Deck 8: Solutions, Colloids and Membranes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Solutions, Colloids and Membranes
1
A vial contains 5 mL of 1% aqueous lidocaine, a dental anesthetic. In this solution,
A) both lidocaine and water are solutes.
B) both lidocaine and water are solvents.
C) lidocaine is the solute and water is the solvent.
D) lidocaine is the solvent and water is solute.
E) there are no solutes nor solvents in this solution.
A) both lidocaine and water are solutes.
B) both lidocaine and water are solvents.
C) lidocaine is the solute and water is the solvent.
D) lidocaine is the solvent and water is solute.
E) there are no solutes nor solvents in this solution.
lidocaine is the solute and water is the solvent.
2
A solute dissolving in a solvent is a _______ because _______.
A) physical change; covalent bonds are broken in the process
B) chemical change; covalent bonds are broken in the process
C) chemical change; ionic attractions are broken in the process
D) physical change; covalent bonds are not broken in the process
E) chemical change; covalent bonds are not broken in the process
A) physical change; covalent bonds are broken in the process
B) chemical change; covalent bonds are broken in the process
C) chemical change; ionic attractions are broken in the process
D) physical change; covalent bonds are not broken in the process
E) chemical change; covalent bonds are not broken in the process
physical change; covalent bonds are not broken in the process
3
A wine label states that it is 12 proof, meaning that it contains 6% ethanol. According to this information,
A) ethanol is a solute in wine and water is the solvent.
B) ethanol is a solvent in wine and water is the solute.
C) ethanol and water are both solvents in wine.
D) ethanol and water are both solutes in wine.
E) wine does not contain any solutes.
A) ethanol is a solute in wine and water is the solvent.
B) ethanol is a solvent in wine and water is the solute.
C) ethanol and water are both solvents in wine.
D) ethanol and water are both solutes in wine.
E) wine does not contain any solutes.
ethanol is a solute in wine and water is the solvent.
4
Which of the following is a heterogeneous mixture?
A) vinegar
B) oil and vinegar salad dressing
C) lemonade
D) bronze
E) air
A) vinegar
B) oil and vinegar salad dressing
C) lemonade
D) bronze
E) air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The chart below illustrates the composition of air. According to this chart, 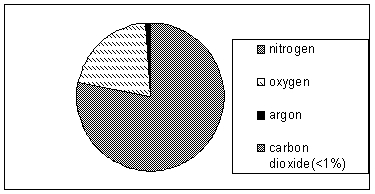
A) nitrogen and oxygen are solutes, while argon and carbon dioxide are solvents.
B) carbon dioxide is the only solute in air.
C) oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are solutes, while nitrogen is the solvent.
D) nitrogen is the solute, while oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are all solvents.
E) nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are all solutes in air.

A) nitrogen and oxygen are solutes, while argon and carbon dioxide are solvents.
B) carbon dioxide is the only solute in air.
C) oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are solutes, while nitrogen is the solvent.
D) nitrogen is the solute, while oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are all solvents.
E) nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are all solutes in air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Table sugar is a
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) element.
D) molecule.
E) suspension .
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) element.
D) molecule.
E) suspension .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a solution, the component present in a larger amount is called the
A) solvent.
B) solute.
C) medium.
D) colloid.
E) solution.
A) solvent.
B) solute.
C) medium.
D) colloid.
E) solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
There are many mixtures in the body. The most common ______ for these mixtures is water.
A) solvent
B) solute
C) medium
D) colloid
E) solution
A) solvent
B) solute
C) medium
D) colloid
E) solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glucose in the blood is a
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) homogenous mixture.
D) colloidal dispersion.
E) suspension.
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) homogenous mixture.
D) colloidal dispersion.
E) suspension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A _______ has components that are evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
A) homogenous mixture
B) heterogeneous mixture
C) pure compound
D) solute
E) solvent
A) homogenous mixture
B) heterogeneous mixture
C) pure compound
D) solute
E) solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT a cause of renal failure?
A) diabetes
B) heart attack
C) low blood pressure
D) severe dehydration
E) infection
A) diabetes
B) heart attack
C) low blood pressure
D) severe dehydration
E) infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Pepto-Bismol, the liquid pink antacid that must be shaken thoroughly before administering, is a
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) homogenous mixture.
D) colloidal dispersion.
E) suspension.
A) solution.
B) solvent.
C) homogenous mixture.
D) colloidal dispersion.
E) suspension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An example of this type of mixture is red blood cells in whole blood.
A) homogenous mixture
B) suspension
C) colloidal dispersion
D) solution
E) solvent
A) homogenous mixture
B) suspension
C) colloidal dispersion
D) solution
E) solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Is gasoline, which is nonpolar, miscible with water?
A) Yes, because they are both liquids
B) Yes, because they have similar polarities
C) No, because they are both liquids
D) No, because they have similar polarities
E) No, because they do not have similar polarities
A) Yes, because they are both liquids
B) Yes, because they have similar polarities
C) No, because they are both liquids
D) No, because they have similar polarities
E) No, because they do not have similar polarities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
We can predict whether or not a solute dissolves in a solvent with the rule "like dissolves like." This rule means that
A) a solute with the same diameter as the solvent will dissolve.
B) a solute with the same phase as the solvent will dissolve.
C) a solvent with the same polarity as the solvent will dissolve.
D) a solute with the same mass as the solvent will dissolve.
E) a solute contains some of the same elements as the solvent it will dissolve.
A) a solute with the same diameter as the solvent will dissolve.
B) a solute with the same phase as the solvent will dissolve.
C) a solvent with the same polarity as the solvent will dissolve.
D) a solute with the same mass as the solvent will dissolve.
E) a solute contains some of the same elements as the solvent it will dissolve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A _______ settles after mixing and contains visible particles.
A) solution
B) solvent
C) homogenous mixture
D) colloidal dispersion
E) suspension
A) solution
B) solvent
C) homogenous mixture
D) colloidal dispersion
E) suspension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
???A typical ______ contains aggregates of atoms, molecules or ions. It can also contain large molecules distributed throughout the medium.
A) solution
B) solvent
C) mixture
D) colloidal dispersion
E) suspension
A) solution
B) solvent
C) mixture
D) colloidal dispersion
E) suspension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a colloidal dispersion, the major component is called the
A) solvent.
B) solute.
C) medium.
D) colloid.
E) solution.
A) solvent.
B) solute.
C) medium.
D) colloid.
E) solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Is ethanol, a polar organic molecule that can hydrogen bond, miscible with water?
A) Yes, because they are both liquids
B) Yes, because they have similar polarities
C) No, because they are both liquids
D) No, because they have similar polarities
E) No, because they do not have similar polarities
A) Yes, because they are both liquids
B) Yes, because they have similar polarities
C) No, because they are both liquids
D) No, because they have similar polarities
E) No, because they do not have similar polarities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The purpose of the kidneys is to
A) oxidize drugs.
B) store cholesterol.
C) digest food.
D) remove waste products from blood.
E) store urine.
A) oxidize drugs.
B) store cholesterol.
C) digest food.
D) remove waste products from blood.
E) store urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following usually occurs when a molecule dissolves in water?
A) The covalent bonds in the molecule break.
B) The covalent bonds in water break.
C) Covalent bonds between the molecule and water form.
D) Covalent bonds between several of the molecules form.
E) Hydrogen bonds form between the molecule and water.
A) The covalent bonds in the molecule break.
B) The covalent bonds in water break.
C) Covalent bonds between the molecule and water form.
D) Covalent bonds between several of the molecules form.
E) Hydrogen bonds form between the molecule and water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When sodium chloride dissolves in water, it forms _______ with water molecules.
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic bonds
C) dipole-dipole interactions
D) covalent bonds
E) ion-dipole interactions
A) hydrogen bonds
B) ionic bonds
C) dipole-dipole interactions
D) covalent bonds
E) ion-dipole interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following substances are NOT physiologically important?
A) CO2
B) Na+
C) glucose
D) HCO3 -
E) All of the above are physiologically important substances.
A) CO2
B) Na+
C) glucose
D) HCO3 -
E) All of the above are physiologically important substances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is NOT an electrolyte?
A) Na+
B) HCO3 -
C) Mg2+
D) HOCH2CH3
E) All of the above are electrolytes.
A) Na+
B) HCO3 -
C) Mg2+
D) HOCH2CH3
E) All of the above are electrolytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Capsaicin is responsible for the heat of peppers. It is common practice to fry capsaicin in oil prior to eating. Which part of the capsaicin molecule forms intermolecular attractive force with oil, a nonpolar solvent? 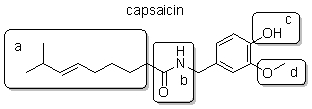
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) All of these interact with oil.

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) All of these interact with oil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When MgCl2 dissolves in water, it produces Mg2+ and Cl- ions. Which statement best describes the interaction between Cl - and water?
A) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial negative charge of oxygen.
B) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial positive charge of oxygen.
C) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial negative charge of hydrogen.
D) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial positive charge of hydrogen.
E) Chloride anions are not attracted to any part of water.
A) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial negative charge of oxygen.
B) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial positive charge of oxygen.
C) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial negative charge of hydrogen.
D) Chloride anions are attracted to the partial positive charge of hydrogen.
E) Chloride anions are not attracted to any part of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which pair of solvents is NOT miscible?
A) hexane and water
B) water and methanol
C) methanol and ethanol
D) hexane and butane
E) ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) and ethanol
A) hexane and water
B) water and methanol
C) methanol and ethanol
D) hexane and butane
E) ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) and ethanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following pictures best represents ethanol dissolved in water? Note that dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. 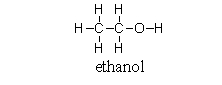
A)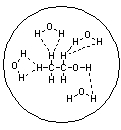
B)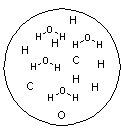
C)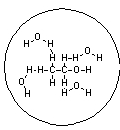
D)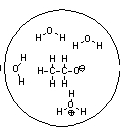
E)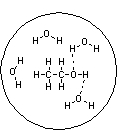
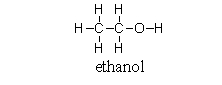
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How does an electrolyte differ from a nonelectrolyte?
A) Electrolytes are smaller than nonelectrolytes.
B) Electrolytes dissolve in water, while nonelectrolytes are insoluble in water.
C) Electrolytes are less polar than nonelectrolytes.
D) Electrolytes produce ions in solution while nonelectrolytes do not.
E) Electrolytes are more reactive than nonelectrolytes.
A) Electrolytes are smaller than nonelectrolytes.
B) Electrolytes dissolve in water, while nonelectrolytes are insoluble in water.
C) Electrolytes are less polar than nonelectrolytes.
D) Electrolytes produce ions in solution while nonelectrolytes do not.
E) Electrolytes are more reactive than nonelectrolytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How many ions of each type are produced when Na3PO4 is dissolved in aqueous solution?
A) 1 Na3PO4
B) 3 Na+, 1 P+, 4 O2 -
C) 3 Na+, 4 PO43 -
D) 3 Na+, 1 PO43 -
E) 1 Na+, 1 PO4 -
A) 1 Na3PO4
B) 3 Na+, 1 P+, 4 O2 -
C) 3 Na+, 4 PO43 -
D) 3 Na+, 1 PO43 -
E) 1 Na+, 1 PO4 -

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which figure best represents the dissolution of MgCl2 in water?
A)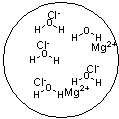
B)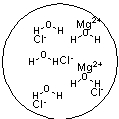
C)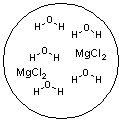
D)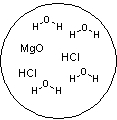
E)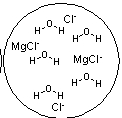
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ethanol dissolving in water is an example of a
A) physical change, because each molecule retains its structural integral and no bonds are broken.
B) chemical change because all bonds to ethanol are broken.
C) chemical change because new bonds form between the hydrogens.
D) physical change because ethanol only loses one hydrogen to water.
E) chemical change because ethanol has a charge in solution.
A) physical change, because each molecule retains its structural integral and no bonds are broken.
B) chemical change because all bonds to ethanol are broken.
C) chemical change because new bonds form between the hydrogens.
D) physical change because ethanol only loses one hydrogen to water.
E) chemical change because ethanol has a charge in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Sugar is stirred into cold iced tea and only some dissolves. The rest remains a solid. This solution is
A) miscible.
B) immiscible.
C) soluble.
D) insoluble.
E) saturated.
A) miscible.
B) immiscible.
C) soluble.
D) insoluble.
E) saturated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following factors affect the solubility of an ionic compound in a solvent?
A) the identity of the ions
B) the strength of the electrostatic interactions between the ions
C) the temperature of the solvent
D) the identity of the solvent
E) All of these are factors in solubility.
A) the identity of the ions
B) the strength of the electrostatic interactions between the ions
C) the temperature of the solvent
D) the identity of the solvent
E) All of these are factors in solubility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Is the solution of MgCl2 in water an electrolyte?
A) Yes, because when MgCl2 dissolves, it forms ions
B) Yes, because the MgCl2 undergoes a chemical change in solution
C) Yes, because MgCl2 and water react with each other
D) No, because MgCl2 does not form ions
E) No, because MgCl2 in water does not conduct electricity
A) Yes, because when MgCl2 dissolves, it forms ions
B) Yes, because the MgCl2 undergoes a chemical change in solution
C) Yes, because MgCl2 and water react with each other
D) No, because MgCl2 does not form ions
E) No, because MgCl2 in water does not conduct electricity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following solutes is most soluble in hexane?
A) pentane, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
B) NaCl
C) KCl
D) methanol, CH3OH
E) acetic acid, CH3COOH
A) pentane, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
B) NaCl
C) KCl
D) methanol, CH3OH
E) acetic acid, CH3COOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An electrolyte is a substance that
A) dissolves in water.
B) does not dissolve in water.
C) hydrogen bonds with water.
D) produces ions when dissolved in water.
E) is an excellent resistor.
A) dissolves in water.
B) does not dissolve in water.
C) hydrogen bonds with water.
D) produces ions when dissolved in water.
E) is an excellent resistor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following does NOT occur when an electrolyte dissolves in water?
A) A chemical change occurs.
B) The positive and negative ions separate from each other.
C) The positive ions interact with the oxygen of water.
D) The negative ions interact with the hydrogen of water.
E) The resulting solution conducts electricity.
A) A chemical change occurs.
B) The positive and negative ions separate from each other.
C) The positive ions interact with the oxygen of water.
D) The negative ions interact with the hydrogen of water.
E) The resulting solution conducts electricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following describes the dissolution of MgCl2 in water?
A) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl2 -
B) MgCl2 → Mg2+ + Cl22 -
C) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl - + Cl
D) MgCl2 → Mg2+ + 2Cl -
E) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl -
A) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl2 -
B) MgCl2 → Mg2+ + Cl22 -
C) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl - + Cl
D) MgCl2 → Mg2+ + 2Cl -
E) MgCl2 → Mg+ + Cl -

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why do kidney stones form?
A) Calcium salt levels in the kidneys reach saturated levels and precipitate.
B) Magnesium levels in the kidneys reach saturated levels and precipitate.
C) Organic toxins build up in the kidney and precipitate.
D) Chloride ions reach saturated levels in the kidney and precipitate.
E) All of the above ions and molecules contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
A) Calcium salt levels in the kidneys reach saturated levels and precipitate.
B) Magnesium levels in the kidneys reach saturated levels and precipitate.
C) Organic toxins build up in the kidney and precipitate.
D) Chloride ions reach saturated levels in the kidney and precipitate.
E) All of the above ions and molecules contribute to the formation of kidney stones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to the following table, are Jane Doe's blood test values within normal limits? 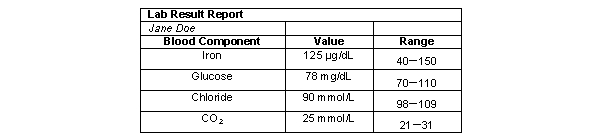
A) Yes.
B) No, glucose is too concentrated.
C) No, glucose is too dilute.
D) No, chloride is too concentrated.
E) No, chloride is too dilute.

A) Yes.
B) No, glucose is too concentrated.
C) No, glucose is too dilute.
D) No, chloride is too concentrated.
E) No, chloride is too dilute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Jane Doe's blood test showed that her iron is 125 mg/dL. How many g/L is 125 mg/dL?
A) 12,500 g/L
B) 1.25 g/L
C) 0.00125 g/L
D) 125 g/L
E) 1250 g/L
A) 12,500 g/L
B) 1.25 g/L
C) 0.00125 g/L
D) 125 g/L
E) 1250 g/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many grams of dextrose are in 100 mL of D5W (5.0% dextrose)?
A) 50 g
B) 5.0 g
C) 0.50 g
D) 0.050 g
E) 0.0050 g
A) 50 g
B) 5.0 g
C) 0.50 g
D) 0.050 g
E) 0.0050 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The permissible level of arsenic in drinking water is 10 ppb in the United States. What is the maximum mass of arsenic, in grams, allowable in 1 L of drinking water?
A) 10 g
B) 1.0 * 10-6 g
C) 1.0 *106 g
D) 1.0 * 10-5 g
E) No amount of arsenic is allowable in drinking water.
A) 10 g
B) 1.0 * 10-6 g
C) 1.0 *106 g
D) 1.0 * 10-5 g
E) No amount of arsenic is allowable in drinking water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 1% epinephrine solution is delivered by inhalation to treat asthma. This concentration is equivalent to
A) 1 g epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.
B) 0.001 g epinephrine dissolved in 1 L of water.
C) 1 mg epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.
D) 0.001 mg epinephrine dissolved in 1 L of water.
E) 1 μg epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.
A) 1 g epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.
B) 0.001 g epinephrine dissolved in 1 L of water.
C) 1 mg epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.
D) 0.001 mg epinephrine dissolved in 1 L of water.
E) 1 μg epinephrine dissolved in 100 mL of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Jane Doe has a blood glucose level of 92 mg/dL. How many grams of glucose does she have in 1 L of her blood?
A) 0.00092 g
B) 0.0092 g
C) 0.092 g
D) 0.92 g
E) 9.2 g
A) 0.00092 g
B) 0.0092 g
C) 0.092 g
D) 0.92 g
E) 9.2 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which container would be the best for preparing 1 L of a 10 g NaCl/L solution? In other words, which container will give the most accurate and precise measure of a large volume?
A) volumetric flask
B) beaker
C) graduated cylinder
D) Erlenmeyer flask
E) syringe
A) volumetric flask
B) beaker
C) graduated cylinder
D) Erlenmeyer flask
E) syringe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How many moles of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) are in 1.31 L of 0.38 M MgCl2?
A) 0.498 moles
B) 0.50 moles
C) 1.49 moles
D) 1.5 moles
E) 0.29 moles
A) 0.498 moles
B) 0.50 moles
C) 1.49 moles
D) 1.5 moles
E) 0.29 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
According to a blood test, a patient has a blood iron value of 125 μg/dL. This value means that
A) the sample of blood contains 125 μg of iron.
B) the patient's body contains 125 μg of iron.
C) the mass of iron in the patient's blood is 125 μg.
D) for every deciliter of body volume, the patient contains 125 μg.
E) one deciliter of the patient's blood contains 125 μg of iron.
A) the sample of blood contains 125 μg of iron.
B) the patient's body contains 125 μg of iron.
C) the mass of iron in the patient's blood is 125 μg.
D) for every deciliter of body volume, the patient contains 125 μg.
E) one deciliter of the patient's blood contains 125 μg of iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What type(s) of unit(s) are represented on this table? 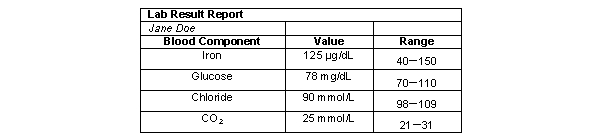
A) % mass/volume
B) mass/volume
C) moles/volume
D) equivalents/volume
E) both B and C

A) % mass/volume
B) mass/volume
C) moles/volume
D) equivalents/volume
E) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The general equation for determining concentration is
A) concentration = amount of solvent/amount of solute.
B) concentration = amount of solute/amount of solution.
C) concentration = amount of solution/amount of solvent.
D) concentration = amount solute/amount of solvent.
E) concentration = amount of solvent/amount of solution.
A) concentration = amount of solvent/amount of solute.
B) concentration = amount of solute/amount of solution.
C) concentration = amount of solution/amount of solvent.
D) concentration = amount solute/amount of solvent.
E) concentration = amount of solvent/amount of solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to a blood test, a patient has a blood calcium concentration of 9.7 mg/dL. Express this concentration in mg/mL.
A) 970 mg/mL
B) 97 mg/mL
C) 9.7 mg/mL
D) 0.97 mg/mL
E) 0.097 mg/mL
A) 970 mg/mL
B) 97 mg/mL
C) 9.7 mg/mL
D) 0.97 mg/mL
E) 0.097 mg/mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
To make 1.0 L of a 10. g NaCl/L solution, 10. g of NaCl is weighed and poured into a volumetric flask. What is the next step?
A) The next step is to measure out 1.0 L of water, pour it into the container, and mix.
B) The next step is to fill the container up to the top of the flask.
C) The next step is to fill the container to the 1.0 L mark while swirling to mix.
D) The next step is to transfer the NaCl to a new flask.
E) None of these. The solute should always be added to the container after the solvent, not before.
A) The next step is to measure out 1.0 L of water, pour it into the container, and mix.
B) The next step is to fill the container up to the top of the flask.
C) The next step is to fill the container to the 1.0 L mark while swirling to mix.
D) The next step is to transfer the NaCl to a new flask.
E) None of these. The solute should always be added to the container after the solvent, not before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The concentration of an adrenalin chloride solution, used to treat acute allergic responses, is 15 mg in 30. mL. Express this concentration in mg/mL (mg per milliliter).
A) 0.50 mg/mL
B) 2.0 mg/ml
C) 5.0 mg/mL
D) 45 mg/mL
E) 450 mg/mL
A) 0.50 mg/mL
B) 2.0 mg/ml
C) 5.0 mg/mL
D) 45 mg/mL
E) 450 mg/mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How many grams of NaCl are in 350 mL of normal saline (0.9% NaCl)?
A) 3150 g
B) 315 g
C) 31.5 g
D) 3.15 g
E) 0.315 g
A) 3150 g
B) 315 g
C) 31.5 g
D) 3.15 g
E) 0.315 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A solution is prepared by dissolving 1.5 g of NaCl in enough water to produce a total solution volume of 750 mL. What is the concentration of the solution in % m/v?
A) 0.20%
B) 2.0%
C) 0.0020%
D) 500%
E) 5.0%
A) 0.20%
B) 2.0%
C) 0.0020%
D) 500%
E) 5.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Drinking water from a well is discovered to have an arsenic concentration of 3.4 * 10-4 g of arsenic per liter. Does this value exceed the permissible level of arsenic in drinking water of 10 ppb?
A) No, 3.4 * 10-4 g is lower than the permissible value of 1.0 * 10-5 g/L.
B) Yes, 3.4 * 10-4 g is higher than the permissible value of 1.0 * 10-5 g/L.
C) No, 3.4 *10-4 g is lower than the permissible value of 1.0 *10-3 g/L.
D) Yes, 3.4 * 10-4 g is higher than the permissible value of 1.0 *10-3 g/L.
E) It is not possible to determine the answer from the information given.
A) No, 3.4 * 10-4 g is lower than the permissible value of 1.0 * 10-5 g/L.
B) Yes, 3.4 * 10-4 g is higher than the permissible value of 1.0 * 10-5 g/L.
C) No, 3.4 *10-4 g is lower than the permissible value of 1.0 *10-3 g/L.
D) Yes, 3.4 * 10-4 g is higher than the permissible value of 1.0 *10-3 g/L.
E) It is not possible to determine the answer from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A patient's blood test shows that his chloride level is 101 mmol/L. Convert this concentration to units of molarity.
A) 1010 M
B) 101 M
C) 10.1 M
D) 1.01 M
E) 0.101 M
A) 1010 M
B) 101 M
C) 10.1 M
D) 1.01 M
E) 0.101 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What volume of a 6.0% solution of ethanol contain 3.0 g of ethanol?
A) 5.0 mL
B) 6.0 mL
C) 10 mL
D) 30 mL
E) 50 mL
A) 5.0 mL
B) 6.0 mL
C) 10 mL
D) 30 mL
E) 50 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Jane Doe's blood test showed that her iron is 125 mg/dL. You would like to convert the value into g/L. Which unit conversion converts 125 mg/dL into g/L?
A)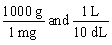
B)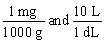
C)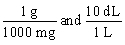
D)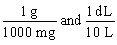
E)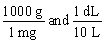
A)
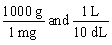
B)
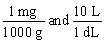
C)
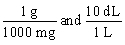
D)
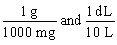
E)
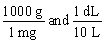

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Carbamazepine is an antiepileptic. A typical daily dose is 1.1
A) 0.22 mL
B) 5.5 mL
C) 22 mL
D) 220 mL
E) 5500 mL
A) 0.22 mL
B) 5.5 mL
C) 22 mL
D) 220 mL
E) 5500 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How many grams of glucose should be weighed out to make 1 liter of a rehydration solution that contains 75 mmol of glucose (the molar mass of glucose is 180 g)?
A) 14 g
B) 1.4 *104 g
C) 0.42 g
D) 4.2*10 - 3 g
E) 4.2*10 - 4 g
A) 14 g
B) 1.4 *104 g
C) 0.42 g
D) 4.2*10 - 3 g
E) 4.2*10 - 4 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An order is given to administer 50. mg of furosemide, a diuretic, over the course of 2 hours by IV. If a 500. mL bag contains 200. mg of furosemide, what volume of solution does the patient need to receive over the course of two hours?
A) 0.50 mL
B) 50. mL
C) 130 mL
D) 20 mL
E) 500 mL
A) 0.50 mL
B) 50. mL
C) 130 mL
D) 20 mL
E) 500 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following compounds passes most easily through the cell membrane?
A) Na+
B) glucose
C) sucrose
D) glycerol
E) O2
A) Na+
B) glucose
C) sucrose
D) glycerol
E) O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Cephadrine is one of many antibiotics that act by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. If a typical daily dosage is 660 mg, how many milliliters of 75 mg/mL suspension of cephadrine should be administered daily?
A) 660 mL
B) 75 mL
C) 0.0088 mL
D) 8.8 mL
E) 1.1 mL
A) 660 mL
B) 75 mL
C) 0.0088 mL
D) 8.8 mL
E) 1.1 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the semipermeable membrane only allows the passage of water, what process will to occur? 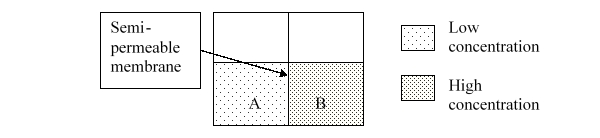
A) nothing
B) mixing
C) dialysis
D) dilution
E) osmosis

A) nothing
B) mixing
C) dialysis
D) dilution
E) osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements describes one way in which osmosis and dialysis are similar?
A) Both involve the movement of molecules from low to high concentration.
B) Both involve the movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
C) Both involve the passage of a solute through a semipermeable membrane.
D) Both require an input of energy.
E) Osmosis and dialysis are in no way similar.
A) Both involve the movement of molecules from low to high concentration.
B) Both involve the movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
C) Both involve the passage of a solute through a semipermeable membrane.
D) Both require an input of energy.
E) Osmosis and dialysis are in no way similar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider solutions A and B separated by a semipermeable membrane. Which diagram best illustrates what the volumes should look like after osmosis occurs? 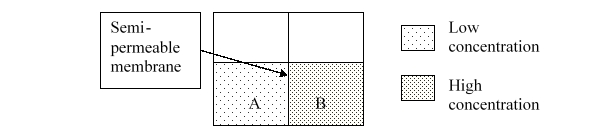
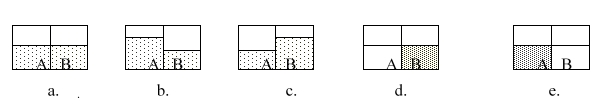
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e


A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It is normal to have about 100 mM (mmol/L) of chloride (Cl - ) in the blood. How many meq is this?
A) 1 *105 meq
B) 100 meq
C) 1 meq
D) 0.1 meq
E) 1*10 - 5 meq
A) 1 *105 meq
B) 100 meq
C) 1 meq
D) 0.1 meq
E) 1*10 - 5 meq

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If A contains 6% NaCl in water and B contains 3% NaCl in water, which of the following will occur? 
A) Water will flow from A to B.
B) Water will flow from B to A.
C) NaCl will flow from A to B.
D) NaCl will flow from B to A.
E) Nothing will happen.

A) Water will flow from A to B.
B) Water will flow from B to A.
C) NaCl will flow from A to B.
D) NaCl will flow from B to A.
E) Nothing will happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the following diagram, A is ______ and B is ______. 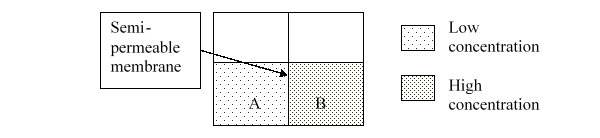
A) hypotonic; hypertonic
B) hypertonic; hypotonic
C) A and B are isotonic.
D) A and B are both hypotonic.
E) A and B are both hypertonic.

A) hypotonic; hypertonic
B) hypertonic; hypotonic
C) A and B are isotonic.
D) A and B are both hypotonic.
E) A and B are both hypertonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A child is given 7.5 mL of a liquid pain reliever as a suspension containing 160 mg/5 mL of the pain reliever. How many milligrams of the pain reliever did the child receive?
A) 1200 mg
B) 21 mg
C) 107 mg
D) 1.5 mg
E) 240 mg
A) 1200 mg
B) 21 mg
C) 107 mg
D) 1.5 mg
E) 240 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A student adds 0.250 L of 200 mM buffer stock solution to a volumetric flask and dilutes the stock to 1.0 L. What is the final concentration of the solution?
A) 0.11 mmol
B) 110 mmol
C) 11 mmol
D) 50 mmol
E) 5.0 mmol
A) 0.11 mmol
B) 110 mmol
C) 11 mmol
D) 50 mmol
E) 5.0 mmol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An order is given to administer 100. mg of furosemide, a diuretic, over the course of 4 hours by IV. If a 500. mL bag contains 200. mg of furosemide, what flow rate, in mL per hour, should be administered to the patient?
A) 25 mg/hour
B) 25 mL/hour
C) 63 mL/hour
D) 10 mL/hour
E) 250 mL/hour
A) 25 mg/hour
B) 25 mL/hour
C) 63 mL/hour
D) 10 mL/hour
E) 250 mL/hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements describes one way in which osmosis and dialysis are different?
A) Osmosis is the movement of molecules from low to high concentration and dialysis is the reverse.
B) Dialysis is the movement of molecules from low to high concentration and osmosis is the reverse.
C) Osmosis refers to the flow of solvent, whereas dialysis refers to the flow of small solutes.
D) Dialysis refers to the flow of solvent, whereas osmosis refers to the flow of small solutes.
E) In dialysis, colloids cannot cross the semipermeable membrane, but they can in osmosis.
A) Osmosis is the movement of molecules from low to high concentration and dialysis is the reverse.
B) Dialysis is the movement of molecules from low to high concentration and osmosis is the reverse.
C) Osmosis refers to the flow of solvent, whereas dialysis refers to the flow of small solutes.
D) Dialysis refers to the flow of solvent, whereas osmosis refers to the flow of small solutes.
E) In dialysis, colloids cannot cross the semipermeable membrane, but they can in osmosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A biologist needs 500 mL of a 10 mM phosphate buffer. The stock solution of the buffer is 100 mM. How much stock solution should be used to make the 10 mM phosphate buffer?
A) 500 mL
B) 5000 mL
C) 50 mL
D) 5.0 mL
E) 0.5 mL
A) 500 mL
B) 5000 mL
C) 50 mL
D) 5.0 mL
E) 0.5 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If A contains 3 mmol NaCl and 3 mmol glucose, while B contains 6 mmol NaCl, which of the following will occur? 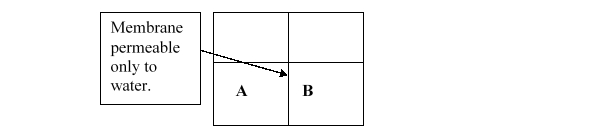
A) Water will flow from A to B.
B) Water will flow from B to A.
C) NaCl will flow from A to B.
D) NaCl will flow from B to A.
E) Nothing will happen.

A) Water will flow from A to B.
B) Water will flow from B to A.
C) NaCl will flow from A to B.
D) NaCl will flow from B to A.
E) Nothing will happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The cell membrane separates the interior of the cell from its surroundings, but it does allow the passage of some small molecules from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. This process is called
A) osmosis.
B) simple diffusion
C) dialysis.
D) dissolution.
E) active transport.
A) osmosis.
B) simple diffusion
C) dialysis.
D) dissolution.
E) active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Convert 0.015 M Ca2+ to equivalents of Ca2+.
A) 0.015 equivalents
B) 7.5 *10 - 4 equivalents
C) 0.030 equivalents
D) 15 equivalents
E) 0.75 equivalents
A) 0.015 equivalents
B) 7.5 *10 - 4 equivalents
C) 0.030 equivalents
D) 15 equivalents
E) 0.75 equivalents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How many moles of glucose are in 0.82 L of a 0.13 M glucose solution?
A) 0.11 moles
B) 0.33 moles
C) 6.3 moles
D) 1.9 moles
E) 0.22 moles
A) 0.11 moles
B) 0.33 moles
C) 6.3 moles
D) 1.9 moles
E) 0.22 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



