Deck 14: Analyzing Results
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Analyzing Results
1
The Chi Square Test Candace studies factors related to students dropping out of school.She constructs a 2 X 2 contingency table (Drinking alcohol: under 5 drinks a week, over 5 drinks a week X Study time: under 15 hours a week, over 15 hours a week).How many degrees of freedom are required by a chi square test of these data?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
1
2
Which Test Do I Use? The level of measurement is important because it
A)determines the appropriate significance level for a statistical test.
B)determines whether a statistical test should be one-tailed or two-tailed.
C)determines whether the research hypothesis should be directional or nondirectional.
D)determines which statistical test may be used.
A)determines the appropriate significance level for a statistical test.
B)determines whether a statistical test should be one-tailed or two-tailed.
C)determines whether the research hypothesis should be directional or nondirectional.
D)determines which statistical test may be used.
determines which statistical test may be used.
3
Statistics for Two Group Experiments Researchers use the ____ to analyze ordinal data obtained from multiple independent groups.
A)Friedman test
B)Kruskal-Wallis test
C)Mann-Whitney U test
D)Wilcoxon test
A)Friedman test
B)Kruskal-Wallis test
C)Mann-Whitney U test
D)Wilcoxon test
Kruskal-Wallis test
4
Which Test Do I Use? An experimenter considers all of these factors when selecting a statistical test except
A)the number of degrees of freedom.
B)the number of independent variables.
C)the number of levels.
D)whether the experiment is within or between subjects.
A)the number of degrees of freedom.
B)the number of independent variables.
C)the number of levels.
D)whether the experiment is within or between subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Chi Square Test Cramer's coefficient Phi estimates the
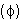
A)degree of association between two categorical variables.
B)power of a chi square test.
C)probability of observed frequencies in a chi square test.
D)size of the treatment effect produced by two categorical variables.
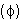
A)degree of association between two categorical variables.
B)power of a chi square test.
C)probability of observed frequencies in a chi square test.
D)size of the treatment effect produced by two categorical variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which Test Do I Use? An epidemiologist investigating sexually transmitted disease classifies subjects into five condom usage categories: 100%, 75-99%, 50-74%, 25-49%, and 0-24%.Which level of measurement is she using?
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which Test Do I Use? Which scale allows us to conclude that the group trained to breathe diaphragmatically experienced half the panic attacks as the control group?
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Chi Square Test A chi square test
A)assumes that the population is normally distributed .
B)compares the difference between treatment means with an estimate of variability in the sampled population.
C)compares the frequencies of responses in our sample with those expected in the population.
D)is more powerful than parametric tests.
A)assumes that the population is normally distributed .
B)compares the difference between treatment means with an estimate of variability in the sampled population.
C)compares the frequencies of responses in our sample with those expected in the population.
D)is more powerful than parametric tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Statistics for Two Group Experiments When you obtain ordinal data from two matched groups, you should use the
A)chi square test.
B)Mann-Whitney U test.
C)t test for matched groups.
D)Wilcoxon test.
A)chi square test.
B)Mann-Whitney U test.
C)t test for matched groups.
D)Wilcoxon test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which Test Do I Use? You should decide which test of significance to use
A)after calculating descriptive statistics on your data.
B)after running all your subjects.
C)after scoring all of the data.
D)as you plan the design of your study.
A)after calculating descriptive statistics on your data.
B)after running all your subjects.
C)after scoring all of the data.
D)as you plan the design of your study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which Test Do I Use? Jack is designing a two-group experiment and asks you which statistical test he should use.The first question you should ask him is:
A)"How many subjects will you run in each condition?"
B)"Is your research hypothesis directional or nondirectional?"
C)"Which level of measurement will you use?"
D)"What significance level are you using?"
A)"How many subjects will you run in each condition?"
B)"Is your research hypothesis directional or nondirectional?"
C)"Which level of measurement will you use?"
D)"What significance level are you using?"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Chi Square Test A chi square test compares
A)observed and expected frequencies.
B)treatment group variability with expected population variability.
C)treatment mean differences and sample variability.
D)treatment means.
A)observed and expected frequencies.
B)treatment group variability with expected population variability.
C)treatment mean differences and sample variability.
D)treatment means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which Test Do I Use? Students interviewed three candidates for Dean of Student Affairs and then ranked them from first to third place.Which level of measurement did they use?
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio
A)interval
B)nominal
C)ordinal
D)ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Statistics for Two Group Experiments The ____ should be used to evaluate ordinal data from two independent groups.
A)chi square test
B)Mann-Whitney U test
C)t test for independent groups
D)Wilcoxon test
A)chi square test
B)Mann-Whitney U test
C)t test for independent groups
D)Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Chi Square Test The degrees of freedom represent
A)how many scores could vary without changing the value of a statistic we already know.
B)the expected variability within each treatment condition.
C)the robustness of a parametric test.
D)the sensitivity of the dependent variable measure.
A)how many scores could vary without changing the value of a statistic we already know.
B)the expected variability within each treatment condition.
C)the robustness of a parametric test.
D)the sensitivity of the dependent variable measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which Test Do I Use? Which two scales provide the most information about magnitude and are preferred by researchers?
A)interval and ordinal
B)interval and ratio
C)nominal and ordinal
D)nominal and ratio
A)interval and ordinal
B)interval and ratio
C)nominal and ordinal
D)nominal and ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Statistics for Two Group Experiments Which statistical test should you use to evaluate nominal data from a two- group experiment?
A)chi square test
B)Mann-Whitney U test
C)t test for independent groups
D)Wilcoxon test
A)chi square test
B)Mann-Whitney U test
C)t test for independent groups
D)Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Statistics for Two Group Experiments Logan randomly assigned subjects to study for a Physiological Psychology exam using one of two study aids (flash cards with text or flash cards with text and diagrams).He should analyze both groups' exam scores, which range from 0-150, using a
A)t test for independent groups.
B)t test for matched groups.
C)two-way ANOVA.
D)Wilcoxon test.
A)t test for independent groups.
B)t test for matched groups.
C)two-way ANOVA.
D)Wilcoxon test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Statistics for Two Group Experiments Blake matched subjects on GPA before randomly assigning them to one of two Graduate Record Exam (GRE) preparation conditions (self-study or workshop).Which statistical test should he use to analyze his dependent variable which is a score from 0-100 on a GRE practice test?
A)t test for independent groups
B)t test for matched groups
C)two-way ANOVA
D)Wilcoxon test
A)t test for independent groups
B)t test for matched groups
C)two-way ANOVA
D)Wilcoxon test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Statistics for Two Group Experiments Samantha's experiment obtained reaction time data using a factorial design with two independent variables.She should use a ____ to evaluate her data.
A)one-way ANOVA
B)t test for independent groups
C)t test for matched groups
D)two-way ANOVA
A)one-way ANOVA
B)t test for independent groups
C)t test for matched groups
D)two-way ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The t Test Sample size affects
A)alpha level.
B)test statistic size.
C)variability.
D)test statistic size and variability.
A)alpha level.
B)test statistic size.
C)variability.
D)test statistic size and variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The t Test If we calculate a t test for matched groups with 20 subjects, there will be ___ degrees of freedom.
A)18
B)19
C)20
D)38
A)18
B)19
C)20
D)38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The t Test Susan's two-group experiment ran 10 subjects in the control condition and 12 subjects in the experimental condition.Calculate the degrees of freedom for a t test for independent groups using these data.
A)11
B)12
C)20
D)22
A)11
B)12
C)20
D)22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The t Test The term extreme refers to a computed t statistic's
A)alpha level.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)effect size.
D)position relative to the critical value.
A)alpha level.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)effect size.
D)position relative to the critical value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The t Test We reject the null hypothesis when.
A)the computed value of t equals the critical value of t.
B)the computed value of t is less extreme than the critical value of t.
C)the computed value of t is more extreme than the critical value of t.
D)the computed value of t is equal to or more extreme than the critical value of t.
A)the computed value of t equals the critical value of t.
B)the computed value of t is less extreme than the critical value of t.
C)the computed value of t is more extreme than the critical value of t.
D)the computed value of t is equal to or more extreme than the critical value of t.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The t Test When we draw small and large samples from the same population, small samples
A)are more normally distributed.
B)produce a more peaked and narrower distribution.
C)result in more degrees of freedom.
D)vary more from the population mean.
A)are more normally distributed.
B)produce a more peaked and narrower distribution.
C)result in more degrees of freedom.
D)vary more from the population mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The t Test An effect size of .60 means that the independent variable in our experiment accounted for approximately ___ of the variance in the dependent variable.
A)30%
B)36%
C)60%
D)90%
A)30%
B)36%
C)60%
D)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The t Test Cohen classifies an effect size as large when r is at least
A).20.
B).30.
C).50.
D).75.
A).20.
B).30.
C).50.
D).75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The t Test We calculate r for a t test for independent groups based on the
A)computed t.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)95% confidence interval.
D)computed t and degrees of freedom.
A)computed t.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)95% confidence interval.
D)computed t and degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The t Test Compared to a t test for matched groups, the critical value for a t test for independent groups is
A)identical.
B)smaller.
C)larger.
D)based on fewer degrees of freedom.
A)identical.
B)smaller.
C)larger.
D)based on fewer degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The t Test With fewer degrees of freedom,
A)t critical will be smaller.
B)t observed will be larger.
C)the most extreme 5% of the t distribution will fall closer to the mean.
D)the risk of committing a Type 2 error will increase.
A)t critical will be smaller.
B)t observed will be larger.
C)the most extreme 5% of the t distribution will fall closer to the mean.
D)the risk of committing a Type 2 error will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The t Test What information do we need in order to find the critical value of t?
A)the degrees of freedom
B)the significance level
C)whether the test is directional or nondirectional
D)all of these
A)the degrees of freedom
B)the significance level
C)whether the test is directional or nondirectional
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The t Test An inferential test like the t test is relatively robust.This means that
A)assumptions can be violated without changing the rate of Type 1 and Type 2 errors.
B)conclusions are valid when there are fewer than 20 subjects in each treatment group.
C)the critical value of t is independent of the number of subjects sampled.
D)the t test can produce valid results with ordinal data.
A)assumptions can be violated without changing the rate of Type 1 and Type 2 errors.
B)conclusions are valid when there are fewer than 20 subjects in each treatment group.
C)the critical value of t is independent of the number of subjects sampled.
D)the t test can produce valid results with ordinal data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The t Test The American Psychological Association's Publication Manual recommends that
A)null hypothesis testing should be abandoned.
B)researchers should analyze data using both parametric and nonparametric statistics.
C)researchers should always qualify p values with 5% confidence intervals.
D)researchers should report confidence intervals for experimental data.
A)null hypothesis testing should be abandoned.
B)researchers should analyze data using both parametric and nonparametric statistics.
C)researchers should always qualify p values with 5% confidence intervals.
D)researchers should report confidence intervals for experimental data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Chi Square Test In the priming experiment described in the text, Cramer's coefficient Phi ( ) was .81.This suggests a ____ degree of association between the priming manipulation and responses to the test question.
A)negligible
B)low
C)medium
D)large
A)negligible
B)low
C)medium
D)large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The t Test If there are at least ___ subjects in each treatment group, a t test is probably safe from violations of its assumptions.
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)50
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The t Test Jeremy plans to use a two-tailed t test to evaluate the results of his experiment.If he uses a one-tailed t test instead, the
A)computed value of t will be larger.
B)critical region will start farther from the mean.
C)critical value of t will be smaller.
D)significance level will be more extreme.
A)computed value of t will be larger.
B)critical region will start farther from the mean.
C)critical value of t will be smaller.
D)significance level will be more extreme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The t Test When a pollster reports that the margin of error is 3, this refers to the survey's
A)confidence interval.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)estimated effect size.
D)robustness.
A)confidence interval.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)estimated effect size.
D)robustness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The t Test Quinn's computed t statistic is 1.79 and the critical value is 1.79.What should she decide if she is using a significance level of p < .05?
A)accept the null hypothesis
B)reject the null hypothesis
C)suspend judgment and replicate the experiment
D)the results were not statistically significant
A)accept the null hypothesis
B)reject the null hypothesis
C)suspend judgment and replicate the experiment
D)the results were not statistically significant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The t Test When calculating a t statistic for independent groups, the numerator is
A)the difference between the treatment group means.
B)the number of degrees of freedom.
C)the squared deviations from each treatment mean.
D)the variances of the groups divided by the number of subjects.
A)the difference between the treatment group means.
B)the number of degrees of freedom.
C)the squared deviations from each treatment mean.
D)the variances of the groups divided by the number of subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A One-Way Analysis of Variance How do you calculate the degrees of freedom for within-groups variance in a one-way analysis of variance?
A)the number of groups minus the number of subjects per group
B)the number of subjects minus one
C)the number of subjects minus the number of treatments
D)the number of treatments minus one
A)the number of groups minus the number of subjects per group
B)the number of subjects minus one
C)the number of subjects minus the number of treatments
D)the number of treatments minus one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A One-Way Analysis of Variance If Zack has 75 subjects and 72 degrees of freedom within groups in a one-way analysis of variance, his independent variable must have ___ levels.
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sources of Variability Within-groups variability is produced by
A)individual differences.
B)undetected mistakes in recording data.
C)variations in testing conditions.
D)all of these
A)individual differences.
B)undetected mistakes in recording data.
C)variations in testing conditions.
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sources of Variability An F ratio compares ____ to
A)between-groups variability; within-groups variability.
B)the difference among treatment means; variability due to error.
C)the effect of the independent variable; the effect of extraneous variables.
D)variability due to treatment; variability due to error.
A)between-groups variability; within-groups variability.
B)the difference among treatment means; variability due to error.
C)the effect of the independent variable; the effect of extraneous variables.
D)variability due to treatment; variability due to error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sources of Variability Theoretically, if an independent variable has no effect in an experiment, the F ratio should be
A)less than 0.
B)0.
C)1.
D)greater than 1.
A)less than 0.
B)0.
C)1.
D)greater than 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Sources of Variability The shape of an F distribution depends on the
A)critical value of F.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)effect size.
D)level of significance.
A)critical value of F.
B)degrees of freedom.
C)effect size.
D)level of significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A One-Way Analysis of Variance A summary table for a one-way analysis of variance shows 3 degrees of freedom between groups and 16 degrees of freedom within groups.How many treatment groups were there in this experiment?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Sources of Variability The single category called error produces variability in subject data
A)between treatment groups.
B)within treatment groups.
C)both between and within treatment groups.
D)only when there is confounding.
A)between treatment groups.
B)within treatment groups.
C)both between and within treatment groups.
D)only when there is confounding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A One-Way Analysis of Variance Calvin designed a between-subjects experiment with one independent variable with four levels.There are 15 subjects in each condition.There are ____ degrees of freedom for between-groups variability.
A)1
B)3
C)11
D)56
A)1
B)3
C)11
D)56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A One-Way Analysis of Variance If Renee has 60 subjects and 2 degrees of freedom between groups in a one-way analysis of variance, her independent variable must have ___ levels.
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A One-Way Analysis of Variance A one-way analysis of variance summary table shows 3 degrees of freedom between groups and 16 degrees of freedom within groups.How many subjects participated in this study?
A)16
B)19
C)20
D)48
A)16
B)19
C)20
D)48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A One-Way Analysis of Variance As the degrees of freedom increase, F critical ____ and statistical power
A)increases; increases.
B)increases; decreases.
C)decreases; increases.
D)decreases; decreases.
A)increases; increases.
B)increases; decreases.
C)decreases; increases.
D)decreases; decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Sources of Variability When a computed F ratio is statistically significant,
A)all treatment means were probably drawn from the same population.
B)the amount of between-groups variability is large compared to within- groups variability.
C)the F ratio is 1 or less.
D)the computed F is less than F critical.
A)all treatment means were probably drawn from the same population.
B)the amount of between-groups variability is large compared to within- groups variability.
C)the F ratio is 1 or less.
D)the computed F is less than F critical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Analyzing Multiple Groups and Factorial Experiments The analysis of variance
A)compares the difference between means to an estimate of variability.
B)compares the difference between pairs of means to an estimate of variability.
C)compares the frequency of responses in a sample to the estimated frequency in the population.
D)divides variability in the data into component parts and then compares and evaluates them for statistical significance.
A)compares the difference between means to an estimate of variability.
B)compares the difference between pairs of means to an estimate of variability.
C)compares the frequency of responses in a sample to the estimated frequency in the population.
D)divides variability in the data into component parts and then compares and evaluates them for statistical significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The t Test A t test for matched groups trades ____ for
A)fewer degrees of freedom; reduced variability due to extraneous variables.
B)more degrees of freedom; reduced rate of Type 1 error.
C)increased variability due to extraneous variables; higher rate of Type 2 error.
D)a smaller t observed; a smaller t critical.
A)fewer degrees of freedom; reduced variability due to extraneous variables.
B)more degrees of freedom; reduced rate of Type 1 error.
C)increased variability due to extraneous variables; higher rate of Type 2 error.
D)a smaller t observed; a smaller t critical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The t Test Compared with a t test for independent groups, a t test for matched groups almost always
A)has a lower chance of Type 2 error.
B)has more degrees of freedom.
C)is more powerful.
D)has a lower chance of Type 2 error and is more powerful.
A)has a lower chance of Type 2 error.
B)has more degrees of freedom.
C)is more powerful.
D)has a lower chance of Type 2 error and is more powerful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Sources of Variability Which of these statements is the null hypothesis for an F test?
A)All treatment groups were drawn from the same population.
B)Between-groups variability exceeds within-groups variability.
C)Between-groups variability is due to the independent variable.
D)The sampled populations are normally distributed.
A)All treatment groups were drawn from the same population.
B)Between-groups variability exceeds within-groups variability.
C)Between-groups variability is due to the independent variable.
D)The sampled populations are normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A One-Way Analysis of Variance Andrew designed a between-subjects experiment with one independent variable with three levels.There are 20 subjects in each condition.There are ____ degrees of freedom for within-groups variability.
A)1
B)3
C)17
D)57
A)1
B)3
C)17
D)57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A One-Way Analysis of Variance Rachel's computed value of F was 7.23 and the table value of F was 3.88 at the .05 level.She should ____ the null hypothesis and conclude that her results were
A)accept; statistically significant.
B)accept; nonsignificant.
C)reject; statistically significant.
D)reject; nonsignificant.
A)accept; statistically significant.
B)accept; nonsignificant.
C)reject; statistically significant.
D)reject; nonsignificant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Sources of Variability We call variability due to random errors, subject variables, and treatment effects
A)between-groups variance.
B)error variance.
C)MSW.
D)within-groups variance.
A)between-groups variance.
B)error variance.
C)MSW.
D)within-groups variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Analyzing Data from a Between-Subjects Factorial Experiment How many degrees of freedom within groups are there in a 2 X 2 factorial experiment with 10 subjects per condition?
A)3
B)9
C)27
D)36
A)3
B)9
C)27
D)36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Interpreting the Results How do a priori tests differ from post hoc tests?
A)A priori tests are more conservative than post hoc tests.
B)A priori tests can be performed instead of an F test, while post hoc tests cannot be performed without a significant F test.
C)A priori tests present a higher risk of Type 1 error than post hoc tests.
D)A priori tests present a higher risk of Type 2 error than post hoc tests.
A)A priori tests are more conservative than post hoc tests.
B)A priori tests can be performed instead of an F test, while post hoc tests cannot be performed without a significant F test.
C)A priori tests present a higher risk of Type 1 error than post hoc tests.
D)A priori tests present a higher risk of Type 2 error than post hoc tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One-Way Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance Puck presented subjects with three different sets of student pictures and asked them to recall as many names as possible from each set.One set contained pictures of cheerleaders.A second featured pictures of glee club members.The final set consisted of pictures of ultimate Frisbee players.Which statistical test should Puck use to analyze his data?
A)one-way between-subjects analysis of variance
B)one-way repeated measures analysis of variance
C)one-way analysis of covariance
D)two-way analysis of variance
A)one-way between-subjects analysis of variance
B)one-way repeated measures analysis of variance
C)one-way analysis of covariance
D)two-way analysis of variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Interpreting the Results Since Bama predicted group differences, he performed three a priori tests to analyze a three-group experiment.What was wrong with this decision?
A)He increased the risk of Type 2 error.
B)He performed too many a priori tests.
C)He should have performed an F test before the a priori tests.
D)He should have performed three t tests because they are more conservative.
A)He increased the risk of Type 2 error.
B)He performed too many a priori tests.
C)He should have performed an F test before the a priori tests.
D)He should have performed three t tests because they are more conservative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Analyzing Data from a Between-Subjects Factorial Experiment A two-way analysis of variance is appropriate for experiments that have
A)only two treatments.
B)only two independent variables with two or more levels per variable.
C)several independent variables with only two levels per variable.
D)two or more dependent variables.
A)only two treatments.
B)only two independent variables with two or more levels per variable.
C)several independent variables with only two levels per variable.
D)two or more dependent variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Two-Way Analysis of Variance In an ANOVA for a 2 X 2 factorial experiment with 8 subjects in each group, there would be ___ df in the numerator and ___ df in the denominator for the F test for the first factor.
A)1, 28
B)2, 28
C)3, 28
D)3, 31
A)1, 28
B)2, 28
C)3, 28
D)3, 31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Interpreting the Results Experimenters use post hoc tests to
A)check the accuracy of analysis of variance computations.
B)compare differences between pairs of means.
C)determine whether an analysis of variance is required.
D)evaluate pairwise differences between treatment means when an analysis of variance is not significant.
A)check the accuracy of analysis of variance computations.
B)compare differences between pairs of means.
C)determine whether an analysis of variance is required.
D)evaluate pairwise differences between treatment means when an analysis of variance is not significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Interpreting the Results When should you perform a post hoc test?
A)after a nonsignificant analysis of variance
B)after a significant analysis of variance
C)instead of an analysis of variance
D)after a significant analysis of variance or instead of an analysis of variance
A)after a nonsignificant analysis of variance
B)after a significant analysis of variance
C)instead of an analysis of variance
D)after a significant analysis of variance or instead of an analysis of variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Two-Way Analysis of Variance There are three levels of factor A and two levels of factor B in a two-way ANOVA.How many degrees of freedom will there be in the numerator of an F test for factor A?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Interpreting the Results Tad made no specific experimental predictions and performed a post hoc test after he found that his computed F was not significant.What mistake did he commit?
A)He should have performed an a priori test instead of a post hoc test
B)He should have performed either the F test or the post hoc test, but not both.
C)He should have performed the post hoc test before the F test.
D)He should have stopped after a nonsignificant F test.
A)He should have performed an a priori test instead of a post hoc test
B)He should have performed either the F test or the post hoc test, but not both.
C)He should have performed the post hoc test before the F test.
D)He should have stopped after a nonsignificant F test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Analyzing Data from a Between-Subjects Factorial Experiment The principal advantage of a two-way analysis of variance over a one-way analysis of variance is that a two-way analysis of variance
A)allows calculation of effect size.
B)evaluates interaction effects.
C)has a lower risk of Type 1 error.
D)performs pairwise comparisons among treatment groups.
A)allows calculation of effect size.
B)evaluates interaction effects.
C)has a lower risk of Type 1 error.
D)performs pairwise comparisons among treatment groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Interpreting the Results We should use post hoc tests instead of a priori tests when
A)the computed F is not significant.
B)we did not predict group differences.
C)we need to perform fewer pairwise comparisons than the number of treatment groups.
D)we want to reduce the risk of Type 2 error.
A)the computed F is not significant.
B)we did not predict group differences.
C)we need to perform fewer pairwise comparisons than the number of treatment groups.
D)we want to reduce the risk of Type 2 error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Analyzing Data from a Between-Subjects Factorial Experiment How many F ratios must we calculate for a two-way analysis of variance?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Interpreting the Results If your experiment had four treatment conditions, how many post hoc tests may you perform at the p < .05 level?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Interpreting the Results We can use an analysis of covariance to
A)adjust treatment effects for any prior differences between treatment groups.
B)refine estimates of error.
C)statistically hold a moderating variable constant.
D)all of these
A)adjust treatment effects for any prior differences between treatment groups.
B)refine estimates of error.
C)statistically hold a moderating variable constant.
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Analyzing Data from a Between-Subjects Factorial Experiment A main effect in a factorial experiment refers to the
A)change in the effect of one independent variable across levels of another.
B)significant variability associated with a single independent variable in a factorial experiment.
C)variability due to the combined action of two or more independent variables.
D)variability in a factorial experiment not due to the individual actions of each independent variable.
A)change in the effect of one independent variable across levels of another.
B)significant variability associated with a single independent variable in a factorial experiment.
C)variability due to the combined action of two or more independent variables.
D)variability in a factorial experiment not due to the individual actions of each independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



