Deck 7: Income From Property
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/6
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Income From Property
1
A public corporation earns $500,000 in pre-tax profits and pays out all of its after-tax earnings in dividends. The corporate tax rate is 27.5% and the sole shareholder is in a 50% tax bracket. The dividend gross-up rate is 1.38 and the total dividend tax credit (federal and provincial) is 27.5%.
Required:
A) Calculate the tax liability for (1) the corporation and (2) the shareholder.
B) Briefly explain how this tax structure illustrates the theory of integration.
Required:
A) Calculate the tax liability for (1) the corporation and (2) the shareholder.
B) Briefly explain how this tax structure illustrates the theory of integration.
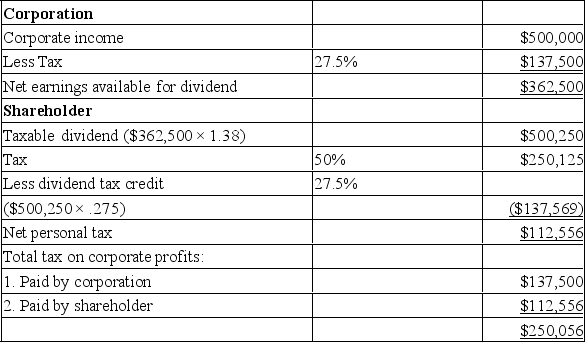 B) (Note: This concept is explained at greater length in Chapter 11.) The total tax paid by the corporation and the shareholder on the corporate profits of $500,000 is $250,056 which is roughly equal to 50% of $500,000. The shareholder is in a 50% tax bracket and would have paid $250,000 in tax if the profits had been received directly ($500,000 * 50%). Therefore, the total tax paid by the two entities is virtually the same due to the optimal combination of the corporate tax rate, the gross-up rate, and the dividend tax credit.
B) (Note: This concept is explained at greater length in Chapter 11.) The total tax paid by the corporation and the shareholder on the corporate profits of $500,000 is $250,056 which is roughly equal to 50% of $500,000. The shareholder is in a 50% tax bracket and would have paid $250,000 in tax if the profits had been received directly ($500,000 * 50%). Therefore, the total tax paid by the two entities is virtually the same due to the optimal combination of the corporate tax rate, the gross-up rate, and the dividend tax credit. 2
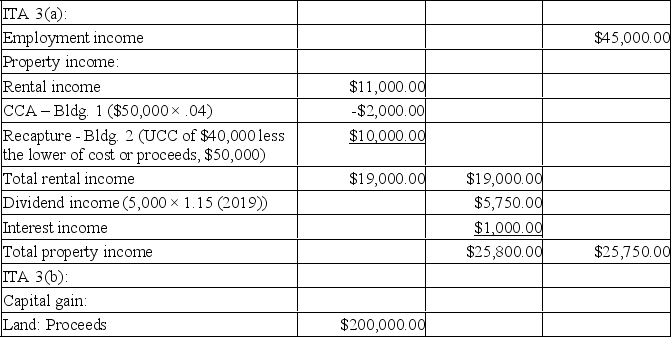
Martha Shine has provided you with the following information for 20xx:
She owns rental properties originally valued at $275,000. (Property 1: land $70,000, building $55,000) (Property 2: land $90,000, building $60,000)
The buildings are Class 1 (4%) properties.
-Net rental income before CCA in 20xx was $11,000.
-The UCC on building 1 at the beginning of 20xx was $50,000.
-The UCC on building 2 at the beginning of 20xx was $40,000.
-Property 2 was sold in 20xx for $250,000 (land $200,000, building $50,000)
She owns shares in ABC Inc. (a CCPC) valued at $50,000.
-She received $5,000 in non-eligible dividends on the shares in 20xx.
Martha purchased a 5-year GIC two years ago for $30,000.
-Interest earned in 20xx was $1,000.
Martha worked full-time as a baker in 20xx, earning a gross salary of $45,000.
Martha is in a 45% tax bracket.
Required:
Calculate Martha's net income for tax purposes in 20xx in accordance with Section 3 of the Income Tax Act. Martha will take the maximum CCA allowed this year on her rental properties. (Assume the tax year is 2019.)
She owns rental properties originally valued at $275,000. (Property 1: land $70,000, building $55,000) (Property 2: land $90,000, building $60,000)
The buildings are Class 1 (4%) properties.
-Net rental income before CCA in 20xx was $11,000.
-The UCC on building 1 at the beginning of 20xx was $50,000.
-The UCC on building 2 at the beginning of 20xx was $40,000.
-Property 2 was sold in 20xx for $250,000 (land $200,000, building $50,000)
She owns shares in ABC Inc. (a CCPC) valued at $50,000.
-She received $5,000 in non-eligible dividends on the shares in 20xx.
Martha purchased a 5-year GIC two years ago for $30,000.
-Interest earned in 20xx was $1,000.
Martha worked full-time as a baker in 20xx, earning a gross salary of $45,000.
Martha is in a 45% tax bracket.
Required:
Calculate Martha's net income for tax purposes in 20xx in accordance with Section 3 of the Income Tax Act. Martha will take the maximum CCA allowed this year on her rental properties. (Assume the tax year is 2019.)
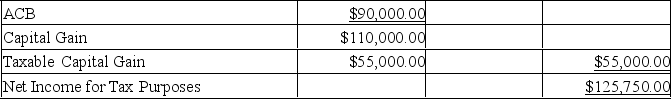
3
Amanda received a $300,000 inheritance on May 1st, 20x2. With the proceeds, she purchased the following investments:
1) Two rental properties: Property A has a value of $85,000, of which $40,000 is allocated to the building. Property B has a value of $110,000, of which $60,000 is allocated to the building. The properties earned a total of $9,750 in rental income before CCA. Both buildings are Class 1 - 4% assets, and the maximum allowable CCA will be claimed each year. The capital growth of the two properties combined is expected to be 5%.
2) A bond: Valued at $50,000 with 10% annual interest paid at maturity
3) Portfolio shares: Worth $10,000 - Eligible dividends in the amount of $700 were paid to Amanda before the end of the year. The capital growth of the shares is expected to be 3%.
The remainder of the money was applied to her mortgage.
Amanda is in a personal marginal tax bracket of 45%. Her marginal tax rate for eligible dividends is 30% and her marginal tax rate for capital gains is 23%.
Required:
A) Calculate Amanda's minimum property income for 20x2.
B) Calculate the annual pre-tax return (as a percentage) for each of the three investments.
C) Calculate the after-tax yield (as a percentage) for each of the three investments based on the information provided.
D) Briefly explain the tax benefit that Amanda could have realized had she used her inheritance to pay off her mortgage and then borrowed funds to make the above investments. (Assume the tax year is 2019.)
1) Two rental properties: Property A has a value of $85,000, of which $40,000 is allocated to the building. Property B has a value of $110,000, of which $60,000 is allocated to the building. The properties earned a total of $9,750 in rental income before CCA. Both buildings are Class 1 - 4% assets, and the maximum allowable CCA will be claimed each year. The capital growth of the two properties combined is expected to be 5%.
2) A bond: Valued at $50,000 with 10% annual interest paid at maturity
3) Portfolio shares: Worth $10,000 - Eligible dividends in the amount of $700 were paid to Amanda before the end of the year. The capital growth of the shares is expected to be 3%.
The remainder of the money was applied to her mortgage.
Amanda is in a personal marginal tax bracket of 45%. Her marginal tax rate for eligible dividends is 30% and her marginal tax rate for capital gains is 23%.
Required:
A) Calculate Amanda's minimum property income for 20x2.
B) Calculate the annual pre-tax return (as a percentage) for each of the three investments.
C) Calculate the after-tax yield (as a percentage) for each of the three investments based on the information provided.
D) Briefly explain the tax benefit that Amanda could have realized had she used her inheritance to pay off her mortgage and then borrowed funds to make the above investments. (Assume the tax year is 2019.)
A) Rental income: $9,750 - ($40,000 * .04 * 1.5) - ($60,000 * .04 * 1.5) = $3,750 Interest income: $0 (Does not have to be included in income until the year of the first anniversary.) Dividend income: $700 * 1.38 = $966 Minimum property income = $3,750 + $0 + $966 = $4,716 B) Rental properties: Net rents (pre - CCA) $9,750/($85,000 + $110,000) = 5% + Capital growth of 5% = 10% Bond: as stated: 10% Shares: Dividends $700/$10,000 = 7% + Capital growth of 3% = 10% C) Rental Property: (.05[1 - .45] + .05[1 - .23]) = 6.6% Bond: (.1[1 - .45]) = 5.5% Shares: (.07[1 - .3] + .03[1 - .23]) = 7.21% D) By paying off her mortgage, Amanda would have eliminated the non-deductible interest payments from her cash outflow. Borrowing against her home and reinvesting the funds would have allowed Amanda to deduct the interest payments from her property income, thereby increasing her cash flow and return on investment. (However, factors such as interest rates and penalties, etc., would all need to be considered.)
4
On March 1, 20x1, Notes Inc. purchased a two-year guaranteed investment certificate (GIC) for $15,000. The interest compounds annually at 8% and will be received at the end of the full term. Notes Inc. has a marginal tax rate of 30%, which will increase to 34% for 20x2 and 20x3. Notes Inc. uses the calendar year as its fiscal year. (These tax rates are used here for illustration purposes only.)
Angela Major also invested $15,000 in a GIC with an 8% annual return, on March 1, 20x1, with interest to be paid at the end of each annual period. Angela's marginal tax rate is 40%.
(Assume there are no leap years in this time period.)
Required:
Calculate the after-tax interest income for each year for Notes Inc. and for Angela. (Round all numbers.)
Angela Major also invested $15,000 in a GIC with an 8% annual return, on March 1, 20x1, with interest to be paid at the end of each annual period. Angela's marginal tax rate is 40%.
(Assume there are no leap years in this time period.)
Required:
Calculate the after-tax interest income for each year for Notes Inc. and for Angela. (Round all numbers.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Jim Smith owns a rental property which had a UCC of $85,000 at the beginning of 20x0. After all allowable expenses other than CCA, Jim's total rental income was $1,000 in 20x0 and $10,000 in 20x1. Jim always deducts the maximum CCA allowed. What is the UCC for his rental property at the end of 20x1? (The property is a Class 1 building amortized at 4%.)
A) $78,336
B)$80,640
C) $84,000
D) $85,000

A) $78,336
B)$80,640
C) $84,000
D) $85,000



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Stella Flier has received an inheritance of $100,000. She is trying to decide what to do with this money and has come to you for some advice. She has an excellent credit rating and no outstanding debts. She would like to buy a $225,000 house and invest $100,000 in bonds as a safety net.
Required:
How could Stella minimize her tax liability, assuming only the facts given?
Required:
How could Stella minimize her tax liability, assuming only the facts given?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



