Deck 7: Growth and Trade Part II: Trade Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Growth and Trade Part II: Trade Policy
1
Suppose country A produces two goods, good X and good Y. Production of good X involves an intensive use of highly skilled workers. However, good Y is a relatively capital-intensive good. If the country experiences a wave of immigration of highly skilled workers, investment in physical capital remaining unchanged, the Rybczynski theorem will predict that:
A)the production of good Y will contract.
B)the production of both the goods will expand in the same proportion.
C)the production of good X will contract.
D)the production of both the goods will increase, but increase in good X will be much higher than increase in good Y.
A)the production of good Y will contract.
B)the production of both the goods will expand in the same proportion.
C)the production of good X will contract.
D)the production of both the goods will increase, but increase in good X will be much higher than increase in good Y.
A
2
Suppose a large country experiences economic growth which results in a reduced willingness to trade. The country's terms of trade will _____ because the fall in demand for imports will cause the price of its exports to _____ relative to the price that it has to pay for its imports.
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; rise
C)improve; fall
D)worsen; rise
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; rise
C)improve; fall
D)worsen; rise
B
3
The Rybczynski theorem asserts that in a two-good model, and assuming that product prices stay constant, growth in the endowment of one factor of production with the other factor remaining unchanged, will result in:
A)an equal increase in the output of both goods.
B)an increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively and a decrease in the output of the other good.
C)an increase in the output of both goods but a relatively greater increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively.
D)an increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively, but the output level of the other good will remain unchanged.
A)an equal increase in the output of both goods.
B)an increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively and a decrease in the output of the other good.
C)an increase in the output of both goods but a relatively greater increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively.
D)an increase in the output of the good that uses the growing factor intensively, but the output level of the other good will remain unchanged.
B
4
Which of the following is one of the fundamental sources of long-run economic growth?
A)An expansion of foreign GDP
B)An increase in demand for the country's importable product
C)An improvement in production technologies
D)An expansion in the export of primary commodities
A)An expansion of foreign GDP
B)An increase in demand for the country's importable product
C)An improvement in production technologies
D)An expansion in the export of primary commodities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Rybczynski theorem suggests that development of new natural resources in a country:
A)will result in balanced growth.
B)may cause the country to export only manufactured products.
C)will increase output in all sectors of the economy.
D)may cause the manufacturing sector of the country to shrink.
A)will result in balanced growth.
B)may cause the country to export only manufactured products.
C)will increase output in all sectors of the economy.
D)may cause the manufacturing sector of the country to shrink.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Assume that a capital-abundant country trades only two goods with the rest of the world, medical equipment and corn. Medical equipment is relatively capital-intensive. According to the Rybczynski theorem, the relative price of the goods remaining unchanged, an increase in the country's endowment of capital will cause the output of medical equipment to _____ and the output of corn to _____.
A)rise; fall
B)fall; rise
C)rise; remain the same
D)remain the same; fall
A)rise; fall
B)fall; rise
C)rise; remain the same
D)remain the same; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose a large country experiences economic growth which results in an increased willingness to trade. The country's terms of trade will _____ because the increase in demand for imports will cause the price of its exports to _____ relative to the price that it has to pay for its imports.
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; rise
C)improve; fall
D)worsen; rise
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; rise
C)improve; fall
D)worsen; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a country that produces only wine and guns, which of the following is least likely to lead to biased growth?
A)The amount of usable land has increased substantially.
B)The relaxation of migration laws has led to a huge influx of unskilled workers.
C)The technology used to produce guns improves while the technology used to produce wine does not change.
D)The relative price of guns in the international market changes.
A)The amount of usable land has increased substantially.
B)The relaxation of migration laws has led to a huge influx of unskilled workers.
C)The technology used to produce guns improves while the technology used to produce wine does not change.
D)The relative price of guns in the international market changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Assume a country that produces only cloth and paddy. Cloth production requires significant amounts of labor and capital, but relatively less land. Assume that paddy production requires relatively less labor and capital, but relatively large amounts of fertile arable land. If there is an increase in the country's endowments of capital and labor, the Rybczynski theorem would predict that:
A)the production of both paddy and cloth will increase.
B)the production of cloth will increase, but that of paddy will remain unchanged.
C)the production of cloth will increase, but that of paddy will decline.
D)the production of paddy will increase, but that of cloth will remain unchanged.
A)the production of both paddy and cloth will increase.
B)the production of cloth will increase, but that of paddy will remain unchanged.
C)the production of cloth will increase, but that of paddy will decline.
D)the production of paddy will increase, but that of cloth will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assume that a large capital-abundant country trades only two goods with the rest of the world, medical equipment and corn. Medical equipment is relatively capital-intensive. An increase in the country's endowment of capital will cause the price of medical equipment relative to the price of corn to:
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)stay the same.
D)rise at first and then fall.
A)rise.
B)fall.
C)stay the same.
D)rise at first and then fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the figure given below, we see an expansion of the production-possibility curve (from PPC1 to PPC2). The two goods produced are wheat and cloth, which are land-intensive and labor-intensive respectively. The outward shift of the production-possibility curve shows: 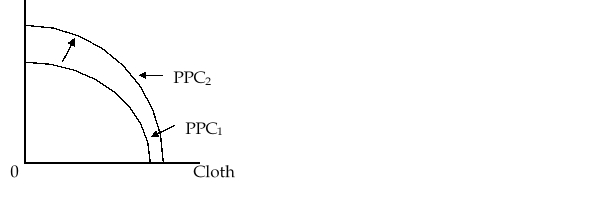
A)biased growth.
B)balanced growth.
C)a move from a no-trade situation to free trade.
D)a fall in production costs of both the goods.
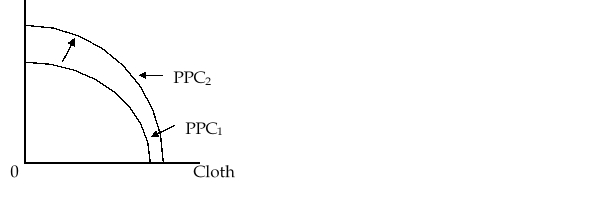
A)biased growth.
B)balanced growth.
C)a move from a no-trade situation to free trade.
D)a fall in production costs of both the goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In international trade jargon, an economy is said to be a large country if:
A)it is a price-taker in the world market.
B)a majority of its production is consumed domestically.
C)a decline in its exports raises the world price of those goods.
D)a decline in its imports does not affect its terms of trade.
A)it is a price-taker in the world market.
B)a majority of its production is consumed domestically.
C)a decline in its exports raises the world price of those goods.
D)a decline in its imports does not affect its terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose a small country experiences economic growth which leads to an increased willingness to trade. The country's terms of trade will _____ because the prices of its exports will _____ relative to the price that it has to pay for its imports.
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; not change
C)remain unaffected; not change
D)remain constant; fall
A)worsen; fall
B)improve; not change
C)remain unaffected; not change
D)remain constant; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Increases in a country's endowments of land, labor, and capital will lead to long-run economic growth.
B)Improvements in the technology used in production can lead to increases in current output levels, but will not affect long-run economic growth.
C)Improvements in production technology do not affect the shape or position of the production-possibility curve.
D)Biased growth leads to a proportionate shift in the production-possibility curve.
A)Increases in a country's endowments of land, labor, and capital will lead to long-run economic growth.
B)Improvements in the technology used in production can lead to increases in current output levels, but will not affect long-run economic growth.
C)Improvements in production technology do not affect the shape or position of the production-possibility curve.
D)Biased growth leads to a proportionate shift in the production-possibility curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assume a country produces only wine and guns. Both wine and gun production use land and labor as their only inputs. Wine production is relatively land-intensive while gun production is relatively labor-intensive. According to the Rybczynski theorem, a significant rise in immigration is most likely to lead to:
A)an increase in the production of both wine and guns.
B)an increase in wine production by a greater proportion than the increase in the size of the labor force due to immigration.
C)an increase in the production of guns by a greater proportion than the increase in the size of the labor force due to immigration.
D)an increase in wine production by a greater proportion than the increase in the production of guns.
A)an increase in the production of both wine and guns.
B)an increase in wine production by a greater proportion than the increase in the size of the labor force due to immigration.
C)an increase in the production of guns by a greater proportion than the increase in the size of the labor force due to immigration.
D)an increase in wine production by a greater proportion than the increase in the production of guns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If trade is consistent with the H-O theory, then growth in a country's scarce factor of production will lead to:
A)an increased willingness to trade.
B)balanced growth.
C)a decreased willingness to trade.
D)a deterioration in the country's terms of trade.
A)an increased willingness to trade.
B)balanced growth.
C)a decreased willingness to trade.
D)a deterioration in the country's terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose country X partially specializes in the production of only two goods, food and clothing. At the initial free trade equilibrium, the country produced 40 units of food and 20 units of clothing. At the same time10 units of food were exported and 10 units of clothing were imported by country X. Now suppose a technological innovation in country X leads to a balanced growth while leaving the relative prices of food and clothing unchanged in the international market. Production of food in country X rises to 50 units and that of clothing rises to 25 units. If consumption of food, on the other hand, rises to 42 units, we can most reasonably conclude that the:
A)consumption of clothing rises to 32 units.
B)the size of country X's trade triangle has increased.
C)country X's willingness to trade declines.
D)consumers in country X are left worse-off.
A)consumption of clothing rises to 32 units.
B)the size of country X's trade triangle has increased.
C)country X's willingness to trade declines.
D)consumers in country X are left worse-off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the figure given below, we see an expansion of the production-possibility curve (from PPC1 to PPC2). The two goods produced are wheat and cloth, which are land-intensive and labor-intensive respectively. The outward shift of the production-possibility curve is likely the result of: 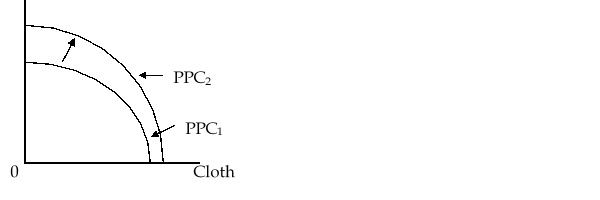
A)a fall in average cost of producing cloth.
B)an increase in the price of cloth.
C)an increase in the size of the labor force, the area under cultivation remaining unchanged.
D)an increase in the national amount of usable land, the size of the labor force remaining unchanged.
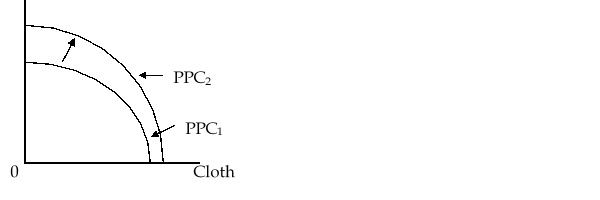
A)a fall in average cost of producing cloth.
B)an increase in the price of cloth.
C)an increase in the size of the labor force, the area under cultivation remaining unchanged.
D)an increase in the national amount of usable land, the size of the labor force remaining unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The rapid accumulation of capital and worker skills in the United States in the 1800's:
A)resulted in an increase in the export of natural resources by the country.
B)made the United States more dependent on imported minerals.
C)made the United States more self-sufficient and led to a reduction in its trade volume.
D)resulted in rapid deindustrialization in the country.
A)resulted in an increase in the export of natural resources by the country.
B)made the United States more dependent on imported minerals.
C)made the United States more self-sufficient and led to a reduction in its trade volume.
D)resulted in rapid deindustrialization in the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose country X partially specializes in the production of only two goods, food and clothing. At the initial free trade equilibrium, the country produced 40 units of food and 20 units of clothing. At the same time10 units of food were exported and 10 units of clothing were imported by country X. Now suppose a technological innovation in country X leads to a balanced growth while leaving the relative prices of food and clothing unchanged in the international market. Production of food in country X rises to 50 units and that of clothing rises to 25 units. If consumption of food rises to 42 units, the consumption of clothing:
A)rises to 33 units.
B)declines to 25 units.
C)rises to 35 units.
D)declines to less than 20 units.
A)rises to 33 units.
B)declines to 25 units.
C)rises to 35 units.
D)declines to less than 20 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose country X is one of the largest exporter of coffee in the world. A recent massive cyclone has destroyed much of the coffee crop in country X and has considerably lowered its exports. Which of the following is a likely consequence of this disaster?
A)The size of country X's trade triangle will increase.
B)The price of coffee in the international market will decline.
C)The price of country X's imports relative to the price of its exports will increase unambiguously.
D)Country X's terms of trade will improve.
A)The size of country X's trade triangle will increase.
B)The price of coffee in the international market will decline.
C)The price of country X's imports relative to the price of its exports will increase unambiguously.
D)Country X's terms of trade will improve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose a capital-abundant country experiences a significant increase in its capital stock. This change in endowments is most likely to lead to:
A)an improvement in the country's terms of trade.
B)a decreased willingness to trade.
C)an increase in the price of the capital-intensive goods relative to the labor-intensive goods.
D)an increased willingness to trade.
A)an improvement in the country's terms of trade.
B)a decreased willingness to trade.
C)an increase in the price of the capital-intensive goods relative to the labor-intensive goods.
D)an increased willingness to trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The figure given below shows a shift in the production-possibility curve of a country from AB to AC. Here, S1 and C1 are the initial production and consumption points respectively. S2 and C2, on the other hand, are the final production and consumption points respectively. Which of the following is illustrated by this figure? 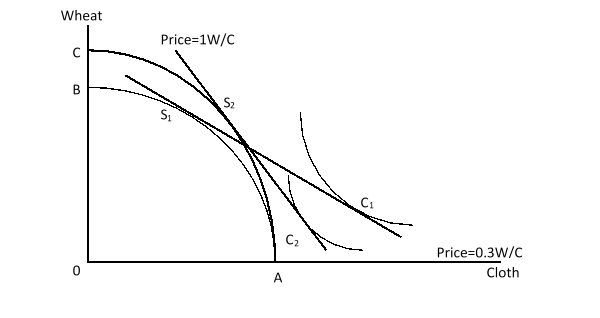
A)A small country experiencing a balanced growth
B)A large country experiencing a balanced growth
C)A small country experiencing growth biased toward cloth production
D)A large country experiencing growth biased toward wheat production.

A)A small country experiencing a balanced growth
B)A large country experiencing a balanced growth
C)A small country experiencing growth biased toward cloth production
D)A large country experiencing growth biased toward wheat production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a small, initially closed country engages in free trade:
A)it always experiences a balanced growth.
B)it experiences a much slower economic growth.
C)it is not likely to suffer from immiserizing growth.
D)its production-possibility curve shifts inward.
A)it always experiences a balanced growth.
B)it experiences a much slower economic growth.
C)it is not likely to suffer from immiserizing growth.
D)its production-possibility curve shifts inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose a labor-abundant country, exporting a labor-intensive good, experiences a significant increase in its capital stock. This change in endowments can:
A)lead to an immiserizing growth.
B)lead to an increase in the export of labor-intensive goods by the country.
C)lead to a reversal of the country's trade pattern.
D)lead to reduced growth rates.
A)lead to an immiserizing growth.
B)lead to an increase in the export of labor-intensive goods by the country.
C)lead to a reversal of the country's trade pattern.
D)lead to reduced growth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The figure given below shows a shift in the production-possibility curve of a country from AB to AC. Here, S1 and C1 are the initial production and consumption points respectively. S2 and C2, on the other hand, are the final production and consumption points respectively. Which of the following is illustrated by this figure? 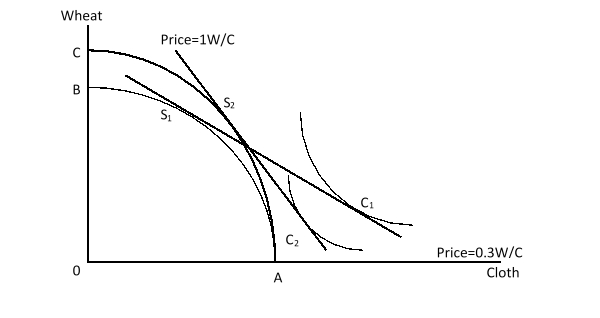
A)The mechanism of reversal in trade pattern
B)The validity of the product cycle hypothesis
C)The immiserizing growth effect in a large country
D)The benefits of trade in a small country

A)The mechanism of reversal in trade pattern
B)The validity of the product cycle hypothesis
C)The immiserizing growth effect in a large country
D)The benefits of trade in a small country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The possibility of immiserizing growth can arise when:
A)a large country expands the production of its export-oriented goods.
B)there is a decline in the research and development investments in a large country.
C)the terms of trade of a small country decline due to changes in the rest of the world.
D)the import-competing goods are overproduced in a large country.
A)a large country expands the production of its export-oriented goods.
B)there is a decline in the research and development investments in a large country.
C)the terms of trade of a small country decline due to changes in the rest of the world.
D)the import-competing goods are overproduced in a large country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true of product cycle hypothesis?
A)It explains how a country completely specializes in the production of the good that was first invented in this country.
B)It ignores the importance of research and development in the improvement of production technology in a country.
C)It explains how an initial exporter of a good ends up importing the good from other countries.
D)It assumes that the demands for various commodities in the countries do not change over time.
A)It explains how a country completely specializes in the production of the good that was first invented in this country.
B)It ignores the importance of research and development in the improvement of production technology in a country.
C)It explains how an initial exporter of a good ends up importing the good from other countries.
D)It assumes that the demands for various commodities in the countries do not change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Heckscher-Ohlin theory suggests that research and development activity is most likely to be concentrated in countries which:
A)are capital-abundant.
B)are skilled-labor-abundant.
C)specialize in the production of primary commodities.
D)are more self-reliant.
A)are capital-abundant.
B)are skilled-labor-abundant.
C)specialize in the production of primary commodities.
D)are more self-reliant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Immiserizing growth is most likely to occur when:
A)the import payments of a country decline relative to its export earnings
B)the increase in population exceeds the increase in national income of a country.
C)the benefits of economic growth are not shared equally by all the residents of the country.
D)economic growth leads to a deterioration of a country's terms of trade.
A)the import payments of a country decline relative to its export earnings
B)the increase in population exceeds the increase in national income of a country.
C)the benefits of economic growth are not shared equally by all the residents of the country.
D)economic growth leads to a deterioration of a country's terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Countries that are open to international trade:
A)cannot suffer from immiserizing growth.
B)tend to grow faster than the closed economies.
C)tend to lose out on the benefits of technological diffusion.
D)do not experience biased growth.
A)cannot suffer from immiserizing growth.
B)tend to grow faster than the closed economies.
C)tend to lose out on the benefits of technological diffusion.
D)do not experience biased growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following refers to individual efforts by businesses that focus on improvements in production technologies for existing products and on new production technologies for new or improved products?
A)Balanced growth
B)Diffusion
C)Import competition
D)Research and development
A)Balanced growth
B)Diffusion
C)Import competition
D)Research and development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Technology-based comparative advantage:
A)can help explain how the United States went from being a net exporter of steel to being a net importer of steel.
B)is totally contradictory to the Heckscher-Ohlin theory of comparative advantage.
C)always results in immiserizing growth.
D)emphasizes that poorer and less industrialized nations cannot compete in world markets with richer and more industrialized nations.
A)can help explain how the United States went from being a net exporter of steel to being a net importer of steel.
B)is totally contradictory to the Heckscher-Ohlin theory of comparative advantage.
C)always results in immiserizing growth.
D)emphasizes that poorer and less industrialized nations cannot compete in world markets with richer and more industrialized nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Large countries are _____ susceptible to immiserizing growth than small countries because when large countries expand their exports, their terms of trade _____.
A)less; improve
B)less; worsen
C)more; improve
D)more; worsen
A)less; improve
B)less; worsen
C)more; improve
D)more; worsen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The figure given below shows a shift in the production-possibility curve of a country from AB to AC. Here, S1 and C1 are the initial production and consumption points respectively. S2 and C2, on the other hand, are the final production and consumption points respectively. The shifts shown in the given figure indicate that: 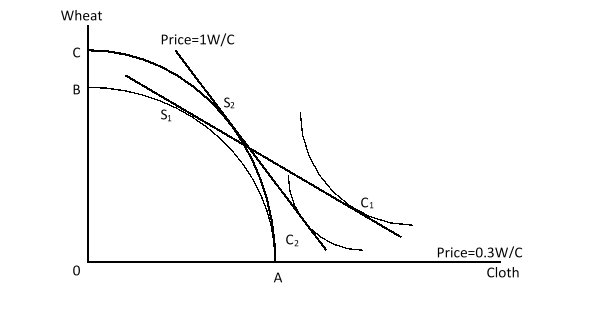
A)the domestic demand for wheat is higher than the demand in the international market.
B)the country can now consume more of both goods.
C)the world price of wheat has increased.
D)the terms of trade for this country have deteriorated.

A)the domestic demand for wheat is higher than the demand in the international market.
B)the country can now consume more of both goods.
C)the world price of wheat has increased.
D)the terms of trade for this country have deteriorated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In Heckscher-Ohlin theory, differences in _____ across countries are considered to be the basis for comparative advantage.
A)consumer tastes and preferences
B)factor endowments
C)production technologies
D)economic freedom
A)consumer tastes and preferences
B)factor endowments
C)production technologies
D)economic freedom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is most unlikely to lead to a reversal of a country's trade pattern?
A)Growth in the country's endowment of the input that is initially scarce
B)A proportionate increase in output in all the sectors of the economy
C)International diffusion of technology
D)Shifting tastes of the country's consumers
A)Growth in the country's endowment of the input that is initially scarce
B)A proportionate increase in output in all the sectors of the economy
C)International diffusion of technology
D)Shifting tastes of the country's consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
_____ first presented the product cycle hypothesis.
A)Adam Smith
B)David Ricardo
C)Eli Heckscher
D)Raymond Vernon
A)Adam Smith
B)David Ricardo
C)Eli Heckscher
D)Raymond Vernon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following conditions is NOT necessary for immiserizing growth to arise in a country?
A)The country's growth must be strongly biased toward expanding the country's supply of exports and the increase in exports must be large enough to have a noticeable impact on world prices.
B)The foreign demand for the country's exports must be price inelastic so that an expansion in the country's export supply leads to a large drop in the international price of the export product.
C)Before the growth, the country must be heavily engaged in trade so that the welfare loss from the decline in the terms of trade is great enough to offset the gains from being able to produce more.
D)The country must specialize in the production of a single exportable good and import all the other goods consumed in the economy.
A)The country's growth must be strongly biased toward expanding the country's supply of exports and the increase in exports must be large enough to have a noticeable impact on world prices.
B)The foreign demand for the country's exports must be price inelastic so that an expansion in the country's export supply leads to a large drop in the international price of the export product.
C)Before the growth, the country must be heavily engaged in trade so that the welfare loss from the decline in the terms of trade is great enough to offset the gains from being able to produce more.
D)The country must specialize in the production of a single exportable good and import all the other goods consumed in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When economic growth in a large country lowers its willingness to trade, it can result in:
A)an improvement in the country's terms of trade.
B)a biased growth.
C)immiserizing growth.
D)the Dutch Disease.
A)an improvement in the country's terms of trade.
B)a biased growth.
C)immiserizing growth.
D)the Dutch Disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Both the Heckscher-Ohlin theory and comparative advantage based on technological differences assume that the techniques of production in various countries do not change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The impact of economic growth on a country's willingness to trade is determined solely by the extent of the shift of its production-possibility curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Any change in the volume of export or import by a small country will have no effect on its terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Discuss how openness to trade can influence economic growth in a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume that corn and cloth are each produced using both land and labor in a country. Corn is relatively land-intensive. If the country experiences an increase in its endowment of labor, product prices remaining unchanged, the Rybczynski theorem will predict that the production of corn will decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a two-commodity world, balanced growth in a country always decreases its willingness to trade because the country becomes self-sufficient in the production of both the goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the presence of free trade, how are the effects of economic growth different for a large country than for a small country?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Increases in a country's endowments of factors of production increase current output, but do not contribute to long-run economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
New technology developed by a multinational corporation in one of its research facilities in a leading developed country can be transferred within the corporation to the affiliates in other developed countries, but not to the affiliates in developing countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Countries that export a diversified selection of export products do not seem to be at much risk of experiencing immiserizing growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
According to the Rybczynski theorem, in a two-good world, with constant product prices, growth in a country's endowment of any one input results in an increase in the production of the good which does not use this input intensively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For a country already engaged in trade, biased growth will essentially lead to an increased willingness to trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Economic growth with an increased willingness to engage in international trade will always improve the economic well-being of a large country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Country X produces two goods, guns and roses, using labor and land. Assume that production of guns is relatively labor-intensive and production of roses is relatively land-intensive. Suppose a large number of workers from a neighboring country migrate to country X. Carefully explain all the predictions of the Rybczynski theorem' about the changes in output of both guns and roses in country X. Be certain to explain any shifts in resources from one industry to the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Explain carefully, with a diagram, the crucial conditions for immiserizing growth to occur. In particular, discuss the effect of the size of the country, the volume of foreign trade, the type of growth the country experiences, and foreign demand for the exports of the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
It is usually safer for a large country to subsidize its export-oriented industries rather than the import-replacing industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose that country A, a relatively capital-abundant country, experiences further expansion in its endowment of capital. Explain how this might affect its volume (amount) of trade and its terms of trade with the rest of the world. Under what conditions (if any) would the economic well-being of country A decline after the increase in its capital endowment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose the United States exports capital-intensive goods like construction equipment to the rest of the world and imports clothing, a labor-intensive good. Both the goods use capital and labor as their only inputs. Recently the capital endowment of the U.S. has increased substantially, but the size of the labor force has remained unchanged.
A)What is the effect of the change in endowment on the shape and position of the production-possibility curve of the U.S.? Illustrate your answer with the help of a suitable diagram.
B)What is the effect of such changes in factor endowment on the actual production quantities of the two goods in the United States, assuming the product price ratio remains unchanged in the international market? Explain and illustrate graphically.
C)What is the effect of such changes in factor endowment on the United States' willingness to trade?
A)What is the effect of the change in endowment on the shape and position of the production-possibility curve of the U.S.? Illustrate your answer with the help of a suitable diagram.
B)What is the effect of such changes in factor endowment on the actual production quantities of the two goods in the United States, assuming the product price ratio remains unchanged in the international market? Explain and illustrate graphically.
C)What is the effect of such changes in factor endowment on the United States' willingness to trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Immiserizing growth is the situation in which the expansion of a country's exporting industry results in an increase in the world price of the exported good and an increase in the economic welfare of the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Dutch disease refers to a situation in which new production of a natural resource results in deindustrialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



