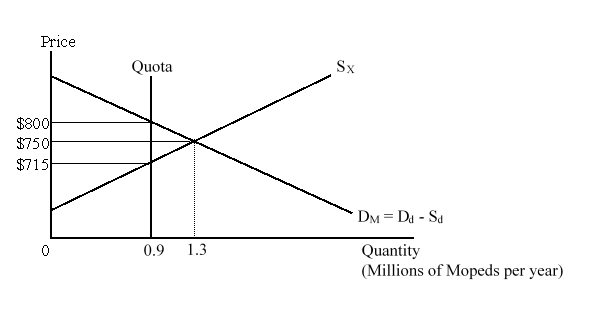 As a result of the quota being imposed on moped imports by this country, the world as a whole will:
As a result of the quota being imposed on moped imports by this country, the world as a whole will:
A)lose $7 million.
B)gain $10 million.
C)lose $17 million.
D)gain $31.5 million.
 As a result of the quota being imposed on moped imports by this country, the world as a whole will:
As a result of the quota being imposed on moped imports by this country, the world as a whole will:A)lose $7 million.
B)gain $10 million.
C)lose $17 million.
D)gain $31.5 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Buy America Act of 1933 mandates that:
A)the sales taxes on goods manufactured by the local labor force must be lower than the sales taxes on goods manufactured by the immigrant workers.
B)durable goods produced locally must be priced lower than comparable imported goods.
C)purchases funded by the U.S.government must favor domestic products.
D)household consumers buying more of local products will be given suitable tax incentives.
A)the sales taxes on goods manufactured by the local labor force must be lower than the sales taxes on goods manufactured by the immigrant workers.
B)durable goods produced locally must be priced lower than comparable imported goods.
C)purchases funded by the U.S.government must favor domestic products.
D)household consumers buying more of local products will be given suitable tax incentives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
With a voluntary export restraint (VER), the economic rent created for the quantitatively limited on trade is collected by:
A)the government of the importing county.
B)the consumers in the importing country.
C)the producers in the importing country.
D)the exporting firms in the foreign countries
A)the government of the importing county.
B)the consumers in the importing country.
C)the producers in the importing country.
D)the exporting firms in the foreign countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following NTBs may generate revenue for the government?
A)Government procurement
B)Voluntary export restraint
C)Import quota
D)Domestic content requirement
A)Government procurement
B)Voluntary export restraint
C)Import quota
D)Domestic content requirement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The figure given below shows the domestic demand (Dd) and supply (Sd) curves of mopeds in a country before an import quota is imposed by the government. After the imposition of quota, the total available supply curve becomes Sd + QQ. 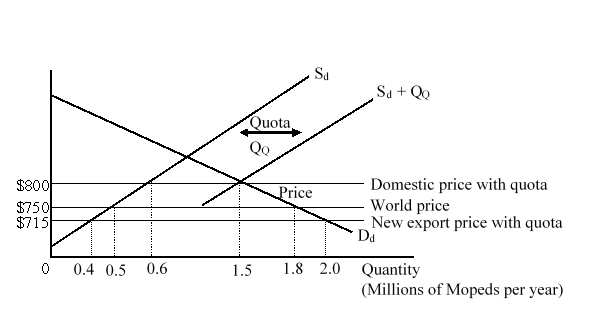 If the government auctions the quota licenses, the importing nation will:
If the government auctions the quota licenses, the importing nation will:
A)lose $10 million.
B)lose $29.75 million.
C)gain $31.5 million.
D)gain $21.5 million.
 If the government auctions the quota licenses, the importing nation will:
If the government auctions the quota licenses, the importing nation will:A)lose $10 million.
B)lose $29.75 million.
C)gain $31.5 million.
D)gain $21.5 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In which of the following cases does an import quota result in a higher welfare loss than a tariff?
A)The domestic firms producing an import-competing product set the product's price equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
B)The government auctions the import licenses to the highest bidders.
C)The quota licenses are allocated through resource-using application procedures.
D)The domestic industry in the importing country is highly competitive.
A)The domestic firms producing an import-competing product set the product's price equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
B)The government auctions the import licenses to the highest bidders.
C)The quota licenses are allocated through resource-using application procedures.
D)The domestic industry in the importing country is highly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The figure given below shows the domestic demand (Dd) and supply (Sd) curves of mopeds in a country before an import quota is imposed by the government. After the imposition of quota, the total available supply curve becomes Sd + QQ. 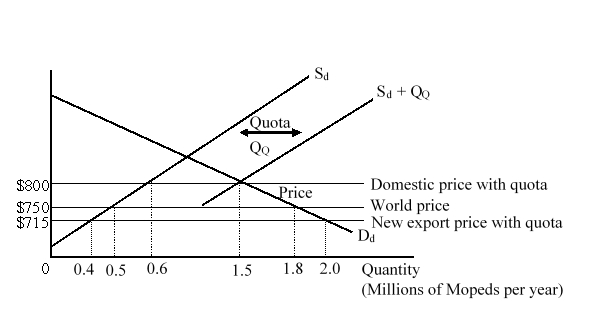 After the quota is imposed by the government, the domestic producers:
After the quota is imposed by the government, the domestic producers:
A)lose $2.5 million.
B)gain $27.5 million.
C)gain $42.5 million.
D)lose $80 million.
 After the quota is imposed by the government, the domestic producers:
After the quota is imposed by the government, the domestic producers:A)lose $2.5 million.
B)gain $27.5 million.
C)gain $42.5 million.
D)lose $80 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A domestic monopoly producing a close substitute of an imported product would prefer to be protected by a quota than a tariff that results in the same amount of imports because:
A)the deadweight loss will be smaller with a quota.
B)after the imposition of the tariff the price of the imported good declines in the domestic market.
C)unlike a tariff, a quota does not generate revenue for the government.
D)a quota allows the firm to charge a higher price.
A)the deadweight loss will be smaller with a quota.
B)after the imposition of the tariff the price of the imported good declines in the domestic market.
C)unlike a tariff, a quota does not generate revenue for the government.
D)a quota allows the firm to charge a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The figure given below shows the domestic demand (Dd) and supply (Sd) curves of mopeds in a country before an import quota is imposed by the government. After the imposition of quota, the total available supply curve becomes Sd + QQ. 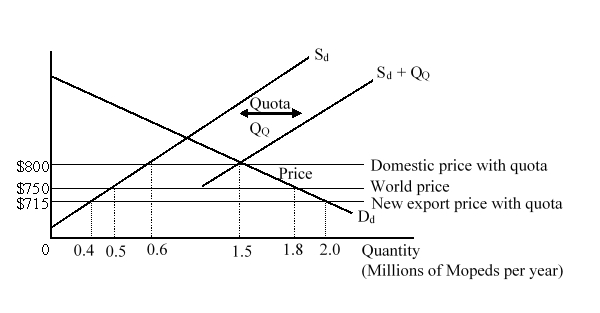 After the quota is imposed, the domestic consumers:
After the quota is imposed, the domestic consumers:
A)gain $7.5 million.
B)lose $21.25 million.
C)lose $82.5 million.
D)gain $97.75 million.
 After the quota is imposed, the domestic consumers:
After the quota is imposed, the domestic consumers:A)gain $7.5 million.
B)lose $21.25 million.
C)lose $82.5 million.
D)gain $97.75 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose a small country sets all of its tariffs at 40% which causes a reduction in imports by 20%. If the total imports affected by the tariffs are 40% of GDP, the net national loss from the tariffs as a percentage of GDP is:
A)1.6%.
B)about 1%.
C)6.4%.
D)3.2%.
A)1.6%.
B)about 1%.
C)6.4%.
D)3.2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the percent reduction in import quantity in a country due to the tariffs imposed by the government, if the country's import tariffs are all 10 percent. The total imports affected by the tariffs are 40 percent of the GDP and the net national loss from the tariffs as a percentage of GDP is 0.6 percent.
A)50 percent
B)40 percent
C)30 percent
D)20 percent
A)50 percent
B)40 percent
C)30 percent
D)20 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The figure given below shows the domestic demand (Dd) and supply (Sd) curves of mopeds in a country before an import quota is imposed by the government. After the imposition of quota, the total available supply curve becomes Sd + QQ. 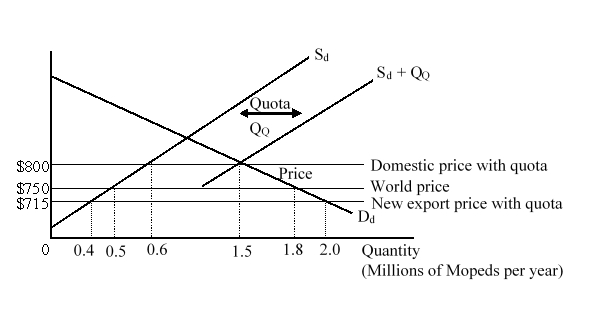 If the government auctions the quota licenses, how much will it collect as revenue?
If the government auctions the quota licenses, how much will it collect as revenue?
A)$31.5 million
B)$45 million
C)$76.5 million
D)$72 million
 If the government auctions the quota licenses, how much will it collect as revenue?
If the government auctions the quota licenses, how much will it collect as revenue?A)$31.5 million
B)$45 million
C)$76.5 million
D)$72 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is true of a voluntary export restraint (VER)?
A)A voluntary export restraint ensures that foreign exporting firms are unable to exercise monopoly power.
B)A voluntary export restraint usually requires that the foreign exporting firms act like a cartel, restricting sales and raising prices.
C)A voluntary export restraint generates more revenue for the government than a tariff or quota.
D)Voluntary export restraints have only been used by the poor and developing nations to protect their domestic industries.
A)A voluntary export restraint ensures that foreign exporting firms are unable to exercise monopoly power.
B)A voluntary export restraint usually requires that the foreign exporting firms act like a cartel, restricting sales and raising prices.
C)A voluntary export restraint generates more revenue for the government than a tariff or quota.
D)Voluntary export restraints have only been used by the poor and developing nations to protect their domestic industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is the least efficient method of allocating import licenses by the government?
A)Fixed favoritism
B)A competitive auction
C)Resource-using application procedures
D)A free lottery
A)Fixed favoritism
B)A competitive auction
C)Resource-using application procedures
D)A free lottery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The general formula used for calculating the net national loss from a trade barrier as a percentage of GDP may fail to account for:
A)the production effect of the trade barrier.
B)the consumption effect of the trade barrier.
C)the government revenue generated from the trade barrier.
D)the rent-seeking costs of the local firms.
A)the production effect of the trade barrier.
B)the consumption effect of the trade barrier.
C)the government revenue generated from the trade barrier.
D)the rent-seeking costs of the local firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a large country imposes an import quota:
A)the product's world price rises.
B)the product's world price falls.
C)the product's domestic price falls.
D)domestic production of the product falls.
A)the product's world price rises.
B)the product's world price falls.
C)the product's domestic price falls.
D)domestic production of the product falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Governments choose to use voluntary export restraints rather than tariffs because:
A)voluntary export restraints have the potential to generate higher revenue.
B)voluntary export restraints do not generate any welfare loss in the importing country.
C)tariffs more obviously violate the international rules of the WTO.
D)the increase in the price of the imported good in the domestic market is much lower in case of VERs than tariffs.
A)voluntary export restraints have the potential to generate higher revenue.
B)voluntary export restraints do not generate any welfare loss in the importing country.
C)tariffs more obviously violate the international rules of the WTO.
D)the increase in the price of the imported good in the domestic market is much lower in case of VERs than tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following allows the president of the United States to negotiate to eliminate unfair trade practices put in place by foreign governments?
A)Tariff-quota requirements
B)The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
C)Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974
D)The United Nations
A)Tariff-quota requirements
B)The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
C)Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974
D)The United Nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Compared to a tariff, a quota gives the government a better control over the quantity of imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What are NTBs? Discuss any three forms of NTBs other than quotas and VERs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If there is only one domestic automobile manufacturing firm in a small country, will there be a difference in terms of national economic well-being between using a tariff and using a quota to protect the firm? If so, what is the difference? Clearly explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
While a large country can either be better off or worse off due to the imposition of a tariff, the same country will necessarily be worse off as a result of imposing an equivalent import quota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The world as a whole is better off, if the trading partners of a nation respond by raising their trade barriers when this country raises its own trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Show graphically and explain the effects of imposition of a quota by a small country under competitive conditions. The quota rights are given away for free to a fixed set of import distributor firms in the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Evidence shows that governments usually impose the same import duties on the import of similar goods even if the goods fall under different product categories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Government procurement practices can restrict imports if the purchasing processes are heavily biased toward products with large local content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Unlike a tariff, quotas do not allow domestic monopolists to assert their monopoly pricing powers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose a country's government is deciding whether or not to impose an import quota to protect the domestic automobile industry. Will the domestic steel-producing firms be in favor of a quota designed to protect the local automobile producers? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain how the cost of a country's tariffs is calculated as a percentage of GDP. Which effects are captured in this process? Why is the true cost of import protection probably larger than what can be shown in simple graphs or as calculated by the net national loss formula?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Briefly discuss different methods of allocating quota licenses to the importers by the government. Also explain the inefficiency implications of each method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The revenue earned by the government in allocating quota licenses through resource-using application procedures is approximately equal to the revenue that it would earn from a tariff that resulted in the same import quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The World Trade Organization has rules that try to limit the use of tariffs but not the use of NTBs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Imposition of trade barriers by one country can cause other countries to retaliate, and may lead to a trade war in which all countries raise high import barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When an importing country compels the foreign exporting country to agree "voluntarily" to restrict its exports to this country, the exporting firms in the foreign country suffer a net welfare loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The VER is not only a politically attractive way of offering protection to an import-competing industry, but is also economically much less inefficient than other trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Unlike a tariff, a quota does not cause either a production effect or a consumption effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Most or all of the mark-up revenue from a quota will be captured by the government if the government auctions off import licenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In an attempt to restrict imports in a country, imposition of a tariff is likely to be more efficient than using voluntary export restraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



