Deck 9: Acids and Bases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Acids and Bases
1
Which of the following equations best describes what will happen to formic acid when it reacts with water?
A)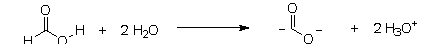
B)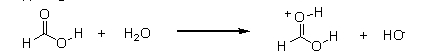
C)
D)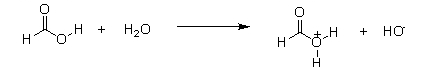
E)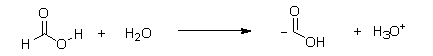
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


2
Which of the following reactions illustrate the reaction of a base? I. NH3 + H2O → +NH4 + -OH
II) HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
III) NaOH → Na+ + -OH
IV) +NH4 + H2O → H3O+ + NH3
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) All of the above are reactions of a base.
II) HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
III) NaOH → Na+ + -OH
IV) +NH4 + H2O → H3O+ + NH3
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) All of the above are reactions of a base.
All of the above are reactions of a base.
3
Ethylene glycol and propylene glycol are both 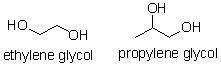
A) hydrocarbons.
B) carboxylic acids.
C) diols.
D) ethers.
E) toxic organic acids.

A) hydrocarbons.
B) carboxylic acids.
C) diols.
D) ethers.
E) toxic organic acids.
diols.
4
Which of the following statements best describes what happens when an acid reacts with water? I. The acid donates a proton.
II. Water donates a proton.
III. Water acts as a base.
IV. Hydronium is formed.
V. Hydroxide is formed.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I, III, and V
D) I, III, and IV
E) II and V
II. Water donates a proton.
III. Water acts as a base.
IV. Hydronium is formed.
V. Hydroxide is formed.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I, III, and V
D) I, III, and IV
E) II and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following atomic diagrams best represents H+? 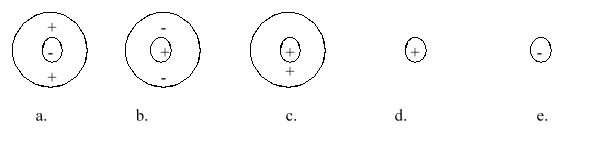
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The boxed species in the following reaction is 
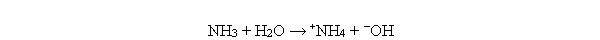
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

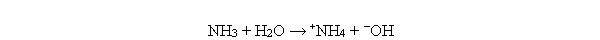
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about acids is NOT true?
A) An example of an acid is HBr.
B) An acid increases the concentration of hydroxide in solution.
C) An acid increases the concentration of protons in solution.
D) An acid increases the concentration of hydronium in solution.
E) An acid is a proton donor.
A) An example of an acid is HBr.
B) An acid increases the concentration of hydroxide in solution.
C) An acid increases the concentration of protons in solution.
D) An acid increases the concentration of hydronium in solution.
E) An acid is a proton donor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following reactions best illustrates the reaction of an acid in aqueous solution?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about bases is NOT true?
A) A base decreases the concentration of hydronium in solution.
B) An example of a base is Ca(OH)2.
C) A base increases the concentration of hydroxide in solution.
D) A base is a proton acceptor.
E) A base is always negatively charged.
A) A base decreases the concentration of hydronium in solution.
B) An example of a base is Ca(OH)2.
C) A base increases the concentration of hydroxide in solution.
D) A base is a proton acceptor.
E) A base is always negatively charged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following types of molecules and ions is NOT a base?
A) an anion
B) a cation
C) a neutral molecule containing a nonbonding pair of electrons
D) a tertiary nitrogen
E) All of these are bases.
A) an anion
B) a cation
C) a neutral molecule containing a nonbonding pair of electrons
D) a tertiary nitrogen
E) All of these are bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following molecules is a base?
A)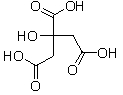
B)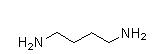
C)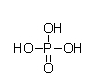
D)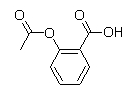
E)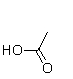
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Not all protons in a molecule can be donated in an acid-base reaction. Below are three molecules, each with the proton donated in an acid-base reaction circled. What do these protons have in common? 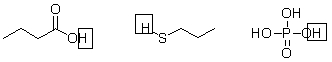
A) They are all attached to oxygen.
B) They are all in a carbon-containing molecule.
C) They are all attached to the most electronegative atom in the molecule.
D) They are the only hydrogens in the molecule.
E) They are all attached to carbon.

A) They are all attached to oxygen.
B) They are all in a carbon-containing molecule.
C) They are all attached to the most electronegative atom in the molecule.
D) They are the only hydrogens in the molecule.
E) They are all attached to carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following compounds is a Brønsted Lowry base, but not an Arrhenius base?
A) HCl
B) NaOH
C) NH3
D) Ca(OH)2
E) CH3COOH
A) HCl
B) NaOH
C) NH3
D) Ca(OH)2
E) CH3COOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The boxed species in the following reaction is 
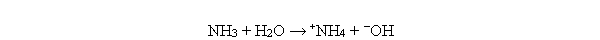
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

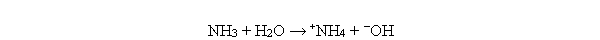
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All acid-base reactions that we consider in this chapter occur in
A) acidic solution.
B) basic solution.
C) neutral solution.
D) water.
E) nonpolar solvents.
A) acidic solution.
B) basic solution.
C) neutral solution.
D) water.
E) nonpolar solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Select the choice that correctly states whether the substance is an acid or a base.
A) Vinegar is basic.
B) Amines are basic.
C) Gastric juice is basic.
D) Sodium hydroxide is acidic.
E) Morphine is acidic.
A) Vinegar is basic.
B) Amines are basic.
C) Gastric juice is basic.
D) Sodium hydroxide is acidic.
E) Morphine is acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the body, ethylene glycol (antifreeze) is metabolized to a(n)
A) hydrocarbon.
B) diol.
C) ether.
D) toxic organic acid.
E) Ethylene glycol is not metabolized.
A) hydrocarbon.
B) diol.
C) ether.
D) toxic organic acid.
E) Ethylene glycol is not metabolized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What do all bases have in common?
A) They contain an -OH group.
B) They contain a nitrogen.
C) They contain an oxygen.
D) They are salts.
E) They contain a nonbonding pair of electrons.
A) They contain an -OH group.
B) They contain a nitrogen.
C) They contain an oxygen.
D) They are salts.
E) They contain a nonbonding pair of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the Arrhenius definition, which of the following compounds is a base? 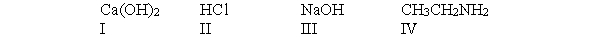
A) I and III only
B) I, II and IV
C) All of these compounds
D) III only
E) IV only
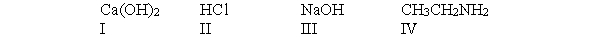
A) I and III only
B) I, II and IV
C) All of these compounds
D) III only
E) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A hydrogen atom without an electron is referred to as
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) an acid.
E) a conjugate base.
A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) an acid.
E) a conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The boxed species in the following reaction is
A)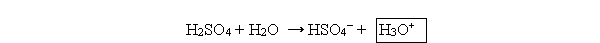 hydroxide.
hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the conjugate base.
A)
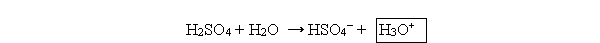 hydroxide.
hydroxide.B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Each circle is a sample of an aqueous acidic or basic solution. Which of the solutions contains a weak acid?
A)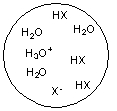
B)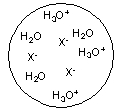
C)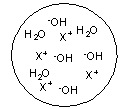
D)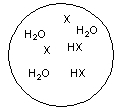
E)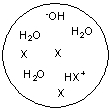
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When a base is dissolved in water, it reacts to give _________ and ________.
A) hydroxide; hydronium
B) hydronium; the conjugate acid
C) hydroxide; the conjugate acid
D) hydronium; the conjugate base
E) hydroxide; the conjugate base
A) hydroxide; hydronium
B) hydronium; the conjugate acid
C) hydroxide; the conjugate acid
D) hydronium; the conjugate base
E) hydroxide; the conjugate base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Each circle is a sample of an aqueous acidic or basic solution. Which of the solutions contains a weak base?
A)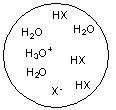
B)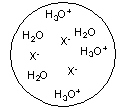
C)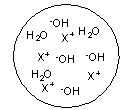
D)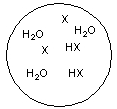
E)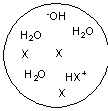
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When an acid is dissolved in water, it reacts to give _________ and ________.
A) hydroxide; hydronium
B) hydronium; the conjugate acid
C) hydroxide; the conjugate acid
D) hydronium; the conjugate base
E) hydroxide; the conjugate base
A) hydroxide; hydronium
B) hydronium; the conjugate acid
C) hydroxide; the conjugate acid
D) hydronium; the conjugate base
E) hydroxide; the conjugate base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following are conjugate acid-base pairs in the acid-base reaction between dopamine and water?  I. H2O and
I. H2O and 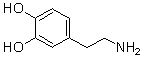 II. H2O and -OH III.
II. H2O and -OH III. 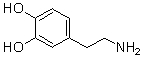 and
and 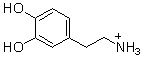 IV.
IV. 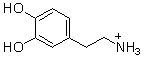 and -OH
and -OH
A) I only
B) I and IV
C) II only
D) II and IV
E) II and III
 I. H2O and
I. H2O and  II. H2O and -OH III.
II. H2O and -OH III.  and
and  IV.
IV.  and -OH
and -OHA) I only
B) I and IV
C) II only
D) II and IV
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following bases is a strong base?
A) LiOH
B)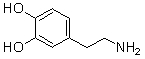
C) NH2CH2COOH
D) NH2CH2CH2CH2NH2
E) All of the above molecules are strong bases.
A) LiOH
B)

C) NH2CH2COOH
D) NH2CH2CH2CH2NH2
E) All of the above molecules are strong bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The boxed species in the following reaction is

A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

A) hydroxide.
B) hydronium.
C) a proton.
D) the acid.
E) the base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following strong acids is found in the body?
A) HNO3
B) HCl
C) H?2SO4
D) HClO4
E) HBr
A) HNO3
B) HCl
C) H?2SO4
D) HClO4
E) HBr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How do strong and weak acids differ?
A) Strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solution and weak acids don't.
B) Only strong acids produce hydronium in aqueous solution.
C) Strong acids donate protons and weak acids do not.
D) Strong acids increase the concentration of -OH in solution.
E) Weak acids degrade less readily than strong acids.
A) Strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solution and weak acids don't.
B) Only strong acids produce hydronium in aqueous solution.
C) Strong acids donate protons and weak acids do not.
D) Strong acids increase the concentration of -OH in solution.
E) Weak acids degrade less readily than strong acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Each circle is a sample of an aqueous acidic or basic solution. Which of the solutions contains a strong base?
A)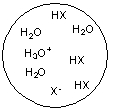
B)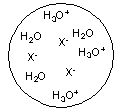
C)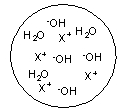
D)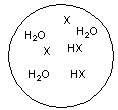
E)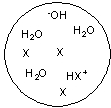
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following molecules is amphoteric?
A) CH3NH2
B) CH3OH
C) CH3COOH
D) H2SO4
E) NaOH
A) CH3NH2
B) CH3OH
C) CH3COOH
D) H2SO4
E) NaOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Water can react as both an acid and a base, depending on its environment. Because of this characteristic, water is a(n) _________ molecule.
A) amphoteric
B) autonomous
C) complex
D) reactive
E) conjugated
A) amphoteric
B) autonomous
C) complex
D) reactive
E) conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following is the reaction of benzoic acid in water. Which of the following choices is a conjugate acid-base pair in this reaction? 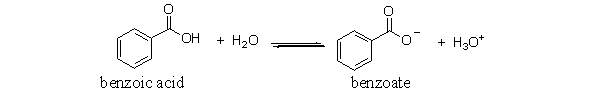
A) benzoic acid and water
B) benzoate and hydronium
C) benzoic acid and hydronium
D) benzoic acid and benzoate
E) benzoate and water
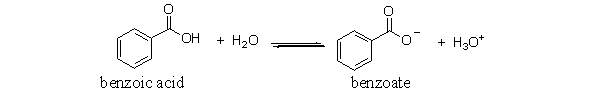
A) benzoic acid and water
B) benzoate and hydronium
C) benzoic acid and hydronium
D) benzoic acid and benzoate
E) benzoate and water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the statements describes the following reaction? Mg(OH)2 → Mg2+ + 2 HO -
A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.
A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements best describes the behavior of water in the acid-base reaction between dopamine and water? 
A) Water is the acid.
B) Water is the base.
C) Water is the conjugate acid.
D) Water is the conjugate base.
E) Water is both an acid and a base.

A) Water is the acid.
B) Water is the base.
C) Water is the conjugate acid.
D) Water is the conjugate base.
E) Water is both an acid and a base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A conjugate acid-base pair is
A) the reactants in an acid-base reaction.
B) the products of an acid-base reaction.
C) two species that differ only by a proton.
D) two species that differ only by a hydroxyl group.
E) a single molecule that can act as both an acid and a base.
A) the reactants in an acid-base reaction.
B) the products of an acid-base reaction.
C) two species that differ only by a proton.
D) two species that differ only by a hydroxyl group.
E) a single molecule that can act as both an acid and a base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Each circle is a sample of an aqueous acidic or basic solution. Which of the solutions contains a strong acid?
A)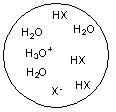
B)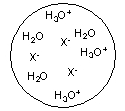
C)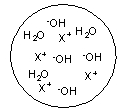
D)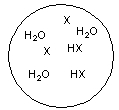
E)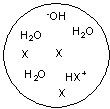
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Generally, strong bases are hydroxide salts of
A) transition metals.
B) the halogens.
C) alkali and alkaline earth metals.
D) the noble gases.
E) any element.
A) transition metals.
B) the halogens.
C) alkali and alkaline earth metals.
D) the noble gases.
E) any element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following acids is not a strong acid?
A) HCl
B) HI
C) HNO3
D) CH3COOH
E) H2SO4
A) HCl
B) HI
C) HNO3
D) CH3COOH
E) H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An alkene has a pKa of 40, while an alkyne has a pKa of 25. Which functional group is more acidic?
A) an alkyne, because it has a higher pKa
B) an alkyne, because it has a lower pKa
C) an alkene, because it has a higher pKa
D) an alkene, because it has a lower pKa
E) They have the same acidity.
A) an alkyne, because it has a higher pKa
B) an alkyne, because it has a lower pKa
C) an alkene, because it has a higher pKa
D) an alkene, because it has a lower pKa
E) They have the same acidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the acid-base reaction between ammonia and water, which of the following statements best describes the concentration of ammonia and ammonium at equilibrium? 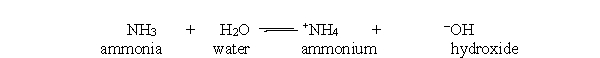
A) The concentration of ammonium is increasing.
B) There is no ammonium at equilibrium.
C) Their concentrations are equal.
D) Their concentrations are constant.
E) There is no ammonia at equilibrium.
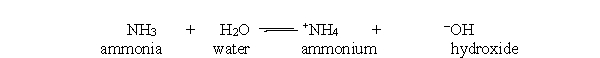
A) The concentration of ammonium is increasing.
B) There is no ammonium at equilibrium.
C) Their concentrations are equal.
D) Their concentrations are constant.
E) There is no ammonia at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the acid-base reaction between ammonia and water, which of the following substances are present at equilibrium? 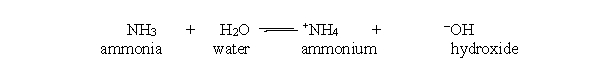
A) Ammonia, water, ammonium, and hydroxide are all present at equilibrium.
B) Only ammonia and water are present at equilibrium.
C) Only ammonium and hydroxide are present at equilibrium.
D) Only hydroxide and hydronium are present at equilibrium.
E) It is not possible to say which molecules will be present at equilibrium.
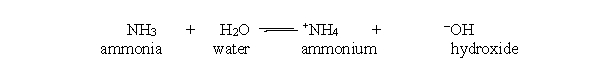
A) Ammonia, water, ammonium, and hydroxide are all present at equilibrium.
B) Only ammonia and water are present at equilibrium.
C) Only ammonium and hydroxide are present at equilibrium.
D) Only hydroxide and hydronium are present at equilibrium.
E) It is not possible to say which molecules will be present at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The pKa of aspirin is 3.5. What is the Ka of aspirin?
A) 3.5
B) 1000
C) 0.54
D) 3.2 * 10-4
E) 3.2 * 103
A) 3.5
B) 1000
C) 0.54
D) 3.2 * 10-4
E) 3.2 * 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Arsenic poisoning is a serious problem in many parts of the world. When arsenic poisoning occurs, arsenic binds to proteins and eventually causes cellular damage. This leads to a variety of symptoms in humans including exhaustion, muscle weakness, organ failure, and cancer. Arsenic poisoning is commonly treated with a drug called dimercaprol (or BAL) that binds arsenic, which sets up a competing equilibrium within the body. Once arsenic reacts to form a complex with BAL, it can be excreted from the body. Arsenic-protein complex  Arsenic + proteins + BAL
Arsenic + proteins + BAL  Arsenic-BAL complex
Arsenic-BAL complex
How does treatment with BAL affect the equilibrium shown above?
A) Adding BAL does not affect the equilibrium.
B) Adding BAL pushes the reaction to the left.
C) Adding BAL pushes the reaction to the right.
D) Adding BAL causes less arsenic-BAL to be made.
E) Adding BAL causes more arsenic-protein complex to be made.
 Arsenic + proteins + BAL
Arsenic + proteins + BAL  Arsenic-BAL complex
Arsenic-BAL complexHow does treatment with BAL affect the equilibrium shown above?
A) Adding BAL does not affect the equilibrium.
B) Adding BAL pushes the reaction to the left.
C) Adding BAL pushes the reaction to the right.
D) Adding BAL causes less arsenic-BAL to be made.
E) Adding BAL causes more arsenic-protein complex to be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Methylamide (CH3CONH2) has a Ka of 1 *10-16. What is the pKa of methylamide?
A) "-16"
B) '0"
C) "16"
D) "1 * 10-16"
E) "-1 * 10-16"
A) "-16"
B) '0"
C) "16"
D) "1 * 10-16"
E) "-1 * 10-16"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which substance is acting as the acid in the reverse reaction of the acid-base reaction below? 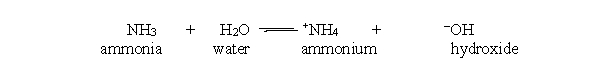
A) ammonia
B) water
C) ammonium
D) hydroxide
E) hydronium
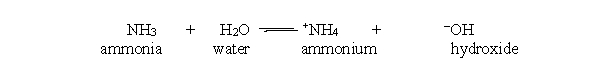
A) ammonia
B) water
C) ammonium
D) hydroxide
E) hydronium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the acid-base reaction between ammonia and water, which bond is made in order to make ammonia and water from ammonium and hydroxide? 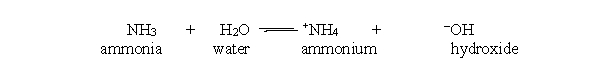
A) H-H
B) N-O
C) N-H
D) O-H
E) All of the above
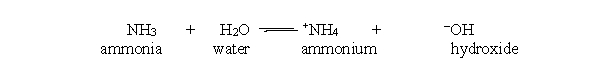
A) H-H
B) N-O
C) N-H
D) O-H
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A weak acid is also a _________ because it produces a low concentration of ions in solution.
A) weak electrolyte
B) strong electrolyte
C) nonelectrolyte
D) weak base
E) strong acid
A) weak electrolyte
B) strong electrolyte
C) nonelectrolyte
D) weak base
E) strong acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is NOT a common use of a base?
A) Many fruits get their sour or tart taste from bases.
B) Amino acids contain bases.
C) Many pharmaceuticals are bases.
D) Cleaning agents are often bases.
E) Neurotransmitters are bases.
A) Many fruits get their sour or tart taste from bases.
B) Amino acids contain bases.
C) Many pharmaceuticals are bases.
D) Cleaning agents are often bases.
E) Neurotransmitters are bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) has a pKa of 4.74, while ethanol (CH3CH2OH) has a pKa of about 16. Which molecule is more acidic?
A) acetic acid, because it has a higher pKa
B) acetic acid, because it has a lower pKa
C) ethanol, because it has a higher pKa
D) ethanol, because it has a lower pKa
E) They have the same acidity.
A) acetic acid, because it has a higher pKa
B) acetic acid, because it has a lower pKa
C) ethanol, because it has a higher pKa
D) ethanol, because it has a lower pKa
E) They have the same acidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements best describes what it means for the acid-base reaction between acetic acid and water to be in equilibrium? 
A) The mass of acetic acid and acetate is equal.
B) The number of moles of acetate equals the number of moles of acetic acid.
C) The number of moles of hydronium equals the number of moles of water.
D) The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate.
E) The reaction is balanced.

A) The mass of acetic acid and acetate is equal.
B) The number of moles of acetate equals the number of moles of acetic acid.
C) The number of moles of hydronium equals the number of moles of water.
D) The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate.
E) The reaction is balanced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the statements best describes the following reaction? HCOOH + H2O  HCOO 1- + H3O+
HCOO 1- + H3O+
A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.
 HCOO 1- + H3O+
HCOO 1- + H3O+A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following acidic functional groups is often involved in biochemical reactions in the body?
A) HO -
B) H2SO4
C) RCOOH
D) H3O+
E) ROR
A) HO -
B) H2SO4
C) RCOOH
D) H3O+
E) ROR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What does Ka measure?
A) the concentration of water at equilibrium
B) the concentration of products divided by reactants at equilibrium
C) the concentration of hydronium at equilibrium
D) the concentration of hydroxide at equilibrium
E) Ka is not a measurement
A) the concentration of water at equilibrium
B) the concentration of products divided by reactants at equilibrium
C) the concentration of hydronium at equilibrium
D) the concentration of hydroxide at equilibrium
E) Ka is not a measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The reaction between acetic acid and water is given below, followed by a list of changes that could be made to the reaction solution. Which of these changes will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left?  Changes that could be made to the solution I. adding more CH3COOH
Changes that could be made to the solution I. adding more CH3COOH
II) removing H2O
III) removing H3O+
IV) adding more CH3COO -
A) All of these changes will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
B) Only I will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
C) Only IV will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
D) I and III will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
E) II and IV will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
 Changes that could be made to the solution I. adding more CH3COOH
Changes that could be made to the solution I. adding more CH3COOHII) removing H2O
III) removing H3O+
IV) adding more CH3COO -
A) All of these changes will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
B) Only I will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
C) Only IV will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
D) I and III will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.
E) II and IV will result in the equilibrium shifting to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the acid-base reaction between ammonia and water, which bond is broken in order to give ammonium and hydroxide? 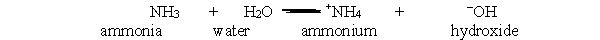
A) H-H
B) N-O
C) N-H
D) O-H
E) All of the above
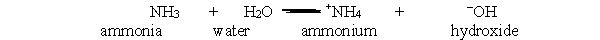
A) H-H
B) N-O
C) N-H
D) O-H
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the statements best describes the following reaction? 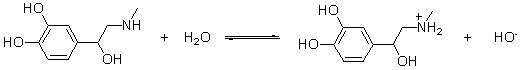
A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.

A) This reaction is the dissociation of a strong acid.
B) This reaction is the dissociation of a weak acid.
C) This is the reaction of a strong base.
D) This is the reaction of a weak base.
E) This is not an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Ammonia and ammonium are both present in water at equilibrium, as shown by the following acid-base equation. What will happen if ammonium is added to a solution of ammonia and ammonium at equilibrium? NH3 + H2O  +NH4 + -OH
+NH4 + -OH
Ammonia water ammonium hydroxide
A) Nothing.
B) The result is not predictable.
C) The ammonium will bubble.
D) The equilibrium will shift to the right.
E) The equilibrium will shift to the left.
 +NH4 + -OH
+NH4 + -OHAmmonia water ammonium hydroxide
A) Nothing.
B) The result is not predictable.
C) The ammonium will bubble.
D) The equilibrium will shift to the right.
E) The equilibrium will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following reaction is a reversible reaction. Which of the following statements best describes what it means for this reaction to be reversible? 
A) This reaction only occurs in the reverse direction as written above.
B) All of the reactant molecules react to make product and then all of the product molecules react to make reactants again.
C) Forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate.
D) Forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously.
E) The rate of the reverse reaction is must faster than the rate of the forward reaction.

A) This reaction only occurs in the reverse direction as written above.
B) All of the reactant molecules react to make product and then all of the product molecules react to make reactants again.
C) Forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate.
D) Forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously.
E) The rate of the reverse reaction is must faster than the rate of the forward reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the pH of a solution with a [H3O+] of 7.9 * 10 - 11 M?
A) "10.1"
B) "-10.1"
C) "3.90"
D) "-3.90"
E) "11.9"
A) "10.1"
B) "-10.1"
C) "3.90"
D) "-3.90"
E) "11.9"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Adding an acid to pure water will change which of the following values: [H3O+], [HO - ], and/or Kw?
A) [H3O+] only
B) [HO - ] only
C) Kw only
D) [H3O+] and [HO - ], but not Kw
E) All of these values will be changed.
A) [H3O+] only
B) [HO - ] only
C) Kw only
D) [H3O+] and [HO - ], but not Kw
E) All of these values will be changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The concentration of H3O+ in a solution is 1 *10-4 M. Which of the following statements describes how the concentration of -OH in the solution could be determined?
A) It is not possible to determine [-OH].
B) Calculate pH
C) Measure the pH with a pH probe or dipstick
D) Solve for [---OH] using the ion-product constant equation
E) The [-OH] is unchanged when an acid is added to a solution.
A) It is not possible to determine [-OH].
B) Calculate pH
C) Measure the pH with a pH probe or dipstick
D) Solve for [---OH] using the ion-product constant equation
E) The [-OH] is unchanged when an acid is added to a solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the pH of a urine sample with a hydronium concentration of 7.9 * 10 - 8?
A) "-7.10"
B) "7.10"
C) "6.90"
D) "-6.90"
E) "7.00"
A) "-7.10"
B) "7.10"
C) "6.90"
D) "-6.90"
E) "7.00"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements does NOT correctly describe pH?
A) pH is a measure of acidity of a solution.
B) pH is a measure of hydronium concentration in a solution.
C) The higher the pH, the more acidic a solution.
D) A pH of 7 is a neutral solution.
E) pH = -log [H3O+].
A) pH is a measure of acidity of a solution.
B) pH is a measure of hydronium concentration in a solution.
C) The higher the pH, the more acidic a solution.
D) A pH of 7 is a neutral solution.
E) pH = -log [H3O+].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following solutions has the highest concentration of [ - OH]?
A) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 5 M
B) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 13 M
C) a solution with a [HO - ] of 1 *10-5 M
D) a solution with a [HO-] of 1 *10-13 M
E) a solution with a [HO1-] of 1 *10-2 M
A) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 5 M
B) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 13 M
C) a solution with a [HO - ] of 1 *10-5 M
D) a solution with a [HO-] of 1 *10-13 M
E) a solution with a [HO1-] of 1 *10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the pH of a solution with a [H3O+] of 1.0 *10 - 5 M?
A) "9.00"
B) "1.0*10 - 5 M"
C) "-5.00"
D) "-9.00"
E) "5.00"
A) "9.00"
B) "1.0*10 - 5 M"
C) "-5.00"
D) "-9.00"
E) "5.00"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the concentration of H3O+ and -OH in pure water at room temperature?
A) 1.0 *10-14 M
B) 1.0 *10-7 M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.0 * 107 M
E) 1.0 *1014 M
A) 1.0 *10-14 M
B) 1.0 *10-7 M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.0 * 107 M
E) 1.0 *1014 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which statement does NOT correctly explain why it is so important for intracellular pH to be maintained between 7.35 and 7.45?
A) In this range, carboxylic acids, phosphate esters, and amines are ionized.
B) In this range, the molecules are trapped within the cell.
C) In this range, the concentration of biomolecules is high enough for key reactions to take place.
D) In this range, molecules in biochemical pathways can bind to enzymes appropriately.
E) In this range, molecules in biochemical pathways are inert.
A) In this range, carboxylic acids, phosphate esters, and amines are ionized.
B) In this range, the molecules are trapped within the cell.
C) In this range, the concentration of biomolecules is high enough for key reactions to take place.
D) In this range, molecules in biochemical pathways can bind to enzymes appropriately.
E) In this range, molecules in biochemical pathways are inert.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the [H3O+] in a solution that has a [OH - ] of 3.2 *10 - 4 M?
A) 3.2 * 10 - 10 M
B) 3.2 *1010 M
C) 3.1 * 10F - 11 M
D) 3.1 * 1011 M
E) 1.0 *10 - 7 M
A) 3.2 * 10 - 10 M
B) 3.2 *1010 M
C) 3.1 * 10F - 11 M
D) 3.1 * 1011 M
E) 1.0 *10 - 7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the pH of a solution with a [ - OH ] of 4.1 *10 - 3 M?
A) "-2.39"
B) "2.39"
C) "11.6"
D) "-11.6"
E) "7.00"
A) "-2.39"
B) "2.39"
C) "11.6"
D) "-11.6"
E) "7.00"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the pH of a solution with a [ - OH ] of 1.0 *10 - 10 M?
A) "1.0 *10 - 10"
B) "10.0"
C) "4.00"
D) "-10.0"
E) "-4.00"
A) "1.0 *10 - 10"
B) "10.0"
C) "4.00"
D) "-10.0"
E) "-4.00"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following solutions has the highest concentration of [ - OH]?
A) a solution with a pH of 4
B) a solution with a pH of 10
C) a solution with a [H3O+] of 6.8 *10 - 5 M
D) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 13 M
E) a solution with a [HO - ] of 1 *10 - 2 M
A) a solution with a pH of 4
B) a solution with a pH of 10
C) a solution with a [H3O+] of 6.8 *10 - 5 M
D) a solution with a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 13 M
E) a solution with a [HO - ] of 1 *10 - 2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the [OH - ] in a solution that has a [H3O+] of 1 *10 - 6 M?
A) 1 *10 - 20 M
B) 1 *10 - 8 M
C) 1 *10 - 6 M
D) 1*10 - 7 M
E) 1 * 107 M
A) 1 *10 - 20 M
B) 1 *10 - 8 M
C) 1 *10 - 6 M
D) 1*10 - 7 M
E) 1 * 107 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
At physiological pH, phosphate esters, such as the molecule of methyl phosphate shown below, are ionized. Which of the following choices is the ionized form of a phosphate ester?
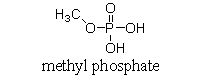
A)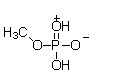
B)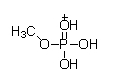
C)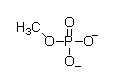
D)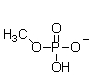
E)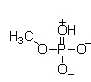
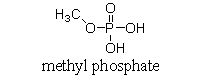
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A blood sample has a pH of 7.42. What is the concentration of hydronium in the sample?
A) "0.87 M"
B) "2.6 * 107 M"
C) "-2.6* 107 M"
D) "3.8 * 108 M"
E) "3.8 *10 - 8 M"
A) "0.87 M"
B) "2.6 * 107 M"
C) "-2.6* 107 M"
D) "3.8 * 108 M"
E) "3.8 *10 - 8 M"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The [H3O+] of a solution with a pH of 2 is ______ the [H3O+] of a solution with a pH of 3.
A) one-tenth
B) ten times
C) one-half
D) twice
E) the same as
A) one-tenth
B) ten times
C) one-half
D) twice
E) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
According to the following table, what is the most acidic fluid in the body? 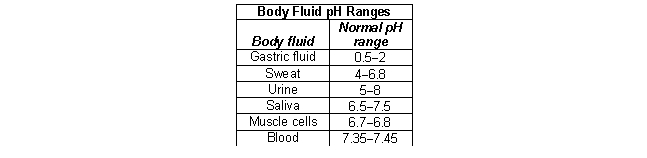
A) gastric juice
B) sweat
C) urine
D) saliva
E) blood

A) gastric juice
B) sweat
C) urine
D) saliva
E) blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following pH ranges is referred to as physiological pH?
A) pH 6 - pH 8
B) pH 7.35 - pH 7.45
C) pH 6.7 - pH 6.8
D) pH 6.5 - pH 7.5
E) pH 5 - pH 8
A) pH 6 - pH 8
B) pH 7.35 - pH 7.45
C) pH 6.7 - pH 6.8
D) pH 6.5 - pH 7.5
E) pH 5 - pH 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A sample of gastric juice has a pH of 1.20. What is the concentration of hydroxide in this sample?
A) 1.6 *10 - 13 M
B) 6.3 *10 - 2 M
C) 1.0 *10 - 7 M
D) 6.3 *1012 M
E) 6.3 *10 - 16 M
A) 1.6 *10 - 13 M
B) 6.3 *10 - 2 M
C) 1.0 *10 - 7 M
D) 6.3 *1012 M
E) 6.3 *10 - 16 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



